Hazard assessment of typical gully debris flow in Anning river:A case study at the Lengzi gully
-
摘要:
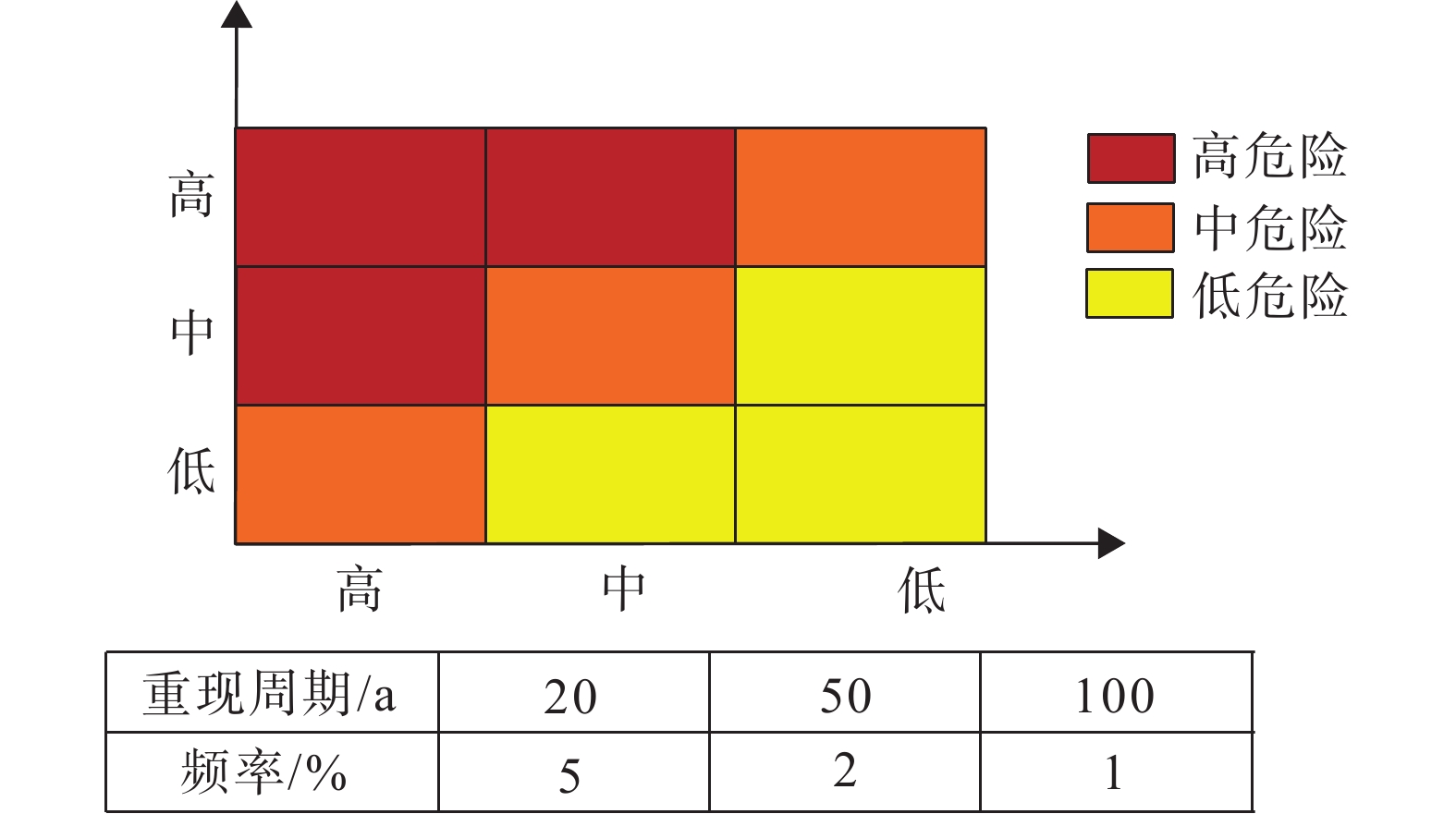
冕宁县安宁河流域为地质灾害密集分布区,安宁河断裂穿越于此,构造复杂,冷渍沟在上游左岸发育。在强降雨条件下,该沟就会暴发泥石流,堵塞安宁河流域和掩埋杀叶马村房屋和道路。冷渍沟泥石流具有流域面积小,主沟长度短,沟床纵比降大等特征,为了研究安宁河流域内泥石流的危险性,以冷渍沟为例,分析不同降雨周期下的泥石流暴发强度,模拟泥石流的运动过程并进行危险性评价。模拟的最大流速、最大堆积深度和降雨强度三者结合建立冷渍沟泥石流危险性评价模型。研究结果表明,冷渍沟泥石流危险范围内高危险区域占27%,主要集中在松散固体物质较多的沟道,中危险性区域和低危险区域各占56%和17%,该结论为危险范围内的居民和重点设施的风险管控提供参考。
Abstract:The Anning river basin is a densely distributed area of geological hazards, where the Anning river rift crosses, with complex tectonics and the Lengzi gully developing in the upper left bank. The gully is subject to mudslides under heavy rainfall conditions, blocking the Anning river basin and burying houses and roads in the village of Yema. Lengzi gully debris flow has the characteristics of small area,a short main trench and a large channel longitudinal slope. To explore these damage, taking Lengzi gully as an example, the intensity of debris flow burst under different rainfall cycles is analyzed, and the movement process of debris flow is simulated and the risk assessment is carried out. Combined with the simulated maximum flow velocity, maximum accumulation depth and rainfall intensity,the hazard assessment model is established.The results show that in the danger range of Lengzi gully debris flow, the high risk area accounts for 27%, mainly distributed in the channel with more loose solid materials, and the medium risk area and low risk area account for 56% and 17%, respectively. this conclusion provides a scientific basis for the monitoring and early warning of key facilities in the danger range.
-
Key words:
- Lengzi gully /
- FLO-2D /
- gully debris flow /
- hazard assessment
-

-
表 1 FLO-2D手册建议的曼宁系数值
Table 1. Manning coefficient values suggested by the FLO-2D manual
地表状况 曼宁系数值 地表状况 曼宁系数值 茂密草地 0.17~0.8 耕地 0.0008~0.012 植物茂密灌木草地 0.17~0.48 轮休耕地 0.06~0.22 杂林灌木、牧草地 0.3~0.4 传统耕地 0.06~0.16 一般草地植生 0.2~0.4 以整地农地 0.3~0.5 植物稀疏粗糙地 0.2~0.3 梯田 0.07~0.17 矮草原 0.1~0.2 无耕农作物 0.17~0.47 稀疏草原 0.05~0.13 有块石分布开阔地 0.1~0.2 有块石分布稀疏植被 0.09~0.34 沥青混凝土 0.02~0.005 表 2 冷渍沟泥石流20年一遇参数选取
Table 2. The parameter of Lengzi gully under 20 years rainfall frequency
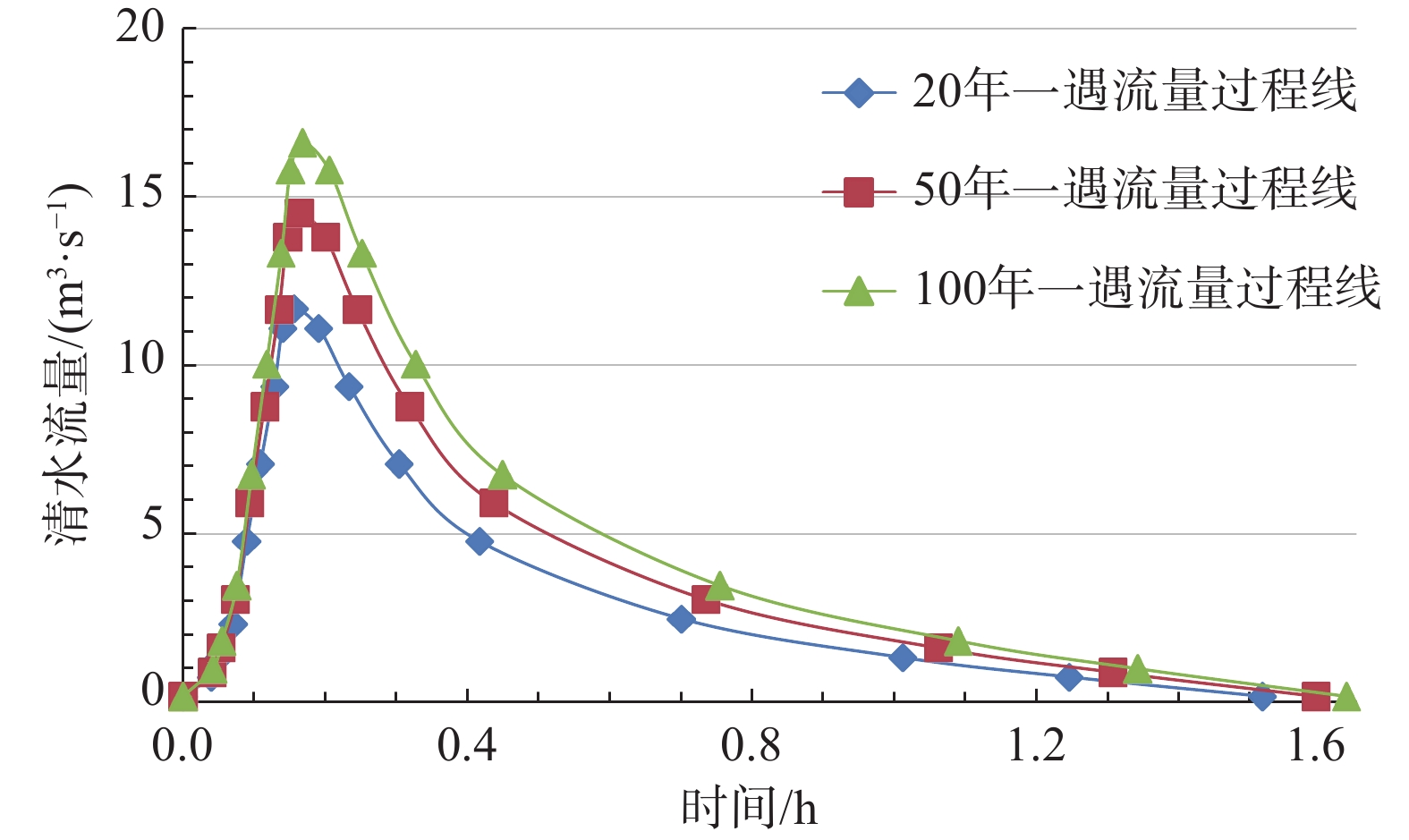
流域面积F/m2 沟道长度L/km 屈服应力τy/MPa 黏滞系数η 层流阻力系数K 曼宁系数nc 0.62×106 1.49 4903 5704 2280 0.18 放大系数BF 径流深度H /cm 汇流时间τ/h 体积浓度/Cv 洪峰流量Qp/(cm3·s−1) 洪水流量Wp/104 m3 2.5 26 1.6 0.6 11.57×106 1.612 表 3 冲沟冷渍沟泥石流对比验证表
Table 3. Comparison and verification table of debris flow in Lengzi gully
泥石流沟道名称 设计频率 /% 最大冲出长度/m 最大冲出宽度/m 冲出范围/(104 m2) 精度/% 模拟 实际 模拟 实际 模拟 实际 重叠 冷渍沟 5.00 207.00 190.00 147.00 187.00 1.52 1.77 1.32 86 表 4 研究区泥石流强度划分表
Table 4. Debris flow intensity division table in the study area
危险等级 最大堆积
深度/m关系式 最大堆积深度/m与
最大流速/(m·s−1)乘积高 H≥2.5 OR VH≥2.5 中 0.5≤H<2.5 AND 0.5≤VH<2.5 低 H<0.5 AND VH<0.5 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范: DZ/T 0220—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. Specification of geological investigation for debris flow stabilization: DZ/T 0220—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006. (in Chinese)
[2] 倪化勇. 人工降雨条件下冲沟型泥石流起动试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(1):111 − 118. [NI Huayong. Field experiments for groove-type debris flow initiation with artificial rainfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(1):111 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NI Huayong. Field experiments for groove-type debris flow initiation with artificial rainfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(1): 111-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李秀珍, 刘希林, 苏鹏程. 四川凉山州安宁河流域泥石流危险性评价[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2005,25(4):426 − 430. [LI Xiuzhen, LIU Xilin, SU Pengcheng. Assessment on regional debris flow hazardousness of Anning River valley in Liangshan prefecture, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Disaster Pnevention and Mitigation Engineering,2005,25(4):426 − 430. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Xiuzhen, LIU Xilin, SU Pengcheng. Assessment on regional debris flow hazardousness of Anning River valley in Liangshan prefecture, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Disaster Pnevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2005, 25(4): 426-430. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] BERTOLO P, WIECZOREK G F. Calibration of numerical models for small debris flows in Yosemite Valley, California, USA[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2005,5(6):993 − 1001. doi: 10.5194/nhess-5-993-2005
[5] 龚柯, 杨涛, 夏晨皓, 等. 基于FLO-2D的泥石流危险性评价:以四川省汶川县绵虒镇簇头沟为例[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2017,28(6):134 − 138. [GONG Ke, YANG Tao, XIA Chenhao, et al. Assessment on the hazard of debris flow based on FLO-2D: A case study of debris flow in Cutou gully, Wenchuan, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2017,28(6):134 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2017.06.23
GONG Ke, YANG Tao, XIA Chenhao, et al. Assessment on the hazard of debris flow based on FLO-2D: a case study of debris flow in Cutou Gully, Wenchuan, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2017, 28(6): 134-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2017.06.23
[6] CHRISTEN M, KOWALSKI J, BARTELT P. RAMMS: Numerical simulation of dense snow avalanches in three-dimensional terrain[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology,2010,63(1/2):1 − 14.
[7] NOCENTINI M, TOFANI V, GIGLI G, et al. Modeling debris flows in volcanic terrains for hazard mapping: the case study of Ischia Island (Italy)[J]. Landslides,2015,12(5):831 − 846. doi: 10.1007/s10346-014-0524-7
[8] QUAN L B, BLAHUT J, VAN W C J, et al. The application of numerical debris flow modelling for the generation of physical vulnerability curves[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science,2011,138(11):2047 − 2060.
[9] 余宏明, 袁宏成, 唐辉明. 巴东县新城区冲沟泥石流危险度评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2003, 30(增刊1): 47 − 49
YU Hongming, YUAN Hongcheng, TANG Huiming. Fuzzy comprehendsive evaluation method to evaluate debris flow risk factor in Badong new city[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2003, 30(Sup 1): 47 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 詹钱登, 萧凯文, 徐郁超, 等. 应用 FLO-2D及 Debris 2D模拟羌黄坑集水区内土石流流动特性差异之研究[J]. 中华防灾学刊,2015,7(2):239 − 247. [ZHAN Qiandeng, XIAO Kaiwen, XU Yuchao, et al. Study on the difference of flow characteristics of soil-rock flow in Qianghuangkeng catchment area by using FLO-2D and Debris 2D[J]. Chinese Journal of Disaster Prevention,2015,7(2):239 − 247. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAN Qiandeng, XIAO Kaiwen, XU Yuchao, et. al. , Study on the difference of flow characteristics of soil-rock flow in Qianghuangkeng catchment area by using FLO-2D and Debris 2D[J]. Chinese Journal of Disaster Prevention. 2015, 7(2): 239-247. ( in Chinese with English abstract
[11] 曹鹏, 侯圣山, 陈亮, 等. 基于数值模拟的群发性泥石流危险性评价:以甘肃岷县麻路河流域为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):100 − 109. [CAO Peng, HOU Shengshan, CHEN Liang, et al. Risk assessment of mass debris flow based on numerical simulation: An example from the Malu River Basin in Min County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):100 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAO Peng, HOU Shengshan, CHEN Liang, et al. Risk assessment of mass debris flow based on numerical simulation: an example from the Malu River Basin in Min County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 100-109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 唐川, 李为乐, 丁军, 等. 汶川震区映秀镇“8·14”特大泥石流灾害调查[J]. 地球科学,2011,36(1):172 − 180. [TANG Chuan, LI Weile, DING Jun, et al. Field investigation and research on giant debris flow on August 14, 2010 in Yingxiu Town, epicenter of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earth Science,2011,36(1):172 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TANG Chuan, LI Weile, DING Jun, et al. Field investigation and research on giant debris flow on August 14, 2010 in yingxiu town, epicenter of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earth Science, 2011, 36(1): 172-180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 崔鹏, 邹强. 山洪泥石流风险评估与风险管理理论与方法[J]. 地理科学进展,2016,35(2):137 − 147. [CUI Peng, ZOU Qiang. Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography,2016,35(2):137 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001
CUI Peng, ZOU Qiang. Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography, 2016, 35(2): 137-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001
[14] 牛全福, 陆铭, 李月锋, 等. 基于灰色关联与粗糙依赖度的甘肃兰州市区泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):48 − 56. [NIU Quanfu, LU Ming, LI Yuefeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province based on methods of grey relation and rough dependence[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):48 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIU Quanfu, LU Ming, LI Yuefeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province based on methods of grey relation and rough dependence[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5): 48-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 常鸣, 唐川. 基于水动力的典型矿山泥石流运动模式研究[J]. 水利学报,2014,45(11):1318 − 1326. [CHANG Ming, TANG Chuan. Study on typical movement model in mine debris flow based on hydrodynamic force conditions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2014,45(11):1318 − 1326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHANG Ming, TANG Chuan. Study on typical movement model in mine debris flow based on hydrodynamic force conditions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 45(11): 1318-1326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 林文, 周伟, 李靖, 等. 基于Flow-R和FLO-2D耦合模型的沟谷型泥石流危险性评价[J/OL]. 人民长江: 1 − 9
LIN Wen, ZHOU Wei, LI Jing, et al. Debris flow hazard assessment based on combination of Flow-R and FLO-2D models[J/OL]. Yangtze River: 1 − 9. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?bcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=RIVE20211008000&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=HFdcQQN9Fr2BnwrB79d72ZrNvTI4uEHW_decSY9iPILe_gw9fCRwPOFDhHUORNjy (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈兴长, 游勇, 陈晓清, 等. 安宁河上游冷渍沟泥石流特征及其发展趋势[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2012,21(1):122 − 128. [CHEN Xingzhang, YOU Yong, CHEN Xiaoqing, et al. Characteristics and development trends of debris flows of lengzi gully in the upper Anning River, southwest Sichuan, China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2012,21(1):122 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Xingzhang, YOU Yong, CHEN Xiaoqing, LIU Jinfeng, HUANG Kai ], YOU Yong, CHEN Xiaoqing, et al. Characteristics and development trends of debris flows of lengzi gully in the upper Anning River, southwest Sichuan, China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2012, 21(1): 122-128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] ADEGBE M, ALKEMA D, JETTEN V G, et al. Post seismic debris flow modelling using FLO-2D: Case study of Yingxiu, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Geography and Geology,2013,5(3):101 − 115.
[19] O’BRIEN J S, JULIEN P Y. Physical properties and mechanics of hyperconcentrated sediment flows[J]. Flash Floods and Debris Flow Hazards in Utah,1985:260 − 279.
[20] 四川省水电局. 四川省水文手册[M]. 四川省水利电力局水文总站图书出版社, 1984
Sichuan Provincial Hydropower Bureau. Sichuan province hydrology manual[M]. Sichuan Provincial Water Resources and Electric Power Bureau Hydrology Station Book Press, 1984. (in Chinese)
[21] PENG S H, LU S C. FLO-2D simulation of mudflow caused by large landslide due to extremely heavy rainfall in southeastern Taiwan during Typhoon Morakot[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2013,10(2):207 − 218. doi: 10.1007/s11629-013-2510-2
[22] 常鸣, 窦向阳, 唐川, 等. 降雨驱动泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(8):2794 − 2802. [CHANG Ming, DOU Xiangyang, TANG Chuan, et al. Hazard assessment of typical debris flow induced by rainfall intensity[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(8):2794 − 2802. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHANG Ming, DOU Xiangyang, TANG Chuan, et al. Hazard assessment of typical debris flow induced by rainfall intensity[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8): 2794-2802. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: