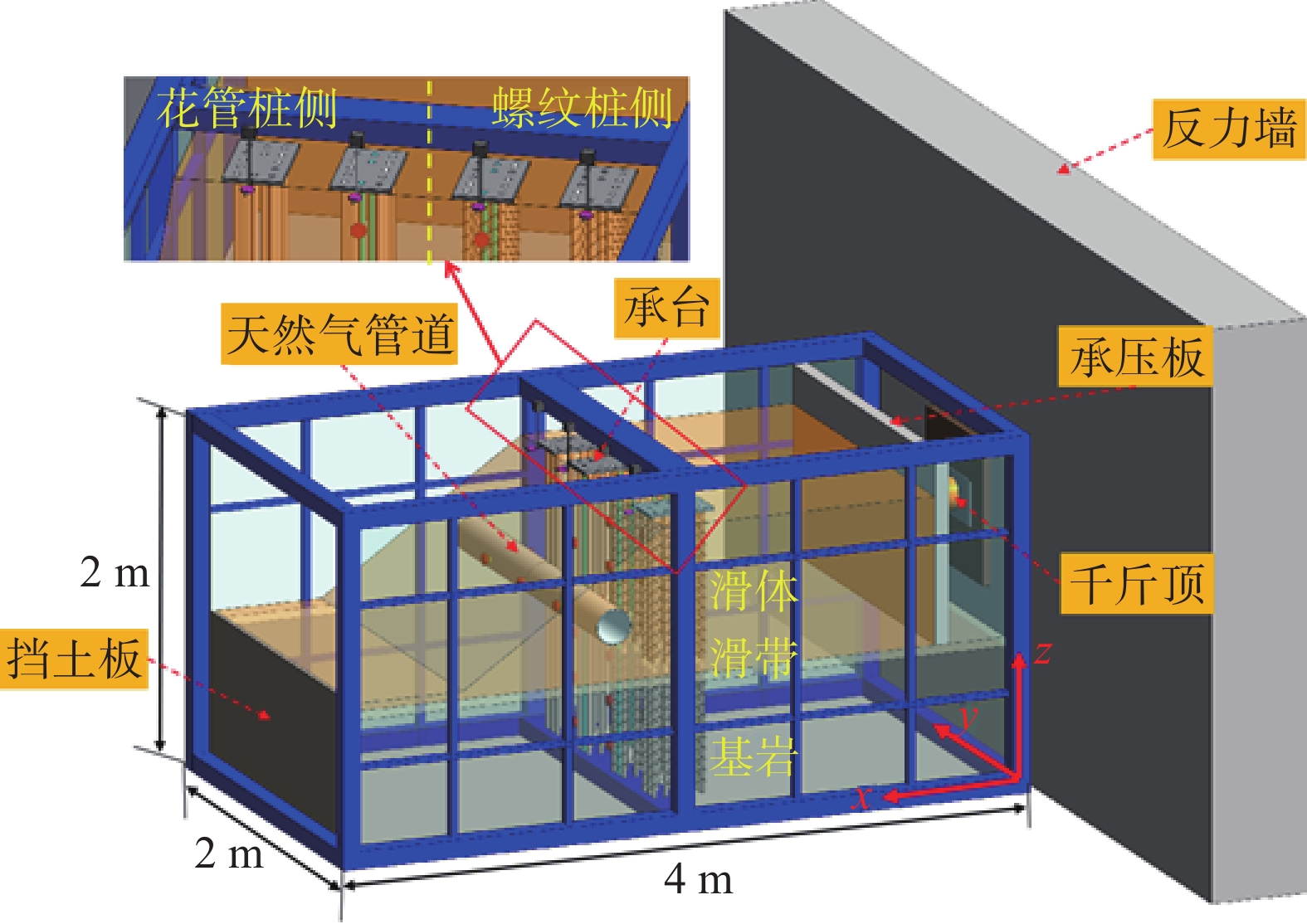
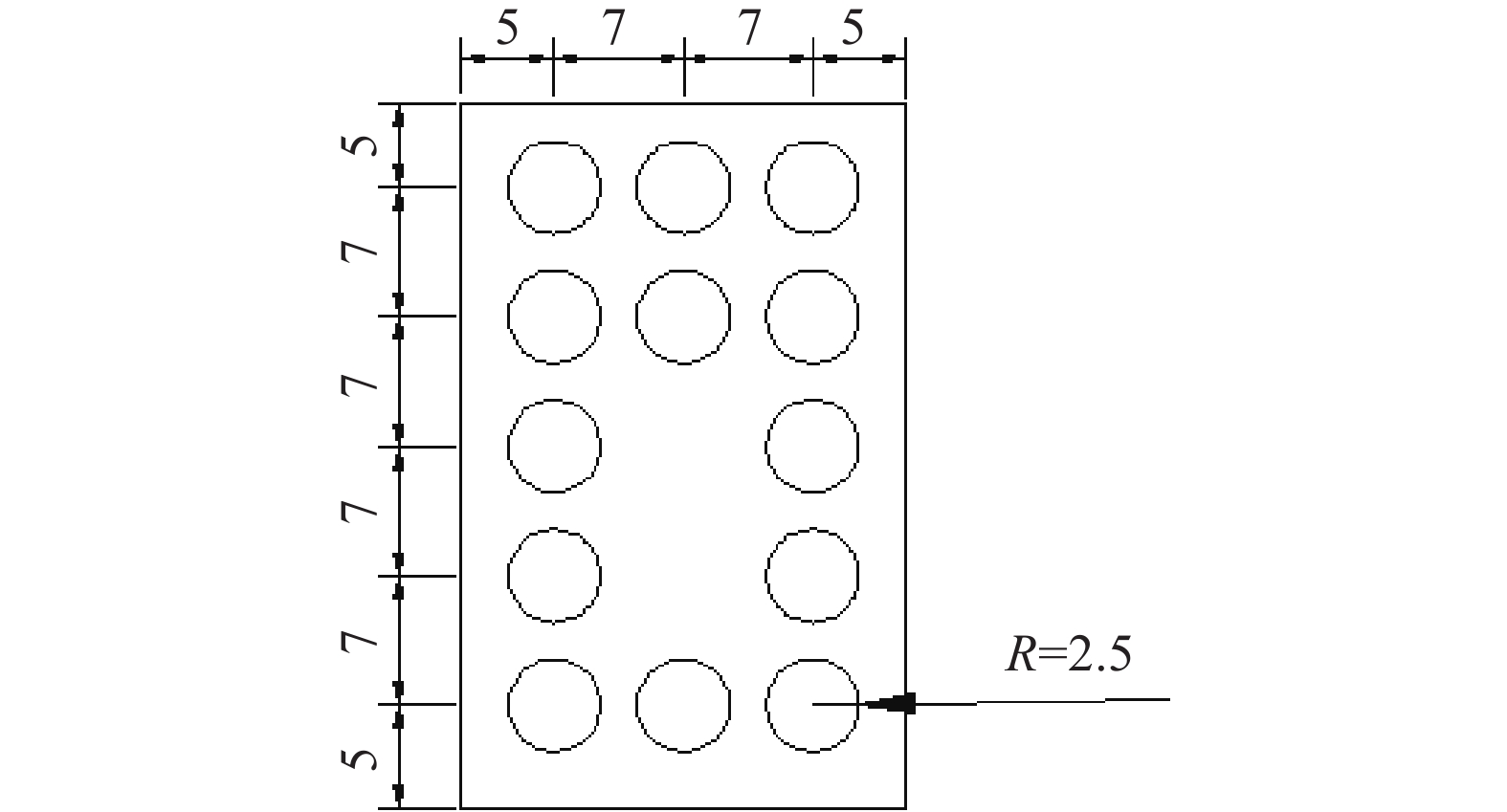
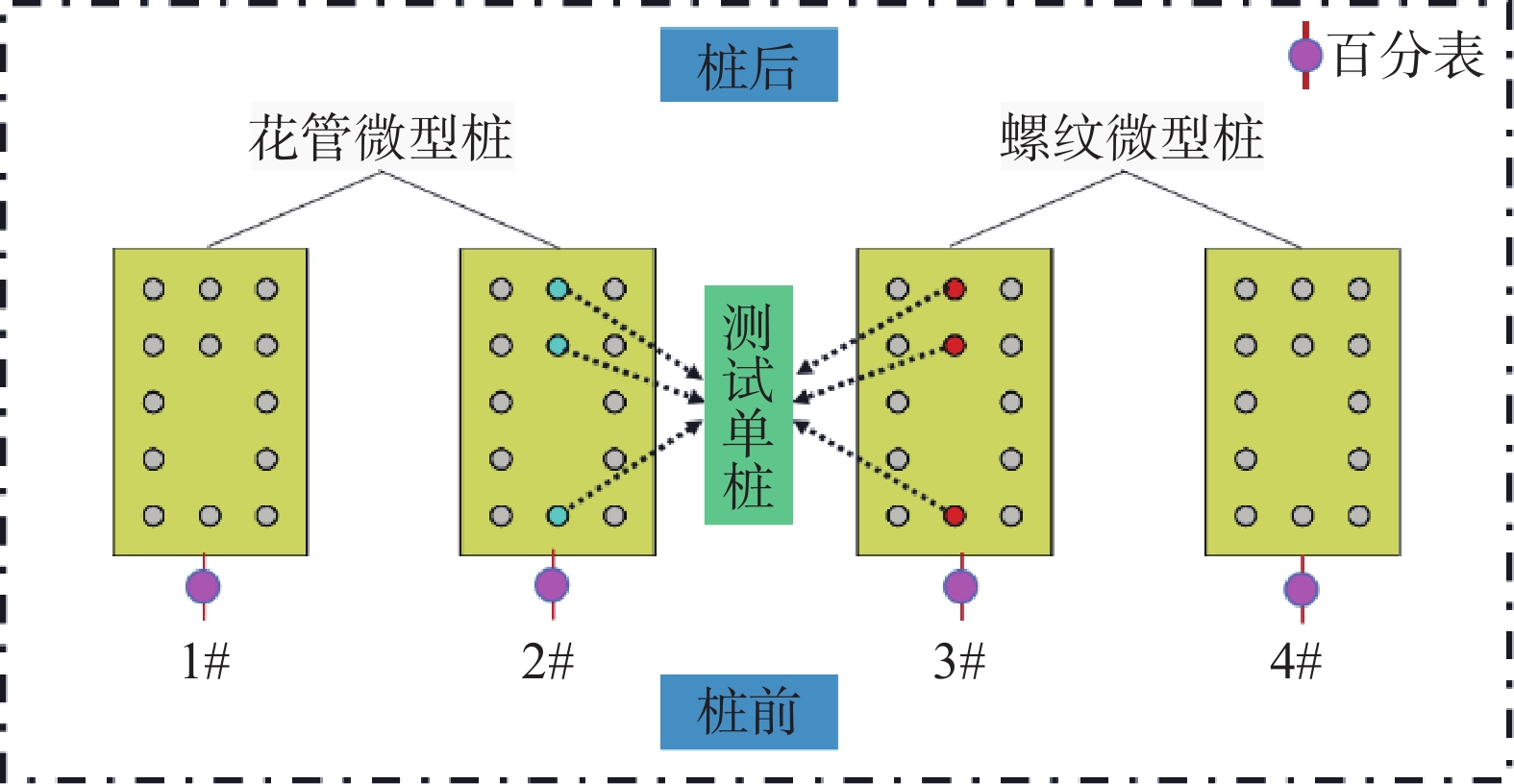
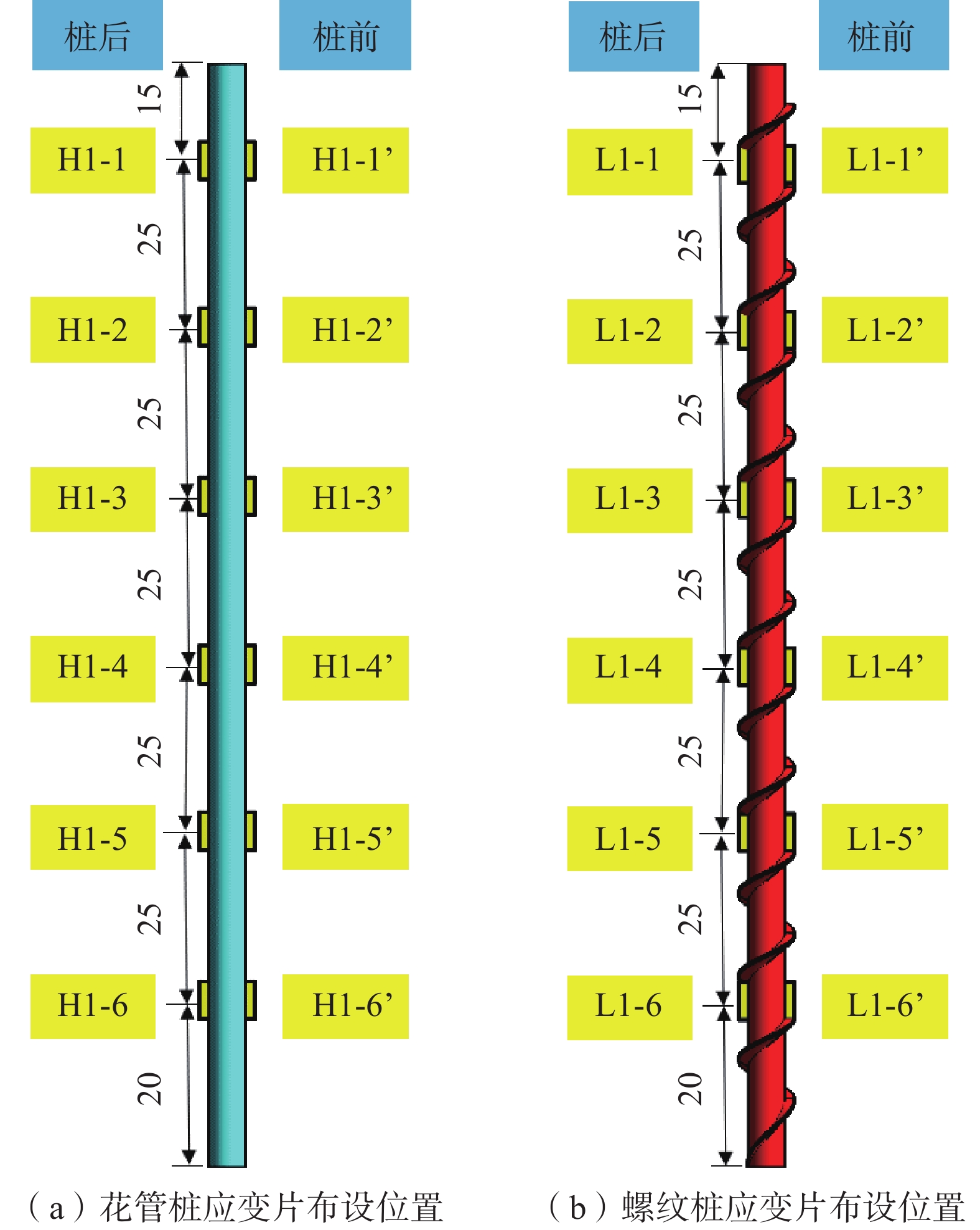
Physical model tests on supporting performance of micro-pile and micro-pile with thread in natural gas pipe-landslide system in mountainous area
-
摘要:
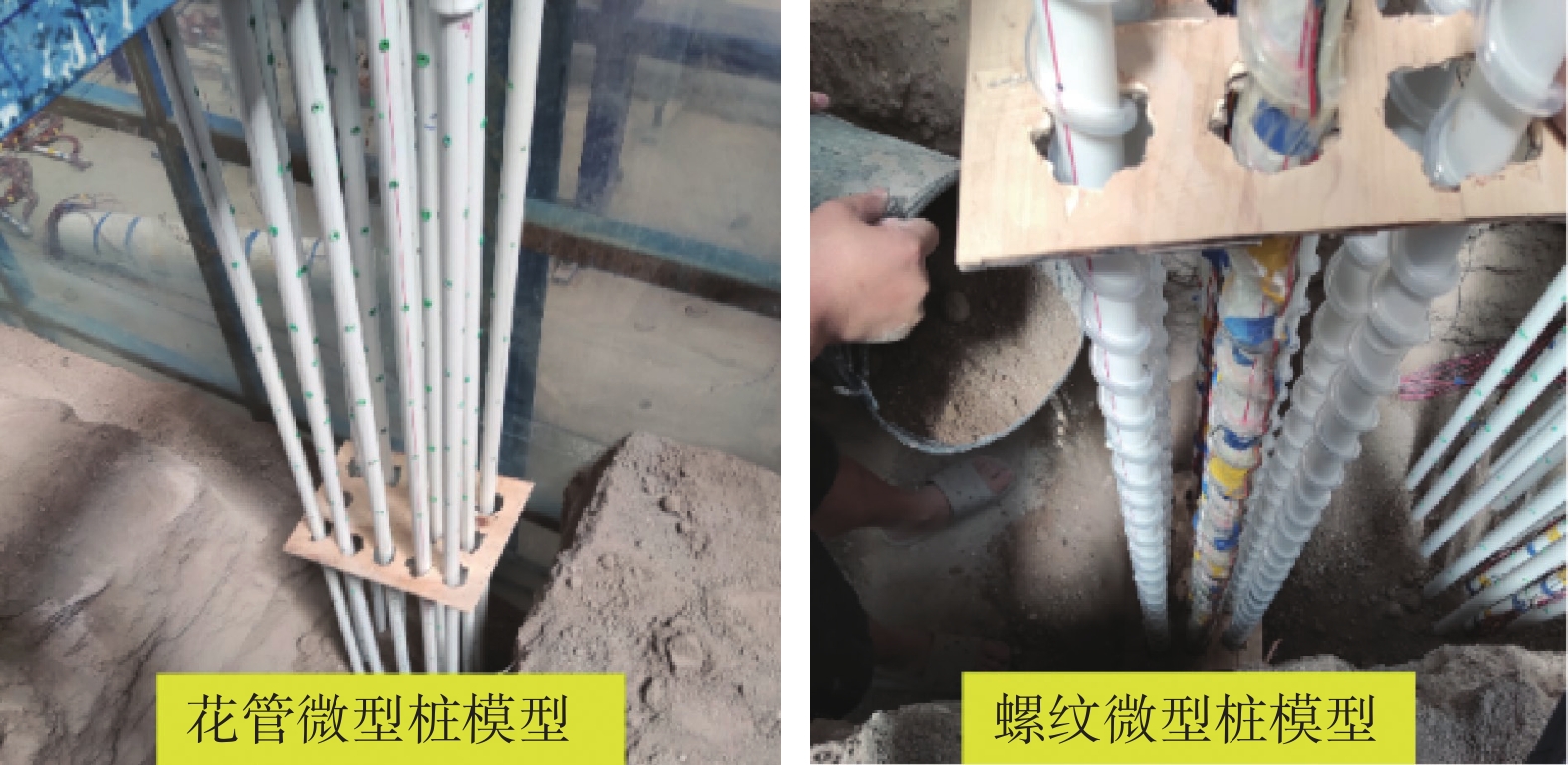
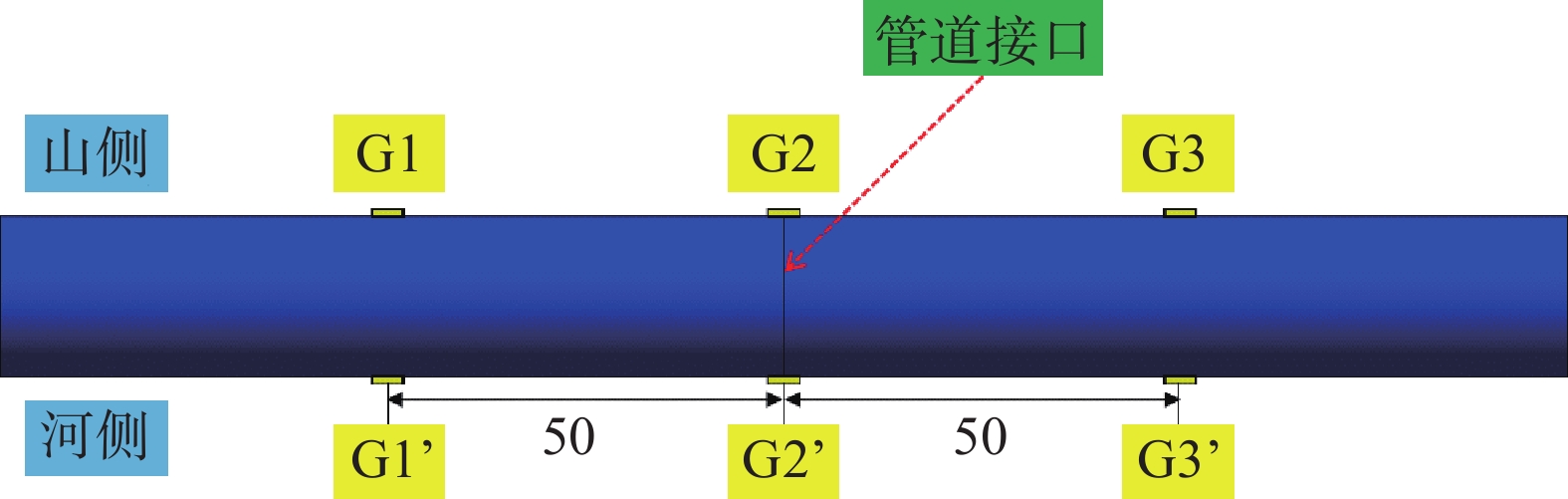
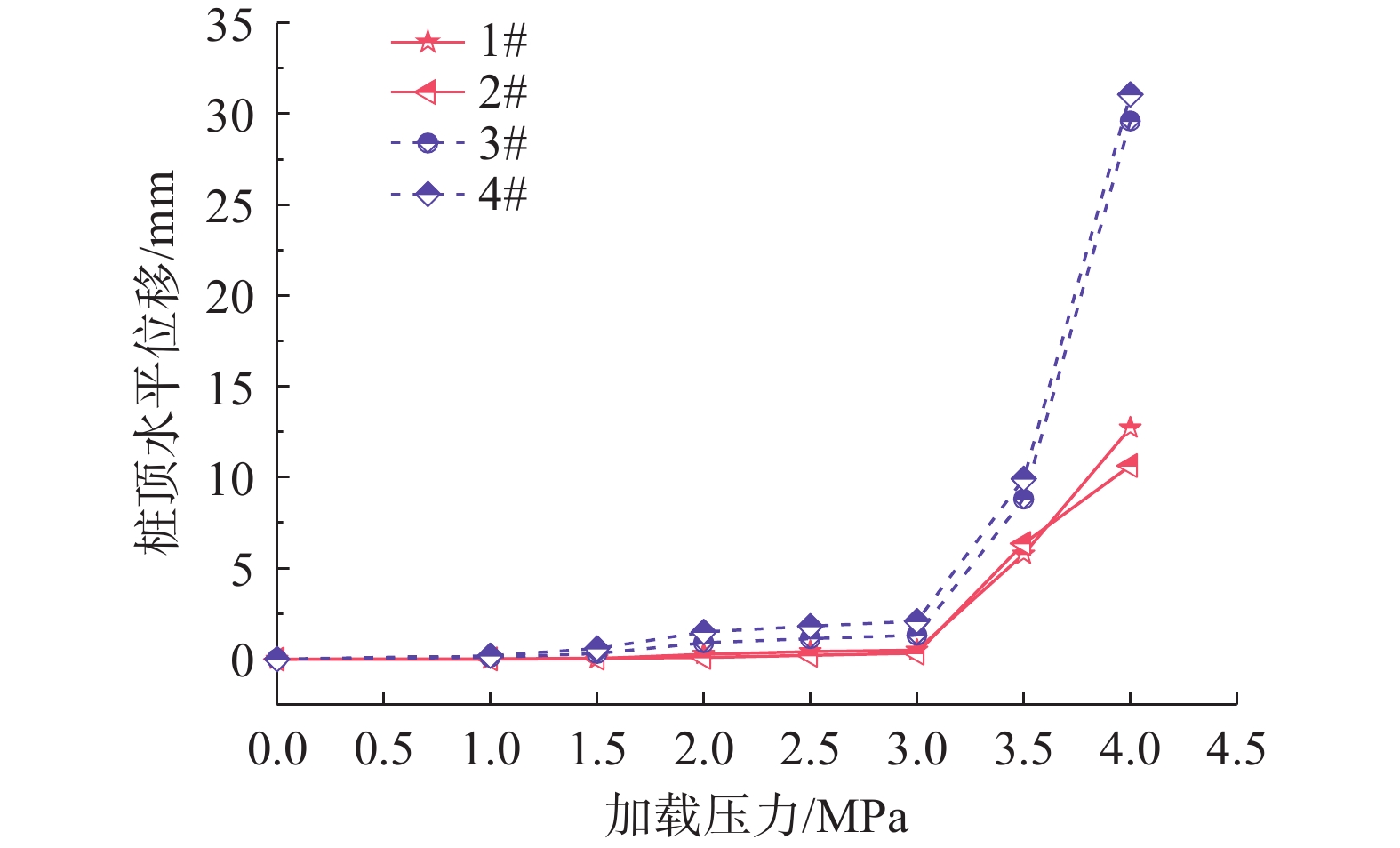
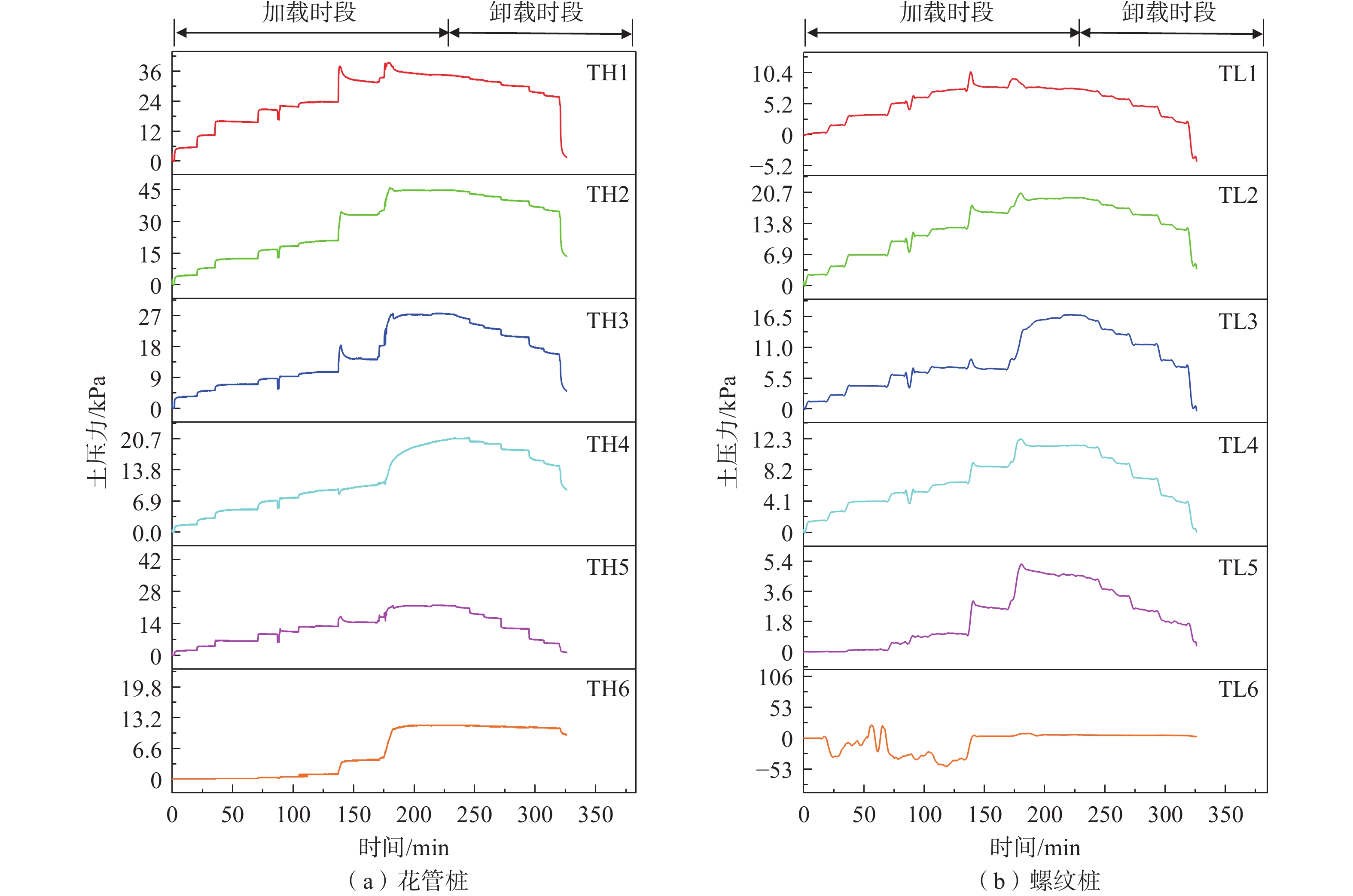
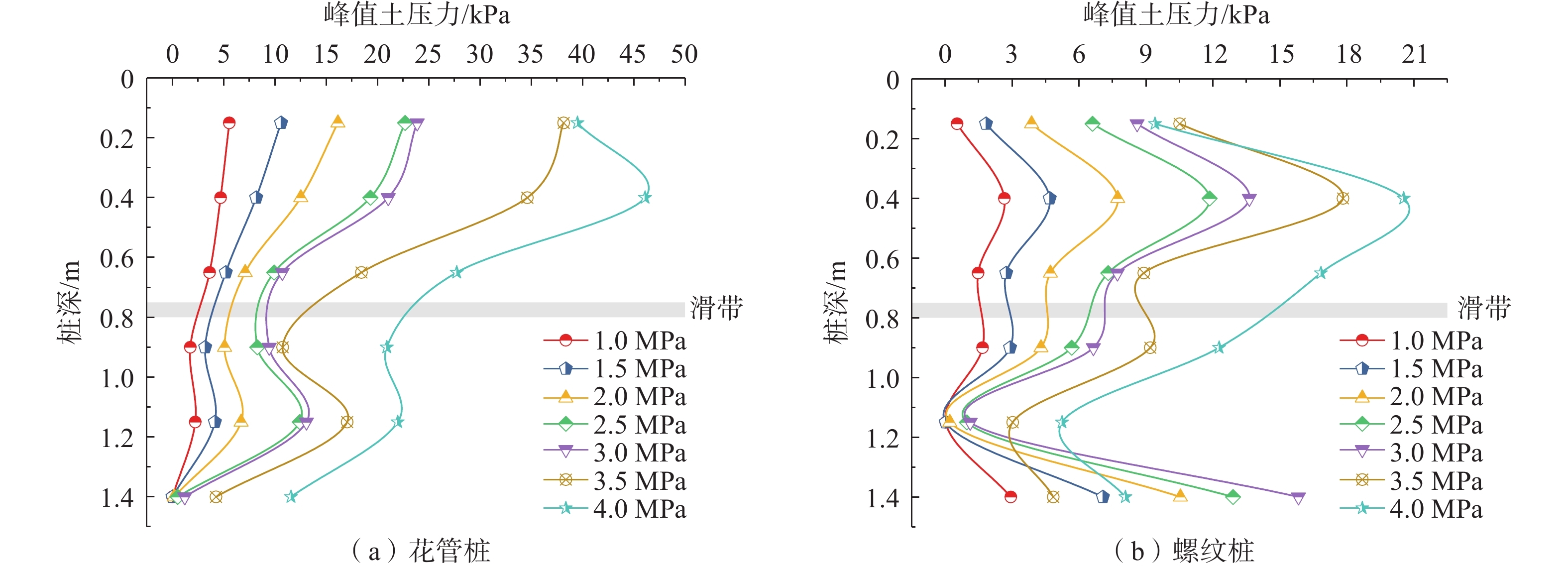
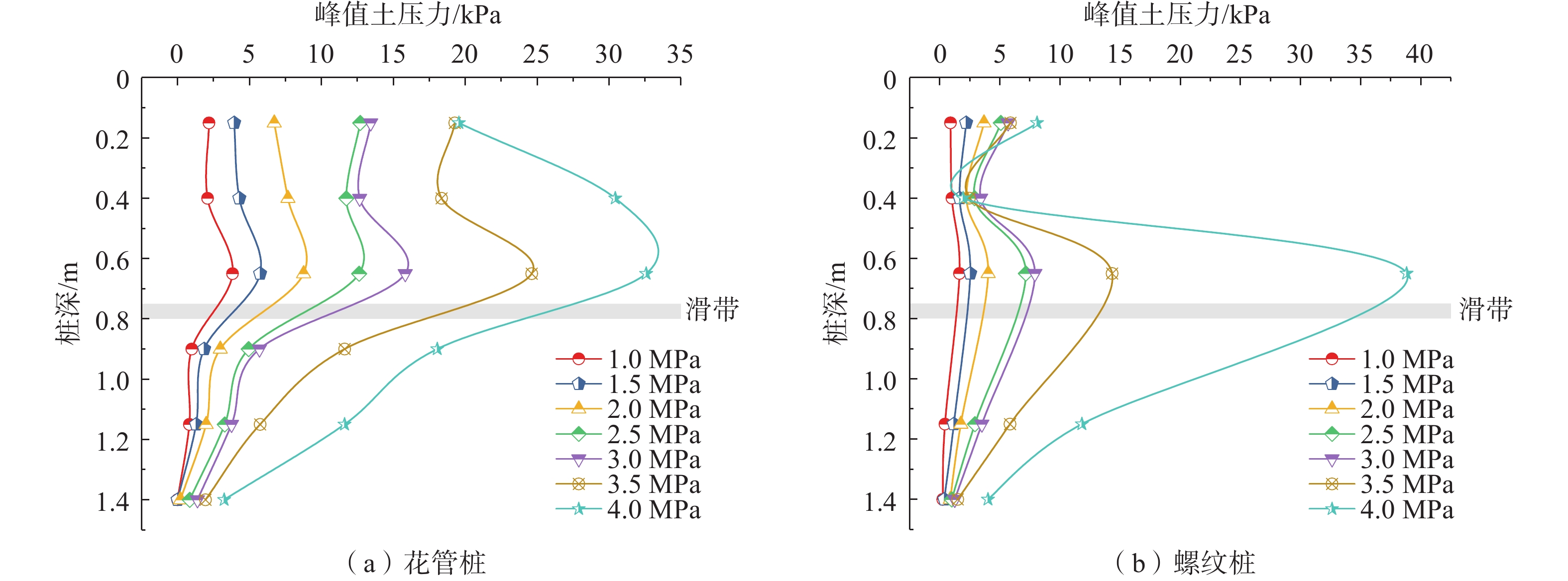
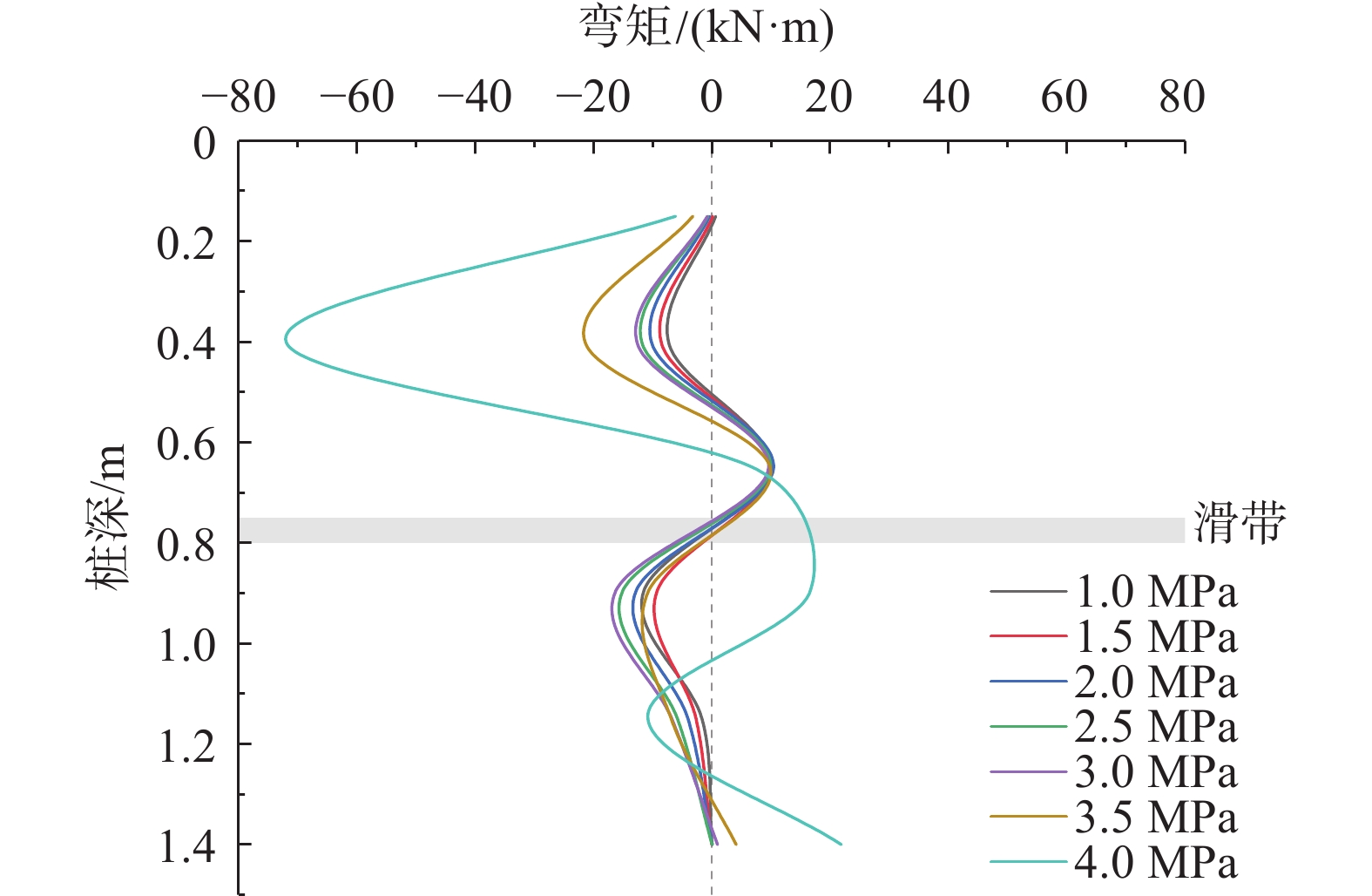
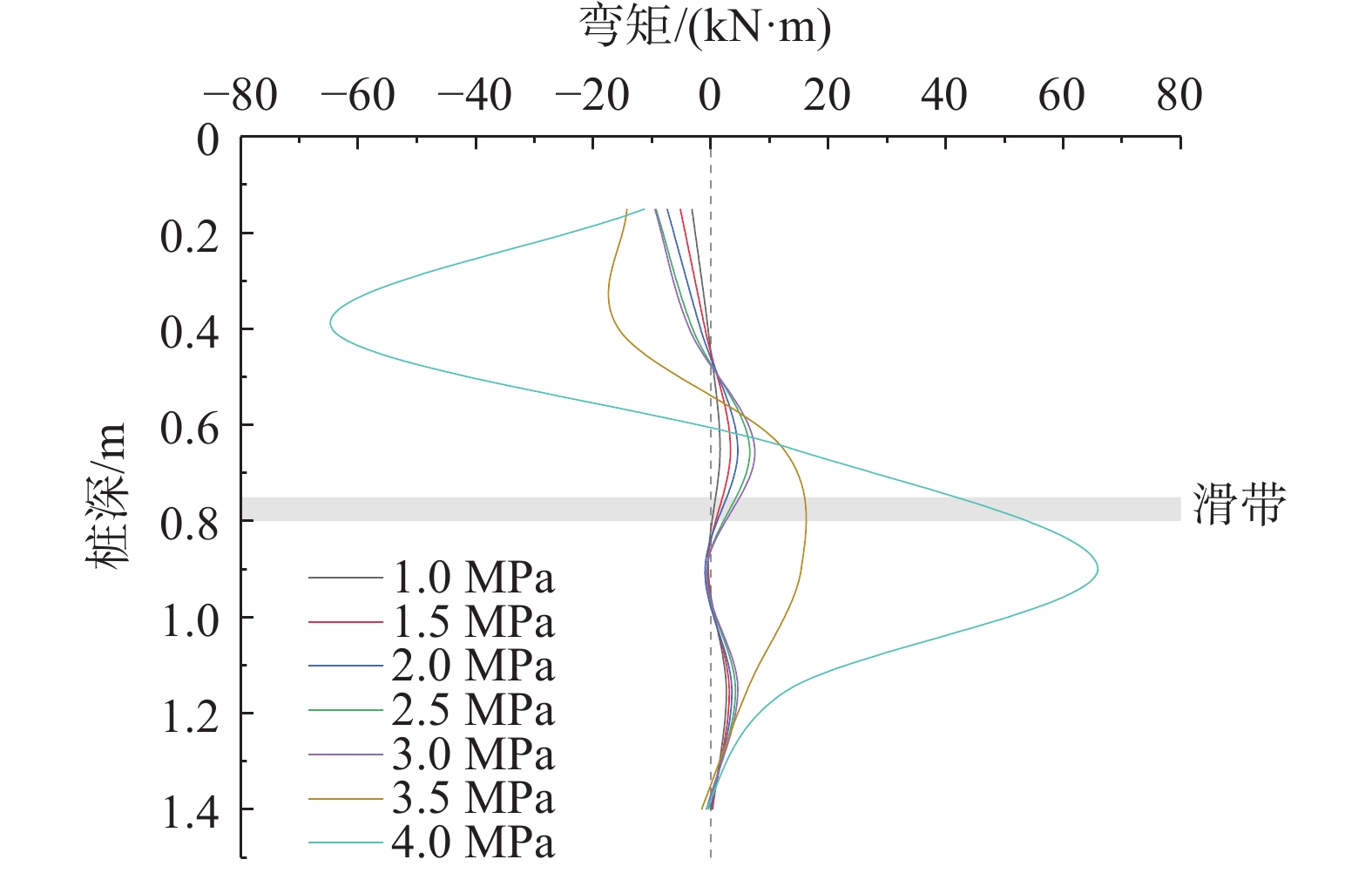
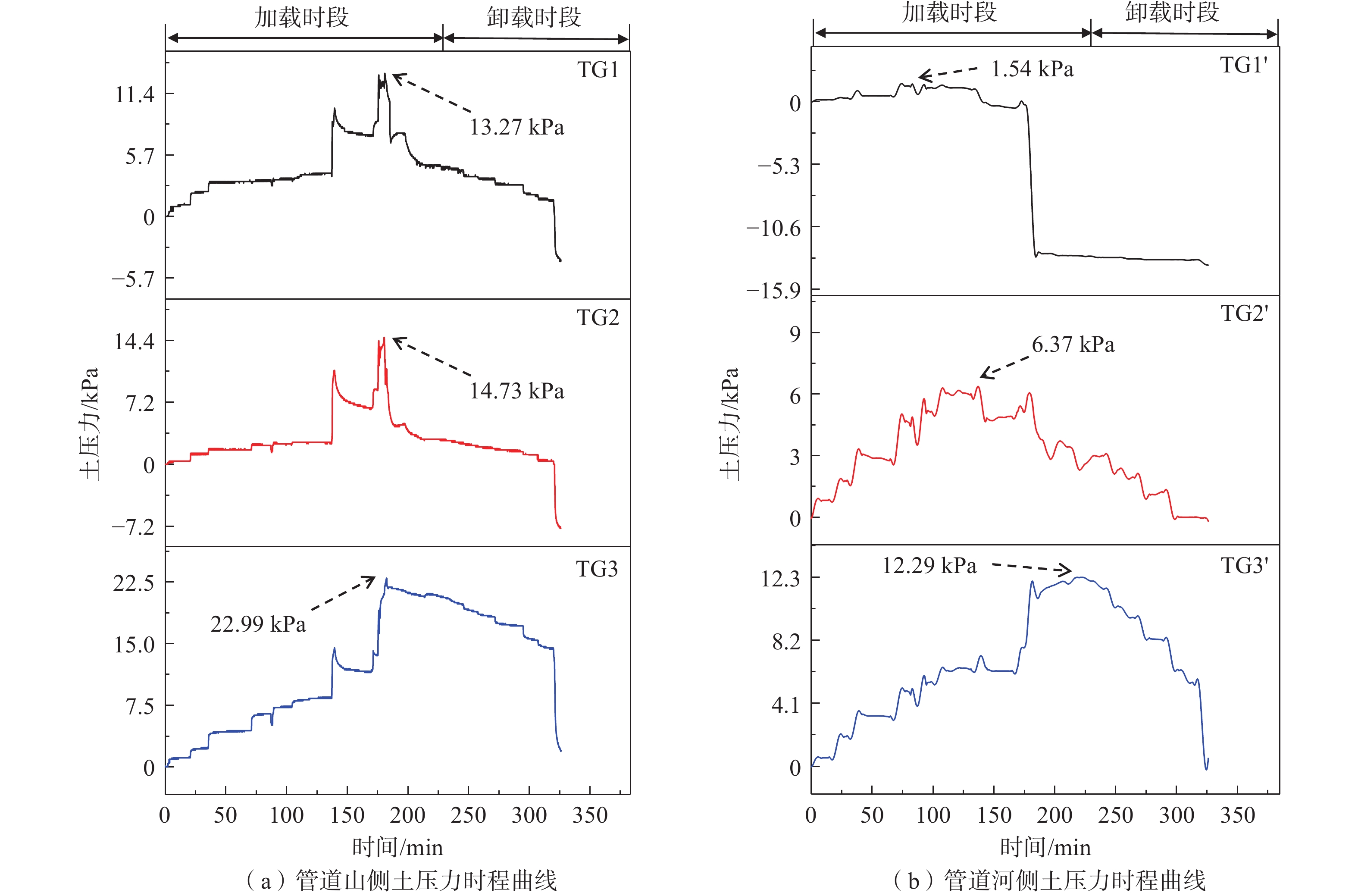
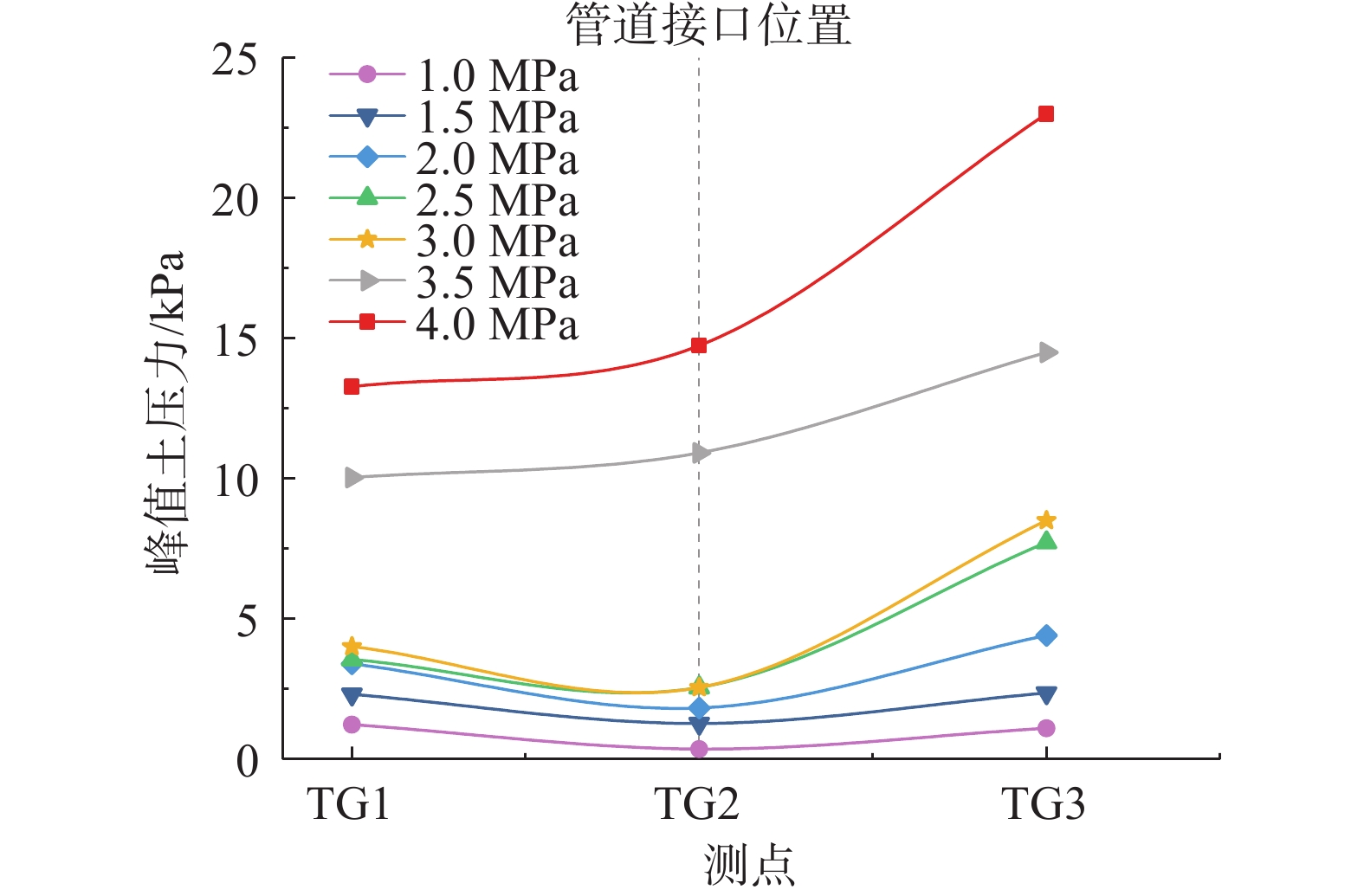
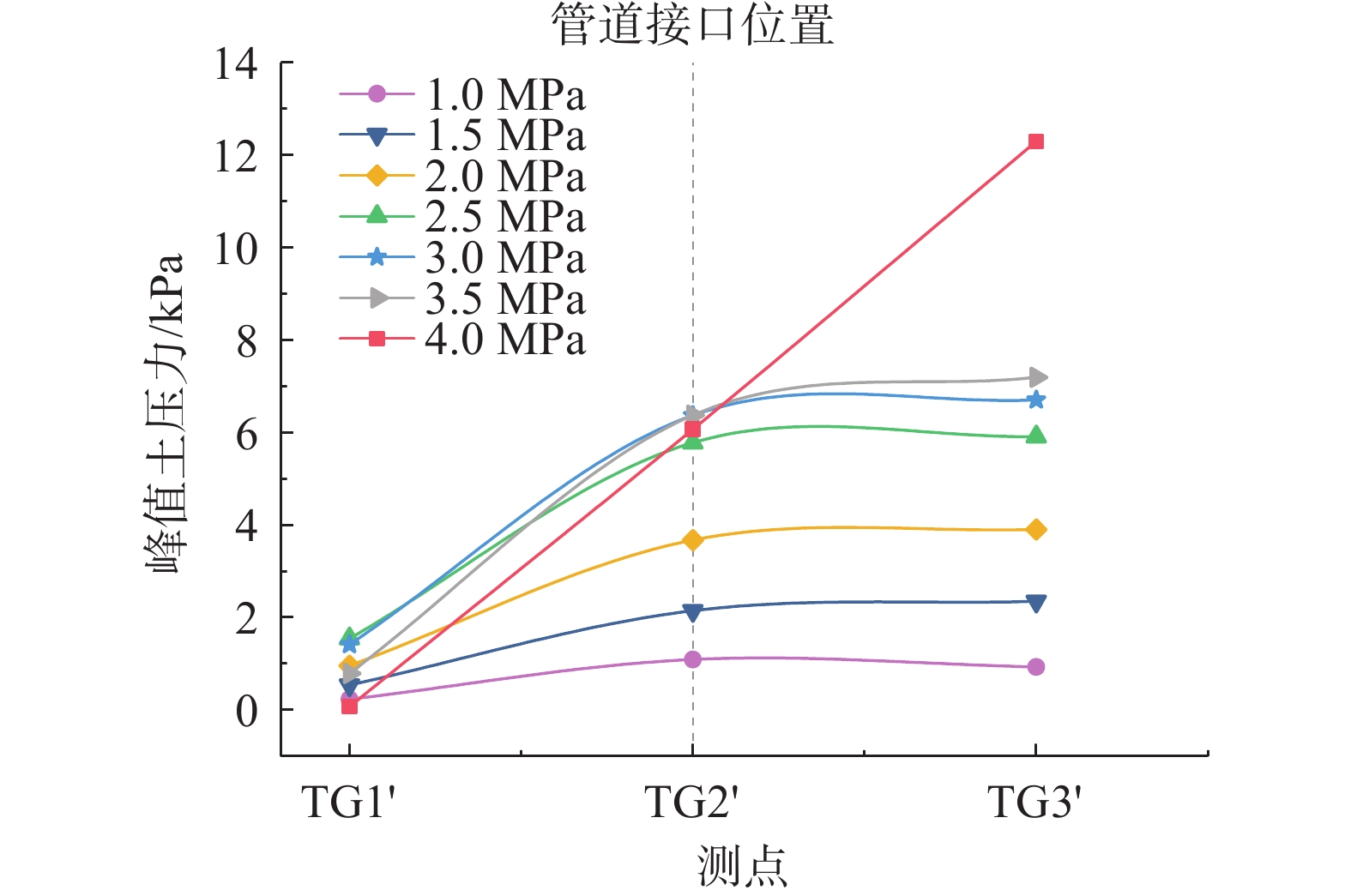
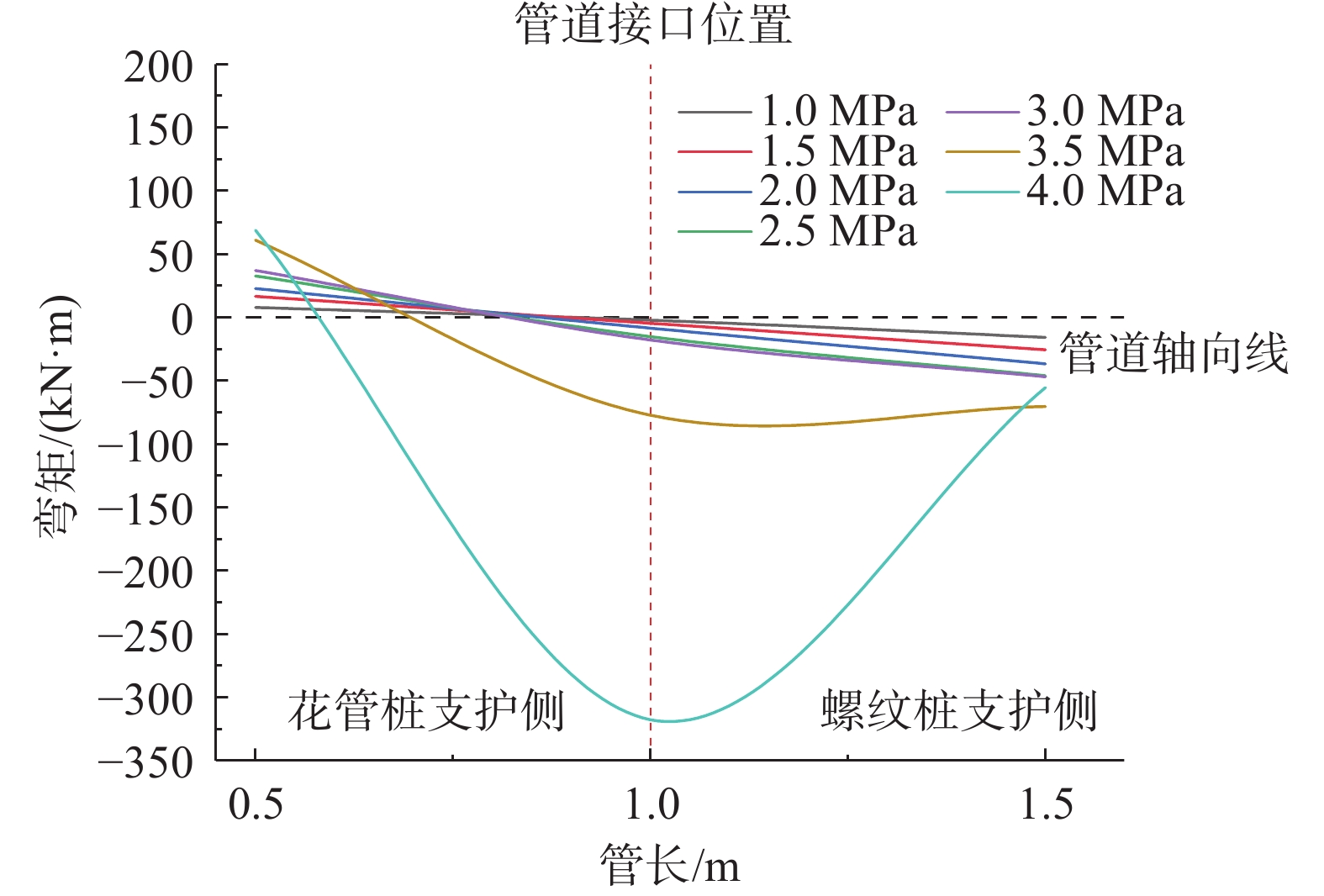
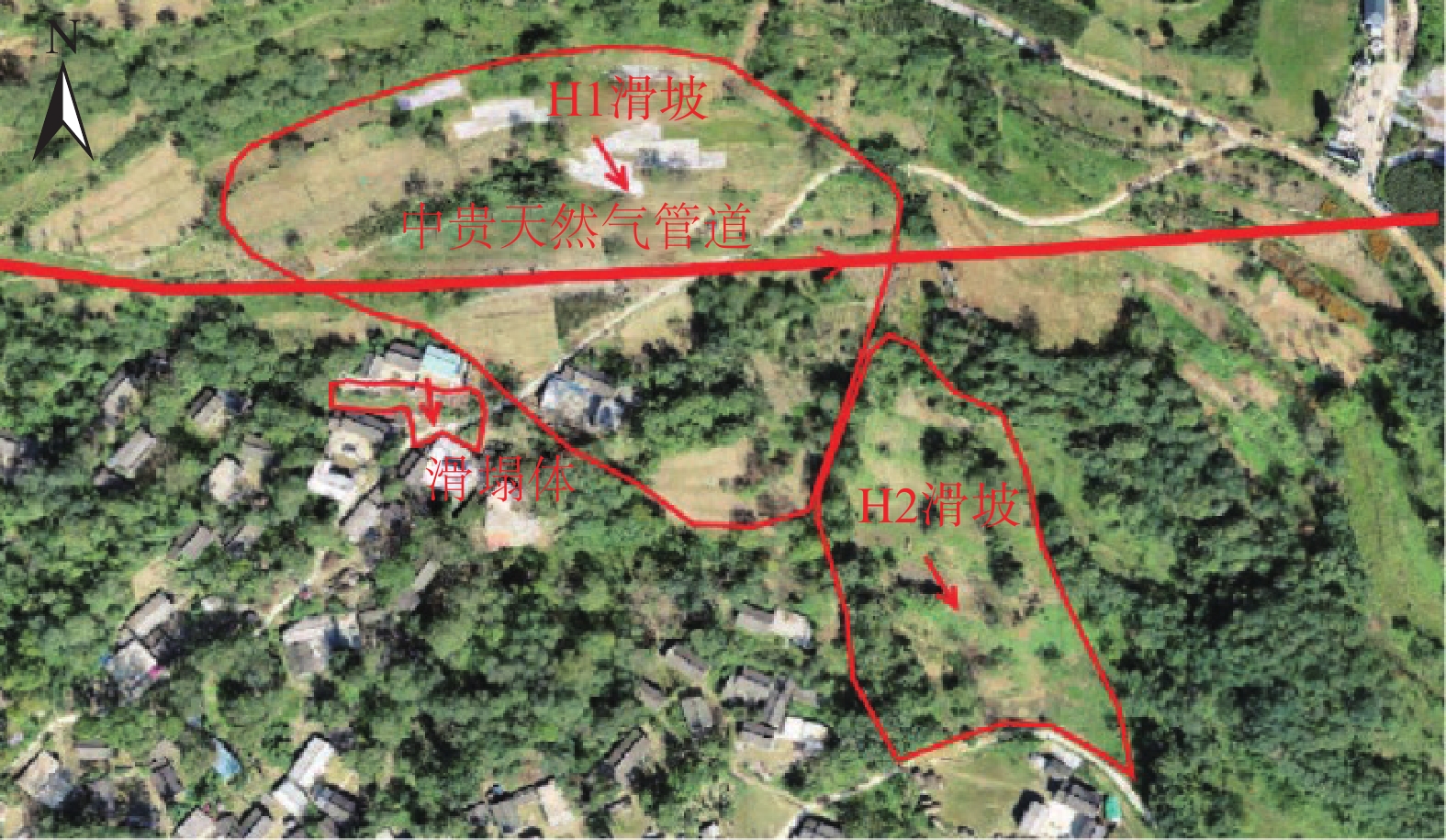
山区天然气管道工程难免会遭遇滑坡等地质灾害的影响,这给穿越滑坡区域的沿线管道的安全运营造成严重威胁。文章以中贵天然气管道K558+700滑坡为工程背景,通过室内大型物理模型试验,研究对比花管微型桩与螺纹微型桩两种新型支挡结构在管道滑坡中的支护机理及适用性。试验表明:(1)花管微型桩山侧及河侧峰值土压力沿桩深分布形式基本相似,大体呈“S”曲线形,桩后土体土拱效应明显,且在各级荷载下分布形式大致保持一致,总体来说花管桩侧土压力分布规律为桩中最大,桩顶次之,桩底最小;滑带附近的桩体周围土压力较大,在抗滑桩设计工作中应重点考虑优化。(2)螺纹桩山侧峰值土压力沿桩深分布图大体呈双“S”曲线形,河侧峰值土压力相比山侧分布形式产生了较大差异,桩底的土压力相比山侧有很大幅度减小;随外部荷载的增加桩周土压力增加幅度较大,表明螺纹微型桩在横向承载性能方面有所欠缺。(3)花管桩桩身弯矩沿深度方向呈“M”形分布,桩身离模拟滑面以上5 cm位置处产生最大正弯矩;螺纹桩桩身弯矩分布沿深度方向呈“S”形,桩体正负弯矩位置在模拟滑面附近大致呈旋转对称分布,滑面以上大部分区段为负弯矩,滑面以下为正弯矩;在相同推力荷载工况下,螺纹微型桩变形程度大于花管微型桩。(4)在滑坡作用下花管微型桩可以有效减小传递到管道的坡体应力,在一定程度上预防管道受力破坏;而螺纹桩在较大横向荷载下抗弯性能不足,变形严重,破坏后不能有效承担滑坡推力,传递到桩前管道的应力较大,从而导致管道变形程度更为强烈。在本试验条件下,花管微型桩对管道的保护效益突出,更适用于作为管道—滑坡区域的支挡结构。
Abstract:Natural gas pipeline projects in mountainous areas are inevitably affected by geological hazards such as landslides, which pose a serious threat to the safe operation of pipelines along the routes through landslide areas. Based on the engineering background of China-Guizhou natural gas pipeline K558 + 700 landslide, this paper studies and compares the supporting mechanism and applicability of two different support structures, namely, flower-tube micro-pile and threaded micro-pile, in pipeline landslide through indoor large-scale physical model tests. The results show that: (1) The distribution pattern of peak soil pressure along the mountain side and river side of flower tube micro-piles is basically similar along the pile depth, which is in the shape of "S" curve. The soil arching effect behind the pile is obvious, and the distribution pattern of soil pressure is generally consistent at all levels of load. In general, the distribution pattern of soil pressure on the side of the flower-pipe pile is the largest among piles, followed by the pile top, and the bottom of the pile. The soil pressure around the pile near the sliding zone is larger, so the optimization should be considered in the design of anti-slide pile. (2) The distribution diagram of the peak earth pressure along the pile depth of the threaded pile presents a double "S" curve. The distribution pattern of the peak earth pressure on the river side is significantly different from that of the mountain side, and the earth pressure at the bottom of the pile decreases greatly compared with that of the mountain side. With the increase of external load, the soil pressure around the pile increases greatly, indicating that the screw micro pile is deficient in lateral bearing capacity. (3) The bending moment of flowered pipe pile presents an "M" shape distribution along the depth direction, and the maximum positive bending moment occurs at the position 5 cm above the simulated slip surface. The pile body bending moment distribution along the depth direction is "S" shape, and the pile body positive and negative bending moment position near the simulated sliding surface roughly rotate symmetrical distribution, most of the region above the sliding surface is negative bending moment, the pile body below the sliding surface is positive bending moment. Under the same thrust load, the deformation degree of the screw micro pile is greater than that of the flower tube micro pile. (4) The load-bearing performance of the splined pipe pile is better than that of the threaded pile under thrust load, which effectively reduces the landslide thrust transferred to the pipeline; Under the large thrust load, the threaded pile can not effectively bear and offset the landslide thrust due to its insufficient flexural performance and serious deformation, and the stress transmitted to the pipe in front of the pile is large, causing more intense deformation of the pipe. Under the condition of this test, the flowered pipe micro-pile has outstanding protection benefit to the pipeline, and is more suitable for the retaining structure of the landslide area of the pipeline.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- natural gas pipeline /
- flower tube micro pile /
- micro thread pile /
- the supporting mechanism
-

-
表 1 相似比设计
Table 1. Design of similarity constant
物理量 相似比 物理量 相似比 几何尺寸 CL=30 变形模量 
质量密度 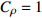
摩擦角 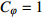
重度 Cy=1 黏聚力 
应变 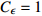
时间 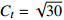
位移 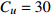
重力加速度 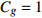
表 2 模型材料与原型材料相关物理性质参数
Table 2. Physical property parameters related to model material and prototype material
物理力学参数 重度/(kN·m−3) 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 弹性模量/MPa 滑体 原型 19.0 30.0 40.0 / 模型 19.0 30.5 1.2 / 滑带 原型 18.5 25.0 30.0 / 模型 18.0 25.0 1.0 / 基岩 原型 27.0 / / 5000 模型 26.7 / / 160 表 3 各级加载工况Q值
Table 3. Q values of loading conditions at all levels
工况 加载压力/MPa 工况 加载压力/MPa 1 1.0 5 3.0 2 1.5 6 3.5 3 2.0 7 4.0 4 2.5 − − -
[1] 高鹏,高振宇,赵赏鑫,等. 2020年中国油气管道建设新进展[J]. 国际石油经济,2021,29(3):53 − 60. [GAO Peng,GAO Zhenyu,ZHAO Shangxin,et al. New progress in China’s oil and gas pipeline construction in 2020[J]. International Petroleum Economics,2021,29(3):53 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7298.2021.03.009
[2] 李智毅,颜宇森,雷海英. 西气东输工程建设用地区的地质灾害[J]. 地质力学学报,2004,10(3):253 − 259. [LI Zhiyi,YAN Yusen,LEI Haiying. Geological hazards in the area for the construction of pipelines in the project of diversion of natural gas from the western to the eastern region[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2004,10(3):253 − 259. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2004.03.006
[3] 潘锋. 注浆钢花管微型桩在路基滑坡治理中的应用[J]. 工程与建设,2017,31(4):527 − 529. [PAN Feng. Application of grouted steel flower pipe micro-pile in subgrade landslide treatment[J]. Engineering and Construction,2017,31(4):527 − 529. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5781.2017.04.033
[4] 陈强,陈炜韬,刘世东,等. 注浆钢管微型桩加固滑坡的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2011,46(5):758 − 763. [CHEN Qiang,CHEN Weitao,LIU Shidong,et al. Model test on application of grouting steel-tube micropiles to landslide reinforcement[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2011,46(5):758 − 763. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.05.008
[5] WANG Kaiyang,SHANG Yanjun. An experimental study of horizontal bearing capacity of vertical steel floral tube micropiles with double grouting[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2018:1 − 11.
[6] 赵建兵. 螺杆桩在铁路路基中的运用[J]. 工程建设标准化,2015(2):105. [ZHAO Jianbing. Application of screw pile in railway subgrade[J]. Standardization of Engineering Construction,2015(2):105. (in Chinese)
[7] KRASIŃSKI A. Numerical simulation of screw displacement pile interaction with non-cohesive soil[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,2014,14(1):122 − 133. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2013.05.010
[8] 方崇,张信贵,彭桂皎. 对新型螺杆灌注桩的受力特征与破坏性状的探讨[J]. 岩土工程技术,2006,20(6):316 − 319. [FANG Chong,ZHANG Xingui,PENG Guijiao. Discussion on the bearing force characteristic and the failure behavior of a new kind half-screwed filling pile[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2006,20(6):316 − 319. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2006.06.013
[9] 叶阳升,蔡德钩,陈晓斌,等. 高速铁路螺杆桩复合地基桩侧摩阻力原位试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(2):1 − 10. [YE Yangsheng,CAI Degou,CHEN Xiaobin,et al. In-situ test study on lateral friction of screw pile composite foundation of high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science,2020,41(2):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.02.01
[10] MALIK A A,KUWANO J,TACHIBANA S,et al. End bearing capacity comparison of screw pile with straight pipe pile under similar ground conditions[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2017,12(2):415 − 428. doi: 10.1007/s11440-016-0482-4
[11] 孟振, 陈锦剑, 王建华, 等. 砂土中螺纹桩承载特性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(增刊1): 141 − 145
MENG Zhen, CHEN Jinjian, WANG Jianhua, et al. Study of model test on bearing capacity of screw piles in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(Sup 1): 141 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 闫玉平,肖世国. 双排抗滑桩后侧推力分布物理模型试验[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):79 − 87. [YAN Yuping,XIAO Shiguo. Physical model test on landslide thrust distribution on double-row stabilizing piles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):79 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-10
[13] 任青阳,赵梦园,谢忠伟,等. 抗滑桩应变特征与内力非线性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):114 − 124. [REN Qingyang,ZHAO Mengyuan,XIE Zhongwei,et al. A study of the strain characteristics and internal force nonlinearity of anti-slide pile[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202004034
[14] 中华人民共和国建设部. 建筑基桩检测技术规范: JGJ 106—2003[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2004
Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation piles: JGJ 106—2003[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[15] 董捷. 悬臂桩三维土拱效应及嵌固段地基反力研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2009
DONG Jie. Study on three-dimensional soil arching effect of cantilever piles and ground resisting force acted on its build-in zone[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 孙书伟,朱本珍,马惠民,等. 微型桩群与普通抗滑桩抗滑特性的对比试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(10):1564 − 1570. [SUN Shuwei,ZHU Benzhen,MA Huimin,et al. Model tests on anti-sliding mechanism of micropile groups and anti-sliding piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2009,31(10):1564 − 1570. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.10.014
[17] 杜衍庆,白明洲,邱树茂,等. 集约式微型桩群水平承载性能试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(4):821 − 830. [DU Yanqing,BAI Mingzhou,QIU Shumao,et al. Experimental study on lateral bearing capacity of concentrated micropiles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(4):821 − 830. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.04.020
-



 下载:
下载: