Development and distribution characteristics of ground fissures in high loess filled ground
-
摘要:
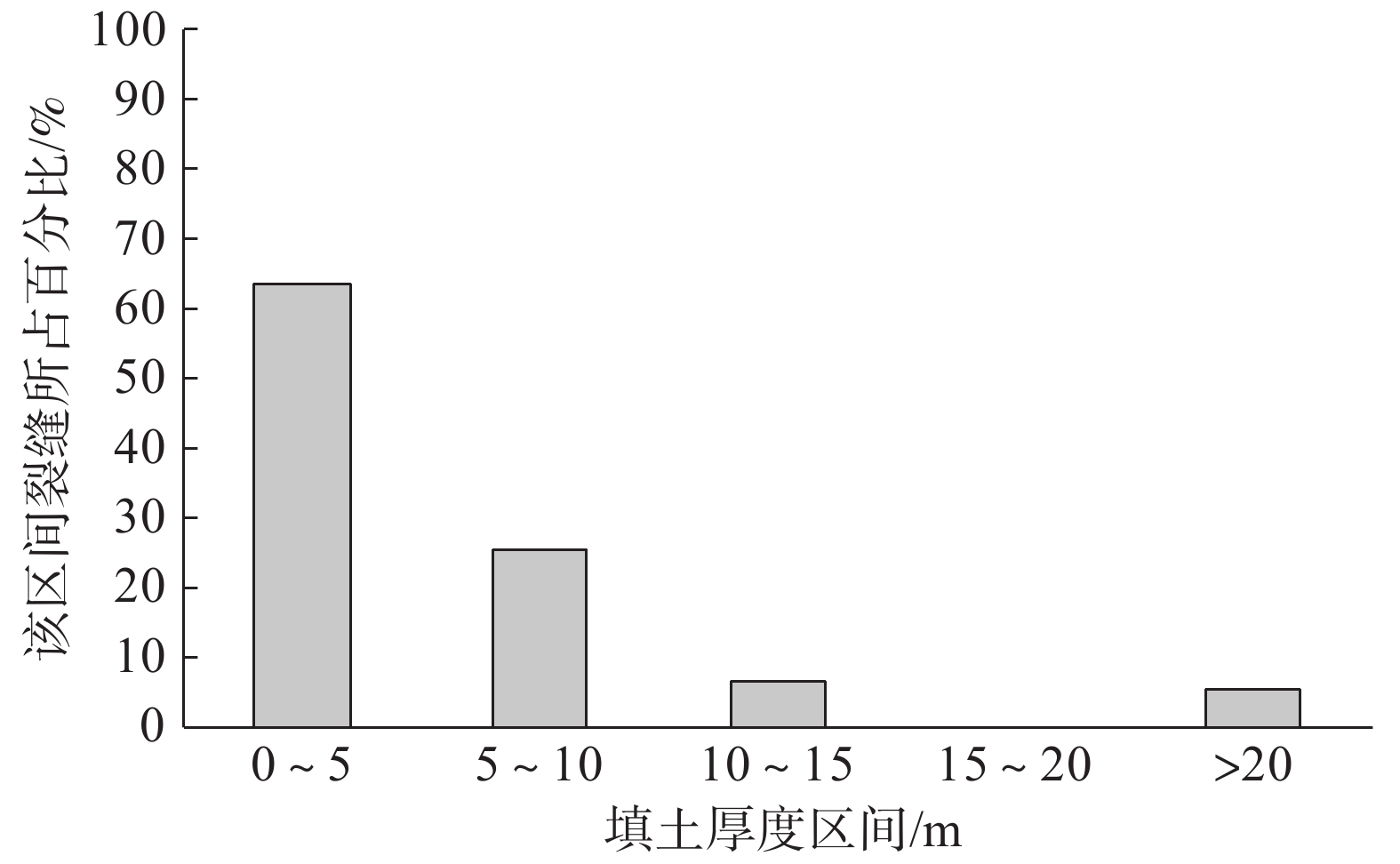
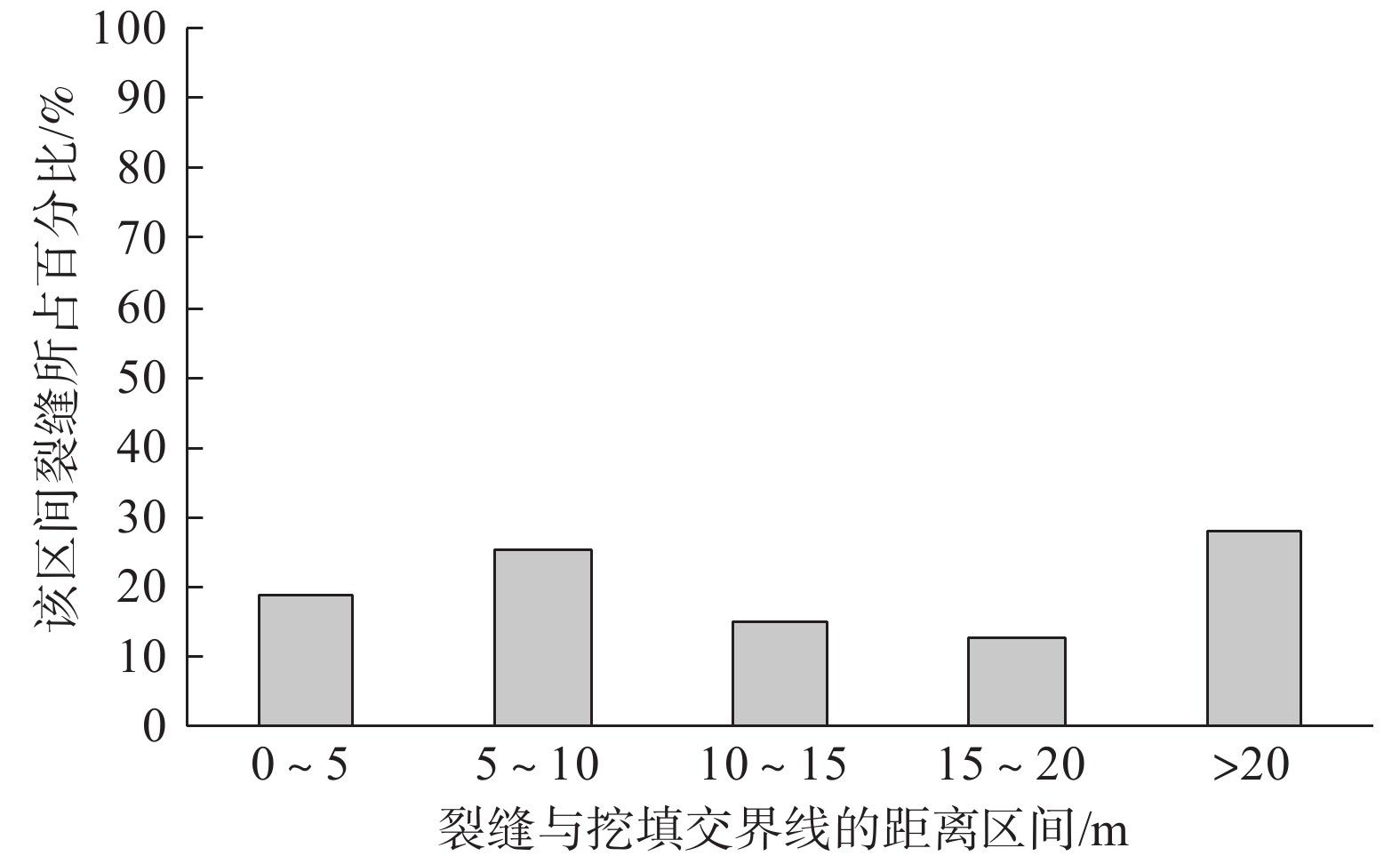
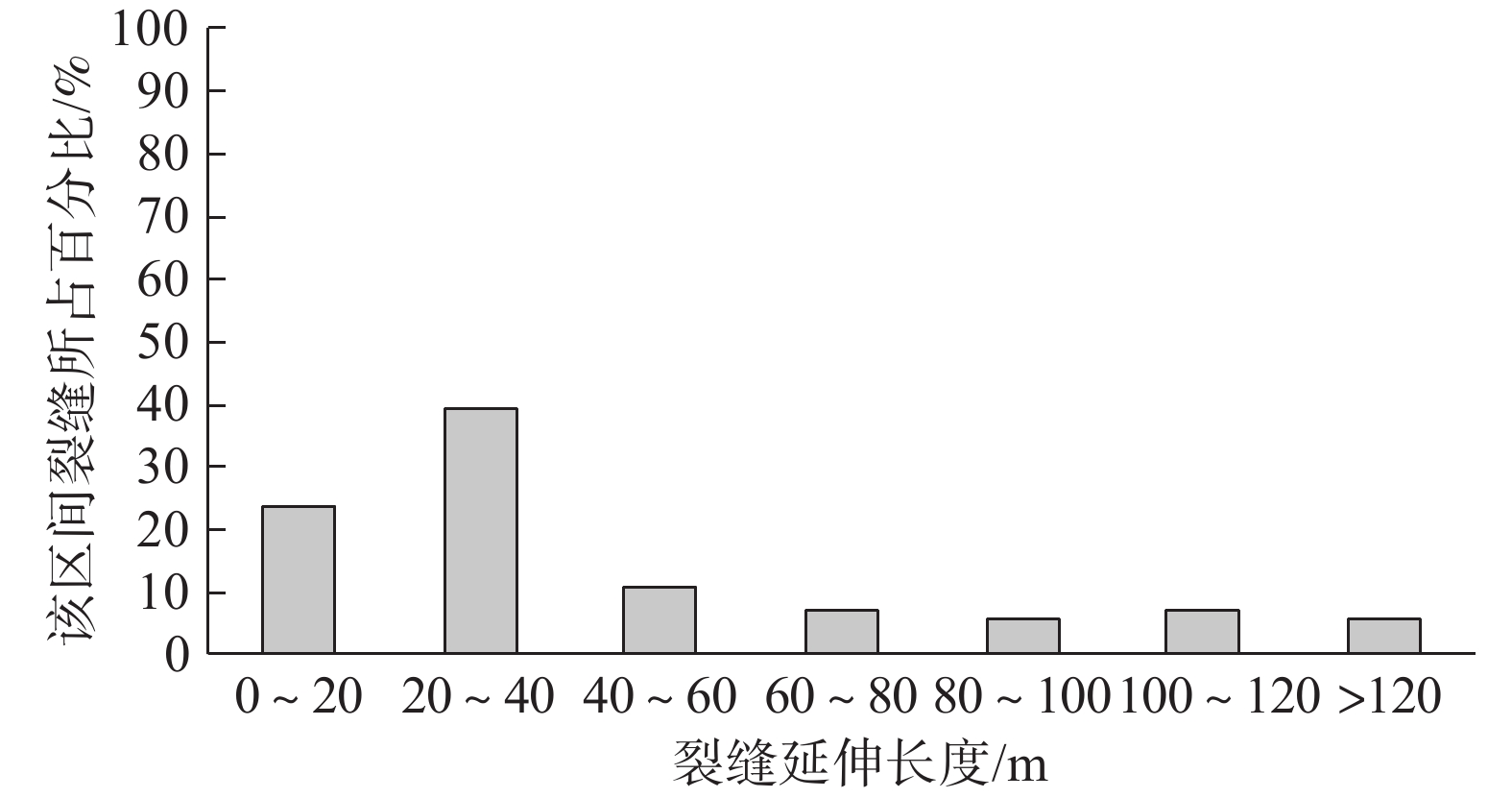
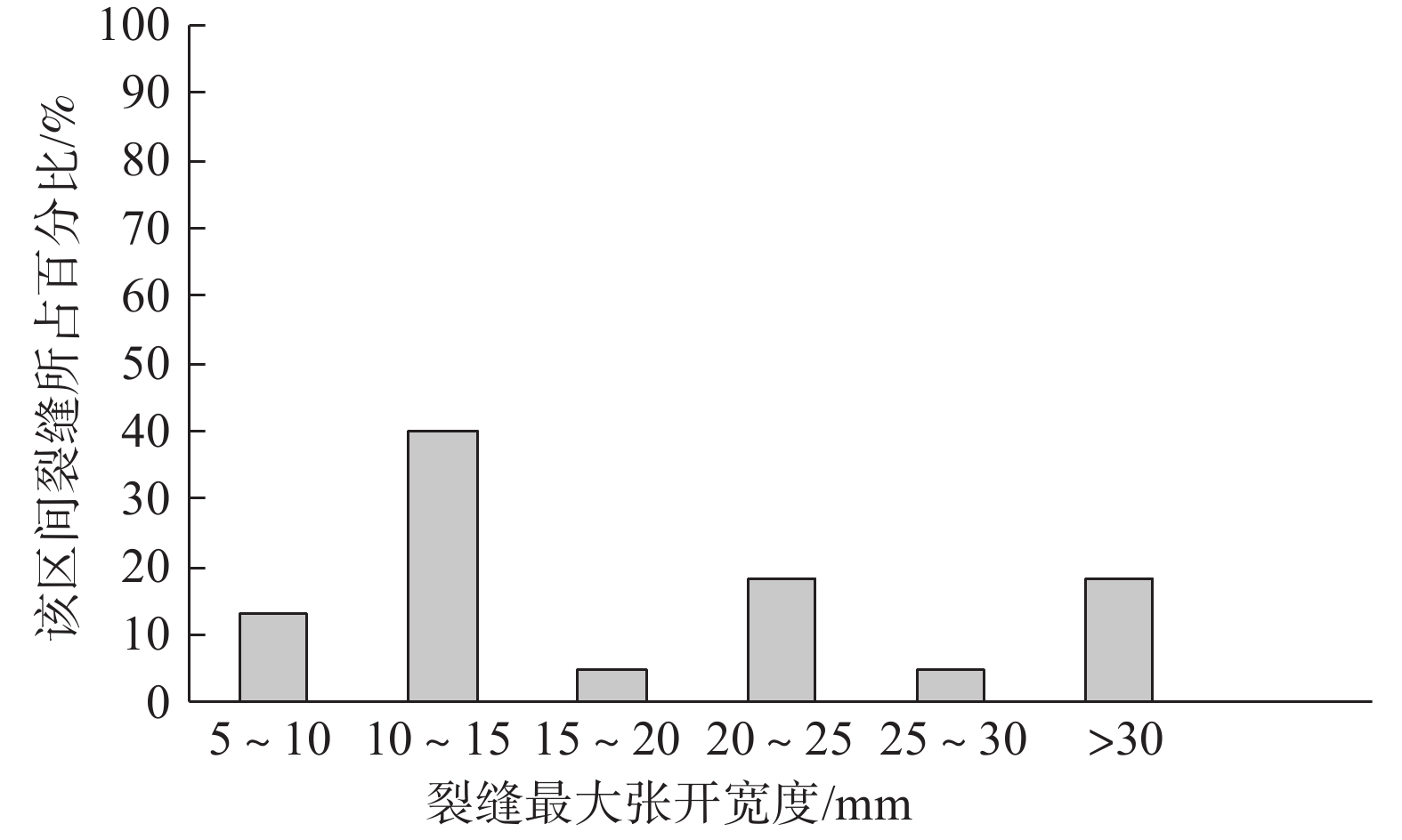
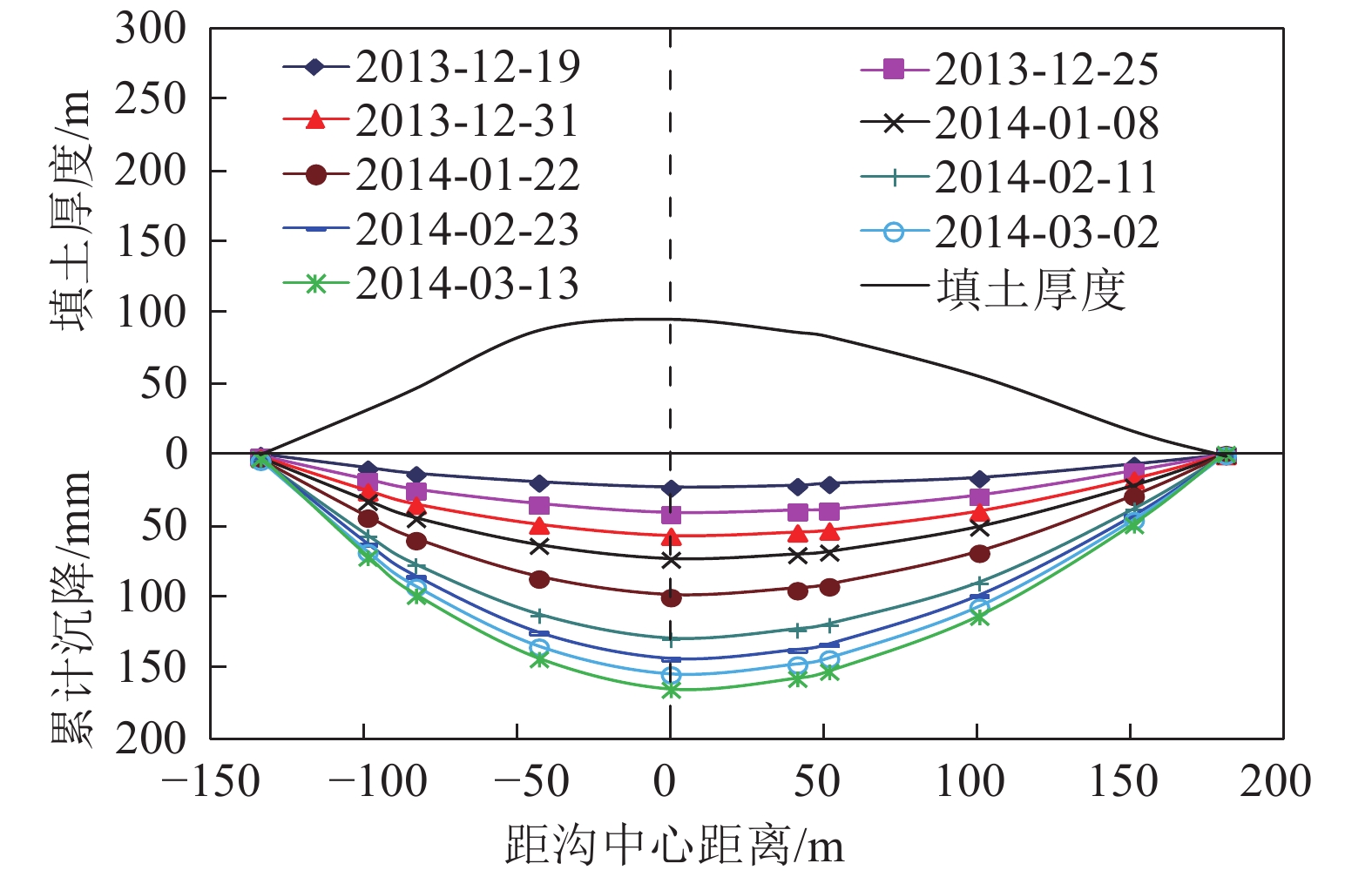
裂缝是高填方场地常见隐患,对工程场地安全和稳定造成影响。基于陕北某黄土高填方场地的裂缝监测和探测资料,分析裂缝的发育特征、分布规律和时间变化,从场地地形条件、填土厚度、变形特征等方面,对裂缝的成因机制进行探讨。研究结果表明,裂缝主要在填方区发育,分布于填方厚度小于15 m及距离挖填分界线20 m以内的区域内,以挖填交界过渡带(挖填厚度≤5 m)为主,裂缝走向与挖填界线或原地基的等高线近似一致;裂缝宽度增大速率逐渐降低,从出现到趋于稳定约需3个月时间;裂缝受降水侵蚀、潜蚀等作用,常伴生发育落水洞,并沿填土与谷坡接茬面延伸发展,距地面最大垂直深度可达7.5 m;沟谷地形、填土厚度差异等引起的差异沉降和水平位移是导致黄土高填方发生裂缝的主要原因。
Abstract:Fissures are common in high filled ground, it is a potential risk for the safety and stability of engineering sites. Based on the monitoring and detection data of ground fissures in a high loess filled ground in Northern Shaanxi, the development characteristics, distribution regularity and time variation of ground fissures are analyzed, and the formation mechanism of fissures is also discussed according to terrain conditions, thickness of filling and deformation characteristics. The results show that the fissures are mainly developed in the filling ground, and they are distributed in the areas with the thickness less than 15 m and 20 m away from the excavation-filling boundary, the main area is the transition zone between excavation and fill (thickness of excavation and filling is less than or equal to 5 m). The trend of fissures is approximately consistent with the excavation-filling boundary or the contour line of original foundation, the increasing rate of the fissure width decreases gradually, and it takes about 3 months from its appearance to stabilization. The fissures often develop with a sinkhole and extends along the joint surface between the filling and valley slope due to the effect of precipitation erosion and subsurface erosion, with a vertical depth of 7.5 m. The differential settlement and horizontal displacement caused by the difference of gully topography and thickness of filling are the main causes of fissures in high loess filled ground.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- high filled ground /
- ground fissure /
- development characteristics /
- distribution regularity
-

-
[1] 王景明. 地裂缝及其灾害的理论与应用[M]. 西安: 陕西省科学技术出版社, 2000.
WANG Jingming. Theory of ground fissures hazards and its application[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science & Technology Press, 2000.(in chinese)
[2] 孟令超, 彭建兵, 卢全中, 等. 山西太原盆地地裂缝群发机制与深部构造关系[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):76 − 85. [MENG Lingchao, PENG Jianbing, LU Quanzhong, et al. Relationship between mechanism of ground fissure group and deep tectonic structures in Taiyuan basin, Shanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):76 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王云广, 郭文兵. 采空塌陷区地表裂缝发育规律分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(1):89 − 95. [WANG Yunguang, GUO Wenbing. Analysis of ground fissure laws of mining subsidence[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(1):89 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 龚绪龙, 杨蕴, 朱锦旗, 等. 苏南平原区地裂缝现状及其需要解决的几个问题[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(2):103 − 109. [GONG Xulong, YANG Yun, ZHU Jinqi, et al. Ground fissures in south plain of Jiangsu province and related issues[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(2):103 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 黄涛, 罗喜元, 邬强, 等. 地表水入渗环境下边坡稳定性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(16):2671 − 2675. [HUANG Tao, LUO Xiyuan, WU Qiang, et al. Model testing study on slope stability under environment of surface water permeation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(16):2671 − 2675. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.002
[6] 谭桔红, 晏鄂川. 水与裂隙对边坡稳定性的影响分析 及工程应用[J]. 山地学报,2004,22(3):373 − 377. [TAN Juhong, YAN Echuan. Influence and implication of water and fissure on slope stability[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2004,22(3):373 − 377. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2004.03.022
[7] 顾淦臣. 土石坝的裂缝和压实质量[J]. 岩土工程学报,1982,4(4):56 − 67. [GU Ganchen. The fissures of earth-rock dams and density of compacted dam zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1982,4(4):56 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1982.04.005
[8] 张丙印, 张美聪, 孙逊. 土石坝横向裂缝的土工离心机模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(5):1254 − 1258. [ZHANG Bingyin, ZHANG Meicong, SUN Xun. Centrifugal modeling of transverse fissureing in earth core dams[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(5):1254 − 1258. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.05.020
[9] 朱维新. 用离心模型研究土石坝心墙裂缝[J]. 岩土工程学报,1994,16(6):82 − 95. [ZHU Weixin. Application of centrifuge to model fissureing of earth-rockfill dam core[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1994,16(6):82 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1994.06.010
[10] 张琰. 高土石坝拉张裂缝开展机理研究与数值模拟[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2009.
ZHANG Yan. Mechanism study and numerical simulation of tensile fissure propagation in high earth and rockfill dam[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2009. (in chinese)
[11] 闫芙蓉, 范文, 邓龙胜, 等. 地表水沿裂缝带入渗对路基路面的影响[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版),2010,30(2):34 − 38. [YAN Furong, FAN Wen, DENG Longsheng. Influence of water seeping fracture and fissure on subgrade and pavement[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition),2010,30(2):34 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 俞清荣. 高填方路基纵向裂缝的预防及处理措施[J]. 路基工程,2011,155(2):166 − 168. [YU Qingrong. Prevention and treatment measures of longitudinal fissures in high fill subgrade[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2011,155(2):166 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2011.03.048
[13] 朱才辉, 李宁, 刘明振, 等. 吕梁机场黄土高填方地基工后沉降时空规律分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2):293 − 301. [ZHU Caihui, LI Ning, LIU Mingzhen, et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of LYULiang airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(2):293 − 301. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张硕, 裴向军, 黄润秋, 等. 降雨诱发黄土高填方支挡边坡失稳机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(4):1094 − 1104. [ZHANG Shuo, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Rainfall induced instability mechanism of high embankment retaining loess slope[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(4):1094 − 1104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张继文, 于永堂, 李攀, 等. 黄土削峁填沟高填方地下水监测与分析[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),2016,48(4):477 − 483. [ZHANG Jiwen, YU Yongtang, LI Pan, et al. Groundwater monitoring and analysis of high fill foundation in loess hilly-gully region[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology(Natural Science Edition),2016,48(4):477 − 483. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 中华人民共和国行业标准编写委员会. 水电水利工程物探规程: DL/T 5010-2005[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2005.
The Professional Standards Compilation Group of People's Republic of China. Code for engineering geophysical exploration of hydropower and water resources: DL/T 5010-2005[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2005. (in chinese)
[17] 郑建国, 曹杰, 张继文, 等. 基于离心模型试验的黄土高填方沉降影响因素分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(3):560 − 571. [ZHENG Jianguo, CAO Jie, ZHANG Jiwen, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of high loess-filled foundation based on centrifugal model tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(3):560 − 571. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: