Distribution of heavy metals in soils and surface sediments along Rizhao coast and environmental assessment
-
摘要:
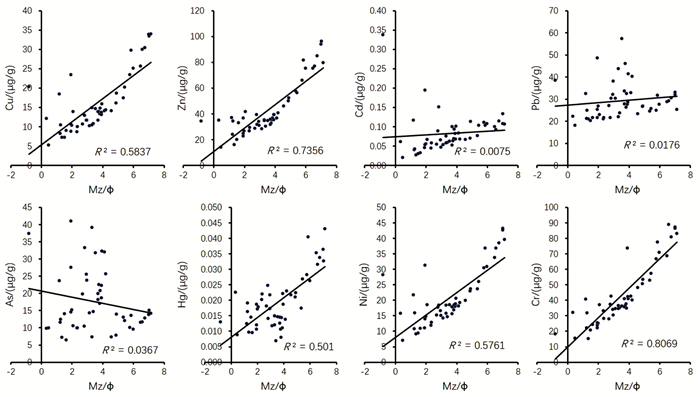
对日照市海岸带土壤和表层沉积物中的重金属(Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Ni、Cd、As和Hg)进行分析,研究了重金属的分布特征和污染状况。结果表明,日照市海岸带土壤重金属高值区主要分布在城镇居民地和工矿用地,与工业污染物密切相关,海域重金属Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni和Hg高值区主要分布在石臼港和岚山港区附近,明显受粒径制约,但元素Cd、Pb和As在东南海域的富集可能与铁锰氧化物的吸附有关。同时,As元素含量高可能与海域As元素本身背景高有关。城镇地区重金属污染和生态风险分别表现为较高和很高,而郊区农田以及海域分别表现为中等和较低。
Abstract:Contents of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, Cd, As and Hg in soils and surface sediments of Rizhao coast have been analyzed in order to detect the distribution and contamination of these elements. Results show that the high values of heavy metals in soils are mainly distributed in the urban residential land, industrial and mining land, which are obviously from industrial pollutants. The high values of Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni and Hg in the nearshore area are mainly distributed in the areas close to Shijiu Port and Lanshan Port, obviously controlled by particle sizes of bottom sediments. However, the enrichment of Cd, Pb and As in the southeastern area might be related to the adsorption of iron and manganese oxides. In addition, As owes its high content to its high background. Ecological risk assessment suggests that the total degree of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals contamination in urban areas are high and very high, but medium or low in suburban farmland and nearshore areas.
-

-
表 1 土壤、海底表层沉积物环境质量标准(据文献[8, 9],单位:μg/g)
Table 1. Environmental quality standard of soils and surface sediments
类别 土壤 表层沉积物 pH <6.5 6.5~7.5 >7.5 - Cd 0.3 0.3 0.6 0.5 Hg 0.3 0.5 1.0 0.2 As(水田) 30 25 20 20 As(旱田) 40 30 25 - Cu(农田) 50 100 100 35 Cu(果园) 150 200 200 - Pb 250 300 350 60 Cr(水田) 250 300 350 80 Cr(旱田) 150 200 250 - Zn 200 250 300 150 Ni 40 500 60 - 注:“-”代表海洋沉积物质量(GB18668-2002), 没有列出相应的参考值。 表 2 潜在生态风险评价指标(据Hakanson,1980修改)
Table 2. The assessment index of potential ecological risk (modified after Hakanson, 1980)
评价等级 单个污染物
污染参数
(Cfi)总体污染
参数(Cd)单个污染物
潜在生态
风险参数
(Eri)潜在生态
风险指数
(RI)低 <1 <8 <40 <150 中 1~3 8~16 40~80 150~300 较高 3~6 16~24 80~160 300~600 高 160~320 很高 ≥6 ≥24 ≥320 ≥600 表 3 日照市海岸带重金属含量统计(单位:μg/g)
Table 3. Heavy metal contents in Rizhao coast
Cr Ni Cu Zn As Cd Hg Pb 最大值 298.10 170.90 148.90 517.80 41.00 0.57 0.98 165.10 最小值 9.80 6.00 1.00 12.20 1.60 0.02 0.01 11.80 平均值 48.86 19.50 14.40 51.72 6.54 0.09 0.02 27.27 中值 48.8 18.8 14.2 50.2 6.63 0.09 0.02 26.9 标准偏差 13.12 5.41 5.77 15.10 1.82 0.02 0.01 3.63 变异系数 27.0% 28.0% 40.0% 29.2% 28.0% 27.0% 38.0% 13.0% 表 4 日照市海岸带重金属元素含量与其他典型区域比较(单位:μg/g)
Table 4. Comparison of heavy metal concentrations in Rizhao coast and other representative areas
Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd As Hg 参考文献 日照市表层土壤 17.04 28.36 55.91 52.43 21.07 0.09 6.54 0.04 本文 日照市近岸海域 15.92 29.23 42.84 43.25 20.75 0.08 17.54 0.019 本文 日照市表层土壤 15.6 26.3 60.3 46 20.2 0.1 4.9 0.03 吕建树等,2012 日照市表层土壤 19.2 26.8 64.7 57.1 24.3 0.113 5.4 0.026 庞旭贵等,2014 海州湾 19.41 18.23 73.29 74.18 0.17 6.62 李飞和徐敏,2014 胶州湾 25.04 32.95 71.15 44.35 0.086 7.59 0.086 何书峰等,2013 莱州湾 21.96 21.99 60.41 60.00 0.12 12.64 0.051 郑懿民等,2015 表 5 日照市海岸带土壤及表层沉积物单项污染指数评价结果
Table 5. Results of individual pollution index of soil and surface sediments in Rizhao coast
% 土壤 表层沉积物 Pi≤1 Pi>1 Pi≤1 Pi>1 As 100.00 0 70.00 30.00 Cd 99.85 0.15 100.00 0 Cr 99.55 0.45 90.00 10.00 Cu 97.15 2.85 100.00 0 Hg 98.20 1.80 100.00 0 Ni 97.45 2.55 100.00 0 Pb 100.00 0 100.00 0 Zn 99.85 0.15 100.00 0 表 6 日照市海岸带重金属单因子污染物污染程度与潜在生态风险程度
Table 6. The degrees of contamination and potential ecological risk in Rizhao coast
重金属 Cfi Eri 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 Cu 0.06 8.27 0.94 0.28 41.36 4.71 Pb 0.47 6.60 1.14 2.36 33.02 5.68 Zn 0.20 8.30 0.88 0.20 8.30 0.88 Cr 0.17 5.24 0.91 0.34 10.48 1.82 Ni 0.23 6.60 0.81 1.16 32.99 4.06 Cd 0.24 6.71 1.08 7.06 201.18 32.39 As 0.28 7.07 1.26 2.76 70.69 12.61 Hg 0.43 61.43 2.67 17.19 2457.00 106.83 $\sum\limits_{(i = 1)}^8 {} $ Cd RI 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 3.07 67.60 9.69 52.62 2518.50 168.99 -
[1] Li X, Wai O W H, Li Y S, et al. Heavy metal distribution in sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary, South China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(5): 567-581. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00072-4
[2] Chapman P M, Wang F. Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries.[J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 2001, 20(1):3. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1002-etc.5620200102/
[3] Loska K, Wiechuta D. Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(8):723-733. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00187-5
[4] Ip C C M, Li X D, Zhang G, et al. Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(2): 311-323. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.028
[5] 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等.日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J].地理学报, 2012, 67(7):109-122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb201207010
LV Jianshu, ZHANG Zulu, LIU Yang, et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(7):109-122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb201207010
[6] 代杰瑞, 王学, 董建, 等.山东省东部地区土壤重金属污染及其生态环境效应[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2012, 34(4):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2012.04.010
DAI Jierui, WANG Xue, DONG Jian, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and its eco-environmental effect in Eastern Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2012, 34(4):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2012.04.010
[7] 宋红瑛, 刘金庆, 印萍, 等.日照近海表层沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 46(3):96-104. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb201603013
SONG Hongying, LIU Jinqing, YIN Ping, et al. Grain size characteristics of the surface sediment and sedimentary environment in Rizhao offshore[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(3):96-104. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb201603013
[8] 国家环境保护局.土壤环境质量标准(GB15618-1995)[S]. 1995: 3.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China. Environmental quality standard for soils(GB15618-1995)[S], 1995: 3.
[9] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.《海洋沉积物质量(GB 18668-2002)》[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002: 2.
Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China.Marine Sediment Quality of China (GB 18668-2002)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. 2002: pp. 2.
[10] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[11] 庞绪贵, 陈钰, 刘汉栋, 等.山东半岛蓝色经济区土壤地球化学基准值与背景值[J].山东国土资源, 2014(8):21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2014.08.005
PANG Xugui, CHEN Yu, LIU Handong, et al. Geochemical baseline values and background values of soils in the Blue Economic Zone of Shandong Peninsula[J].Shandong Land and Resources, 2014, (8): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2014.08.005
[12] 赵沁娜, 徐启新, 杨凯.潜在生态危害指数法在典型污染行业土壤污染评价中的应用[J].华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2005(1):111-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hdsfdxxb200501019
ZHAO Qinna, XU Qixin, YANG Kai. Application of potential ecological risk index in soil pollution of typical pollution industries[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2005(1):111-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hdsfdxxb200501019
[13] 李飞, 徐敏.海州湾表层沉积物重金属的来源特征及风险评价[J].环境科学, 2014, 35(3):1035-1040. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201403031
LI Fei, XU Min. Source characteristics and contamination evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Haizhou Bay[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3):1035-1040. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201403031
[14] 何书锋, 李广雪, 史经昊.胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征及其影响因素[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(4):41-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201304007
HE Shufeng, LI Guangxue, SHI Jinghao. Distribution of heavy metals in surficial sediments of Jiaozhou Bay and its influencing factors[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(4):41-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201304007
[15] 郑懿珉, 高茂生, 刘森, 等.莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及生态环境评价[J].海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(3):354-360. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhjkx201503006
ZHENG Yimin, GAO Maosheng, LIU Sen, et al. Distribution patterns and ecological assessment on heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(3):354-360. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhjkx201503006
[16] 朱而勤, 王琦.中国沿岸海域的铁锰结核[J].地质论评, 1985, 31(5):404-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1985.05.004
ZHU Erqin, WANG Qi. Ferromanganese nodules in the offshore areas of China[J]. Geological Review, 1985, 31(5):404-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1985.05.004
[17] Post J E. Manganese oxide minerals: crystal structures and economic and environmental significance.[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(7):3447-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3447
[18] 刘金庆, 印萍, 张勇, 等.滦河口沉积物重金属分布及生态风险评价[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):43-52. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ca0de6ff-0d37-4a3f-9c5c-1d1ca5601662
LIU Jinqing, YIN Ping, ZHANG Yong, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Luanhe River Estuary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5):43-52. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ca0de6ff-0d37-4a3f-9c5c-1d1ca5601662
[19] Sherman L S, Blum J D, Dvonch J T, et al. The use of Pb, Sr, and Hg isotopes in Great Lakes precipitation as a tool for pollution source attribution[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 502:362-374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.034
[20] Pacyna E G, Pacyna J M, Steenhuisen F, et al. Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(22):4048-4063. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.03.041
[21] UNEP, 2013. Global Mercury Assessment 2013: Sources, Emissions, Releases and Environmental Transport[R]. UNEP Chemicals Branch, Geneva, Switzerland.
-




 下载:
下载: