Analysis of basic characteristics and deformation mechanism of loess potential landslide of terrace: Taking loess hilly region in southern Ningxia as an example
-
摘要:
黄河流域地质构造活跃、地貌演化迅速、气候区域分异显著,导致流域内重大灾害类型多、分布广、突发性强。文章以宁夏南部黄土丘陵区为研究区,引入梯田型黄土滑坡隐患的概念,通过结合历史资料收集、遥感影像解译、现场调查和数理统计等手段,分析了梯田型黄土滑坡隐患的发育特征、分布规律及形成原因。结果表明:(1)研究区梯田型黄土滑坡隐患共26处,主要分布于第四系黄土中,中长边坡数量较多,主要为浅层与中层梯田型黄土滑坡隐患,规模以小型为主。(2)梯田型黄土滑坡隐患在空间上主要分布在黄土梁峁区和大起伏山地区,1 800~2 000 m的高程区间,坡向为东南、南、西南时分布较多;在时间上主要分布在雨季或地震活动时期。(3)地形地貌、地层结构、降雨、地表水和人类工程活动是梯田型黄土滑坡隐患发育的主要因素。研究结果对于宁夏南部黄土丘陵区以及黄河流域梯田型黄土滑坡隐患风险识别与风险管理具有指导和借鉴意义。
Abstract:The Yellow River Basin has active geological structure, rapid geomorphic evolution and significant regional differentiation of climate, resulting in many types of major disasters in the basin, wide distribution and strong paroxysm. Taking the Loess Hilly Region in the south of Ningxia as the research area, this paper introduces the concept of loess potential landslide of terrace. By combining historical data collection, remote sensing image interpretation, field investigation and mathematical statistics, it analyzes the development characteristics and distribution rules of loess potential landslide of terrace, and analyzes its formation reasons. The results show that: (1)There are 26 loess potential landslide of terrace in the study area, which are mainly distributed in the Quaternary loess, with a larger number of medium and long slopes, mainly loess potential landslide of terrace of shallow and middle-level, and the scale is mainly small. (2)The loess potential landslide of terrace are mainly distributed in loess hilly areas and large undulating mountain areas, the elevation interval of 1 800~2 000 m, and the slope direction is southeast, South and southwest in space; It is mainly distributed in rainy season or seismicity period in time. (3)Topography, stratum lithologic, rainfall, surface water and human engineering activities are the main factors for the loess potential landslide of terrace. The research results have guiding and reference significance for the risk identification and risk management of loess potential landslide of terrace in the Loess Hilly Region in Southern Ningxia and the Yellow River Basin.
-

-
表 1 研究区滑坡隐患点
Table 1. Potential landslides points in the study area
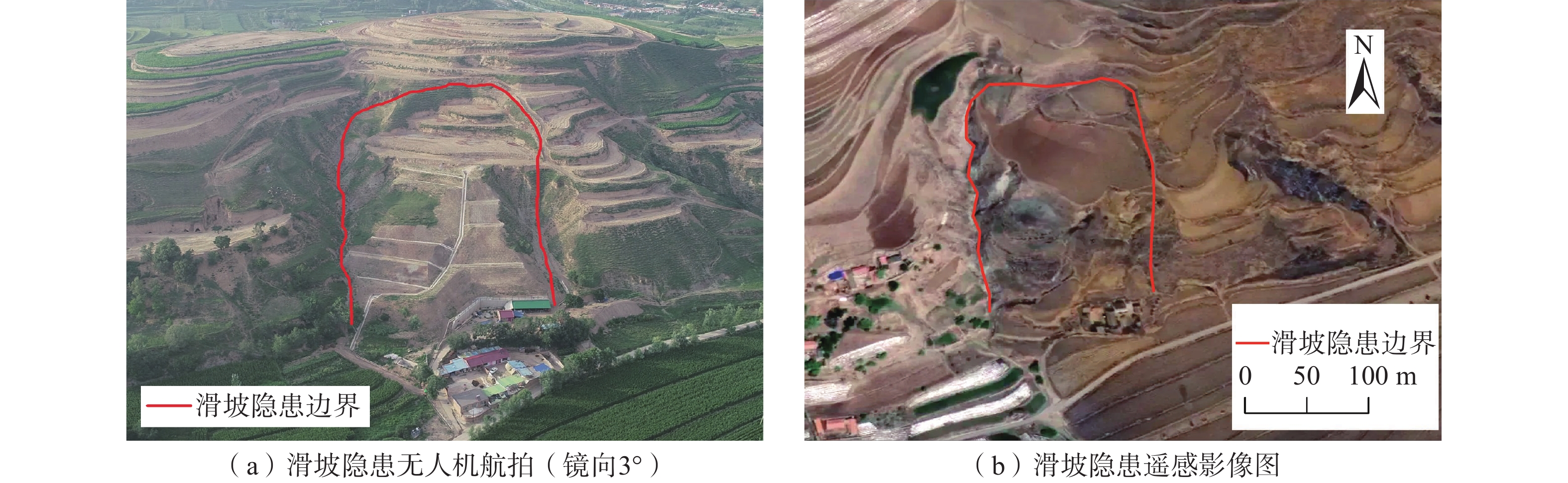
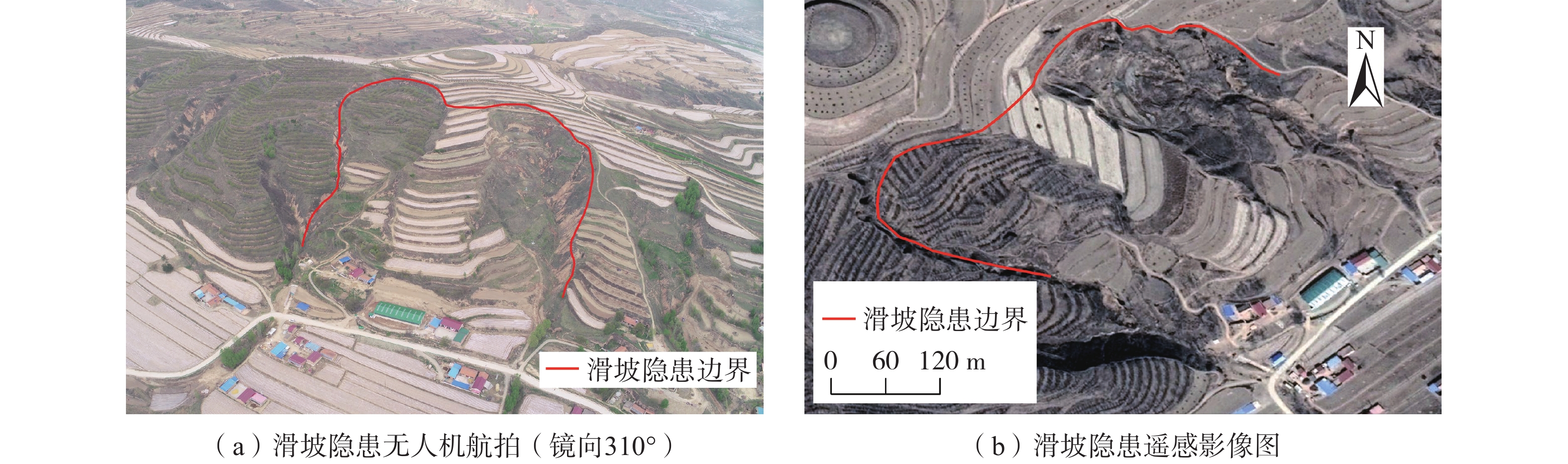
编号 区县 点位 隐患类型 HY-01 海原县 关庄乡马圈村 梯田型 HY-02 关庄乡宋庄村井滩组 梯田型 HY-03 李俊乡联合村双沟组 梯田型 HY-04 树台乡龚湾村 非梯田型 YZ-01 原州区 开城镇上青石村三组 梯田型(图2) YZ-02 官厅镇高红村二组 梯田型 YZ-03 张易镇驼巷五组 梯田型 YZ-04 张易镇陈沟村一组1号 梯田型 YZ-05 开城镇上青石村一组 梯田型,在古(老)滑坡上 YZ-06 张易镇陈沟村一组2号 梯田型 YZ-07 张易镇宋洼村一组1号 梯田型,在古(老)滑坡上 YZ-08 张易镇宋洼村一组2号 梯田型 YZ-09 张易镇盐泥村二组 梯田型 YZ-10 开城镇郭庙村八组 非梯田型 XJ-01 西吉县 马建乡刘垴村上垴组 非梯田型 XJ-02 马建乡台子村毛家湾组 非梯田型 XJ-03 火石寨乡大庄一组 非梯田型 XJ-04 白崖乡白崖村二组 非梯田型 XJ-05 偏城乡花儿岔村白套子组 梯田型,在古(老)滑坡上,见图3 XJ-06 硝河乡新庄村南湾组 梯田型,在古(老)滑坡上,见图4 XJ-07 震湖乡孟湾村孟湾组 梯田型 LD-01 隆德县 程靳乡民联村三组 梯田型 LD-02 城关镇杨店村二组 梯田型 LD-03 温堡乡杨家坡二组 梯田型 LD-04 凤岭乡巩龙村四组 梯田型 LD-05 沙塘镇许川村一组 非梯田型 LD-06 城关镇三合村一组 梯田型 LD-07 二中滑坡 梯田型 JY-01 泾源县 香水镇太阳村四组 梯田型 JY-02 香水镇米岗村二组 非梯田型 JY-03 香水镇卡子村三组 梯田型 JY-04 六盘山镇张堡村三组 梯田型 JY-05 兴盛乡红旗村五组 非梯田型 PY-01 彭阳县 古城镇挂马沟村郭庄 梯田型(图5) PY-02 白阳镇余沟村杨树茆 梯田型 表 2 梯田型黄土滑坡隐患行政区分布统计
Table 2. Administrative region distribution statistics of loess potential landslides of terrace
行政区 面积/km2 人口/万人 隐患数量/处 占比/% 人口密度/(人·km−2) 隐患密度/(处·100km−2) 隆德县 1004.66 10.95 6 23.07 108.99 0.60 西吉县 3116.13 31.58 3 11.54 101.34 0.10 彭阳县 2534.62 16.05 2 7.69 63.32 0.08 泾源县 1111.16 8.50 3 11.54 76.50 0.27 原州区 2760.79 47.13 9 34.62 170.71 0.33 海原县 4995.22 33.35 3 11.54 66.76 0.06 -
[1] 新华社. 第三次全国国土调查主要数据公报[EB/OL]. (2021-08-26)[2022-05-07].
Xinhua News Agency.The third national land survey main data bulletin[EB/OL]. (2021-08-26)[2022-05-07].(in Chinese)
[2] 王祯,吴金华,白帅,等. 延安市坡耕地资源时空变化及其土壤侵蚀效应[J]. 水土保持研究,2022,29(3):1 − 11. [WANG Zhen,WU Jinhua,BAI Shuai,et al. Spatiotemporal changes of sloping farmland resources and its soil erosion effects in Yan’an City[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,29(3):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2022.03.019
[3] 焦菊英,王万中. 黄土高原水平梯田质量及水土保持效果的分析[J]. 农业工程学报,1999,15(2):65 − 69. [JIAO Juying,WANG Wanzhong. Quality and soil-water conservation effectiveness of level terrace on the loess plateau[J]. Transactions of the CSAE,1999,15(2):65 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 薛萐,刘国彬,张超,等. 黄土高原丘陵区坡改梯后的土壤质量效应[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(4):310 − 316. [XUE Peng,LIU Guobin,ZHANG Chao,et al. Effects of terracing slope cropland on soil quality in hilly region of loess plateau[J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2011,27(4):310 − 316. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2011.04.054
[5] 周波. 甘肃省标准化梯田建设综合技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2017
ZHOU Bo. Research on comprehensive technology of standardized Terrace Construction in Gansu Province[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 陈蝶,卫伟,陈利顶,等. 梯田生态系统服务与管理研究进展[J]. 山地学报,2016,34(3):374 − 384. [CHEN Die,WEI Wei,CHEN Liding,et al. Progress of the ecosystem services and management of terraces[J]. Mountain Research,2016,34(3):374 − 384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王彦武,牛莉婷,张峰,等. 黄土区高标准梯田生态服务功能及其价值[J]. 水土保持学报,2019,33(6):190 − 196. [WANG Yanwu,NIU Liting,ZHANG Feng,et al. Ecological service function and its value of high-standard terrace in loess region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,33(6):190 − 196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张宏鸣,胡勇,杨勤科,等. 基于影像与坡度数据融合的梯田田块分割方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(4):249 − 256. [ZHANG Hongming,HU Yong,YANG Qinke,et al. Segmentation method of terraced fields based on image and gradient data[J]. Journal of agricultural machinery,2018,49(4):249 − 256. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.04.028
[9] 王爱云. 1978—1985年的农村扶贫开发[J]. 当代中国史研究,2017,24(3):36 − 50. [WANG Aiyun. Rural poverty alleviation and development from 1978 to 1985[J]. Contemporary China History Studies,2017,24(3):36 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李万源. 基于GEE和机器学习的固原市黄土梯田时空变化遥感监测[D]. 宁夏: 宁夏大学, 2021
LI Wanyuan. Remote sensing monitoring of temporal and spatial changes of loess terraces in Guyuan City Based on GEE and machine learning[D]. Ningxia: Ningxia University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] GIORDAN D,CIGNETTI M,BALDO M,et al. Relationship between man-made environment and slope stability:the case of 2014 rainfall events in the terraced landscape of the Liguria region (northwestern Italy)[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2017,8(2):1833 − 1852. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2017.1391129
[12] CAMERA C A S,APUANI T,MASETTI M. Mechanisms of failure on terraced slopes:the Valtellina case (northern Italy)[J]. Landslides,2014,11(1):43 − 54. doi: 10.1007/s10346-012-0371-3
[13] WEN Y,GAO P,MU X,et al. Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall[J]. Water,2021,13(3):270. doi: 10.3390/w13030270
[14] BERCIC T,AZMAN-MOMIRSKI L. Parametric terracing as optimization of controlled slope intervention[J]. Water,2020,12(3):634. doi: 10.3390/w12030634
[15] 史绪国,张路,许强,等. 黄土台塬滑坡变形的时序InSAR监测分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. [SHI Xuguo,ZHANG Lu,XU Qiang,et al. Monitoring slope displacements of loess terrace using time series InSAR analysis technique[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘茹,张庚,王思楚,等. 宁南黄土丘陵沟壑区土地类型与土地利用耦合分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(3):426 − 434. [LIU Ru,ZHANG Geng,WANG Sichu,et al. Coupling analysis of land type and land use in Ningnan hilly-gully area[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science),2018,54(3):426 − 434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘佳丽,田佳,郑田恬,等. 基于边坡稳定的黄土梯田优化设计[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2020,18(4):21 − 28. [LIU Jiali,TIAN Jia,ZHENG Tiantian,et al. Optimized design of loess terrace based on slope stability[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,18(4):21 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 徐峻龄,马惠民,郑静,等. 滑坡的规律研究与防治[J]. 铁道工程学报,2005(增刊 1):333 − 339. [XU Junling,MA Huimin,ZHENG Jing,et al. Research in the rules and controlling of landslide[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2005(Sup 1):333 − 339. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王恭先. 滑坡学与滑坡防治技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2004: 3 − 4
WANG Gongxian. Landslide science and landslide prevention technology[M]. Beijing: China Railway Press, 2004: 3 − 4. (in Chinese)
[20] 殷跃平. 滑坡防治技术指南[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 3 − 4
YIN Yueping. Technical guide for landslide prevention and control[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018: 3 − 4. (in Chinese)
[21] 波波夫. 工程地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1957: 95 − 96
И. В. Попов. Engineering geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1957: 95 − 96. (in Chinese)
[22] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanism in China since the 20th Century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[23] 朱庆,曾浩炜,丁雨淋,等. 重大滑坡隐患分析方法综述[J]. 测绘学报,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. [ZHU Qing,ZENG Haowei,DING Yulin,et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaeticaet Cartographica Sinica,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张茂省,孙传尧,校培喜,等. 延安市宝塔区地质灾害详细调查示范[J]. 西北地质,2007,40(2):29 − 55. [ZHANG Maosheng,SUN Chuanyao,XIAO Peixi,et al. A demonstration project for detailed geo-hazard survey in the Baota District,Yan’an City[J]. Northwestern Geology,2007,40(2):29 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2007.02.002
[26] 陈春利,贺凯,李同录. 坡脚开挖诱发古滑坡复活的机制分析[J]. 西北地质,2014,47(1):255 − 260. [CHEN Chunli,HE Kai,LI Tonglu. Research on the mechanism of the ancient landslide resurrection triggered by slope toe excavation[J]. Northwestern Geology,2014,47(1):255 − 260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.01.024
[27] 《工程地质手册》编委会. 北京: 工程地质手册第5版[M]. 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018: 651 − 653
Editorial board of engineering geology manual. Engineering geology manual[M]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2018: 651 − 653. (in Chinese)
[28] 樊晓一,张友谊,杨建荣. 汶川地震滑坡发育特征及其影响因素[J]. 自然灾害学报,2012,21(1):128 − 134. [FAN Xiaoyi,ZHANG Youyi,YANG Jianrong. Developmental characteristics and influence factors of landslides in Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2012,21(1):128 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2012.0119
[29] 王兰民, 蒲小武, 吴志坚, 等. 地震和降雨耦合作用下黄土边坡失稳滑移的振动台试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(增刊2): 3873 − 3883
WANG Lanmin, PU Xiaowu, WU Zhijian, et al. The shaking table test of the instability sliding of loess slope under the coupling effects of earthquake and rainfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(Sup 2): 3873 − 3883. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 李泊良, 张帆宇. 降雨和地震条件下浅层黄土滑坡三维稳定性评价[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(3): 440 − 450.
LI Poliang, ZHANG Fanyu. Three-dimensional stability evaluation of shallow loess landslides under rainfall and earthquake conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 440 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 曹生奎,刘峰贵,张海峰,等. 青海高原地震重灾区的灾害特点及成因探析[J]. 灾害学,2005,20(1):77 − 80. [CAO Shengkui,LIU Fenggui,ZHANG Haifeng,et al. An Analysis on characteristics and causes of earthquake disaster in heavy disastered area in the Qinghai Plateau[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2005,20(1):77 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 王高峰,王爱军,陈宗良,等. 六盘山东麓断裂带滑坡类型与变形机理研究—以泾河源区为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):102 − 109. [WANG Gaofeng,WANG Aijun,CHEN Zongliang,et al. Study on types and deformation mechanism of landslide in the fauli zone of eastern Liupanshan:Taking the source district of Jinghe River as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):102 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.16
[33] 张茂省,李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):530 − 540. [ZHANG Maosheng,LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):530 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
[34] 温永福,高鹏,穆兴民,等. 黄土高原丘陵沟壑区梯田边坡侵蚀过程对雨强的响应[J]. 泥沙研究,2017,42(6):46 − 51. [WEN Yongfu,GAO Peng,MU Xingmin,et al. Response of soil erosion to rainfall intensity in terraced slope in the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2017,42(6):46 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2017.06.008
-




 下载:
下载: