Climate change since the last glacial stage recorded in Jingbian loess section
-
摘要:
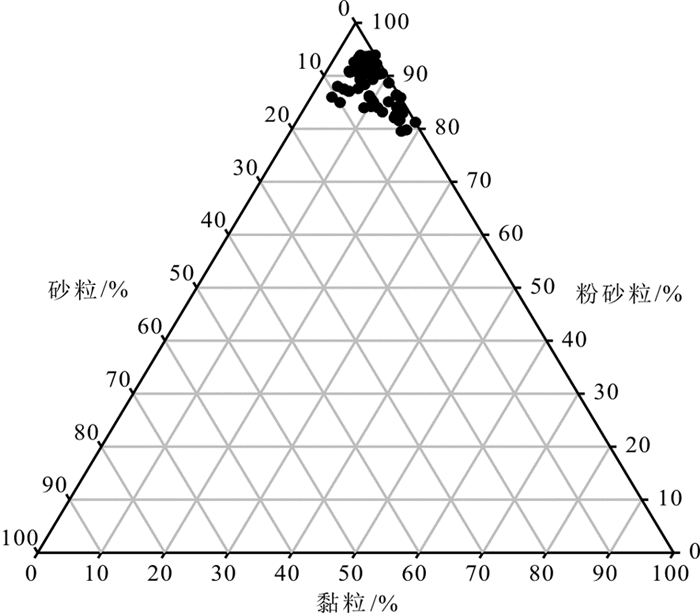
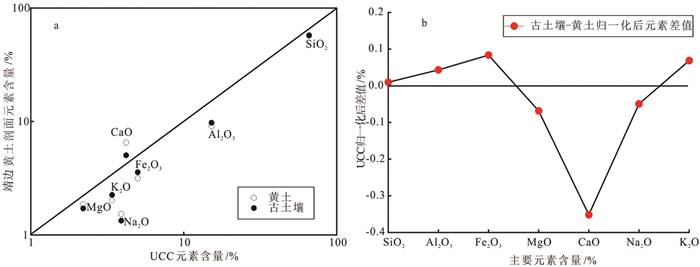
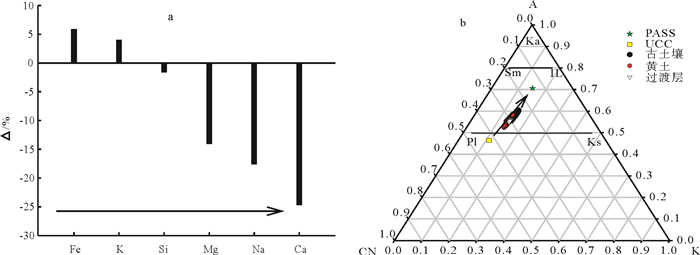
靖边黄土剖面位于黄土-沙漠的过渡区,能更加敏感地记录第四纪东亚季风气候变化。对位于靖边县南15km的三道沟黄土剖面(0~7.2m)进行年代学、磁化率、粒度、元素地球化学分析,粒度数据显示靖边黄土剖面沉积物以粉砂为主,占比高达80%以上;年龄曲线显示靖边黄土剖面存在千年尺度的沉积间断;元素地球化学数据表明,古土壤向黄土层中的元素迁移顺序为Ca>Na>Mg>Si>Al>K>Fe,剖面黄土处于初级风化阶段;多指标综合分析表明,靖边黄土剖面末次冰期以来的气候变化经历了MIS3气候相对温暖湿润且震荡激烈、末次冰盛期气候极度冷干、冰消期气候好转和全新世气候温暖湿润4个阶段。
Abstract:The Jingbian loess section is located in the transition zone between the loess plateau and desert, which is more sensitive than others to the Quaternary East Asian monsoon climate changes. The analyses of chronology, susceptibility, grain size and geochemical elements of the loess section in the south of Jingbian county were carried out. The Jingbian loess is a kind of eolian deposits composed of more than 80% of silty sand. Dating age suggests that there is a millennial scale sedimentary discontinuity in the section. The chemical data shows that the loess is in a primary weathering stage and the element abundance is in an order of Ca > Na > Mg > Si > Al > K > Fe. The comprehensive multi-index analyses suggest that the loess section has suffered four stages of climatic changes since the Last Glacial Period. The MIS3 was relatively warm, humid and oscillated. The Last Glacial Maximum was extremely cold and dry. The Last Deglaciation was under an improving climate condition and the Holocene warm and humid.
-
Key words:
- susceptibility /
- grain size /
- element /
- climate change /
- Jingbian loess
-

-
表 1 靖边黄土剖面岩性描述
Table 1. Lithologic description of Jingbian loess section
深度/m 岩性描述 0~1.40 黑垆土,颜色发黑,菌丝体发育,根孔和虫孔发育,可见大量植物根系,0.5m以下稍致密 1.4~1.80 黑垆土到黄土的过渡层,灰黄色粉砂 1.80~3.50 灰黄色粉细砂,偶见根系,含少量灰黑色铁锰质斑点,偶见钙斑,含石英、长石颗粒 3.50~6.20 灰黄色粉砂,质地疏松 6.20~10.60 灰黄色细砂,质地疏松,含水分,较湿润 10.60~11.10 上部20cm为亚砂土,含泥质,较湿润;下部30cm为灰黄色黄土 表 2 靖边黄土剖面14C测年数据
Table 2. Depth and 14C age of samples in Jingbian loess section
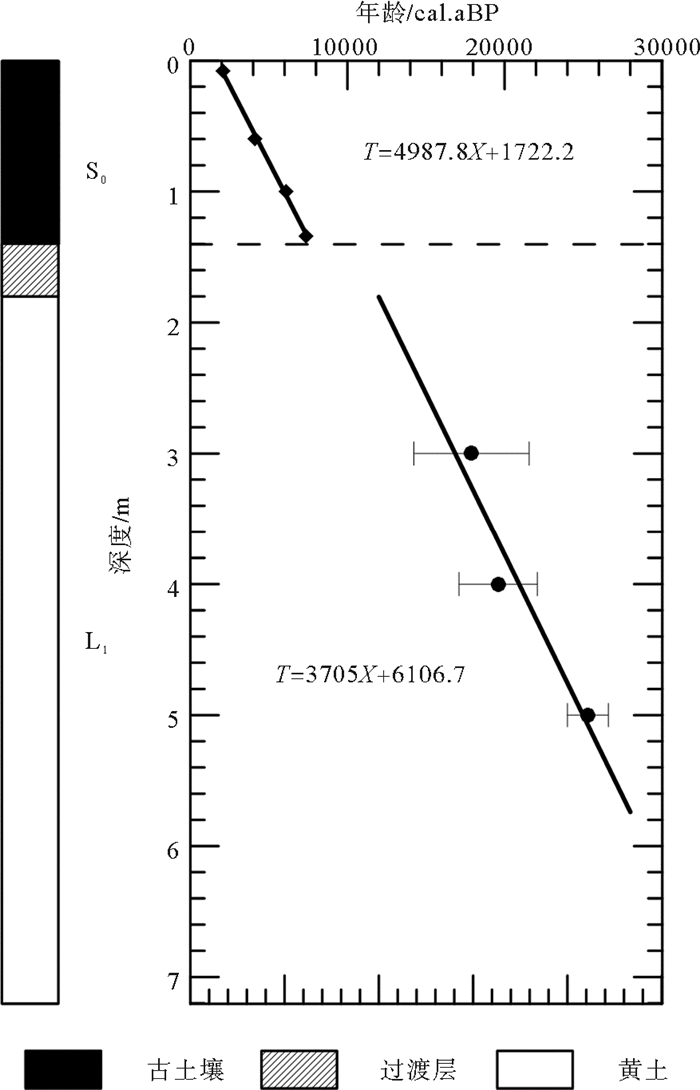
样品编号 实验室编号 深度/cm 测年材料 年龄*/aBP 校正年龄#/cal.aBP 测试单位 JB004 BA131585 6~8 全岩有机质 2090±25 2061±67 北京大学 JB030 BA131586 58~60 全岩有机质 4110±30 4669±145 北京大学 JB050 Beta-400776 98~100 全岩有机质 6120±30 7033±123 BETA实验室 JB067 BA131587 132~134 全岩有机质 7380±45 8189±141 北京大学 *运用样品相对于现代(1950年)大气14C活度的分数(FM)和半衰期5568a计算的传统 14C年龄;
#树轮校正的14C年龄.表 3 靖边黄土剖面光释光测年数据
Table 3. Results of optically stimulated luminescence dating of Jingbian loess section
样品编号 埋深/cm 测年材料 U/10-6 Th/10-6 K/% 含水率/
%年剂量/
(Gy·ka-1)等效剂量/Gy 年龄/a 测试单位 OSL-13-03 300 细颗粒石英 1.78 8.46 1.63 15±5 2.51±0.09 44.85±9.07 17890±3670 中科院地环所 OSL-13-04 400 细颗粒石英 1.95 9.21 1.62 15±5 2.56±0.09 50.14±6.14 19590±2490 中科院地环所 OSL-13-05 500 细颗粒石英 2.96 17.52 1.62 7 4.40±0.18 111.28±3.37 25300±1300 地科院水环所 -
[1] 刘东生, 等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.
LIU Tungsheng, et al.Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1985.
[2] 刘东生.黄土与干旱环境[M].合肥:安徽科学技术出版社, 2009.
LIU Tungsheng.Loess and Arid Environment[M]. Hefei:Anhui Science & Technology Publishing House, 2009.
[3] An Z S, Liu T S, Lu Y C, et al.The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7:91-95. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/1040618290900423
[4] Ding Z L, Xiong S F, Sun J M, et al.Pedostratigraphy and paleomagnetism of a ~7.0 Ma eolian loess-red clay sequence at Lingtai, Loess Plateau, north-central China and the implications for paleomonsoon evolution[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 152:49-66. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00034-6
[5] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al.Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416:159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[6] Sun J M.Provenance of loess material and formation of loess deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 203:845-859. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00921-4
[7] Yuan D X, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al.Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon[J]. Science, 2004, 304:575-578. doi: 10.1126/science.1091220
[8] Guan H C, Zhu C, Zhu T X, et al.Grain size, magnetic susceptibility and geochemical characteristics of the loess in the Chaohu lake basin:Implications for the origin, palaeoclimatic change and provenance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 117:170-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.013
[9] 鹿化煜, 安芷生.洛川黄土粒度组成的古气候意义[J].科学通报, 1997, 42(1):66-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.01.020
LU Huayu, AN Zhisheng.Paleoclimatic significance of grain size composite of loess deposit in Luochuan[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(1):66-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.01.020
[10] 鹿化煜, 安芷生.黄土高原黄土粒度组成的古气候意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(3):278-283. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801030972
LU Huayu, AN Zhisheng.Paleoclimatic significance of grain size of loess-palaeosol deposit in Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Science in China(Series D), 1998, 41(6):626-631. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801030972
[11] 孙东怀, 鹿化煜, Rea D, 等.中国黄土粒度的双峰分布及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18(3):327-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.001
SUN Donghuai, LU Huayu, Rea D, et al.Bimode grain-size distribution of Chinese loess and its paleoclimate implication[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3):327-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.001
[12] 孙东怀, 安芷生, 苏瑞侠, 等.最近2.6 Ma中国北方季风环流与西风环流演变的风尘沉积记录[J].中国科学D辑, 2003, 33(6):497-504. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200306001
SUN Donghuai, AN Zhisheng, SU Ruixia, et al.Eolian sedimentary records for the evolution of monsoon and westerly circulations of northern China in the last 2.6 Ma[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2003, 33(6):497-504. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200306001
[13] 纪友亮, 胡光明, 张善文, 等.沉积层序界面研究中的矿物及地球化学方法[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 32(4):455-460. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjdxxb200404008
JI Youliang, HU Guangming, ZHANG Shanwen, et al.Mineralogical and geochemical methods in study of sedimentary sequence boundary[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2004, 32(4):455-460. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjdxxb200404008
[14] Yang S L, Ding F, Ding Z L.Pleistocene chemical weathering history of Asian arid and semi-arid regions recorded in loess deposits of China and Tajikistan[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70:1695-1709. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.12.012
[15] 程燕, 张小曳, 鹿化煜, 等.最近140ka以来黄土元素地球化学演化及其古气候意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):103-108. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=7e5611c4-ddc6-4fed-ac03-8a7a718b7abb
CHEN Yan, ZHANG Xiaoye, LU Huayu, et al.Variations of elemental geochemistry in Chinese loess during the last 140 ka BP and their paleoclimatological implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3):103-108. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=7e5611c4-ddc6-4fed-ac03-8a7a718b7abb
[16] 李铮华, 王玉海.黄土沉积的地球化学记录与古气候演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(2):41-47. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ba2b81a5-a36a-492a-ad0a-bcec6dcb7c4c
LI Zhenghua, WANG Yuhai.The geochemical record of loess deposit and paleoclimatic evolution[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1998, 18(2):41-47. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ba2b81a5-a36a-492a-ad0a-bcec6dcb7c4c
[17] 杨守业, 李从先.长江与黄河沉积物元素组成及地质背景[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):21-28. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c1cfd796-4a1a-4dfd-bea5-6bc812581bdf
YANG Shouye, LI Congxian.Characteristic element compositions of the Yangtze and the Yellow River sediments and their geological background[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2):21-28. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c1cfd796-4a1a-4dfd-bea5-6bc812581bdf
[18] 王成, 龚庆杰, 李刚, 等.从南海沉积物中的主量元素比值变化看沉积物源区化学侵蚀变化[J].海洋地质动态, 2007, 23(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.01.001
WANG Chen, GONG Qingjie, LI Gang, et al.Chemical weathering changes in sediment source areas showed by changes in major element ratios of sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2007, 23(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.01.001
[19] 毛沛妮, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等.汉江上游黄土常量元素地球化学特征及区域对比[J].地理学报, 2017, 72(2):279-291. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb201702008
MAO Peini, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al.Chemical weathering characteristics and regional comparative study of the loess deposits in the upper Hanjiang River[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(2):279-291. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb201702008
[20] 顾兆炎, 韩家懋, 刘东生.中国第四纪黄土地球化学研究进展[J].第四纪研究, 2000, 20(1):41-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.01.010
GU Zhaoyan, HAN Jiamao, LIU Tungsheng.Progress in geochemical research on the loess and other Quaternary deposits in China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2000, 20(1):41-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.01.010
[21] Sun J M, Ding Z L, Liu T S, et al.580, 000-year environmental reconstruction from aeolian deposits at the Mu Us Desert margin, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1999, 18(12):1351-1364. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(98)00086-9
[22] 靳鹤龄, 董光荣, 苏志珠, 等.全新世沙漠-黄土边界带空间格局的重建[J].科学通报, 2001, 46(7):538-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.07.003
JIN Heling, DONG Guangrong, SU Zhizhu, et al.Reconstruction of the Holocence spatial pattern in the desert-loess boundary belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(7):538-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.07.003
[23] 丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 刘东生.上新世以来毛乌素沙地阶段性扩张的黄土-红粘土沉积证据[J].科学通报, 1999, 44(3):324-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb199903022
DING Zhongli, SUN Jimin, LIU Tungsheng, et al.Stepwise advance of the Mu Us desert since late Pliocene:Evidence from a red clay-loess record[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(13):1211-1214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb199903022
[24] Stevens T, Lu H Y, Thomas D, et al.Optical dating of abrupt shifts in the Late Pleistocene East Asian monsoon[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(5):315-418. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1130-G24524A.1/
[25] Stevens T, Armitage S J, Lu H Y, et al.Sedimentation and diagenesis of Chinese loess: Implications for the preservation of continuous, high-resolution climate records[J]. Geology, 2006, 51(18):2253-2259. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/38173787_Sedimentation_and_diagenesis_of_Chinese_loess_implications_for_the_preservation_of_continuous_high-resolution_climate_records?ev=prf_cit
[26] Lv H Y, Stevens T, Yi S W, et al.An erosional hiatus in Chinese loess sequences revealed by closely spaced optical dating[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(18):2253-2259. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2097-x
[27] Buylaert J P, Vandenberghe D, Murray A S, et al.Luminescence dating of old (>70ka) Chinese loess: A comparison of single-aliquot OSL and IRSL techniques[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1):9-14. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1871101406000574
[28] 丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 刘东生.联系沙漠-黄土演变过程中耦合关系的沉积学指标[J].中国科学D辑, 1999, 29(1):81-87. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199901013
DING Zhongli, SUN Jimin, LIU Tungsheng.A sedimentological proxy indicator linking changes in loess and deserts in the Quaternary[J]. Science in China(Series D), 1999, 42(2):146-152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199901013
[29] 张永双, 曲永新.陕北晋西砂黄土的胶结物与胶结作用研究[J].工程地质学报, 2005, 13(1):18-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.01.003
ZHANG Yongshuang, QU Yongxin.Cements of sand loess and their cementation in North Shaanxi and West Shanxi[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2005, 13(1):18-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.01.003
[30] 郭泽泽, 李喜安, 陈阳, 等.基于SEM-EDS的湿陷性黄土黏土矿物定量分析[J].工程地质学报, 2016, 24(5):899-906. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201605024
GUO Zeze, LI Xi'an, CHEN Yang, et al.Analysis of clay minerals in collapsible loess with SEM-EDS[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(5):899-906. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201605024
[31] Gallet S, Jahn B M, Torii M.Geochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence, China, and paleoclimatic implications[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133(1-4):67-88. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00070-8
[32] 陈骏, 汪永进, 季峻峰, 等.陕西洛川黄土剖面的Rb/Sr值及其气候地层学意义[J].第四纪研究, 1999, 19(4):350-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.007
CHEN Jun, WANG Yongjin, JI Junfeng.Rb/Sr variations and its climatic stratigraphical significance of a loess-paleosol profile from Luochuan, Shaanxi Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 19(4):350-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.007
[33] 庞奖励, 黄春长, 刘安娜, 等.黄土高原南部全新世黄土-古土壤序列若干元素分布特征及意义[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(3):357-364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.03.007
PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, LIU Anna, et al.Ba/Sr and Rb/Sr ratio of Holocene loess-palaeosol sequences and its significance in South Loess Plateau, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(3):357-364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.03.007
[34] 李拓宇, 莫多闻, 朱高儒, 等.晋南全新世黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J].地理研究, 2013, 32(8):1411-1420. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201308004
LI Tuoyu, MO Duowen, ZHU Gaoru, et al.Geochemical characteristics of major elements and its paleoenvironmental significance of Holocene loess profile in southern Shanxi, China[J]. Geographical Research, 2013, 32(8):1411-1420. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201308004
[35] 黄俊华, 胡超涌, 周群峰, 等.长江中游和尚洞石笋的高分辨率同位素、微量元素记录及古气候研究[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(3):442-446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.013
HUANG Junhua, HU Chaoyong, ZHOU Qunfeng, et al.Study on high-resolution carbon, oxygen isotope and trace element records and paleoclimate from Heshang Cave, the middle reach of the Yangtse River[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(3):442-446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.013
[36] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al.The Holocene Asian monsoon: Links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723):854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296
[37] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al.Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224000 years[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7182):1090-1093. doi: 10.1038/nature06692
-




 下载:
下载: