Long-runout characteristics of the Yongguang 1# loess flowslide in Minxian County, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
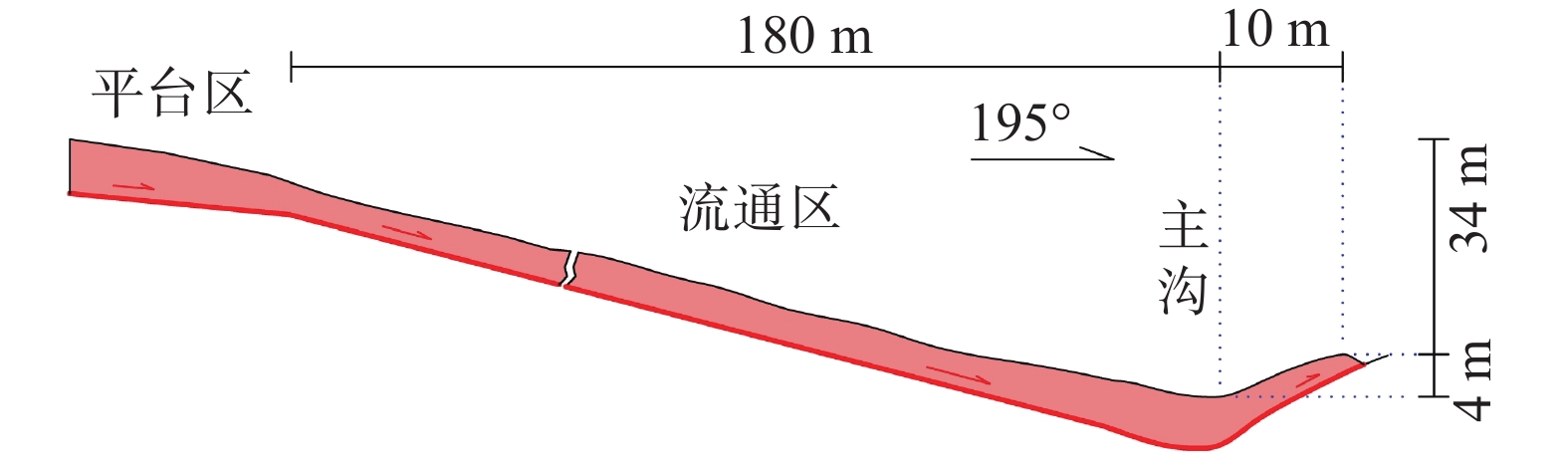
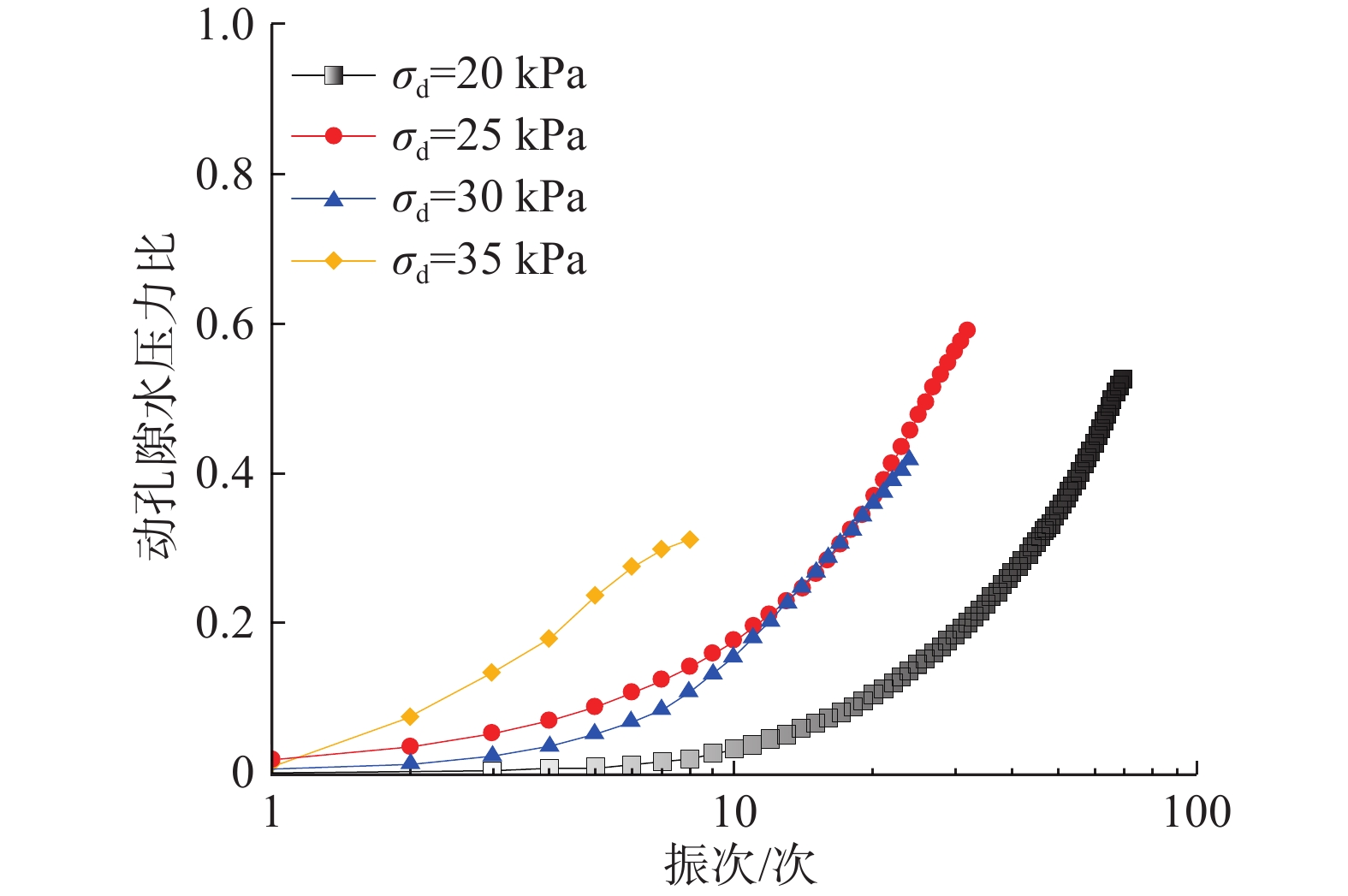
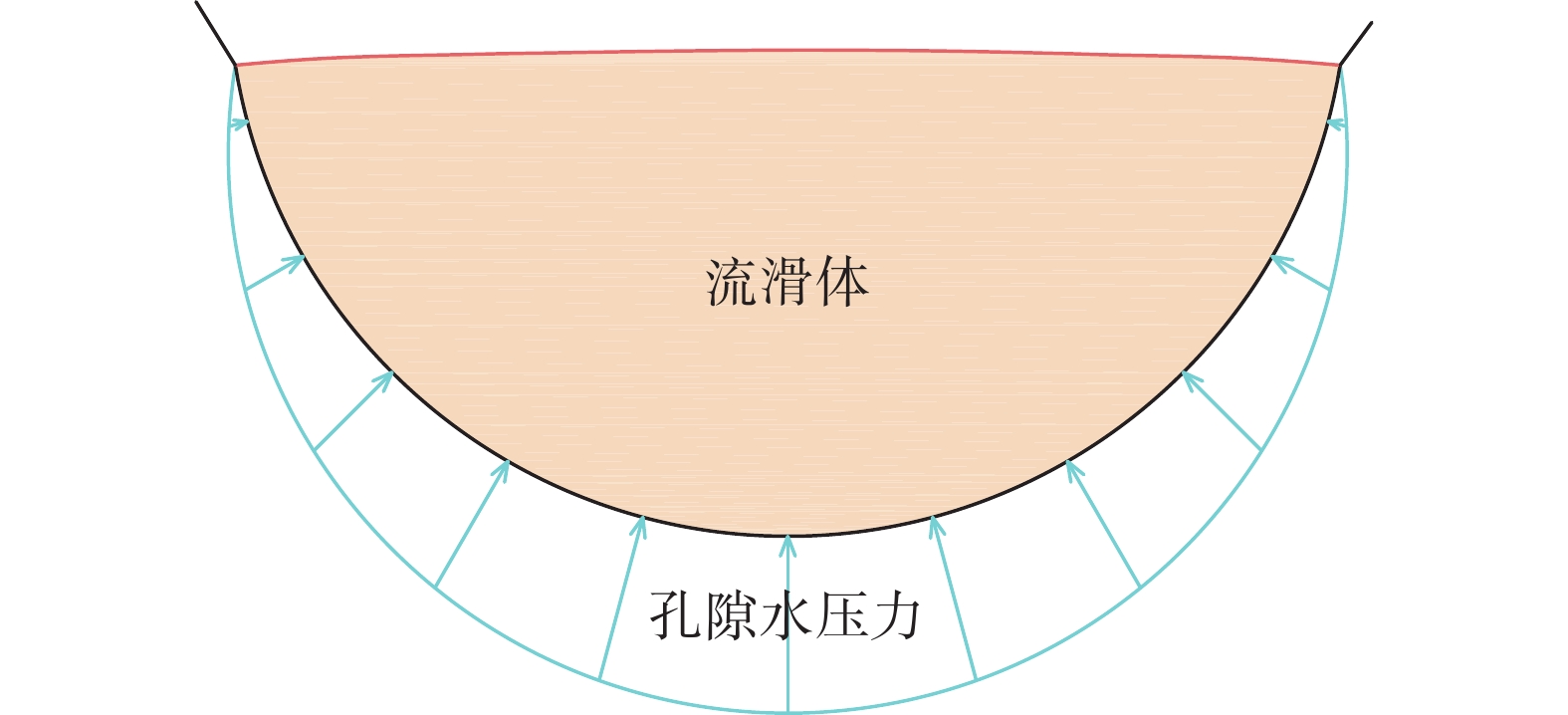
流滑型黄土滑坡是黄土地区沿沟道或斜坡远程滑动和堆积的长条状特殊类型滑坡,常造成难以预料的严重灾害。2013年7月22日7时45分,甘肃岷县漳县Ms6.6级地震诱发的岷县永光1#滑坡体积约23×104 m3,造成12人遇难。滑坡前后缘高差175 m,总长度1030 m,高长比值为0.17,属远程滑坡。通过现场调查和对滑动过程观察资料的综合分析,探讨了其滑动过程特征、不同部位的滑速及变化情况,分析了滑动机理。受地震作用促发和地形条件等影响,永光1#滑坡经历了2次加速—减速的复杂滑动过程,滑坡首先在前部平台区整体滑动50~130 m,前缘约6×104 m3滑体再沿前部沟道滑动740 m,最大滑距达870 m,滑动总历时约7 h,最大滑速约10.6 m/s,平均滑速0.034 m/s。永光1#滑坡由地震和前期降水耦合作用形成,地震前大量降水的入渗和软化,滑动过程中高含水率滑带土产生高孔隙水压力,甚至导致液化发生,圈闭的沟道地形和滑带土的低渗透性,使孔隙水压力消散非常缓慢,在全滑程中滑带土摩阻力大幅降低,持速效应明显,是永光1#滑坡远程滑动的主要原因。
Abstract:Flowslide in loessic regions, characterized by their elongated shape and tendency to slide and accumulate along channels or gentle hillslopes, frequently lead to devastating and unpredictable disasters. The Yongguang 1# flowslide in Minxian County, Gansu Province, caused by the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms6.6 earthquake at 7:45AM on July 22, 2013, claimed twelve lives and had a volume of approximately 23×104 m3. The landslide had a vertical difference of 175m between its front and rear edges, a total length of 1 030 m, and a ratio of 0.17, classifying it as a long-runout landslide. This paper explored the characteristics of the sliding process and the sliding velocities of different portions of the flowslide through field survey and a comprehensive analysis of the observation data of the sliding process, while also analyzing the sliding mechanism. Triggered by earthquake, the runout process of the flowslide has been affected by local terrain. The flowslide experienced two complex sliding stages of acceleration and deceleration. Initially, the landslide slid as a whole in the front platform area for 50 to 130 m, and then the front sliding body with an volume of about 6×104 m3 continued to slide along the front channel for 740 m, resulting in a maximum runout distance of 870 m. The entire sliding process lasted about 7 hours, with a maximum sliding speed of approximately 10.6 m/s, and an average sliding speed of 0.034 m/s. The formation of the Yongguang 1# landslide was influenced by the coupled effects of seismic activity and early-precipitation. The earthquake, preceded by heavy rainfall, led to infiltration and softening of the soil. During the sliding process, the high water content in the sliding zone generated high pore water pressure, and in some cases, liquefaction occurred. The channel-shaped topography and low permeability of the sliding zone soil caused a very slow dissipation of pore water pressure, resulting in a significant reduction in frictional resistance in the sliding zone soil throughout the entire sliding process, with a noticeable velocity-sustaining effect. These factors are the primary reasons for the long-runout of the Yongguang 1# landslide.
-
Key words:
- flowslides in loess /
- long-runout flowslide /
- pore water pressure /
- liquefaction
-

-
[1] 中国科学院兰州冰川冻土研究所,甘肃省交通科学研究所. 甘肃泥石流[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社,1982. [Lanzhou Institute of Glaciology and Geocrrylogy,Chinese Academy of Science,Gansu Province Insititution of Ttansportatiohn Research. Debris Flow in Gansu,China[M]. Beijing:Communications Press,1982. (in Chinese)
Lanzhou Institute of Glaciology and Geocrrylogy, Chinese Academy of Science, Gansu Province Insititution of Ttansportatiohn Research. Debris Flow in Gansu, China[M]. Beijing: Communications Press, 1982. (in Chinese) [2] JIANBING,PENG. Heavy rainfall triggered loess-mudstone landslide and subsequent debris flow in Tianshui,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,186:79 − 90. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.015
[3] ZHANG F Y,KANG C,DAVE C,et al. A Study of a Flowslide with Significant Entrainmentin Loess Areas in China[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2017,42(14):2295 − 2305. doi: 10.1002/esp.4184
[4] 翟张辉,沈伟,李同录,等. 天水市大沟滑坡-泥石流运动过程模拟分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(增刊1):400 −406. [ZHAI Zhanghui,SHEN Wei,LI Tonglu,et al. Analysis and simulation of the landslide-debris flow hazard in Dagou Village,Tianshui City[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(Sup1):400 − 406. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAI Zhanghui, SHEN Wei, LI Tonglu, et al . Analysis and simulation of the landslide-debris flow hazard in Dagou Village, Tianshui City[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017 ,25 (Sup1 ):400 −406 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] HEIM A. Bergsturz und Menschen Leben[M]. Zurich:Fretz & Was-muth Verlag,1932:218.
[6] KENT P E. The transport mechanism in catastrophic rock falls[J]. The Journal of Geology,1966,74(1):79 − 83. doi: 10.1086/627142
[7] SASSA K. Geotechnical model for the motion of landslides (Special lecture)[J].Proc^ Int.symp.on Landslides, 1988.
[8] 汪发武. 地震诱发的高速远程滑坡过程中土结构破坏和土粒子破碎引起的两种不同的液化机理[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):98 − 107. [WANG Fawu. Liquefactions caused by structure collapse and grain crushing of soils in rapid and long runout landslides triggered by earthquakes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):98 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-034
WANG Fawu . Liquefactions caused by structure collapse and grain crushing of soils in rapid and long runout landslides triggered by earthquakes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019 ,27 (1 ):98 −107 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] HUTCHINSON J N,BHANDARI R K. Undrained loading,A fundamental mechanism of mudflows and other mass movements[J]. Géotechnique,1971,21(4):353 − 358.
[10] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):153 − 166. [YIN Yueping. Rapid and long Run-out features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):153 − 166(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002
YIN Yueping . Rapid and long Run-out features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009 ,17 (2 ):153 −166 (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 刘传正. 论崩塌滑坡—碎屑流高速远程问题[J]. 地质论评,2017,63(6):1563 − 1575. [LIU Chuanzheng. Research on high speed and long-distance of the avalanches or landslide—debris streams[J]. Geological Review,2017,63(6):1563 − 1575. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2017.06.011
LIU Chuanzheng . Research on high speed and long-distance of the avalanches or landslide—debris streams[J]. Geological Review,2017 ,63 (6 ):1563 −1575 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 胡广韬. 滑坡动力学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1995. [HU Guangtao. Landslide dynamics[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1995. (in Chinese)
HU Guangtao. Landslide dynamics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1995. (in Chinese) [13] 段钊,彭建兵,王启耀. 泾阳南塬黄土滑坡的运动规律与液化效应[J]. 水土保持通报,2016,36(3):46 − 49. [DUAN Zhao,PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao. Motion law and liquefaction effect of loess landslides in South Jingyang Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2016,36(3):46 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2016.03.009
DUAN Zhao, PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao . Motion law and liquefaction effect of loess landslides in South Jingyang Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2016 ,36 (3 ):46 −49 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 王玉峰,林棋文,李坤,等. 高速远程滑坡动力学研究进展[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2021,43(1):164 − 181. [WANG Yufeng,LIN Qiwen,LI Kun,et al. Review on rock avalanche dynamics[J]. Journal of Earch Sciences and Environment,2021,43(1):164 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2020.10001
WANG Yufeng, LIN Qiwen, LI Kun, et al . Review on rock avalanche dynamics[J]. Journal of Earch Sciences and Environment,2021 ,43 (1 ):164 −181 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] ZHUANG Yu,XING Aiguo,CHENG Qiangong,et al. Characteristics and numerical modeling of a catastrophic loess flow slide triggered by the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake in Yongguang Village,Minxian,Gansu,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(1):439 − 449. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01542-x
[16] 吴志坚,陈豫津,王谦,等. 岷县漳县6•6级地震永光村滑坡致灾机制分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(增刊2):165 − 168. [WU Zhijian,CHEN Yujin,WANG Qian,et al. Disaster-causing mechanism of Yongguang landslide under Minxian-Zhangxian M S 6.6 Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,41(Sup2):165 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Zhijian, CHEN Yujin, WANG Qian, et al . Disaster-causing mechanism of Yongguang landslide under Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019 ,41 (Sup2 ):165 −168 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 刘琨. 降雨影响下黄土斜坡的地震失稳机制及其稳定性评价[D]. 兰州:兰州大学:30 − 51. [LIU Kun. Earthquake instability mechanism and stability evaluation of loess slope under the influence of rainfall[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University:30 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Kun. Earthquake instability mechanism and stability evaluation of loess slope under the influence of rainfall[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University: 30 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 何文贵,郑文俊,王爱国,等. 临潭-宕昌断裂新活动特征与岷县漳县 MS6.6地震关系研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2013,35(4):751 − 760. [HE Wengui,ZHENG Wenjun,WANG Aiguo,et al. New activities of Lintan-Dangchang fault and its relations to Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake[J]. [J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2013,35(4):751 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.04.751
HE Wengui, ZHENG Wenjun, WANG Aiguo, et al . New activities of Lintan-Dangchang fault and its relations to Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake[J]. [J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2013 ,35 (4 ):751 −760 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1973,5(4):231 − 236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796
[20] STEPHEN G,Evans. Dynamics of the 1984 rock avalanche and associated distal debris flow on Mount Cayley,British Columbia,Canada; implications for landslide hazard assessment on dissected volcanoes[J]. Engineering Geology,2001,61(1):29 − 51. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00118-6
[21] 李同录,李颖喆,赵丹旗,等. 对水致黄土斜坡破坏模式及稳定性分析原则的思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):25 − 32. [LI Tonglu,LI Yingzhe,ZHAO Danqi,et al. Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-04
LI Tonglu, LI Yingzhe, ZHAO Danqi, et al . Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (2 ):25 −32 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 王谦. 饱和黄土地震液化特征与新型抗震处理方法[D]. 兰州:兰州大学. [WANG Qian. Characteristics of seismic liquefaction of saturated loess and new seismic treatment methods[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Qian. Characteristics of seismic liquefaction of saturated loess and new seismic treatment methods[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 吴玮江, 宋丙辉, 刘迪, 等. 黄土塬区包气带水分运移特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):12 − 22. [WU Weijiang, SONG Binghui, LIU Di, et al. Research on the characteristics of water transport in the aeration zone of loess tableland[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):12 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Weijiang, SONG Binghui, LIU Di, et al . Research on the characteristics of water transport in the aeration zone of loess tableland[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (3 ):12 −22 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[24] 郭富赟, 张龙生, 王信, 等. 甘肃黑方台罗家坡滑坡演化过程及运动机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):11 − 20. [GUO Fuyun, ZHANG Longsheng, WANG Xin, et al. Analysis on evolution process and movement mechanism of the Luojiapo landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):11 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Fuyun, ZHANG Longsheng, WANG Xin, et al . Analysis on evolution process and movement mechanism of the Luojiapo landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (2 ):11 −20 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[25] 冉林, 马鹏辉, 彭建兵, 等. 甘肃黑方台 “10·5” 黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):1 − 9. [RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10·5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al . The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10·5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (6 ):1 −9 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] 吴玮江, 王国亚, 刘兴荣, 等. 甘肃舟曲县牙豁口滑坡发育特征与成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2021,43(2):544 − 554. [WU Weijiang, WANG Guoya, LIU Xingrong, et al. The development characteristics and causes of the Yahuokou landslide in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2021,43(2):544 − 554. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Weijiang, WANG Guoya, LIU Xingrong, et al . The development characteristics and causes of the Yahuokou landslide in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2021 ,43 (2 ):544 −554 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: