Types and development characteristics of high geological disasters in Chalonglongbaqu gully, Bomi , Xizang
-
摘要:
茶隆隆巴曲位于帕隆藏布右岸,陡变地形孕育了大量高位地质灾害,威胁下游线性工程。采用多源、多期次高分辨率遥感数据,建立高位地质灾害遥感解译标志,厘定了研究区高位地质灾害类型,并详细阐述了其发育特征。结果表明,研究区主要地质灾害类型包括高位冰崩、高位崩塌、高位滑坡。其中高位冰崩发育3处,均位于沟谷上游南坡海拔5000 m斜坡,面积在15×104 m2以上。高位崩塌体发育19处,多分布于沟谷中游及上游主沟两侧高陡岸坡,北坡多于南坡。高位滑坡发育2处,位于沟谷上游,滑体以冰碛物为主。上述高位地质灾害在强震或强降雨作用下,极易发生失稳、堵沟,且堵沟后极易诱发洪水、泥石流等次生灾害链,对下游帕隆藏布造成堵江风险。
Abstract:Chalonglongbaqu gully is located on the right bank of Parlung Zangbo. The steeply changing topography has bred a large number of high-level geological disasters, threatening the downstream linear engineering. Therefore, this paper uses multi-source and multi-phase high-resolution remote sensing data to establish remote sensing interpretation signs of high-level geological disasters, determines the types of high-level geological disasters in the study area, and elaborates their development characteristics. The results show that the main types of geological disasters in the study area include high-level ice avalanches, high-level avalanches, and high-level landslides. Among them, there are 3 high-level ice avalanches, all of which are located on a slope with an altitude of 5000 m above the south slope of the upper reaches of the valley, with an area of more than 15×104 m2. There are 19 high-level avalanches, which are mostly distributed in the middle reaches of the valley and high and steep bank slopes on both sides of the upper main ditch. The northern slope is more than the southern slope. There are two high-level landslides located in the upper reaches of the valley, and the landslide is dominated by moraines. Under the action of strong earthquakes or heavy rainfall, the above-mentioned high-level geological disasters are prone to instability and blockage of ditch. After blocking the ditch, it is easy to induce secondary disaster chains such as floods and mudslides, which will cause the risk of blocking the river downstream of Parlung Zangbo.
-

-
表 1 研究区光学遥感数据一览表
Table 1. Summary of optical remote sensing data in the study area
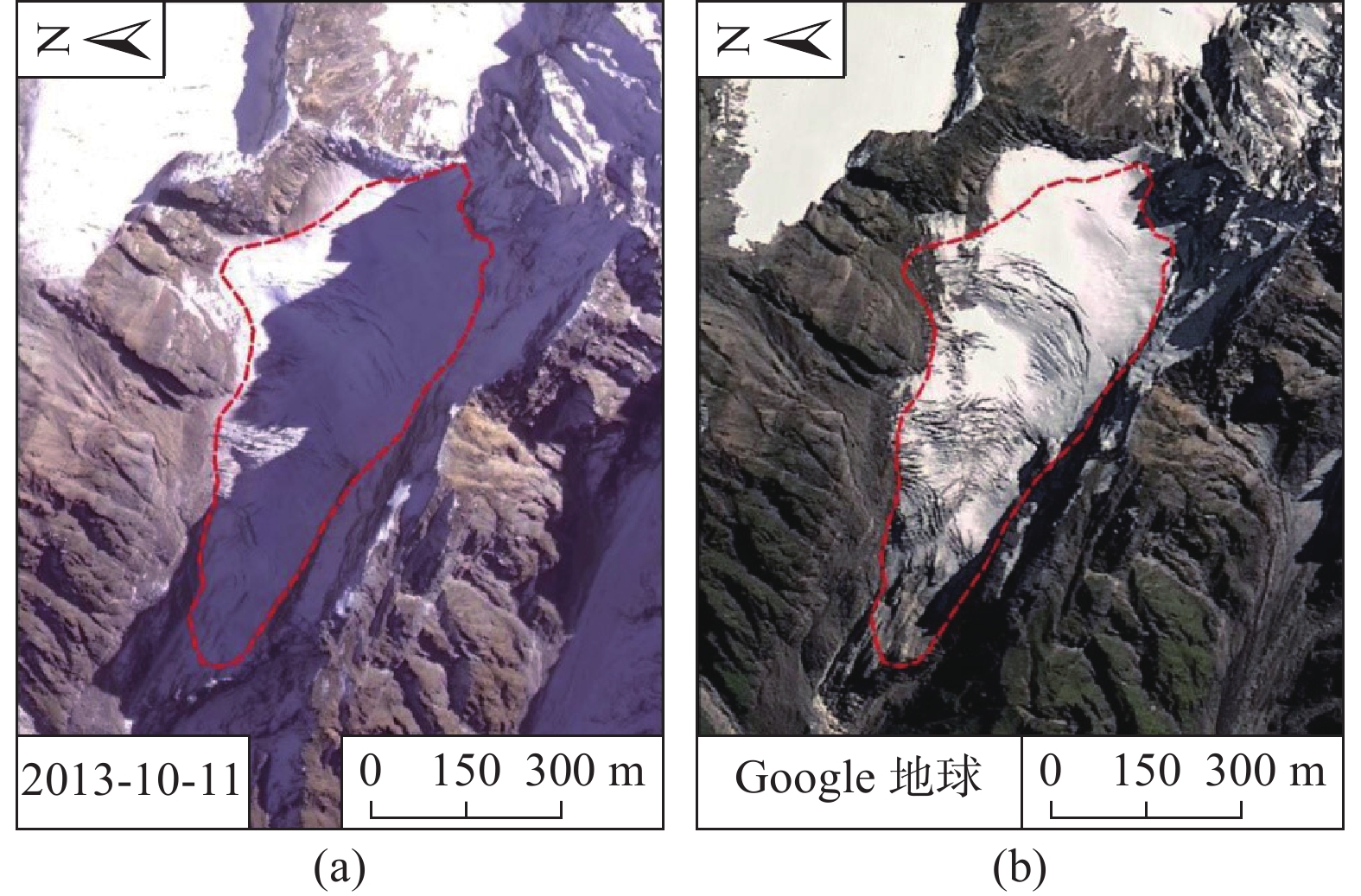
序号 日期 数据来源 分辨率 备注 1 2013-10-11 资源三号卫星 全色2.1 m,多光谱5.8 m 2 2015-07-25 高分一号 全色2 m,多光谱8 m 3 2016-12-22 资源三号卫星 全色2.1 m,多光谱5.8 m 4 2019-11-07 高分一号 全色2 m,多光谱8 m 5 — Google地球 2.0 m 融合数据 6 2020-08-18 无人机航空
正射影像0.5 m 沟道中下部 7 2020-08-18 无人机航空
倾斜影像0.5 m 沟道中下部 表 2 高位冰崩发育特征
Table 2. Development characteristics of high ice avalanche
编号 位置 前缘高程/m 后缘高程/m 前后缘高差/m 落差/m 面积/m2 BC01 南坡 3692 5208 1516 2983 719633 BC02 南坡 4490 4973 483 2748 204033 BC03 南坡 4471 4878 407 2653 185347 表 3 研究区典型高位崩塌发育特征
Table 3. Development characteristics of typical high-level avalanches in the study area
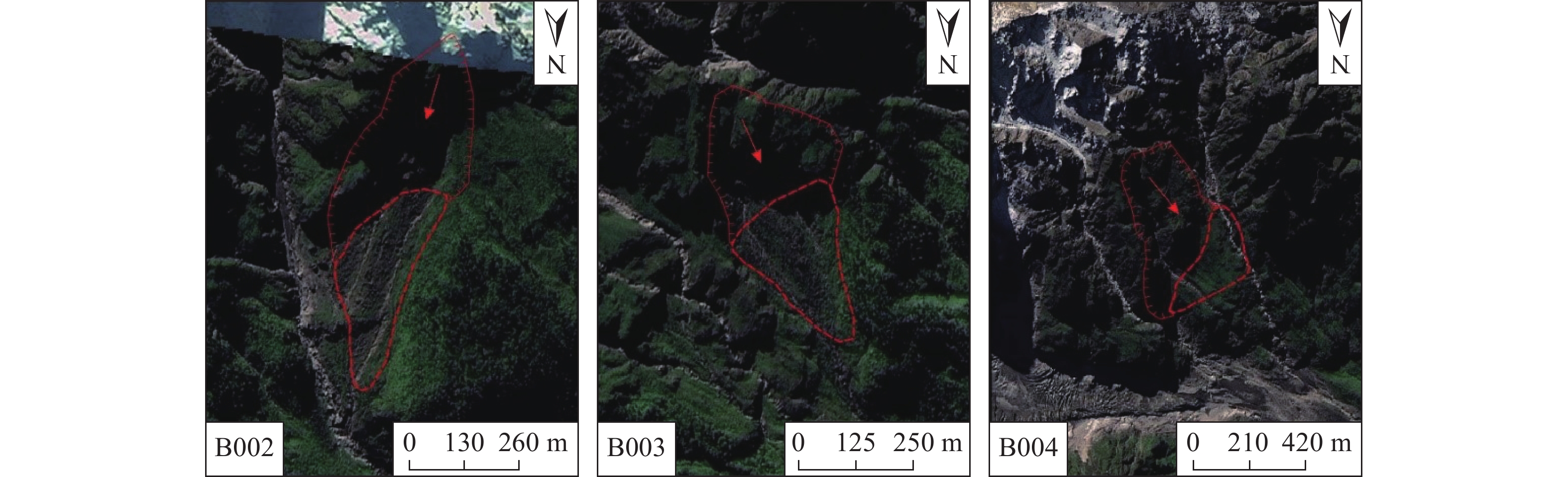
编号 位置 崩源区面积/m2 崩塌堆积区面积/m2 总体积/m3 落差/m B002 南坡 88912 63029 1.50×106 1000 B003 南坡 55894 56498 10.8×104 1400 B004 南坡 122602 56498 2.15×106 1500 B009 北坡 284287 83414 4.04×106 1000 B011 北坡 158946 397191 5.14×106 880 B016 北坡 53017 17352 0.35×106 1100 -
[1] 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡概况[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2000,11(2):1. [YIN Yueping. Overview of giant landslides on the Bomi-Yigong Expressway in Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2000,11(2):1. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.02.001
[2] 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡特征及减灾研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2000,27(4):8 − 11. [YIN Yueping. Research on the characteristics and disaster mitigation of giant landslides on the Bomi-Yigong Expressway in Xizang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2000,27(4):8 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.04.003
[3] 鲁安新, 邓晓峰, 赵尚学, 等. 2005 年西藏波密古乡沟泥石流暴发成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2006,28(6):956 − 960. [LU Anxin, DENG Xiaofeng, ZHAO Shangxue, et al. Analysis of the causes of the debris flow outbreak in the Guxiang Gully, Bomi, Xizang in 2005[J]. Glaciology and Geocryology,2006,28(6):956 − 960. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.06.023
[4] 陶明刚. Landsat-TM遥感影像岸线变迁解译研究—以九龙江河口地区为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(1):107 − 110. [TAO Minggang. Research on interpretation of shoreline changes of Landsat-TM remote sensing image: Taking Jiulong River Estuary as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(1):107 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.01.028
[5] 薛东剑, 张东辉, 何政伟. 多源遥感影像融合技术在地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2011,26(5):664 − 669. [XUE Dongjian, ZHANG Donghui, HE Zhengwei. Application of multi-source remote sensing image fusion technology in geological disaster investigation[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2011,26(5):664 − 669. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2011.5.664
[6] 方成, 孙晓明, 康慧, 等. 遥感技术在曹妃甸海岸带地质环境调查中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(3):119 − 127. [FANG Cheng, SUN Xiaoming, KANG Hui, et al. Application of remote sensing technology in the geological environment investigation of Caofeidian coastal zone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(3):119 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] LAUKNES T R, PIYUSH S A, DEHLS J F, et al. Detailedrockslidemapping in northern norway with small baseline and persistent scatterer interferometric SAR time series methods[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2010,114:2097 − 2109. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.04.015
[8] FRANCESCA B, IVAN C, PAOLO M, et al. Displacement patterns of a landslide affected by human activities: Insightsfromground-based InSAR monitoring[J]. Natural Hazards,2011,59:1377 − 1396. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9840-6
[9] HU X, WANG T, PIERSON T C, et al. Detecting seasonal landslide movement within the cascade landslide complex(Washington) using time-series SAR imagery[J]. RemoteSensing of Environment,2016,187:49 − 61.
[10] 孙家抦. 遥感原理与应用[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2003.
SUN Jiabing. Principle and application of remote sensing [M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2003. (in Chinese)
[11] 刘佳, 赵海军, 马凤山, 等. 基于改进变异系数法的G109拉萨—那曲段泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):63 − 70. [LIU Jia, ZHAO Haijun, MA Fengshan, et al. Risk assessment of G109 Lhasa-Naqu Debris flow based on improved coefficient of variation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):63 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王立朝, 温铭生, 冯振, 等. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡灾害研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):1 − 9. [WANG Lichao, WEN Mingsheng, FENG Zhen, et al. esearches on the baige landslide at Jinshajiang river, Xizang, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 杨军杰, 张志, 王旭, 等. 汶川县地震次生山地地质灾害遥感调查[J]. 山地学报,2008,26(6):755 − 760. [YANG Junjie, ZHANG Zhi, WANG Xu, et al. Remote sensing survey of secondary mountain geological disasters in Wenchuan County[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2008,26(6):755 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2008.06.017
[14] 王猛, 王军, 江煜, 等. 汶川地震地质灾害遥感调查与空间特征分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2010,12(4):480 − 486. [WANG Meng, WANG Jun, JIANG Yu, et al. Wenchuan Earthquake Geological Disaster Remote Sensing Investigation and Spatial Feature Analysis[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2010,12(4):480 − 486. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2010.00480
[15] 梁京涛, 成余粮, 王军, 等. 基于无人机遥感技术的汶川震区典型高位泥石流动态监测—以绵竹文家沟泥石流为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(3):54 − 61. [LIANG Jingtao, CHENG Yuliang, WANG Jun, et al. Dynamic monitoring of typical high-level debris flow in Wenchuan earthquake area based on UAV remote sensing technology: taking Wenjiagou debris flow in Mianzhu as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(3):54 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: