Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis
-
摘要:
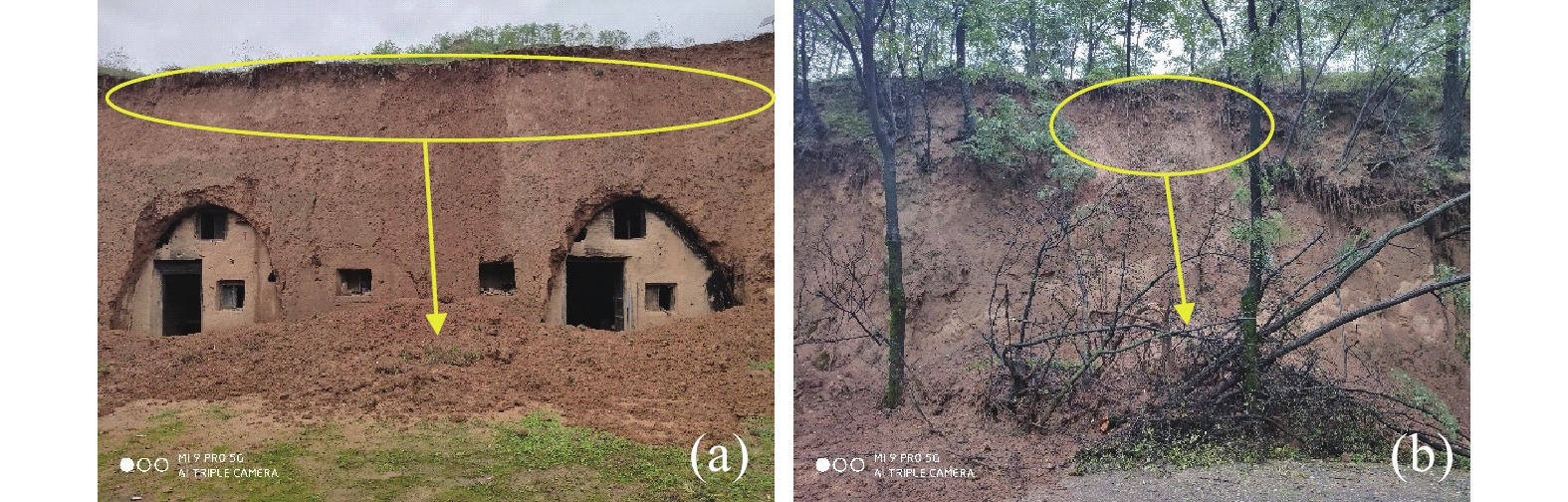
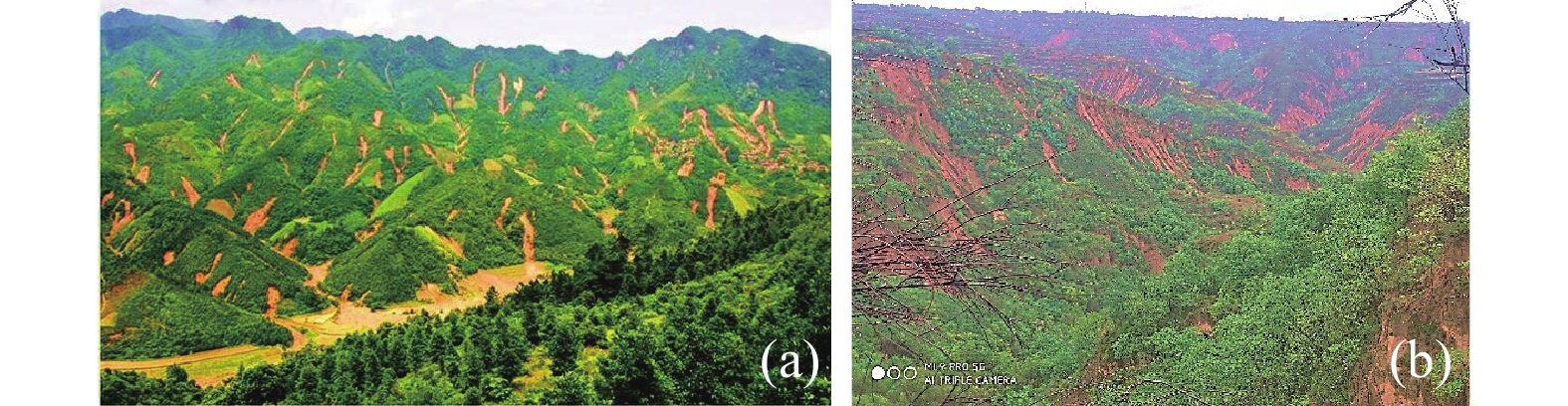
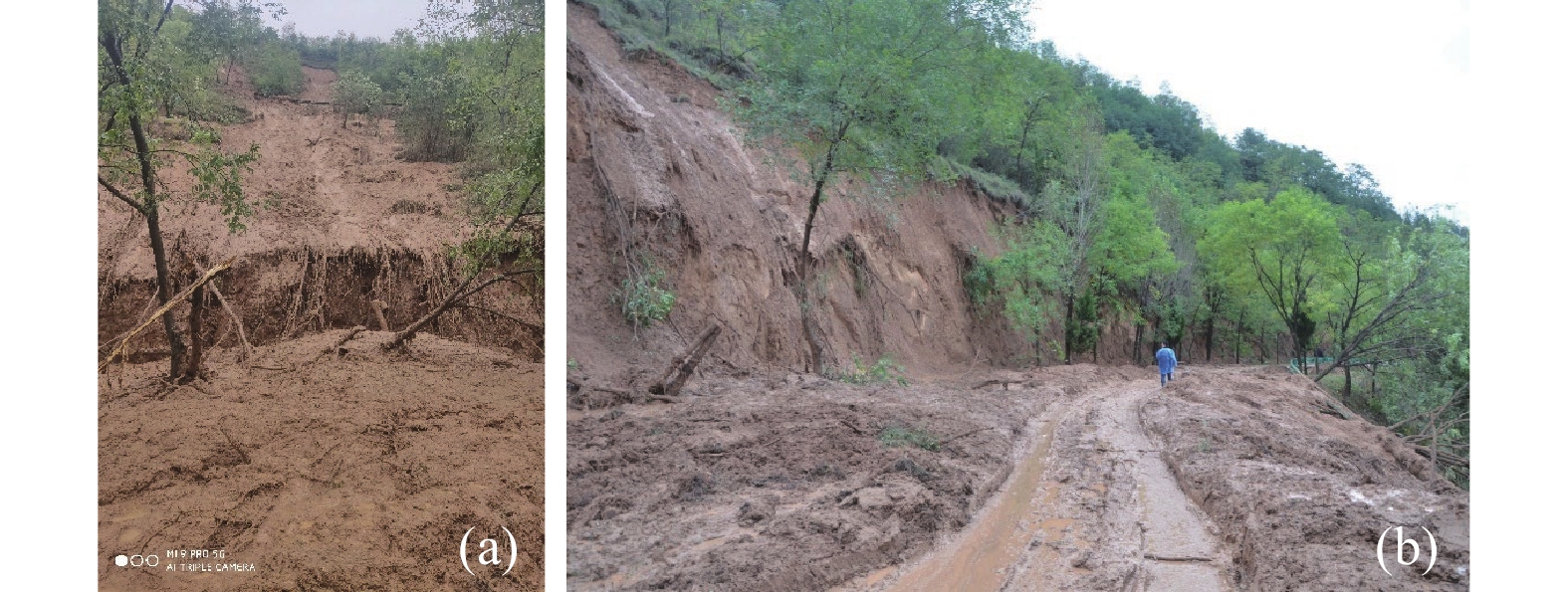
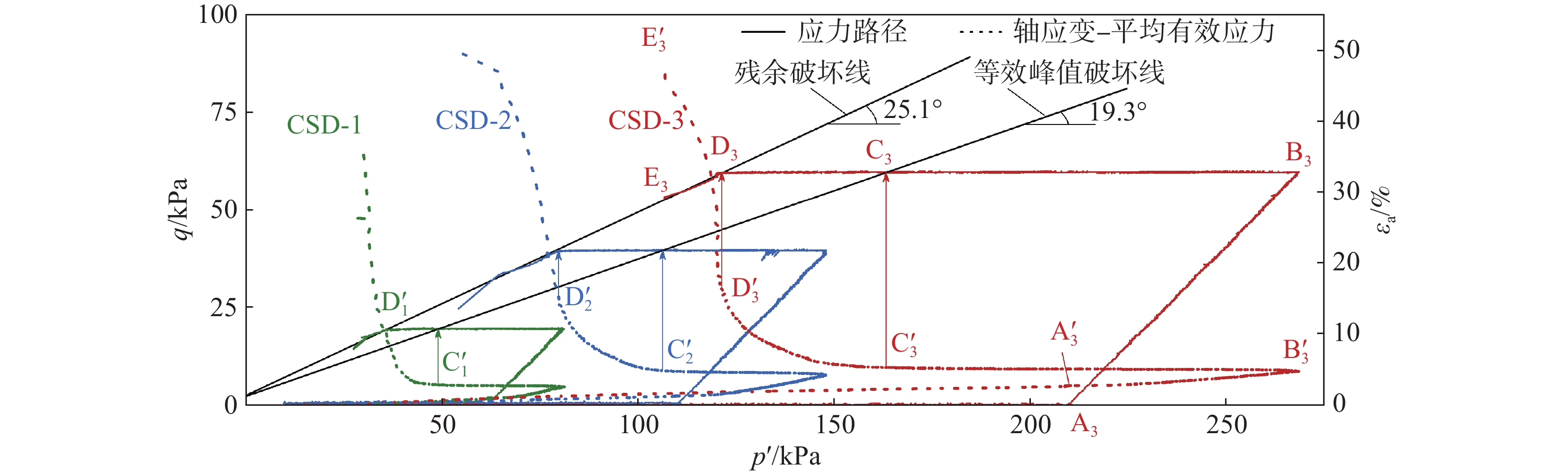
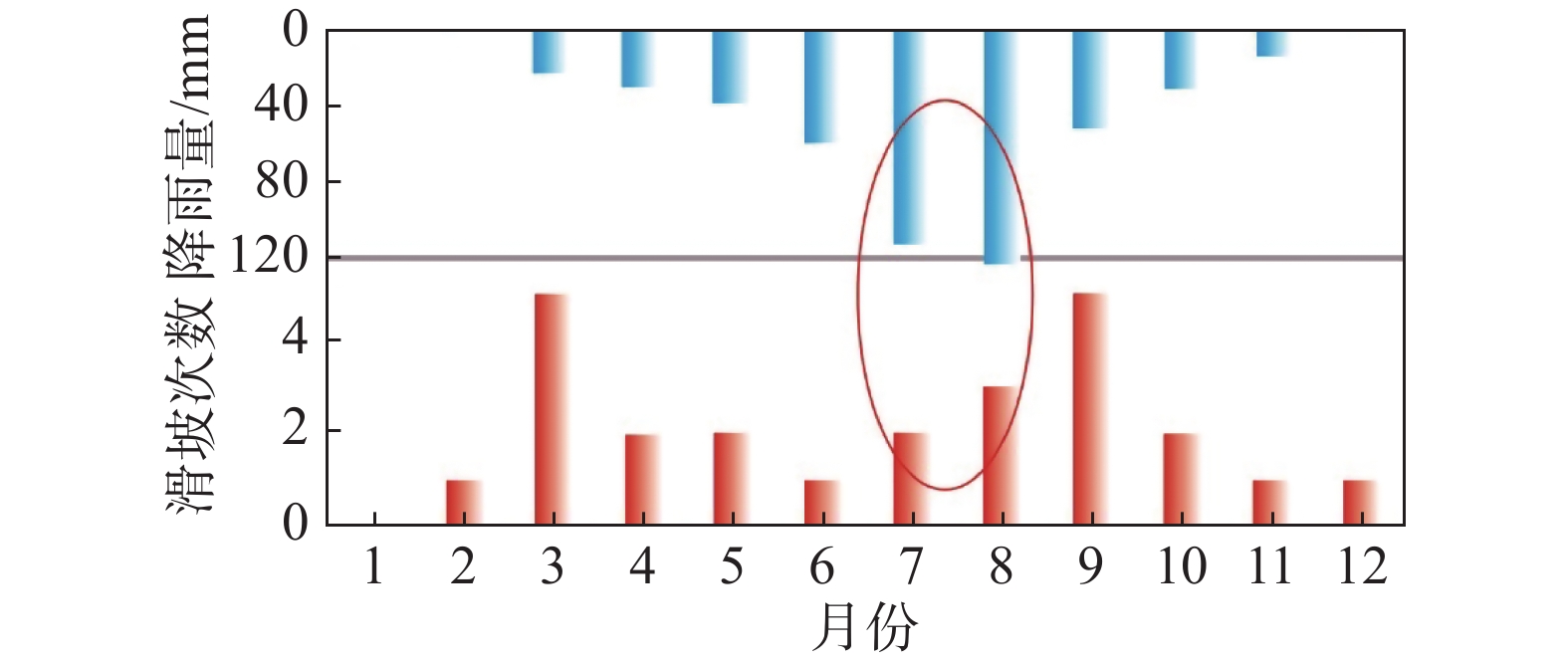
水对斜坡作用包括地表水流动作用和地表水入渗作用,地表水流动作用,如水库、河流的岸坡破坏,由水动力侵蚀所引起。目前黄土中地表水入渗影响下的斜坡稳定性分析存在一些概念含糊的问题,如忽略了入渗过程的应力路径,只考虑其破坏时的应力状态,这会导致对其破机理和稳定性计算参数取值的误判,文章只针对该类问题进行辨析讨论。黄土中地表水的入渗一般有降雨和灌溉两种,伴随降雨入渗多引起斜坡浅层破坏;灌溉导致地下水位上升则引起深层滑移。地表水入渗对斜坡总应力改变不大,水致斜坡破坏主要是孔隙水压力上升,土体有效应力降低所致。非饱和黄土中的初始孔隙水压力为负值,降雨入渗后的浅层黄土仍处于非饱和状态,孔压最大升到0;灌溉会引起地下水位抬升,潜水位下为正的孔隙水压力。明确了孔压变化过程,就可以用有效强度评价边坡稳定性。同时,目前一些观点认为关于流动性黄土滑坡是静态引起,这颠倒了因果关系,是滑移引起了液化,而不是液化导致的滑移。
Abstract:The action on water slope includes surface water flow and surface water infiltration, and surface water flow, such as slope damage of reservoir and river banks, is caused by hydrodynamic erosion. At present, there are some vague concepts in slope stability analysis under the influence of surface water infiltration in loess. For example, ignoring the stress path in the infiltration process and only considering the stress state at the time of its failure will lead to misjudgment of its failure mechanism and the value of stability calculation parameters. This paper aims to analyses and clarify the issues. There are two sources of groundwater in loess, those are rainfall and irrigation. Rainfall infiltration produces shallow slope failure during raining time, while irrigation causes groundwater level rising to trigger deep seated slide. Surface water infiltration can make a remarkable rising of pore water pressure, but minor change of the total stress, and a consequent decreasing of effective stress in the slope, which is the cause of slope failure triggered by water. The initial pore water pressure in unsaturated loess is negative, and the shallow loess after rainfall infiltration is still in unsaturated state, and the pore water pressure rises to 0 at the maximum. Irrigation will cause the groundwater level to rise, and the pore water pressure under the water table will be positive. When the change process of pore water pressure is made clear, the slope stability can be evaluated by effective strength. At the same time, at present, some opinions think that the landslide of flowing loess is caused by static state, which reverses the causality, and it is the slip that causes liquefaction, not the slip caused by liquefaction.
-
Key words:
- loess slope /
- shallow failure /
- deep seated slide /
- rainfall /
- irrigation
-

-
[1] 张茂省, 李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):530 − 540. [ZHANG Maosheng, LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):530 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
[2] WANG G L, LI T L, XING X L, et al. Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an, NW China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,73(12):7933 − 7944. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3951-9
[3] 习羽, 李同录, 邢鲜丽. 灌渠渗漏诱发的黄土滑坡泥流触发机理分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2017,39(1):135 − 142. [XI Yu, LI Tonglu, XING Xianli. Analysis of the triggering mechanism of a loess flowslide induced by water canal leakage[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2017,39(1):135 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.01.011
[4] TU X B, KWONG A K L, DAI F C, et al. Field monitoring of rainfall infiltration in a loess slope and analysis of failure mechanism of rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 105(1/2): 134-150.
[5] XU L, DAI F C, THAM L G, et al. Field testing of irrigation effects on the stability of a cliff edge in loess, North-west China[J]. Engineering Geology,2011,120(1/2/3/4):10 − 17.
[6] 邢鲜丽, 李同录, 李萍, 等. 黄土抗剪强度与含水率的变化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(3):53 − 59. [XING Xianli, LI Tonglu, LI Ping, et al. Variation regularities of loess shear strength with the moisture content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(3):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李同录, 习羽, 侯晓坤. 水致黄土深层滑坡灾变机理[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(5): 1113-1120
LI Tonglu, XI Yu, HOU Xiaokun. Mechanism of surface water infiltration induced deep loess landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5): 1113-1120. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[8] 李萍, 李同录, 侯晓坤, 等. 黄土中毛细上升速率的现场测试[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(6): 503-507
LI Ping, LI Tonglu, HOU Xiaokun, et al. Field experiment on rate of capillary rise in loess[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2014, 42(6): 503-507. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[9] 李宝平, 杨倩, 张玉, 平高权, 等. 初始固结应力对平面应变黄土剪切破坏特性影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):92 − 99. [ LI Baoping, YANG Qian, ZHANG Yu, PING Gaoquan, et al. Effect of initial solidification stress on shear failure characteristics of loess under the plane strain condition[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):92 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 强菲, 李萍, 李同录. 黄土完全软化强度与残余强度的对比试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(5):832 − 838. [QIANG Fei, LI Ping, LI Tonglu. Comparative test study between fully softened and residual strengths of loess[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(5):832 − 838. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] VANAPALLI S K, FREDLUND D G, PUFAHL D E, et al. Model for the prediction of shear strength with respect to soil suction[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1996,33(3):379 − 392. doi: 10.1139/t96-060
[12] 吴宏伟. 大气–植被–土体相互作用: 理论与机理[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(1):1 − 47. [WU Hongwei. Atmosphere-plant-soil interactions: Theories and mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(1):1 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 徐则民, 黄润秋, 唐正光, 等. 植被护坡的局限性及其对深层滑坡孕育的贡献[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(3):438 − 450. [XU Zemin, HUANG Runqiu, TANG Zhengguang, et al. Limitations of biotechnical slope protection and contribution of vegetation to deep seated landslide preparation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(3):438 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 孙长忠, 黄宝龙, 陈海滨, 等. 黄土高原人工植被与其水分环境相互作用关系研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报,1998,20(3):10 − 17. [SUN Changzhong, HUANG Baolong, CHEN Haibin, et al. Study on the interaction between artificial vegetation and its water environment in the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,1998,20(3):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 韩勇, 郑粉莉, 徐锡蒙, 等. 子午岭林区浅层滑坡侵蚀与植被的关系—以富县“7·21”特大暴雨为例[J]. 生态学报,2016,36(15):4635 − 4643. [HAN Yong, ZHENG Fenli, XU Ximeng, et al. Relationship between shallow landslide erosion and vegetation in the Ziwuling forest area: A case study of the "7·21" disaster in Fuxian County[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(15):4635 − 4643. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 许领, 戴福初, 闵弘, 等. 泾阳南塬黄土滑坡类型与发育特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2010,35(1):155 − 160. [XU Ling, DAI Fuchu, MIN Hong, et al. Loess landslide types and topographic features at south Jingyang plateau, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences,2010,35(1):155 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.016
[17] 程秀娟, 张茂省, 朱立峰, 等. 季节性冻融作用及其对斜坡土体强度的影响-以甘肃永靖黑方台地区为例[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(6):904 − 909. [CHENG Xiujuan, ZHANG Maosheng, ZHU Lifeng, et al. Seasonal freeze-thaw action and its effect on the slope soil strengthin Heifangtai area Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(6):904 − 909. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.06.013
[18] 亓星, 许强, 李斌, 等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡地表水入渗机制初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(3):418 − 424. [QI Xing, XU Qiang, LI Bin, et al. Preliminary study on mechanism of surface water infiltration at Heifangtai loess landslides in Gansu[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(3):418 − 424. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 金艳丽, 戴福初. 地下水位上升下黄土斜坡稳定性分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(5):599 − 606. [JIN Yanli, DAI Fuchu. Analysis of loess slope stability due to groundwater rise[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(5):599 − 606. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.05.004
[20] 张常亮, 李萍, 李同录, 等. 黄土中降雨入渗规律的现场监测研究[J]. 水利学报,2014,45(6):728 − 734. [ZHANG Changliang, LI Ping, LI Tonglu, et al. In-situ observation on rainfall infiltration in loess[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2014,45(6):728 − 734. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] ZHANG C l, LI T L, LI P. Rainfall infiltration in Chinese loess by in situ observation[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2014, 19(9): 06014002.
[22] 李萍, 李同录, 付昱凯, 等. 非饱和黄土中降雨入渗规律的现场监测研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(10):3551 − 3560. [LI Ping, LI Tonglu, FU Yukai, et al. In-situ observation on regularities of rainfall infiltration in loess[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2014,45(10):3551 − 3560. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] ZHANG Y G, LI T L, SHEN W, et al. Hydraulic model of transition of transient to steady flows in the vadose zone[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering,2019,24(12):04019052. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001843
[24] 金艳丽, 戴福初. 饱和黄土的静态液化特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(12):3293 − 3298. [JIN Yanli, DAI Fuchu. Experimental investigation of static liquefaction of saturated loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(12):3293 − 3298. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.12.021
[25] 张一希, 许强, 刘方洲, 等. 不同地区饱和原状黄土静态液化特性试验研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(5):229 − 233. [ZHANG Yixi, XU Qiang, LIU Fangzhou, et al. Experimental investigation of static liquefaction of undisturbed saturated loess in different regions[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(5):229 − 233. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] SASSA K. Geotechnical model for the motion of slides[C]. Proceedings of 5th International Symposium on landslides, 1988, I: 37 − 56.
-




 下载:
下载: