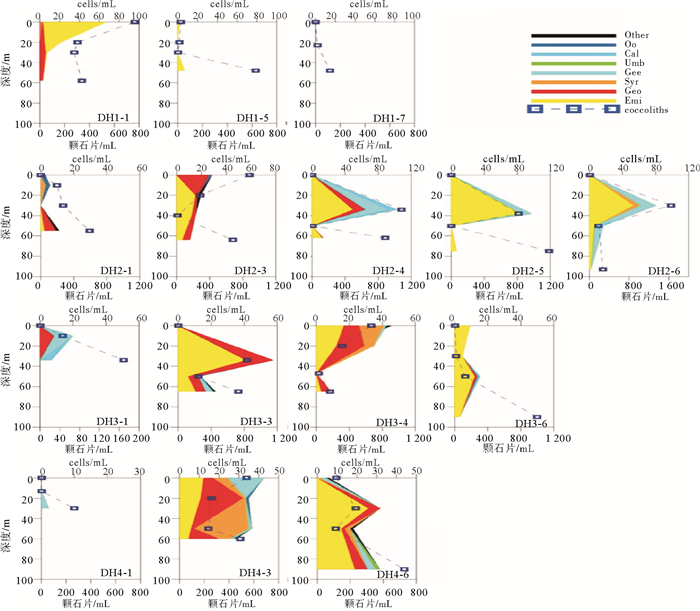
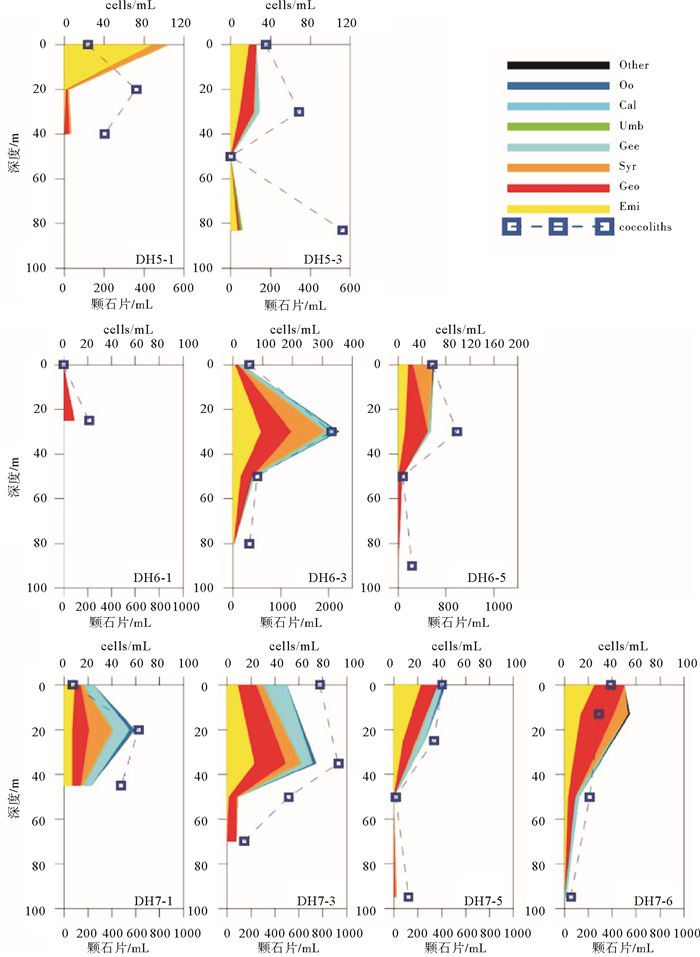
DISTRIBUTION PATTERN OF MODERN COCCOLITHOPHORES IN THE EAST CHINA SEA IN SPRING, 2014 AND THEIR RESPONSES TO ENVIRONMENT
-
摘要:
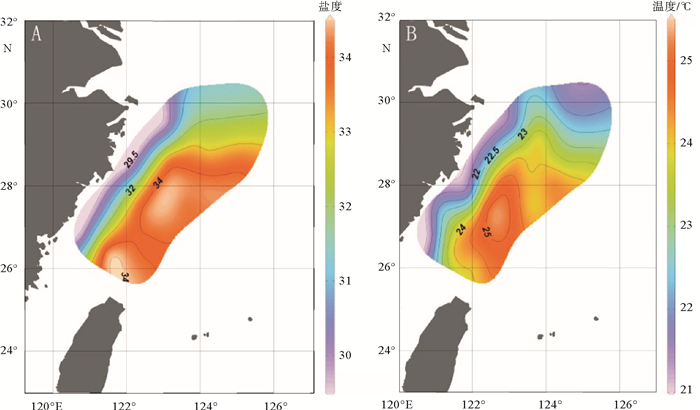
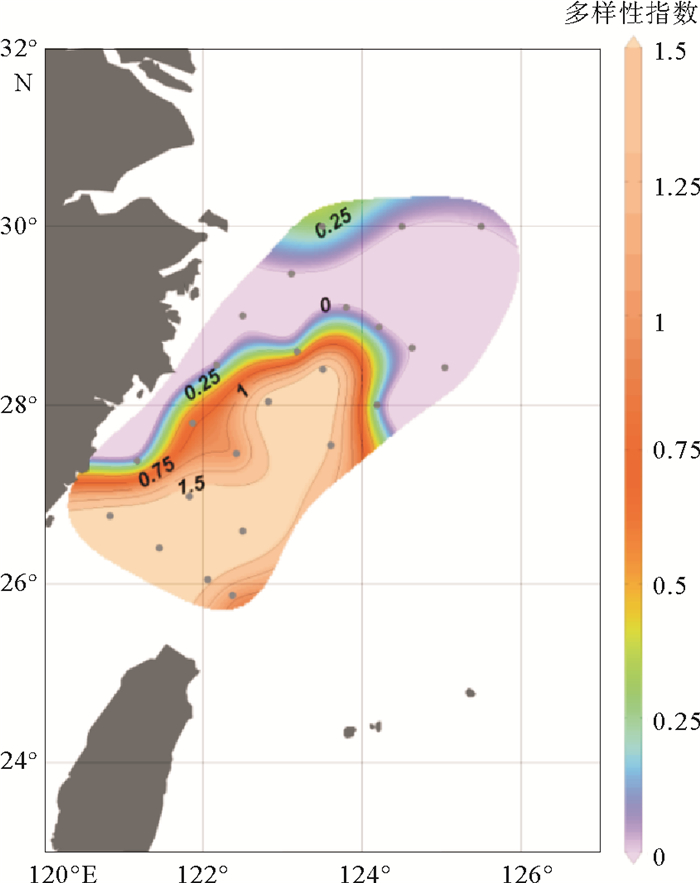
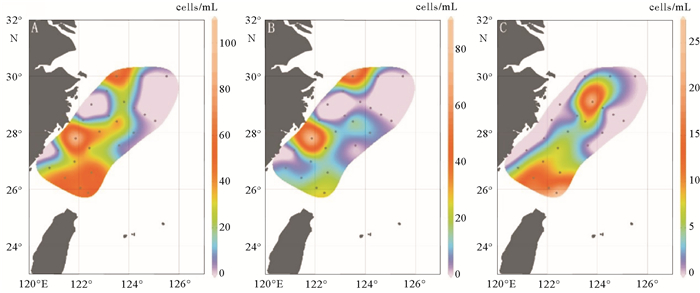
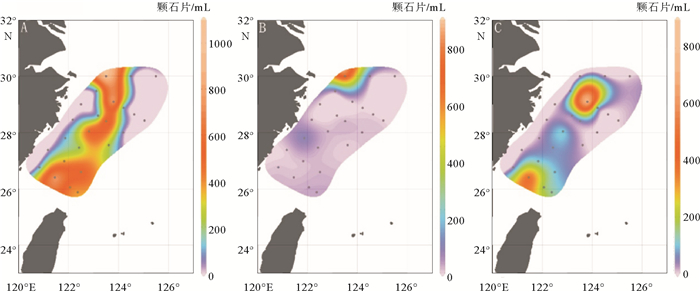
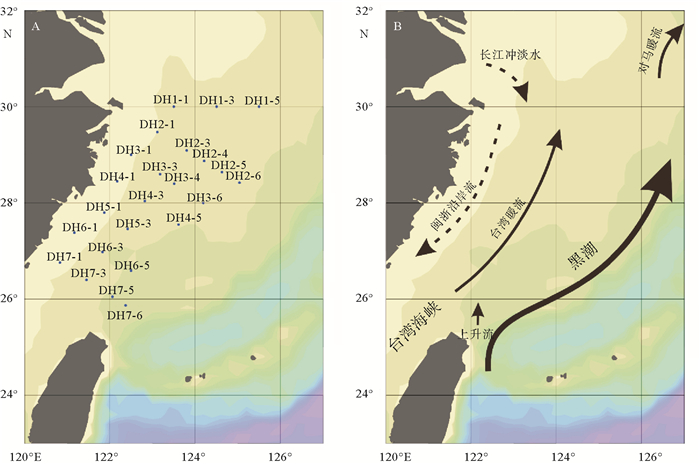
通过对2014年5月东海89个水样进行颗石藻扫描电子显微镜分析,得到本海域春季现生颗石藻群落组成及空间分布,并分析了环境因子对现生颗石藻分布的影响。结果表明:春季优势种为Emiliania huxleyi、Gephyrocapsa oceanica、Syracosphaera spp.、Gephyrocapsa ericsoni等。现生颗石藻总量为0~356.40 cells/mL,颗石片为0~2 062.38/mL。现生颗石藻多分布于0~50 m水层中,颗石片在底层多有分布。无论在表层水体还是垂直水体中,现生颗石藻的分布均呈现近岸到外海、由西北到东南,丰度升高、多样性增多的趋势,这与东海复杂水团系统导致的温盐、营养盐等环境因子变化有关。
Abstract:The community of coccolithophores in the East China Sea during the spring (18th May to 13th June) of 2014 are studied in this research. The community composition and spatial distribution of living coccolithophores (LCs) in the survey area are revealed and the influence of environmental factors discussed. 89 plankton samples are analyzed by scanning electronic microscope with Emiliania huxleyi, Gephyrocapsa oceanica, Syracosphaera spp., Gephyrocapsa ericsoni as dominant species. The cell abundance of coccolithophores ranges in 0~356.40 cells/mL and the abundance of coccoliths is in the range of 0~2 062.38/mL. LCs are mainly distributed in 0 to 50 m water depth. Coccoliths increase rapidly in the deepest water layer.No matter in surface water or vertical water, the LCs cell abundance and diversity index demonstrate a rising tendency both from costal to ocean and from northwest to southeast.Temperature, salt and nutrient concentrations are suggested as the major environmental factors controlling the distribution of LCs in the ECS.
-

-
表 1 2014年春季东海现生颗石藻常见属种
Table 1. Common living coccolithophores of the East China Sea in spring 2014
属种 出现频率 优势度 (f/%) Y Emiliania huxleyi 62.921 0.304 043 Gephyrocapsa oceanica 56.180 0.146 316 Umbellosphaera tenuis 2.247 0.000 037 Helicosphaera carteri 3.371 0.000 110 Umbilicosphaera siboge 1.124 0.000 009 Calcidiscus leptoporus 4.494 0.000 294 Syracosphaera pulchra 25.843 0.022 647 Gephyrocapsa ericsoni 30.337 0.031 555 Calciosolenia murray 5.618 0.000 736 Syracosphaera spp* 11.236 0.003 589 Oolithotus fragilis 4.494 0.000 221 Calciosolenia brasiliensis 2.247 0.000 037 Calciosolenia caudatus 1.124 0.000 009 Florisphaera profunda 1.124 0.000 009 表 2 2014年春季东海颗石片常见属种
Table 2. Common coccoliths of the East China Sea in spring 2014
属种 出现频率 优势度 (f/%) Y Emiliania huxleyi 85.393 0.467 106 Gephyrocapsa oceanica 82.022 0.321 324 Umbellosphaera tenuis 14.607 0.000 264 Helicosphaera carteri 13.483 0.000 168 Umbilicosphaera siboge 26.966 0.001 356 Calcidiscus leptoporus 24.719 0.001 397 Syracosphaera rotula 1.124 0.000 005 Syracosphaera pulchra 53.933 0.017 246 Discophaera tubifera 1.124 0.000 001 Gephyrocapsa ericsoni 14.607 0.000 685 Calciosolenia murray 6.742 0.000 240 Syracosphaera spp* 13.483 0.000 747 Oolithotus fragilis 6.742 0.000 038 Calciosolenia brasiliensis 1.124 0.000 005 Calciosolenia caudatus 1.124 0.000 003 注:Syracosphaera spp*包括Syracosphaera pirus、Syracosphaera ampliora、Syracosphaera borealis、Syracosphaera nodosa -
[1] Winter A, Siesser W G. Coccolithophores[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2006.
[2] Young J R. Functions of coccoliths[M]//Coccolithophores. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1994: 63-82.
[3] Frada M, Young J, Cachão M, et al. A guide to extant coccolithophores (Calcihaptophycidae, Haptophyta) using light microscopy[J]. J. Nannoplankt. Res., 2010, 31: 58-112. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3a76b68aa7ef4edcde3579103834179b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] 刘超, 康建成, 王国栋, 等.东海黑潮区营养盐及其限制作用的月际空间分异[J].资源科学, 2012, 34(7): 1375-1381. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zykx201207024
LIU Chao, KANG Jiancheng, WANG Guodong, et al. Monthly Spatial Variation of Nutrients and Nutrient Limitation in Kuroshio of East China Sea[J]. Resources Science, 2012, 34(7): 1375-1381. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zykx201207024
[5] 米铁柱, 姚庆祯, 孟佳, 等. 2011年春, 夏季黄海, 东海营养盐分布特征研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3):678-688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201203054
MI Tiezhu, YAO Qingzhen, MENG Jia, et al. Distributions of nutrients in the Southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea in spring and summer 2011[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3):678-688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201203054
[6] Fan K. On upwelling off northeastern shore of Taiwan[J]. Acta Oceanogr. Taiwan, 1980, 11: 105-117.
[7] 栾青杉, 孙坚强, 左涛, 等.东海陆架区的颗石藻[J].渔业科学进展, 2013(3):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2013.03.001
LUAN Qingshan, SUN Jianqiang, ZUO Tao, et al. Coccolithophores in the shelf waters of East China Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013(3):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2013.03.001
[8] 靳少非, 孙军, 刘志亮. 2010秋季东海今生颗石藻的空间分布[J].生态学报, 2013(1):120-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201301014
JIN Shaofei, SUN Jun, LIU Zhiliang. The distribution of living coccolithophore in East China Sea in autumn, 2010[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013(1):120-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201301014
[9] 孙军, 靳少非.中国近海今生颗石藻物种多样性初步研究[J].生物多样性, 2011(6):787-797. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdyx201106020
SUN Jun, JIN Shaofei. Species diversity of living coccolithophores in Chinese sea waters[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2011(6):787-797. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdyx201106020
[10] Bai J, Gu X, Feng Y, et al. Autumn living coccolithophores in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(8):83-94. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0481-y
[11] Sun J, Gu XY, Feng YY, et al. Summer and winter living coccolithophores in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 2014, 11(3):779-806. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-779-2014
[12] Bollmann J, Cortés MY, Haidar AT, et al. Techniques for quantitative analyses of calcareous marine phytoplankton[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2002, 44(3):163-185. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b33ae4fc2dbd6919fd7efcda99fb29a1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] Shannon C E, Weaver W. The mathematical theory of communication[M]. University of Illinois Press, 2015.
[14] Young J R, Ziveri P. Calculation of coccolith volume and it use in calibration of carbonate flux estimates[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2000, 47(9): 1679-1700. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a6ec9cc3fc9928134425478c515a2a5b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Cortés MY, Bollmann J, Thierstein HR. Coccolithophore ecology at the HOT station ALOHA, Hawaii[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2001, 48(8):1957-1981. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222551942_Coccolithophore_ecology_at_the_HOT_station_ALOHA_Hawaii
[16] Haidar AT, Thierstein HR. Coccolithophore dynamics off Bermuda (N. Atlantic) [J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2001, 48(8):1925-1956. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HighWire000002060173
[17] Okada H, McIntyre A. Seasonal distribution of modern coccolithophores in the western North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Marine Biology, 1979, 54(4):319-328. doi: 10.1007/BF00395438
[18] Okada H, McIntyre A. Modern coccolithophores of the Pacific and North Atlantic oceans[J]. Micropaleontology, 1977:1-55. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=709804a7dce3b3c96b58a128c5c1697f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[19] Saavedra-Pellitero M, Baumann K H, Flores J A, et al. Biogeographic distribution of living coccolithophores in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2014, 109: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2014.03.003
[20] 王芳, 康建成, 周尚哲, 等.东海外海海域营养盐的时空分布特征[J].资源科学, 2008, 30(10):1592-1599. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.10.022
WANG Fang, KANG Jiancheng, ZHOU Shangzhe, et al. Nitrate and phosphate conditions and fishery resources in the offshore area of the East China Sea[J]. Resources Sci., 2008, 30(10):1592-1599. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.10.022
[21] Margalef R. Life-forms of phytoplankton as survival alternatives in an unstable environment[J]. Oceanologica Acta, 1978, 1(4): 493-509. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=330ac264338406426fee1dfc491cb16f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] 郭术津, 孙军, 戴民汉, 等. 2009年冬季东海浮游植物群集[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(10): 3266-3278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201210033
GUO Shujin, SUN Jun, DAI Minhan, et al. Phytoplankton assemblages in East China Sea in winter 2009[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(10): 3266-3278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201210033
[23] 吴玉霖, 傅月娜, 张永山, 等.长江口海域浮游植物分布及其与径流的关系[J].海洋与湖沼, 2004, 35(3): 246-251. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2004.03.008
WU Yulin, FU Yuena, ZHANG Yongshan, et al. Phytoplankton distribution and its relation to the runoff in the changjiang (yangzte) estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2004, 35(3):246-251. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2004.03.008
[24] Iglesias-Rodríguez M D, Brown C W, Doney S C, et al. Representing key phytoplankton functional groups in ocean carbon cycle models: Coccolithophorids [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2002, 16(4):47-1--20. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef86da8cb81d9974ad5f141446d1a80a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] 赵保仁, 任广法, 曹德明, 等.长江口上升流海区的生态环境特征[J].海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32(3):327-333. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.03.014
ZHAO Baoren, REN Guangfa, CAO Deming, et al. Characteristics of the ecological environment in upwelling area adjacent to the Changjiang River Estuary [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2001, 32(3):327-333. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.03.014
[26] 刘先炳, 苏纪兰.浙江沿岸上升流和沿岸锋面的数值研究[J].海洋学报, 1991, 13(3):305-314. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=508707
LIU Xianbing, SU Jilan.Numerical simulation of tideindeced upwelling in coastal areas of the East China Sea[J].Acta Oceanologic Sinca, 1991, 13(3):305-314. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=508707
[27] Yang T N, Wei K Y, Chen M P, et al. Summer and winter distribution and malformation of coccolithophores in the East China Sea [J]. Micropaleontology, 2004:157-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f68eb57e55807eb0b05e8c65d4f0fd43
[28] Bonomo S, Cascella A, Alberico I, et al. Coccolithophores from near the Volturno estuary (central Tyrrhenian Sea) [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2014, 111:26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2014.06.001
[29] 张传松, 王修林, 石晓勇, 等.东海赤潮高发区营养盐时空分布特征及其与赤潮的关系[J].环境科学, 2007, 28(11):2416-2424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.11.002
ZHANG Chuansong, WANG Xiulin, SHI Xiaoyong, et al. Seasonal variation and spatial distribution of nutrients and their relationships with harmful algal blooms in coastal area of the East China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2007, 28(11):2416-2424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.11.002
[30] 王保栋.黄海和东海营养盐分布及其对浮游植物的限制[J].应用生态学报, 2003, 14(7):1122-1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.07.018
WANG Baodong. Nutrient distributions and their limitation on phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(7):1122-1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.07.018
[31] 王玉衡, 董恒霖, 任典勇.春秋季黑潮及其邻近海区化学要素的分布和相互关系的探讨[J].海洋学报, 1992, 14(3):65-75. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=508707
WANG Yuheng, DONG Henglin, REN Dianyong. The distribution and interrelation of Kuroshio chemical parameters in spring and autumn[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1992, 14(3):65-75. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=508707
-



 下载:
下载: