Study on the activities of the massive debris flows and sediment transport characteristics in the Grand Bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River Gorge, Xizang
-
摘要:
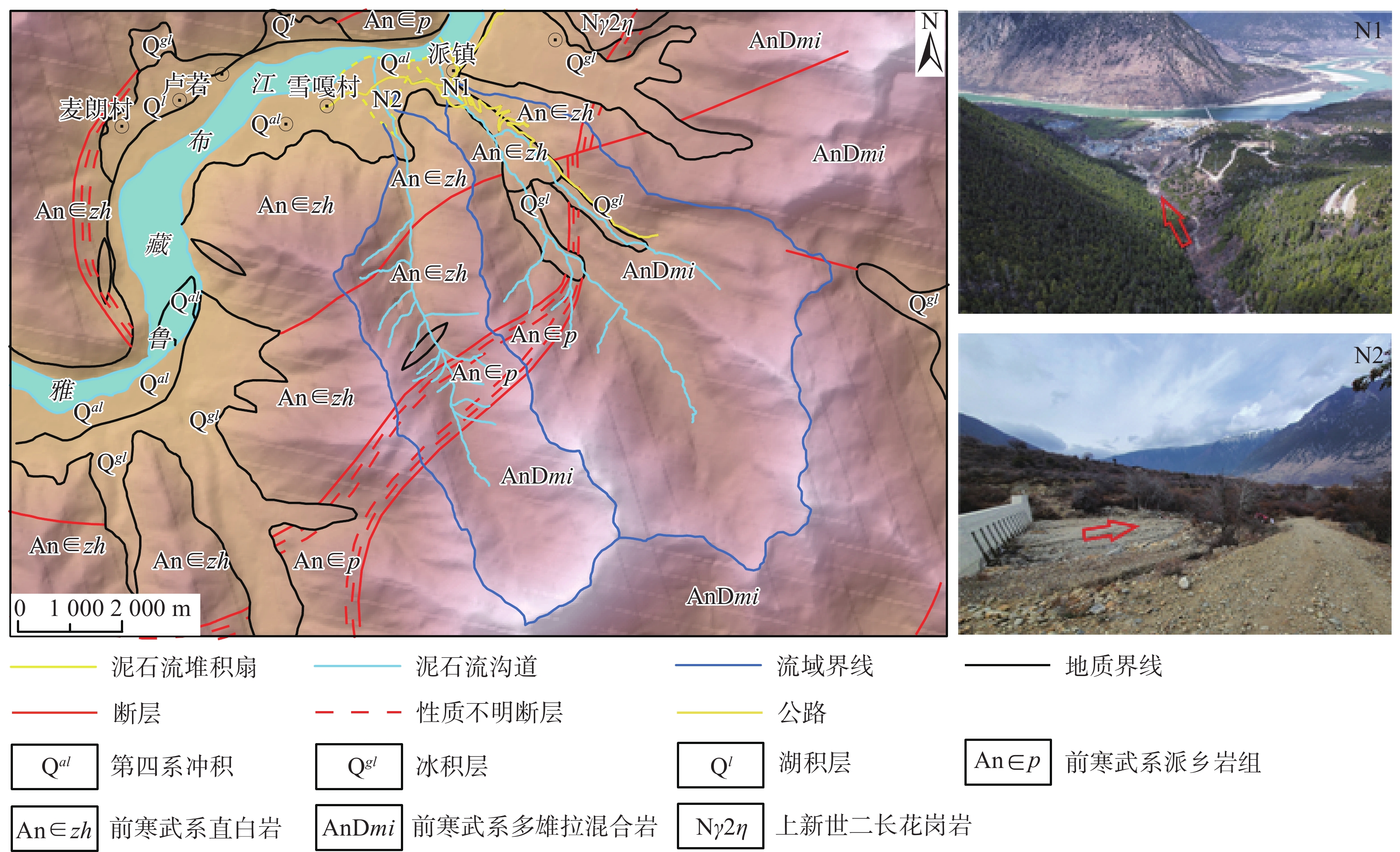
雅鲁藏布江大拐弯地处流域中下游分界处,为中国泥石流灾害活动极为发育的地区之一。以雅鲁藏布江大拐弯入口段南岸的派巴沟和曲鲁沟为例,基于该地区50年来历史光学卫星影像数据,采用多期遥感对比解译与现场调查相结合的方式,开展泥石流物源发育分布特征、泥沙输移特征、活动历史演化特征研究,结果表明:1980—2023年,派巴沟进入主河道的年平均泥沙量1 900 m3;在2016年修建拦挡坝前,曲鲁沟进入主河道的年平均泥沙量700 m3。派巴沟和曲鲁沟均于1980年左右暴发过大规模泥石流,此后40余年间,派巴沟以洪水及小型泥石流为主;曲鲁沟则暴发过多次规模不等的泥石流活动。近年来派巴沟流域内物源数量及面积增长幅度较小,泥石流易发性中等;曲鲁沟流域内发育大量沟道堆积物源以及坡面堆积物源,且近年来物源数量及面积增长幅度较为明显,泥石流易发性高,此前建成的治理工程运行良好,可有效降低泥石流的风险性。
Abstract:The Grand bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River, located at the boundary between the middle and lower reaches of the basin, is one of the most developed areas for debris flow activities in China. This study focuses on the Paiba gully and Qulu Valley on the south bank of the entrance section of the Yarlung Zangbo River’s grand bend. We collected and sorted out the historical optical satellite image data of the region in the past 50 years. By combining multi-period remote sensing image comparative interpretation and field investigation, we carried out the research on the characteristics of the development and distribution of debris flow sources, the characteristics of sediment transport, and the historical evolution of debris flow activities. The results show that from 1980 to 2023, the annual average sediment volume of the Paiba gully entering the main river was about 1900 m3. Before the construction of a retaining dam in 2016, the annual average sediment volume of the Qulu Valley entering the main river channel was about 700 m3. Both Paiba gully and Qulu Valley experienced large-scale debris flow around 1980. Over the next 40 years, Paiba gully was mainly characterized by floods and small-scale debris flow, while Qulu Valley experienced multiple debris flow events of varying scales. In recent years, the number and area of material sources in Paiba gully have increased relatively slowly, and the susceptibility of debris flows is moderate. In contract, Qulu Valley has seen significant increases in the quantity and area of channel and slope material sources, leading to high debris flow susceptibility. Sources developed in the Qulu Valley, and the quantity and area of these material sources have increased significantly in recent years. The susceptibility of debris flows is high, and the previously built control projects are functioning well and can effectively reduce the risk of debris flows.
-

-
表 1 研究区泥石流流域基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of the watershed within the study area
编号 沟道名称 流域面积/km2 主沟道长度/km 平均纵比降/‰ N1 派巴沟 40.19 9.9 251 N2 曲鲁沟 23.45 10.7 237 表 2 遥感信息源一览表
Table 2. List of remote sensing data
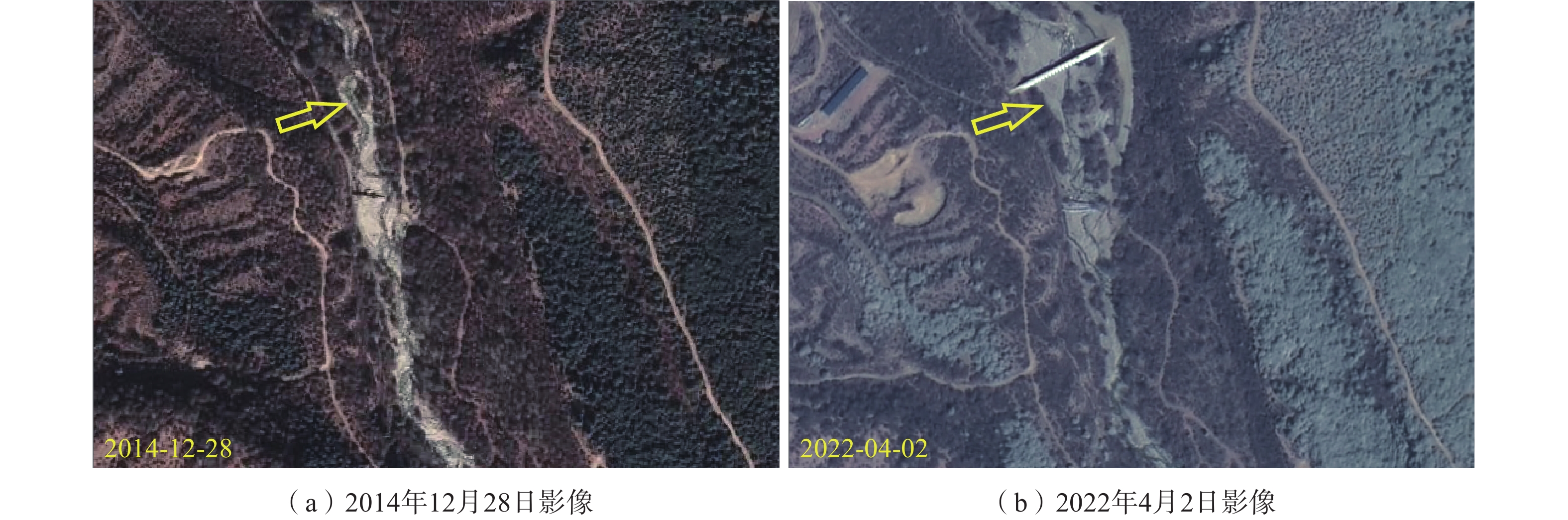
数据源 空间分辨率 影像时间 GF2 全色0.8 m,多光谱3.2 m 2021-12-04/2021-02-12/
2022-04-02Worldview-2 全色0.46 m,多光谱1.84 m 2014-12-28 ETM 多光谱15 m 1987-03-08/2000-11-09 KH-1 全色3~6 m 1972-11-28 表 3 研究区内泥石流物源分布及时空变化特征
Table 3. Distribution and spatiotemporal variation of debris flow material sources in the study area
编号 泥石流名称 物源类型 2014年 2022年 数量/处 总面积/m2 数量/处 总面积/m2 N1 派巴沟泥石流 崩滑堆积物源 2 106696 — — 沟道堆积物源 5 713774 — — 坡面堆积物源 3 59507 2 44078 总计 10 879977 2 44078 N2 曲鲁沟泥石流 崩滑堆积物源 1 15211 2 23613 沟道堆积物源 4 413779 3 5692 坡面堆积物源 17 305160 2 26104 总计 22 734150 7 55409 表 4 泥石流冲刷与淤积区域面积统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of the area of debris flow erosion and sedimentation areas
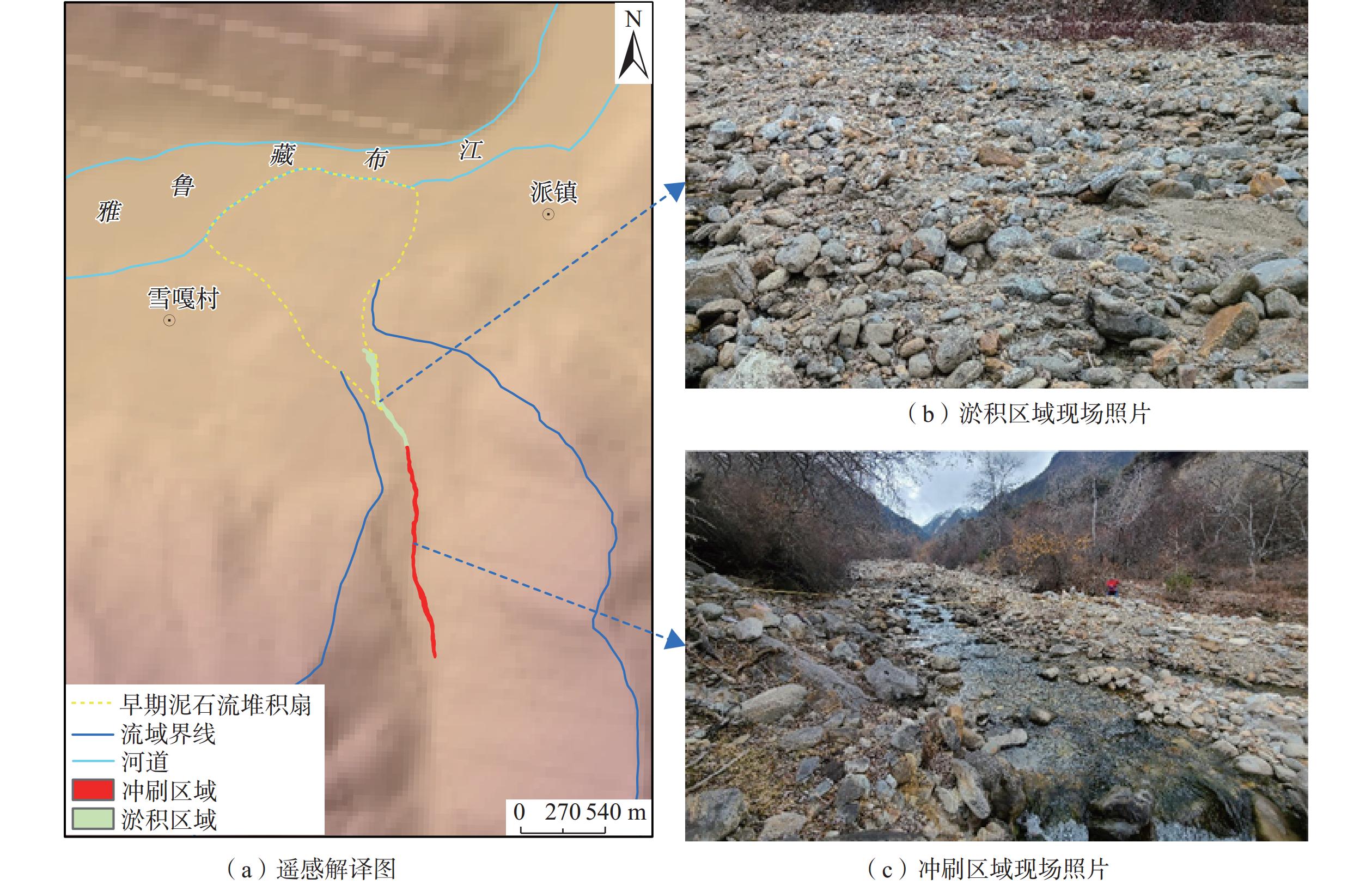
编号 泥石流名称 类型 面积/m2 N1 派巴沟泥石流 冲刷区域 56026 淤积区域 2912 N2 曲鲁沟泥石流 冲刷区域 18397 淤积区域 15397 -
[1] BEAYMONT C,JAMIESON R A,NGUYEN M H,et al. Crustal channel flows:1. Numerical models with applications to the tectonics of the Himalayan-Xizang orogeny[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2004,109(B6).
[2] 雷永良,钟大赉,季建清,等. 东喜马拉雅构造结更新世两期抬升-剥露事件的裂变径迹证据[J]. 第四纪研究,2008,28(4):584 − 590. [LEI Yongliang,ZHONG Dalai,JI Jianqing,et al. Fission track evidence for two pleistocene uplift – exhumation events in the eastern himaiayan syntaxis[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2008,28(4):584 − 590. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.04.010
LEI Yongliang, ZHONG Dalai, JI Jianqing, et al. Fission track evidence for two pleistocene uplift – exhumation events in the eastern himaiayan syntaxis[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(4): 584 − 590. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.04.010
[3] 康文君, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 等. 南迦巴瓦峰第四纪隆升期次划分的热年代学证据[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(5):1753 − 1761. [KANG Wenjun, XU Xiwei, YU Guihua, et al. Thermochronological evidence for division of Quaternary uplifting stages of Mt. Namjagbarwa[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(5):1753 − 1761. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
KANG Wenjun, XU Xiwei, YU Guihua, et al. Thermochronological evidence for division of Quaternary uplifting stages of Mt. Namjagbarwa[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(5): 1753 − 1761. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张沛全,刘小汉. 雅鲁藏布江大拐弯入口段泥石流特征及应对措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2008,19(1):12 − 17. [ZHANG Peiquan,LIU Xiaohan. Debris flow distribution and preventions at the great turning in the gorge of Yarlung Zangbo River,southeastern Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2008,19(1):12 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.01.003
ZHANG Peiquan, LIU Xiaohan. Debris flow distribution and preventions at the great turning in the gorge of Yarlung Zangbo River, southeastern Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2008, 19(1): 12 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.01.003
[5] 彭补拙,杨逸畴,等. 南迦巴瓦峰地区自然地理与自然资源[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1996. [PENG Buzhuo,YANG Yichou,et al. Geography and Resources in Namche Baiwa Region [M]. Beijing:Science Press,1996. (in Chinese)]
PENG Buzhuo, YANG Yichou, et al. Geography and Resources in Namche Baiwa Region [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. (in Chinese)
[6] 朱平一,罗德富,寇玉贞. 西藏古乡沟泥石流发展趋势[J]. 山地研究,1997,15(4):296 − 299. [ZHU Pingyi,LUO Defu,KOU Yuzhen. Debris flow development trend of Guxiang Ravine,Xizang[J]. Mountain Research,1997,15(4):296 − 299. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Pingyi, LUO Defu, KOU Yuzhen. Debris flow development trend of Guxiang Ravine, Xizang[J]. Mountain Research, 1997, 15(4): 296 − 299. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 吕立群,王兆印,漆力健,等. 西藏古乡沟泥石流堰塞湖演化规律[J]. 泥沙研究,2015(5):14 − 18. [LYU Liqun,WANG Zaoyin,QI Lijian,et al. Evolution of debris-flow dammed lake at Guxiang gully in Xizang[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2015(5):14 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LYU Liqun, WANG Zaoyin, QI Lijian, et al. Evolution of debris-flow dammed lake at Guxiang gully in Xizang[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2015(5): 14 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘建康,程尊兰. 西藏古乡沟泥石流与气象条件的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程,2015,15(9):45 − 49. [LIU Jiankang,CHENG Zunlan. Meteorology conditions for frequent debris flows from Guxiang Valley in Xizang,China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2015,15(9):45 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.09.007
LIU Jiankang, CHENG Zunlan. Meteorology conditions for frequent debris flows from Guxiang Valley in Xizang, China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(9): 45 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.09.007
[9] 余忠水,德庆卓嘎,马艳鲜,等. 西藏波密天摩沟“9•4”特大泥石流形成的气象条件[J]. 山地学报,2009,27(1):82 − 87. [YU Zhongshui,DEQING Zhuoga,MA Yanxian,et al. Analysis of meteorological conditions about “9•4” debris flow in Tianmo gully Bomi country of Xizang[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2009,27(1):82 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2009.01.012
YU Zhongshui, DEQING Zhuoga, MA Yanxian, et al. Analysis of meteorological conditions about “9•4” debris flow in Tianmo gully Bomi country of Xizang[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2009, 27(1): 82 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2009.01.012
[10] 余忠水,德庆卓嘎,罗布次仁,等. 西藏波密县天摩沟“9•4”特大泥石流灾害成因初步分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(1):6 − 10. [YU Zhongshui,DEQING Zhuoga,LUOBU Ciren,et al. Preliminary analysis about the cause of “9•4” debris flow disaster in Tianmogou,Bomi,Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2009,20(1):6 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.01.002
YU Zhongshui, DEQING Zhuoga, LUOBU Ciren, et al. Preliminary analysis about the cause of “9•4” debris flow disaster in Tianmogou, Bomi, Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2009, 20(1): 6 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.01.002
[11] 高波,张佳佳,王军朝,等. 西藏天摩沟泥石流形成机制与成灾特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):144 − 153. [GAO Bo,ZHANG Jiajia,WANG Junchao,et al. Formation mechanism and disaster charateristics of debris flow in the Tianmo gully in Xizang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):144 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Bo, ZHANG Jiajia, WANG Junchao, et al. Formation mechanism and disaster charateristics of debris flow in the Tianmo gully in Xizang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(5): 144 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 童立强,涂杰楠,裴丽鑫,等. 雅鲁藏布江加拉白垒峰色东普流域频繁发生碎屑流事件初步探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1552 − 1561. [TONG Liqiang,TU Jienan,PEI Lixin,et al. Preliminary discussion of the frequently debris flow events in Sedongpu Basin at Gyalaperi peak,Yarlung Zangbo River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1552 − 1561. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TONG Liqiang, TU Jienan, PEI Lixin, et al. Preliminary discussion of the frequently debris flow events in Sedongpu Basin at Gyalaperi peak, Yarlung Zangbo River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(6): 1552 − 1561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘传正,吕杰堂,童立强,等. 雅鲁藏布江色东普沟崩滑-碎屑流堵江灾害初步研究[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(2):219 − 234. [LIU Chuanzheng,LYU Jietang,TONG Liqiang,et al. Research on glacial/ rock fall-landslide-debris flows in Sedongpu basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Xizang[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(2):219 − 234. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12029/gc20190201
LIU Chuanzheng, LYU Jietang, TONG Liqiang, et al. Research on glacial/ rock fall-landslide-debris flows in Sedongpu basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Xizang[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 219 − 234. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20190201
[14] 李壮,李滨,高杨,等. 雅鲁藏布江下游色东普沟高位地质灾害发育特征遥感解译[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):33 − 41. [LI Zhuang,LI Bin,GAO Yang,et al. Remote sensing interpretation of development characteristics of high-position geological hazards in Sedongpu gully,downstream of Yarlung Zangbo River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):33 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Zhuang, LI Bin, GAO Yang, et al. Remote sensing interpretation of development characteristics of high-position geological hazards in Sedongpu gully, downstream of Yarlung Zangbo River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(3): 33 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡桂胜,陈宁生,邓明枫,等. 西藏林芝地区泥石流类型及形成条件分析[J]. 水土保持通报,2011,31(2):193 − 197. [HU Guisheng,CHEN Ningsheng,DENG Mingfeng,et al. Classification and initiation conditions of debris flows in Linzhi Area,Xizang[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,31(2):193 − 197. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Guisheng, CHEN Ningsheng, DENG Mingfeng, et al. Classification and initiation conditions of debris flows in Linzhi Area, Xizang[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(2): 193 − 197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 铁永波,徐伟,向炳霖,等. 西南地区地质灾害风险“点面双控”体系构建与思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):106 − 113. [TIE Yongbo,XU Wei,XIANG Binglin,et al. The thoughts on construction of “double-control of point and zone” system of geological hazard risk in southwest China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIE Yongbo, XU Wei, XIANG Binglin, et al. The thoughts on construction of “double-control of point and zone” system of geological hazard risk in southwest China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 铁永波,张宪政,龚凌枫,等. 西南山区典型地质灾害链成灾模式研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1071 − 1080. [TIE Yongbo,ZHANG Xianzheng,GONG Lingfeng,et al. Research on the pattern of typical geohazard chains in the southwest mountainous region,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,28(6):1071 − 1080. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIE Yongbo, ZHANG Xianzheng, GONG Lingfeng, et al. Research on the pattern of typical geohazard chains in the southwest mountainous region, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 1071 − 1080. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 铁永波,葛华,高延超,等. 二十世纪以来西南地区地质灾害研究历程与展望[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2022,42(4):653 − 665. [TIE Yongbo,GE Hua,GAO Yanchao,et al. The research progress and prospect of geological hazards in southwest China since the 20th Century[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2022,42(4):653 − 665. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIE Yongbo, GE Hua, GAO Yanchao, et al. The research progress and prospect of geological hazards in southwest China since the 20th Century[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2022, 42(4): 653 − 665. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李翠平,王萍,钱达,等. 雅鲁藏布江大峡谷入口河段最近两期古堰塞湖事件的年龄[J]. 地震地质,2015,37(4):1136 − 1146. [LI Cuiping,WANG Ping,QIAN Da,et al. Ages of the recent two episodes of glacially dammed lakes along the upstream of the Yarlung Zangbo Gorge[J]. Seismology and Geology,2015,37(4):1136 − 1146. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Cuiping, WANG Ping, QIAN Da, et al. Ages of the recent two episodes of glacially dammed lakes along the upstream of the Yarlung Zangbo Gorge[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2015, 37(4): 1136 − 1146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 常鸣,唐川,苏永超,等. 雅鲁藏布江米林段泥石流堆积扇危险范围预测模型[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(6):971 − 978. [CHANG Ming,TANG Chuan,SU Yongchao,et al. Prediction model for debris flow hazard zone on alluvial fan in Milin section of Yarlungzangbo River,Xizang[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(6):971 − 978. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.008
CHANG Ming, TANG Chuan, SU Yongchao, et al. Prediction model for debris flow hazard zone on alluvial fan in Milin section of Yarlungzangbo River, Xizang[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(6): 971 − 978. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.008
[21] 王俊豪,管建军,魏云杰,等. 德钦县城直溪河泥石流成灾模式及运动过程模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):187 − 195. [WANG Junhao,GUAN Jianjun,WEI Yunjie,et al. A study of the disaster model and movement process simulation of debris flow in the Zhixi River of Deqin County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):187 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Junhao, GUAN Jianjun, WEI Yunjie, et al. A study of the disaster model and movement process simulation of debris flow in the Zhixi River of Deqin County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 187 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘波,胡卸文,何坤,等. 西藏洛隆县巴曲冰湖溃决型泥石流演进过程模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):150 − 160. [LIU Bo,HU Xiewen,HE Kun,et al. Characteristics and evolution process simulation of the Baqu gully debris flow triggered by ice-lake outburst in Luolong County of Xizang,China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):150 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Bo, HU Xiewen, HE Kun, et al. Characteristics and evolution process simulation of the Baqu gully debris flow triggered by ice-lake outburst in Luolong County of Xizang, China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 150 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 柴波,陶阳阳,杜娟,等. 西藏聂拉木县嘉龙湖冰湖溃决型泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(12):4630 − 4639. [CHAI Bo,TAO Yangyang,Du Juan,et al. Hazard Assessment of debris flow triggered by outburst of Jialong Glacial lake in Nyalam County,Xizang[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(12):4630 − 4639. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHAI Bo, TAO Yangyang, Du Juan, et al. Hazard Assessment of debris flow triggered by outburst of Jialong Glacial lake in Nyalam County, Xizang[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(12): 4630 − 4639. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 黄艳婷,郭永刚. 考虑降雨敏感度的泥石流危险性评价——以藏东南地区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):129 − 138. [HUANG Yanting,GUO Yonggang. Debris flow risk assessment considering different rainfall sensitivity:A case study in southeast Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):129 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Yanting, GUO Yonggang. Debris flow risk assessment considering different rainfall sensitivity: A case study in southeast Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1): 129 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 龚凌枫,张运达,铁永波,等. 雅鲁藏布江大拐弯典型泥石流全新世以来发育历史及活动特征[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1024 − 1034. [GONG Lingfeng,ZHANG Yunda,TIE Yongbo,et al. Development history and activity characteristics of typical debris flows in the Grand Bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River since the Holocene[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022,28(6):1024 − 1034. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GONG Lingfeng, ZHANG Yunda, TIE Yongbo, et al. Development history and activity characteristics of typical debris flows in the Grand Bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River since the Holocene[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(6): 1024 − 1034. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载:








