Sedimentation rate and geochemical characters of the lagoonal deposits in the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands
-
摘要:
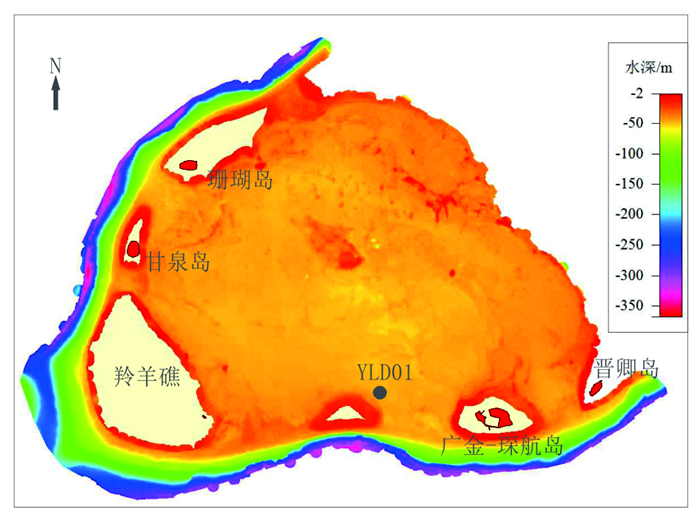
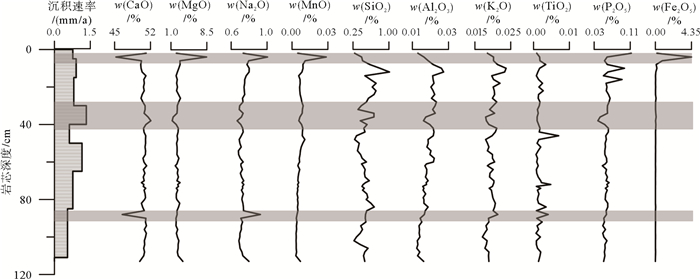
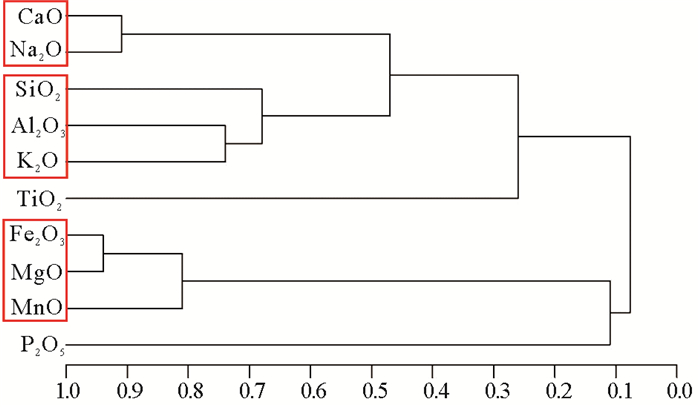
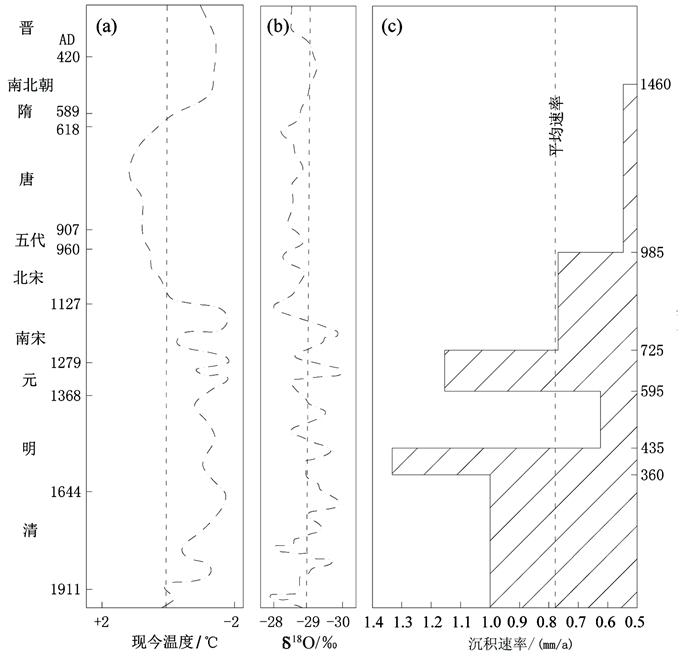
西沙群岛环礁海底沉积物的沉积速率及其地球化学特征是环礁沉积地貌环境演化研究的重要指标。为了探讨永乐环礁晚全新世以来沉积速率的变化和常量化学元素垂向分布与变化特征,我们在西沙群岛永乐环礁瀉湖内进行了详细的取样,开展了重力柱状样的AMS14C同位素测年和沉积物地球化学分析。永乐环礁晚全新世海底沉积物沉积速率约0.778mm/a;根据沉积物常量地球化学含量测试,CaO含量最高,其次是MgO,其他元素含量均小于1%,可以将常量元素组分分为5类。CaCO3含量和MgO/Al2O3含量比值都非常高,说明本区沉积物的来源主要为生物成因,极少量来自其他物质输入;与晚全新世气候相比,总体上永乐环礁瀉湖沉积速率随SST增加而升高。
Abstract:A gravity core, labeled as Core YLD01, was collected from the lagoon of the Yongle Atoll. AMS14C isotopic dating and geochemical analysis were carried out aiming to reveal the changes in sedimentation rate during Holocene as well as the vertical variation in major chemical elements with time. The AMS14C isotope dating suggests that the sedimentation rate in the lagoon of Yongle Atoll is about 0.778mm/a since the Holocene. Geochemical composition of the sediments indicated that CaO dominates the lagoonal deposits followed by MgO, and the others are all lower than 1 %. The major elements can be grouped into five categories. Both the CaCO3 content and the ratio of MgO/Al2O3 are very high, indicating that the major source of sediments is from native organisms. Other source of materials from outside is very little. Compared the data with Late Holocene climatic change, the sedimentation rate of the lagoonal deposits was obviously increased with the rise of SST on the Yongle Atoll.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary rate /
- geochemical character /
- Holocene /
- Yongle Atoll
-

-
表 1 西沙群岛永乐环礁YLD01柱状沉积物AMS14C测年结果
Table 1. The AMS14C isotopic dating data, calendar years and sedimentation rate
层位/cm AMS14C
测年/aBP日历年/
aBP沉积速率/
(mm/a)5 430±30 65 0.769 15 540±30 175 0.909 30 730±30 360 0.811 40 800±30 435 1.333 50 1030±30 595 0.625 65 1200±30 725 1.154 85 1450±30 985 0.769 111 1930±30 1460 0.547 表 2 YLD01与其他海区柱状沉积物常量元素含量分析结果
Table 2. Chemical analysis results of major elements
% 海区 Al2O3 CaO TFe2O3 MgO K2O SiO2 Na2O TiO2 MnO P2O5 YLD01 平均值 0.018 50.634 0.129 2.460 0.020 0.506 0.733 0.002 0.006 0.06 最大值 0.027 52.070 4.350 8.440 0.024 1.010 1.010 0.007 0.029 0.11 最小值 0.012 45.260 0.008 1.260 0.017 0.270 0.670 0.001 0.003 0.04 南海南部[19] 平均值 20.13 1.14 7.10 2.28 2.78 48.66 2.57 0.43 0.24 0.11 最大值 21.38 7.80 7.80 2.60 2.93 51.17 3.38 0.54 0.50 0.40 最小值 18.66 0.20 5.90 1.90 2.42 45.77 2.16 0.34 0.14 0.06 南海北部[20] 平均值 12.22 15.62 5.27 2.16 2.49 40.36 2.20 \ \ \ 最大值 13.92 18.87 5.84 2.43 2.87 44.65 2.80 \ \ \ 最小值 10.50 11.79 4.87 1.99 2.28 37.32 1.50 \ \ \ 地壳平均值 15.10 5.50 6.28 3.70 2.40 61.50 3.20 0.68 0.10 0.18 表 3 西沙群岛永乐环礁YLD01柱状沉积物常量元素之间相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis among major elements
Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 MgO K2O SiO2 Na2O TiO2 MnO P2O5 Al2O3 1 CaO -0.03 1 Fe2O3 -0.08 -0.74 1 MgO -0.02 -0.80 0.94 1 K2O 0.74 -0.31 0.04 0.14 1 SiO2 0.49 -0.10 -0.07 -0.04 0.68 1 Na2O 0.13 -0.91 0.73 0.71 0.44 0.30 1 TiO2 0.19 -0.23 0.00 0.05 0.24 0.04 0.26 1 MnO 0.36 -0.62 0.84 0.81 0.26 0.01 0.61 0.08 1 P2O5 0.24 -0.13 0.02 0.11 0.42 0.14 0.18 0.01 0.11 1 -
[1] Levitan M A, Stein R. History of sedimentation rates in the sea-ice sedimentation zone during the last 130ka[J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2008, 43(1): 65-75. doi: 10.1134/S0024490208010069
[2] Baiyegunhi Christopher, Liu Kuiwu, Gwavava Oswald. Sedimentation rate and subsidence history of the southeastern Karoo Basin, South Africa, using 1D backstripping method[J]. Arab J. Geosci., 2017, 10: 225. doi: 10.1007/s12517-017-3009-x
[3] 许冬, 龙江平, 等.海南岛近海海域7个沉积岩芯的现代沉积速率及其分布特征[J].海洋学研究, 2008, 26(3): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.03.002
XU Dong, LONG Jiangping, et al. The modern sedimentation rate and the distribution character of 7 cores in Hainan Island offshore[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26 (3): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.03.002
[4] 黄维, 汪品先.末次冰期以来南海深水区的沉积速率[J].中国科学D辑, 1998(28): 13-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800285885
HUANG Wei, WANG Pinxian. Sedimentary Rates in the Deep Waters of the South China Sea Since the Last Ice Age[J]. Science in China (Series D), 1998(28): 13-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800285885
[5] 张志忠, 李双林, 董岩翔, 等.浙江近岸海域沉积物沉积速率及地球化学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(3): 15-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200503003
ZHANG Zhizhong, LI Shuanglin, DONG Yanxiang, et al. Deposition rate and geochemical characters of sediments in Zhejiang offshore[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(3): 15-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200503003
[6] 李传顺, 江波, 李安春, 等.冲绳海槽西南端中全新世以来的沉积速率与物源分析[J].科学通报, 2009, 54(9): 1303-1310. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200909024
LI Chuanshun, JIANG Bo, LI Ancun, et al. Sedimentation rates and provenance analysis in the Southwestern Okinawa Trough since the mid-Holocene[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 2009, 54(9): 1303-1310. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200909024
[7] 陈芳, 苏新, Nurnberg D, 等.南海东沙海域末次冰期最盛期以来的沉积特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(6): 9-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200606002
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, Nurnberg D, et al. Lithologic features of sediments characterized by high sedimentation rates since the last glacial maximum from Dongsha area of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(6): 9-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200606002
[8] 李粹中.南海深海沉积物14C测年和近代沉积速率的研究[J].海洋学报, 1990, 12(3): 340-346. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBXK198506011.htm
LI Cuizhong. A study on the14C dating and modern sedimentary rates of deep-sea sediments in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(3): 340-346. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBXK198506011.htm
[9] 王律江, Sarnthein M.南海北部陆坡近四万年的高分辨率古海洋学记录[J].第四纪研究, 1999, 29(1):27-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.01.003
WANG Lvjiang, Sarnthein M. High-resolution paleoceanographic records during the last 40 000 years from the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 29(1): 27-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.01.003
[10] 徐尚, 王英民, 彭学超, 等.台湾峡谷HD133和HD77柱状样的沉积构成和发育背景[J].沉积学报, 2013, 31(2): 325-330. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb201302012
XU Shang, WANG Yingmin, PENG Xuechao, et al. Depositional Elements and Settings of HD133 and HD77 cores in the Taiwan Canyon[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(2): 325-330. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb201302012
[11] 徐兆凯, 崔镇勇, 等.日本海西南陆坡全新世对马暖流演化的沉积学和地球化学记录[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(1): 55-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201001008
XU Zhaokai, CHUI Jinyong, et al. Evolution of the tsushima warm current during the Holocene: sedimentological and geochemical recordson the southwestern slope of East/Japan Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(1): 55-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201001008
[12] Taylor B, Hayes D E. Origin and History of the South China Sea[C]//The tectonics and geological evolution of Southeast Asia Seas and islands.American Geophysical Union Monography, 1983, 23: 89-104.
[13] 朱伟林, 王振峰, 米立军, 等.南海西沙西科1井层序地层格架与礁生长单元特征[J].地球科学, 2015, 40(4): 677-687. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201504009
ZHU Weilin, WANG Zhenfeng, Mi Lijun, et al. Sequence Stratigraphic framework and reef growth unit of well Xike-1 from Xisha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(4): 677-687. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201504009
[14] 吴时国, 秦蕴珊.南海北部陆坡深水沉积体系研究[J].沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 922-930. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200905016
WU Shiguo, QIN Yunshan. The research of deepwater depositional system in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 922-930. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200905016
[15] Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia[J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44:167-180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778
[16] Stuiver M, Reimer P J. Extended14C data base and revised CALIB 3.014C age calibration program[J]. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35:215-230. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200013904
[17] Stuiver M, Reime, P J, Reimer R W.2018, CALIB 7.1[WWW program] at http://calib.org, accessed 2018-2-9.
[18] 赵焕庭, 温孝胜, 王丽荣.南沙群岛永暑礁环礁-湖的沉积速率与气候变化[J].热带地理, 2000, 20(4): 247-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2000.04.004
ZHAO Huanting, WEN Xiaosheng, WANG Lirong. Climate change and the depositional velocity in the lagoon of Yongshu atoll, Nansha Islands[J]. Tropical Geography, 2000, 20(4): 247-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2000.04.004
[19] 乔培军, 邵磊.南海南部末次冰期以来的沉积物特点及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(2): 73-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200302011
QIAO PeiJun, SHAO Lei. Characteristics of sediments in the southern South China Sea since the last glaciation and their paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(2): 73-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200302011
[20] 颜文, 古森昌, 等.南海97-37柱样的主元素特征及其潜在的古环境指示作用[J].热带海洋学报, 2002, 21(2): 75-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.009
YAN Wen, GU Senchang, et al. Characteristics of major elements of sediments in core 97-37 from southern South China Sea and its potential implications to paleoenvironment[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2002, 21(2): 75-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.009
[21] 赵宏樵, 韩喜彬, 等.南海北部191柱状沉积物主元素特征及其古环境意义[J].海洋学报, 2008, 30(6): 85-93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.06.010
ZHAO Hongqiao, HAN Xibin, et al. Charicteristics of main elements and their palaeoenvironment significance of Core 191 in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 30(6): 85-93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.06.010
[22] 何建林. R型聚类分析的简便计算算法[J].物化探计算技术. 1985, 7(3): 259-263.
HE Jianlin. A simple and convenient computing method of the r-model cluster analysis[J]. Computing Techniques for Ceophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1985, 7(3): 259-263.
[23] 章伟艳, 张富元, 等.南海深水区晚更新世以来沉积速率_沉积通量与物质组成[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(4):668-674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.022
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, et al. Constituents of Matter and Sedimentation Fluxes and Sedimentation Rates of Deep-water Sedimentation during the Late Pleistocene in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(4):668-674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.022
[24] 竺可桢.中国近五千年来气候变迁的初步研究[J].中国科学, 1973(2): 168-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xsj201210011
ZHU Kezhen. A preliminary study on climate change in China in the last 5000 years[J]. Science in China, 1973(2): 168-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xsj201210011
[25] 晏宏, 孙立广, 邵达, 等.砗磲记录的南海西沙晚全新世温暖期的高海温特征[J].科学通报, 2014, 59: 1761-1768.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201418010.htm YAN Hong. SUN Liguang, SHAO Da, et al. Higher sea surface temperature[J]. in the northern South China Sea during the natural warm periods of late Holocene than recent decades[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2014, 59, doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0317-3.
[26] Ma T Y. On the growth rate of reef corals and its relation to sea water temperature[J]. Palaeontolgia Sinica (Seires B), 1937, 6: 21-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=WK_MED201901211283
[27] 张会领, 余克服, 施祺, 等.珊瑚生长率重建西沙海域中晚全新世海温变化[J].第四纪研究, 2014, 34(6): 1296-1305. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201406019
ZHANG HuiLing, YU Kefu, SHI Qi, et al. Sea surface temperature variations during the mid-late Holocene reconstructed by porites coral growth rates in the Xisha Islands[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(6):1296-1305. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201406019
-



 下载:
下载: