Evaluation methods for performance of post-construction settlement prediction models in thick loess filled ground
-
摘要:
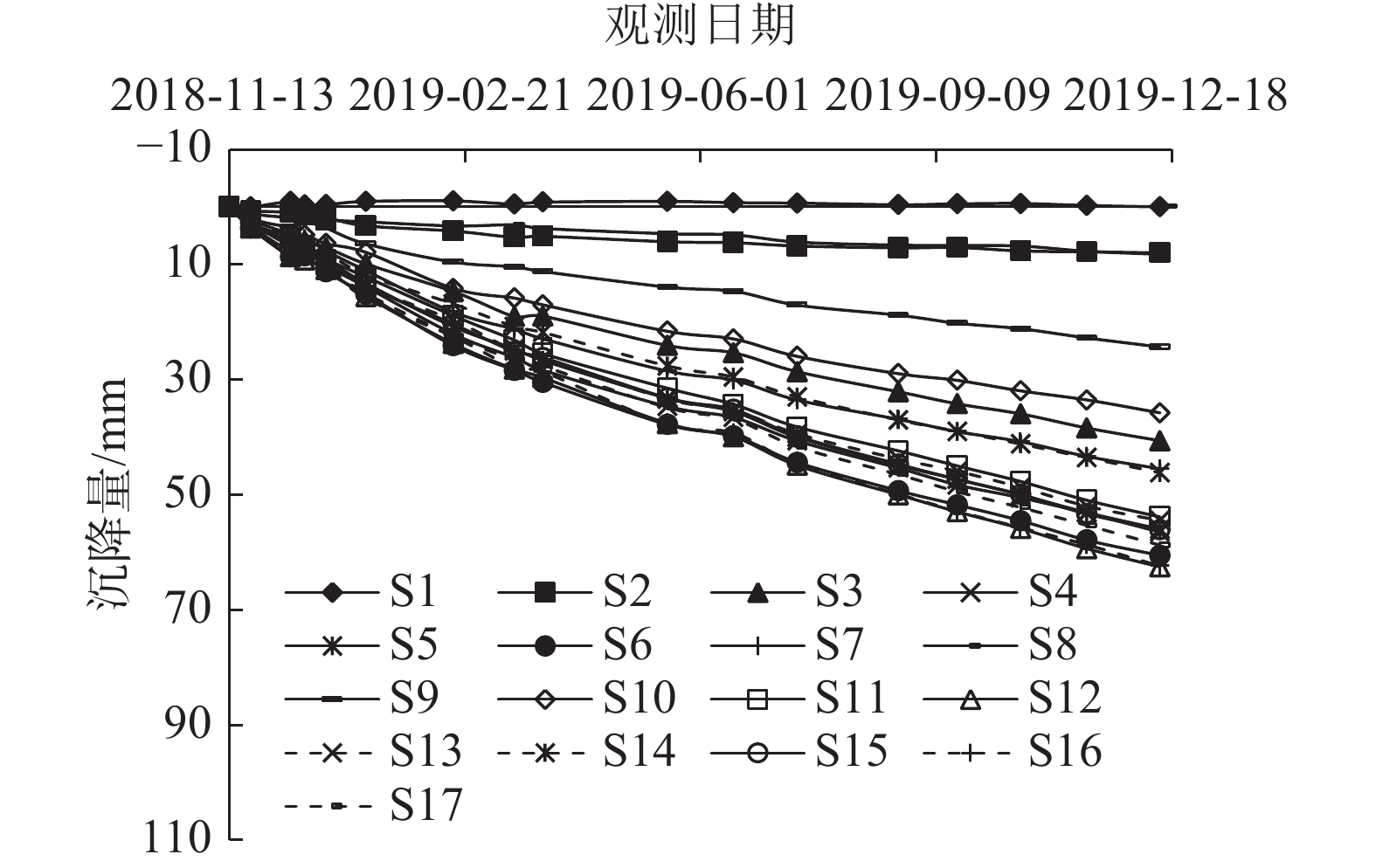
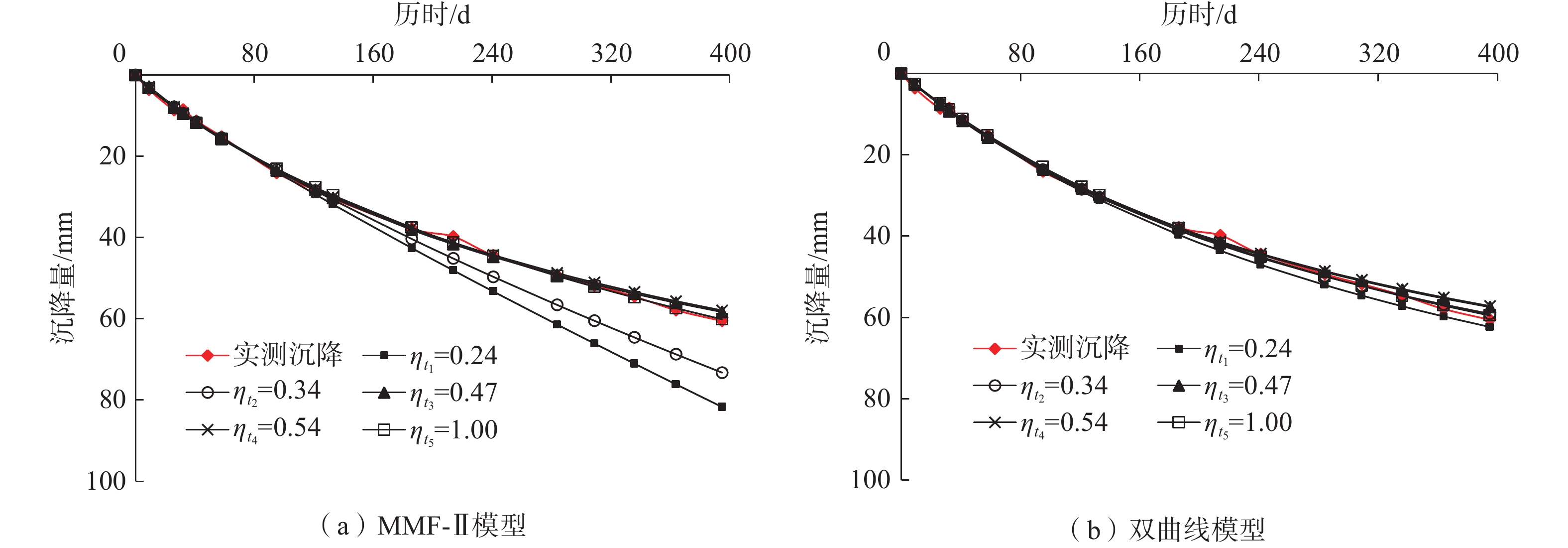
工后沉降预测结果是黄土高填方场地变形稳定性评价和建筑物规划布局的重要参考依据。为遴选适合黄土高填方场地的工后沉降预测模型,基于某典型黄土高填方工程的实测沉降数据,分析了工后沉降曲线的变化规律和发展趋势,建立了17种回归参数模型,提出了模型预测效果的评价指标和方法。结果表明:(1)该工程填方区工后沉降历时曲线呈“缓变型”变化,土方填筑完工初期无陡增段,随时间增加沉降速率逐步降低,尚未出现沉降趋于稳定的水平段;(2)将外推预测误差、内拟合误差和后验误差比最小化作为综合控制目标,可遴选出理想的回归参数模型;(3)MMF模型(Ⅱ型)和双曲线模型具有较高的预测精度、较好的稳定性和较强的适应性,在17种模型中的预测效果最佳;(4)沉降数据的变化越平稳,模型预测效果越好;(5)增大建模数据的时间跨度,会提升预测精度,但增大至一定值后,预测精度提升效果不再显著。
Abstract:The prediction of post-construction settlement is an important reference for the evaluation of deformation stability evaluation and building layout planning in thick loess filled ground. To choose suitable models for predicting post-construction settlement in thick loess filled grounds, the characteristics of post-construction settlement curves are analyzed based on the measured settlement of a thick loess fill ground project. Seventeen regression parameter models are established, and some evaluation indexes and methods for models are proposed. The best prediction models for post-construction settlement prediction are optimized. The results indicate that the post-construction settlement curves of the filling area change slowly, with no steep increase in the initial stage of earthwork filling. The settlement rate gradually decreases with time, and there is no horizontal section where the settlement tends to be stable. The optimal regression parameter model can be selected by minimizing the extrapolation prediction error, the internal fitting error, and the posteriori error ratio as the comprehensive control objective. The MMF model (TypeⅡ) and hyperbolic model show high prediction accuracy, good stability, and strong adaptability, with the prediction effect being the best among the 17 models. The more stable the settlement data changes, the better the model prediction effect. Increasing the time span of modeling data would improve the prediction accuracy, but the improvement effect on prediction accuracy would no longer be significant after reaching a certain value.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- thick loess fill ground /
- post-construction settlement /
- prediction model /
- evaluation index
-

-
表 1 沉降预测中常用的回归参数预测模型
Table 1. Summary of regression parameter prediction models for settlement prediction
类型 模型名称 数学表达式 沉降速率 备 注 第
Ⅰ
类
模
型Logistic 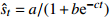
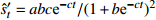
收敛模型 Gompertz 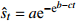
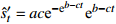
收敛模型 Usher 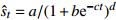
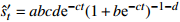
收敛模型 Weibull 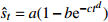
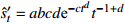
收敛模型 MMF-Ⅰ 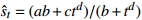
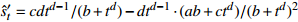
收敛模型 MMF-Ⅱ 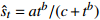
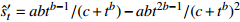
收敛模型 Richards 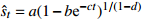
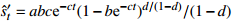
收敛模型 Knothe-Ⅰ 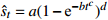
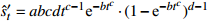
收敛模型 Knothe-Ⅱ 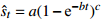

收敛模型 Bertalanffy 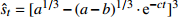
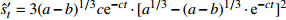
收敛模型 邓英尔 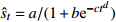
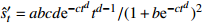
收敛模型 第
Ⅱ
类
模
型Spillman 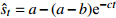
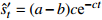
收敛模型 指数曲线 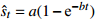
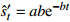
收敛模型 双曲线 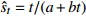
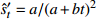
收敛模型 幂函数 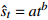
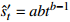
发散模型 平方根函数 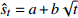
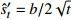
发散模型 对数函数 
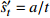
发散模型 对数抛物线 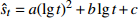
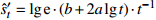
发散模型 星野法 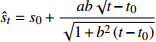
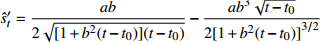
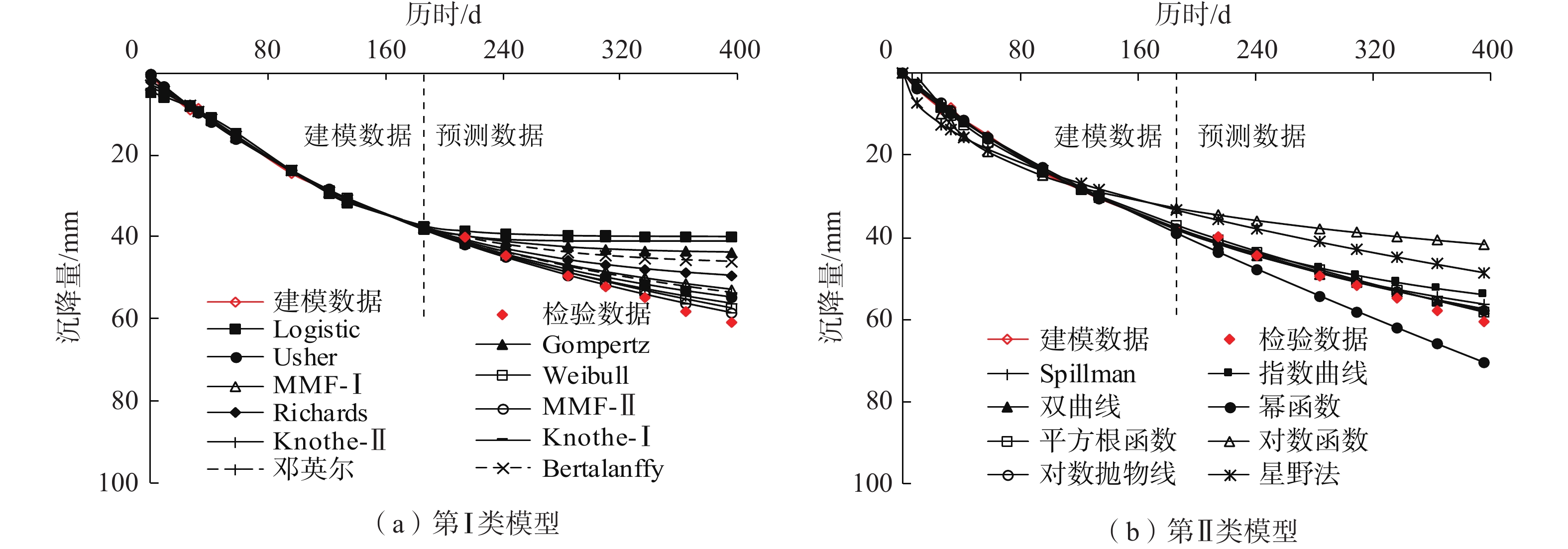
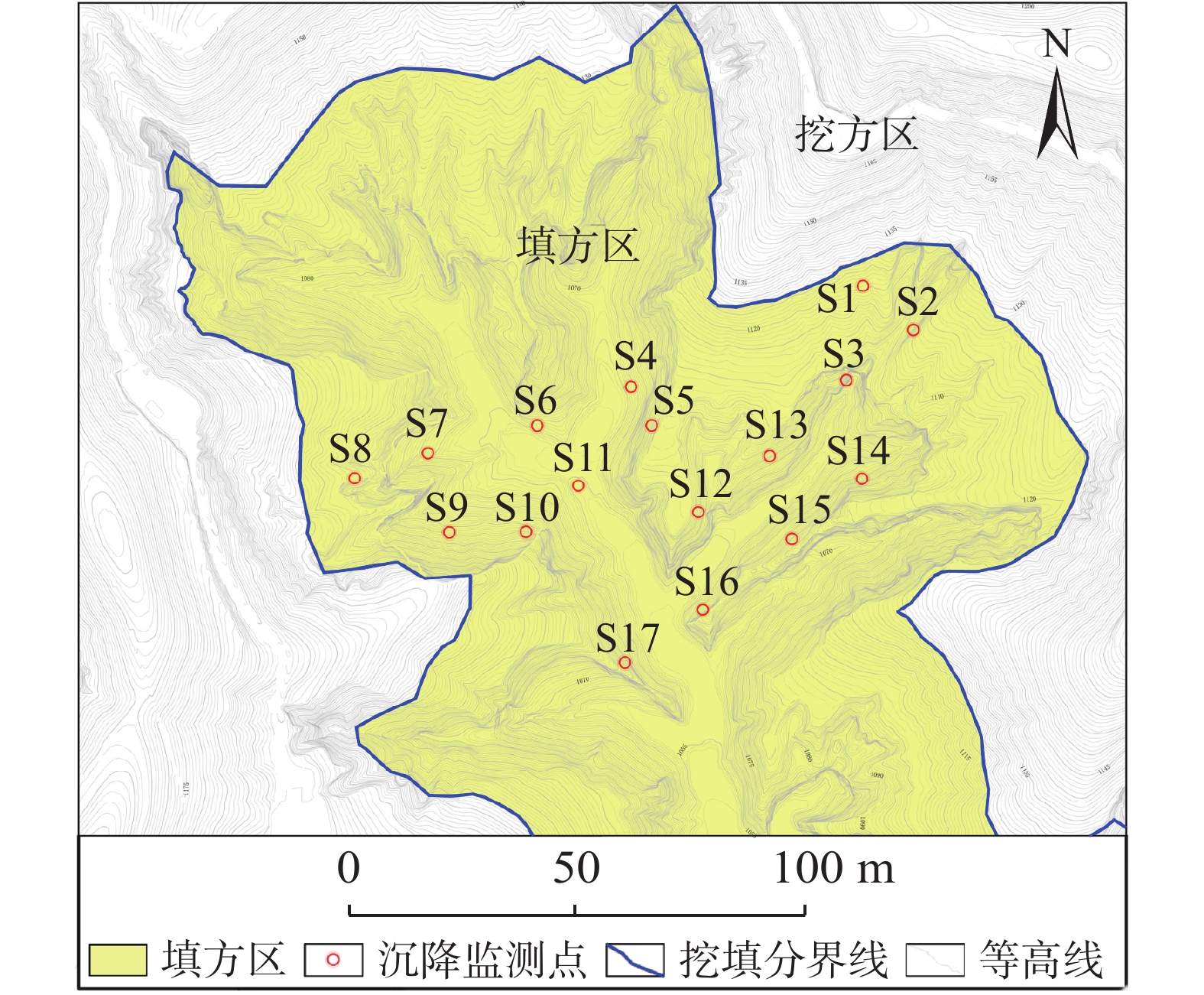
收敛模型 表 2 各模型对典型监测点S6实测数据的内拟合及外推预测结果
Table 2. Internal-fitting and extrapolation prediction results of each model for the measured settlement data at a typical monitoring point S6
类型 模型名称 模型参数 内拟合效果 外推预测效果 后验误差
比Cia b c d MAPE* /% SSE RMSE R2 MAPE /% MAD MSE MFE 第
Ⅰ
类
模
型Logistic 39.7540 7.6080 0.0252 — 9.88 8.06 0.95 0.9928 21.66 11.77 179.32 11.77 2.19 Gompertz 43.7854 0.9395 0.0150 — 6.10 3.09 0.59 0.9973 16.39 8.99 111.11 8.99 2.69 Usher 64.0873 −0.9931 0.0049 −1.0149 5.16 2.72 0.52 0.9981 5.03 2.74 10.97 2.31 0.98 Weibull 3.3377 −52.2248 14.7577 −0.4232 3.58 2.04 0.45 0.9986 3.09 1.65 3.87 1.21 0.86 MMF-Ⅰ 2.4888 869.7498 68.8715 1.3199 3.26 1.71 0.44 0.9985 7.18 3.93 21.54 3.62 2.20 MMF-Ⅱ 113.9160 0.9777 329.4676 — 5.84 3.04 0.55 0.9979 2.05 1.05 1.77 0.41 0.35 Richards 51.8874 0.8687 0.0085 0.3724 3.18 1.66 0.43 0.9985 9.98 5.49 42.78 5.25 3.13 Knothe-Ⅰ 41.0949 0.0000 4.0687 0.2098 4.49 2.17 0.49 0.9981 18.75 10.31 147.80 10.31 4.18 Knothe-Ⅱ 68.6817 240.2071 0.9562 — 5.65 2.87 0.56 0.9975 3.79 2.05 6.41 1.58 0.67 Bertalanffy 46.8972 36.1948 0.0116 — 4.45 2.03 0.47 0.9982 13.42 7.39 76.86 7.32 3.02 邓英尔 3.2623 −0.9558 28.7664 −1.2368 3.24 1.81 0.42 0.9987 6.32 3.45 16.62 3.11 1.95 第
Ⅱ
类
模
型Spillman 68.5727 0.7074 0.0043 — 4.50 2.47 0.52 0.9978 3.59 1.93 5.67 1.38 0.80 指数曲线 62.6226 0.0050 — — 5.95 3.01 0.58 0.9973 5.71 3.12 13.95 2.74 0.96 双曲线 3.1221 0.0095 — — 6.00 3.06 0.55 0.9979 2.75 1.46 3.16 0.93 0.46 幂函数 0.6425 0.7852 — — 4.34 5.38 0.73 0.9963 11.67 6.15 42.57 -6.15 2.69 平方根函数 −8.9505 3.3748 — — 13.18 14.00 1.25 0.9876 2.90 1.54 2.78 1.36 0.22 对数函数 11.6931 −28.2990 — — 26.75 113.31 3.55 0.8993 24.20 12.77 182.58 12.77 0.90 对数抛物线 21.4982 −43.5385 25.8604 — 4.12 2.83 0.56 0.9975 2.75 1.46 2.83 1.07 0.67 星野法 1367.0000 0.0018 — — 32.50 114.39 3.38 0.9205 16.81 8.80 84.05 8.80 0.52 注:“—”表示无此参数。 表 3 优选模型对不同监测点沉降数据的内拟合和外推预测结果
Table 3. Internal-fitting and extrapolation prediction of settlement data for different monitoring points using the optimal model
监测点 模型名称 模型参数 内拟合效果
R2外推预测效果 后验误差比
Cia b c MAPE /% MFE S2 双曲线 15.8265 0.0747 — 0.9805 8.33 −0.60 0.58 MMF-Ⅱ 7.4942 1.5515 829.1400 0.9880 7.42 0.56 0.55 S3 双曲线 4.9610 0.0145 — 0.9969 3.28 1.31 0.73 MMF-Ⅱ 64.7724 1.0199 344.1345 0.9969 4.11 1.60 0.88 S4 双曲线 3.4475 0.0099 — 0.9973 0.78 0.56 0.12 MMF-Ⅱ 90.2525 1.0341 350.0908 0.9974 2.21 1.28 0.32 S5 双曲线 3.7677 0.0095 — 0.9990 2.34 1.29 0.64 MMF-Ⅱ 86.2061 1.0584 397.9812 0.9991 4.82 2.51 1.14 S6 双曲线 3.1247 0.0095 — 0.9978 1.42 0.92 0.24 MMF-Ⅱ 112.9076 0.9804 329.8660 0.9979 0.57 0.46 0.10 S7 双曲线 4.4275 0.0108 — 0.9944 2.15 −0.75 0.22 MMF-Ⅱ 71.2408 1.0794 416.6811 0.9946 1.30 0.64 0.13 S8 双曲线 9.8039 0.1899 — 0.9419 31.96 2.24 3.26 MMF-Ⅱ −1.0396 0.1205 −2.3030 0.9814 0.55 −0.05 0.11 S9 双曲线 7.9448 0.0288 — 0.9816 8.11 1.79 0.54 MMF-Ⅱ 35.3201 0.9936 274.5082 0.9999 7.88 1.74 0.53 S10 双曲线 5.5294 0.0167 — 0.9908 4.16 1.37 0.40 MMF-Ⅱ 166.3711 0.8423 540.3470 0.9917 3.30 −0.98 0.36 S11 双曲线 4.0073 0.0100 — 0.9981 3.51 1.75 0.69 MMF-Ⅱ 143.1599 0.9305 451.8395 0.9982 0.26 0.22 0.06 S12 双曲线 3.0885 0.0101 — 0.9981 5.40 3.11 1.01 MMF-Ⅱ 139.2267 0.9179 325.7170 0.9984 1.82 1.14 0.40 S13 双曲线 3.6537 0.0104 — 0.9989 2.59 1.37 0.68 MMF-Ⅱ 145.9022 0.9138 397.9244 0.9992 1.51 −0.60 0.72 S14 双曲线 4.4223 0.0123 — 0.9986 3.52 1.52 0.73 MMF-Ⅱ 74.2716 1.0255 358.6842 0.9986 4.61 1.96 0.94 S15 双曲线 3.8173 0.0093 — 0.9982 1.93 1.12 0.38 MMF-Ⅱ 77.3464 1.1049 426.3157 0.9986 6.28 3.26 1.20 S16 双曲线 3.3989 0.0084 — 0.9967 1.54 1.02 0.22 MMF-Ⅱ 160.0072 0.9428 447.0479 0.9968 1.24 −0.51 0.20 S17 双曲线 3.2720 0.0110 — 0.9968 5.66 3.08 0.78 MMF-Ⅱ 100.1378 0.9706 296.3921 0.9968 4.46 2.46 0.63 注:“—”表示无此参数。 -
[1] 高建中, 郑建国, 魏弋锋, 等. 延安新区黄土丘陵沟壑区域工程造地实践[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019
GAO Jianzhong, ZHENG Jianguo, WEI Yifeng, et al. Engineering practice of land reclamation in loess hilly gully areas in Yan’an an new district[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 朱才辉,李宁,刘明振,等. 吕梁机场黄土高填方地基工后沉降时空规律分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2):293 − 301. [ZHU Caihui,LI Ning,LIU Mingzhen,et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of LYUliang Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(2):293 − 301. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU Caihui, LI Ning, LIU Mingzhen, et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of Lüliang Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(2): 293-301. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 姚仰平,黄建,张奎,等. 机场高填方蠕变沉降的数值反演预测[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(10):3395 − 3404. [YAO Yangping,HUANG Jian,ZHANG Kui,et al. Numerical back-analysis of creep settlement of airport high fill[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(10):3395 − 3404. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0402
YAO Yangping, HUANG Jian, ZHANG Kui, et al. Numerical back-analysis of creep settlement of airport high fill[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 3395-3404. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0402
[4] 宰金珉,梅国雄. 全过程的沉降量预测方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2000,21(4):322 − 325. [ZAI Jinmin,MEI Guoxiong. Forecast method of settlement during the complete process of construction and operation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2000,21(4):322 − 325. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2000.04.003
ZAI Jinmin, MEI Guoxiong. Forecast method of settlement during the complete process of construction and operation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2000, 21(4): 322-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2000.04.003
[5] 刘射洪, 袁聚云, 赵昕. 地基沉降预测模型研究综述[J]. 工业建筑, 2014, 44(增刊1): 738 − 741
LIU Shehong, YUAN Juyun, ZHAO Xin. Review of settlement prediction models of foundation[J]. Industrial Construction, 2014, 44(Sup 1): 738 − 741. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 周艳萍. 基于灰色Verhulst模型的山西太原地面沉降趋势分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(2):94 − 99. [ZHOU Yanping. Land subsidence trend of Taiyuan City,Shanxi based on Grey Verhust Model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(2):94 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.02.15
ZHOU Yanping. Land subsidence trend of Taiyuan City, Shanxi based on Grey Verhust Model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(2): 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.02.15
[7] 范珊珊,郭海朋,朱菊艳,等. 线性回归模型在北京平原地面沉降预测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(1):70 − 74. [FAN Shanshan,GUO Haipeng,ZHU Juyan,et al. Application of linear regression model for land subsidence prediction in Beijing plain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(1):70 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.01.016
FAN Shanshan, GUO Haipeng, ZHU Juyan, et al. Application of linear regression model for land subsidence prediction in Beijing plain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(1): 70-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.01.016
[8] 韩相超,吕远强. 内蒙古黄旗海湿地软土路基的沉降规律分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(1):75 − 78. [HAN Xiangchao,LYU Yuanqiang. Settlement analysis of soft subgrade in Huangqihai wetlands,Inner Mongolia[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(1):75 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.01.005
HAN Xiangchao, LV Yuanqiang. Settlement analysis of soft subgrade in Huangqihai wetlands, Inner Mongolia[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(1): 75-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.01.005
[9] 葛苗苗,李宁,郑建国,等. 基于一维固结试验的压实黄土蠕变模型[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(11):3164 − 3170. [GE Miaomiao,LI Ning,ZHENG Jianguo,et al. A creep model for compacted loess based on 1D oedometer test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(11):3164 − 3170. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.11.017
GE Miaomiao, LI Ning, ZHENG Jianguo, et al. A creep model for compacted loess based on 1D oedometer test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(11): 3164-3170. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.11.017
[10] 宰金珉,梅国雄. 泊松曲线的特征及其在沉降预测中的应用[J]. 重庆建筑大学学报,2001,23(1):30 − 35. [ZAI Jinmin,MEI Guoxiong. Feature of poisson curve and its application to displacement forecast[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University,2001,23(1):30 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZAI Jinmin, MEI Guoxiong. Feature of Poisson curve and its application to displacement forecast[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, 2001, 23(1): 30-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 曹文贵, 印鹏, 贺敏, 等. 考虑实测数据新旧程度的恭候澄江单项模型预测方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(6): 65 − 70
CAO Wengui, YIN Peng, HE Min, et al. A prediction method for post-construction settlement ofa single model with the consideration of the new or old degree of the measured data[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(6): 65 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] VAGHI C,RODALLEC A,FANCIULLINO R,et al. Population modeling of tumor growth curves and the reduced Gompertz model improve prediction of the age of experimental tumors[J]. PLoS Computational Biology,2020,16(2):e1007178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007178
[13] 余闯,刘松玉. 路堤沉降预测的Gompertz模型应用研究[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(1):82 − 86. [YU Chuang,LIU Songyu. A Study on prediction of embankment settlement with the gompertz model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(1):82 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YU Chuang, LIU Songyu. A Study on prediction of embankment settlement with the gompertz model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(1): 82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 胡顺强,崔东文. 基于AEO-Schumacher-Usher模型的径流及地下水位预测[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2020(11):28 − 34. [HU Shunqiang,CUI Dongwen. Runoff and groundwater level prediction based on AEO-schumacher-usher model[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2020(11):28 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2020.11.006
HU Shunqiang, CUI Dongwen. Runoff and groundwater level prediction based on AEO-schumacher-usher model[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2020(11): 28-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2020.11.006
[15] DE OLIVEIRA FERREIRA D J,DE MATTOS FIUZA M P,CARDOSO M,et al. Use of the Weibull model on sizing thickeners-Part I:Sedimentation curve representation[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering,2021,99(3):708 − 724. doi: 10.1002/cjce.23904
[16] 刘国辉. Weibull模型在地基沉降预测中的应用[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,28(2):111 − 114. [LIU Guohui. The application of weibull model to settlement prediction of foundation[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences),2011,28(2):111 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2011.02.029
LIU Guohui. The application of weibull model to settlement prediction of foundation[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 28(2): 111-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2011.02.029
[17] 王军保,刘新荣,李鹏,等. MMF模型在采空区地表沉降预测中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(3):411 − 415. [WANG Junbao,LIU Xinrong,LI Peng,et al. Study on prediction of surface subsidence in mined-out region with the MMF model[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2012,37(3):411 − 415. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2012.03.024
WANG Junbao, LIU Xinrong, LI Peng, et al. Study on prediction of surface subsidence in mined-out region with the MMF model[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(3): 411-415. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2012.03.024
[18] ZREIQ R,KAMEL S,BOUBAKER S,et al. Generalized Richards model for predicting COVID-19 dynamics in Saudi Arabia based on particle swarm optimization Algorithm[J]. AIMS Public Health,2020,7(4):828 − 843. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2020064
[19] HUANG Changfu,LI Qun,WU Shunchuan,et al. Application of the richards model for settlement prediction based on a bidirectional difference-weighted least-squares method[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2018,43(10):5057 − 5065. doi: 10.1007/s13369-017-2909-0
[20] HU Qingfeng,CUI Ximin,WANG Guo,et al. Key technology of predicting dynamic surface subsidence based on knothe time function[J]. Journal of Software,2011,6(7):1273 − 1280.
[21] CHEN Lei,ZHANG Liguo,TANG Yixian,et al. Analysis of mining-induced subsidence prediction by exponent knothe model combined with insar and leveling[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry,Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,2018,IV-3:53 − 59.
[22] 高超,徐乃忠,孙万明,等. 基于Bertalanffy时间函数的地表动态沉陷预测模型[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(8):2740 − 2748. [GAO Chao,XU Naizhong,SUN Wanming,et al. Dynamic surface subsidence prediction model based on Bertalanffy time function[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(8):2740 − 2748. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GAO Chao, XU Naizhong, SUN Wanming, et al. Dynamic surface subsidence prediction model based on Bertalanffy time function[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(8): 2740-2748. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] LEE L,ATKINSON D,HIRST A G,et al. A new framework for growth curve fitting based on the von Bertalanffy Growth Function[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):1 − 12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4
[24] 邓英尔,谢和平. 全过程沉降预测的新模型与方法[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(1):1 − 4. [DENG Yinger,XIE Heping. New model and method of forecasting settlement during complete process of construction and operation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(1):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.01.001
DENG Yinger, XIE Heping. New model and method of forecasting settlement during complete process of construction and operation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(1): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.01.001
[25] 王志亮,吴克海,李永池,等. 一个预测路堤沉降的新经验公式模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(12):2013 − 2017. [WANG Zhiliang,WU Kehai,LI Yongchi,et al. A new empirical formula model for settlement prediction of embankments[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(12):2013 − 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.12.003
WANG Zhiliang, WU Kehai, LI Yongchi, et al. A new empirical formula model for settlement prediction of embankments[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(12): 2013-2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.12.003
[26] REDDY B R,OJHA A. Performance of maintainabilityiindex prediction models:A feature selection based study[J]. Evolving Systems,2019,10(2):179 − 204. doi: 10.1007/s12530-017-9201-0
[27] 方薇,陈向阳.考虑次固结的软基分级加载全过程沉降模型[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2015, 26(2): 110-115
FANG Wei, CHEN Xiangyang.Foundation settlement model considering secondary consolidation during multi-stage loading[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard andControl, 2015, 26(2): 110-115.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 韩相超, 吕远强.内蒙古黄旗海湿地软土路基的沉降规律分析[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2013, 24(1): 75-78.
HAN Xiangchao, LYU Yuanqiang. Settlement analysis of soft subgrade in Huangqihai wetlands, Inner Mongolia[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(1): 75-78.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] LI Shouju,YU Shen,SHANGGUAN Zichang,et al. Estimating model parameters of rockfill materials based on genetic algorithm and strain measurements[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering,2016,10(1):37 − 48. doi: 10.12989/gae.2016.10.1.037
[30] 甘友文,王志亮, 郑华.地基沉降预测中的双曲线模型修正[J].水文地质工程地质, 2004, 31(1): 98-100.
GAN Youwen, WANG Zhiliang, ZHENG Hua. Modification of hyperbolic model in foundation settlement prediction[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2004, 31(1): 98-100.(in Chinese)
[31] 刘宏,李攀峰,张倬元. 九寨黄龙机场高填方地基工后沉降预测[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(1):90 − 93. [LIU Hong,LI Panfeng,ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Prediction of the post-construction settlement of the high embankment of Jiuzhai-Huanglong Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(1):90 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.01.015
LIU Hong, LI Panfeng, ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Prediction of the post-construction settlement of the high embankment of Jiuzhai-Huanglong Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(1): 90-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.01.015
[32] 王海英,常肖,阮祺,等. 建筑垃圾填埋路基沉降预测的三点-星野法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2017,14(3):473 − 479. [WANG Haiying,CHANG Xiao,RUAN Qi,et al. Subsidence prediction of subgrade filled by construction waste based on three point-hoshino algorithm[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2017,14(3):473 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2017.03.006
WANG Haiying, CHANG Xiao, RUAN Qi, et al. Subsidence prediction of subgrade filled by construction waste based on three point-hoshino algorithm[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2017, 14(3): 473-479. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2017.03.006
[33] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑变形测量规范: JGJ 8—2016[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for deformation measurement of building and structure: JGJ 8—2016[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. (in Chinese)
[34] LEWIS C D. Industrial and business forecasting methods: A practical guide to exponential smoothing and curve fitting[M]. London: Butterworth Scientific, 1982.
-



 下载:
下载: