Climatic environment changes during the last interglacial-glacial cycle in Zhifu loess section: Revealed by grain-size end-member algorithm
-
摘要:
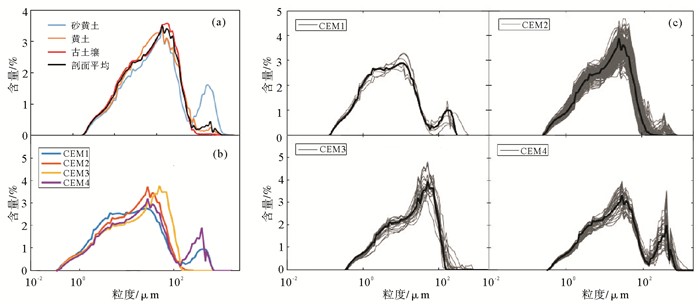
山东半岛北部芝罘剖面末次间冰期—末次冰期(124.9~62.85kaBP)层段由砂黄土、黄土、古土壤叠覆堆积组成。为获取反映该地区气候变化的环境敏感粒组,应用端元分析模型对粒度数据进行反演,得出4个粒度端元。各端元在垂直方向上呈现出有规律的峰谷变化,结合平均粒径及测年结果,认为CEM1与CEM2主要反映了末次间冰期间冰阶夏季风强盛,气候暖湿,古土壤发育的沉积环境; CEM3反映了末次间冰期冰阶冬季风短暂增强,气候相对干冷,黄土发育的沉积环境; CEM4反映了末次冰期强冬季风主导下黄土堆积速率加快,成壤作用弱的沉积环境。各端元揭示的冷暖气候振荡,与朝那黄土磁化率指示的夏季风强弱、西峰黄土>32μm粒组指示的冬季风强弱以及渤海底栖有孔虫记录的沿岸海侵/海退事件具有较高的同步性。
Abstract:The last interglacial-glacial Zhifu loess section on the northern Shandong Peninsula is mainly composed of sandy loess、loess and palaeosol. Grain-size analysis suggest that silty sand dominate the loess (74.95%), followed by the clay (10.05%) and very fine sand (9.57%). In terms of mean grain size, paleosoil is finer than sandy loess with loess in between. End-member algorithm is used in the study of grain size composition of the Zhifu section. Four clustering end members (CEM) are recognized. Based on the clustering end member frequency curves and optical stimulated luminescence dating results, it is concluded that CEM1 and CEM2 represent the strong summer monsoon and warm summer climate respectively during the MIS5e, MIS5c and MIS5a periods; CEM3 represents the environment during the MIS5d and MIS5b periods with intensified winter monsoon and relatively cold climate; while the CEM4 represents the extremely strong winter monsoon environment during the MIS4 period. These fluctuations show a strong coherence with the magnetic susceptibility of the Loess Plateau and intensity of the winter monsoon indicated by the content of grains >32μm in the Xifeng loess section, as well as the transgression/regression events along the Bohai Bay recorded by benthic foraminifera.
-
Key words:
- grain-size /
- end-member algorithm /
- paleoenvironment /
- the Zhifu Section /
- last interglacial /
- last glacial
-

-
表 1 芝罘剖面OSL年代的测定结果及其参数
Table 1. OSL ages of Zhifu section and their datingl parameters
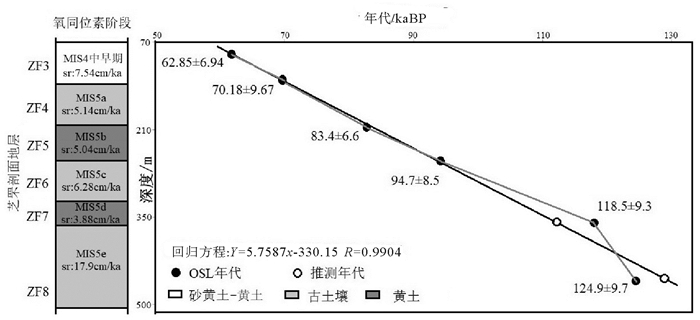
野外编号 U/10-6 Th/10-6 K/% 深度/m 年剂量/(Gy/ka) 等效剂量/Gy 实测结果/ka ZF3顶 2.02 12.20 2.08 0.72 4.06 255.46±11.95 62.85±6.94 ZF3底 2.05 12.00 2.24 1.28 4.47 313.66±29.71 70.18±9.67 ZF4底 0.700 3.390 2.700 1.89 3.12±0.24 260.1±5.9 83.4±6.6 ZF6顶 2.490 11.700 2.080 2.63 3.44±0.24 325.8±18.4 94.7±8.5 ZF8顶 1.320 6.780 1.780 3.91 2.72±0.20 322.1±10.0 118.5±9.3 ZF8底 1.660 7.440 2.030 4.96 2.55±0.19 318.5±9.1 124.9±9.7 表 2 芝罘剖面不同沉积相的粒度参数、粒级含量和CEM值
Table 2. The grain size distribution parameters and CEM of sedimentary types in Zhifu section
沉积相 全剖面 砂黄土—黄土 黄土 古土壤 黏土/% 变化范围 6.87~14.35 7.31~11.34 6.87~12.59 7.44~14.35 平均值 10.05 8.05 8.66 11.92 粉砂/% 变化范围 59.06~83.98 59.06~77.48 61.11~80.43 62.56~83.98 平均值 74.95 68.89 71.86 76.75 极细砂/% 变化范围 3.21~16.06 6.32~15.44 3.21~16.02 3.67~16.06 平均值 9.57 11.32 8.42 9.15 细砂/% 变化范围 0~10.25 5.32~10.25 2.22~9.87 0~2.20 平均值 1.75 9.74 7.63 1.35 中粗砂/% 变化范围 0~8.03 0.08~7.31 2.37~8.03 0~1.33 平均值 2.21 2.63 1.23 0.63 Mz/Φ 变化范围 4.86~6.13 4.86~5.85 5.63~6.09 5.55~6.13 平均值 5.77 5.09 5.83 6.06 σ 变化范围 1.79~2.86 1.79~2.31 1.89~2.31 1.94~2.86 平均值 2.05 1.95 2.01 2.47 Sk 变化范围 -0.16~0.37 -0.16~0.21 0.02~0.37 0.06~0.29 平均值 0.14 0.04 0.19 0.15 Kg 变化范围 0.78~1.19 0.89~1.19 0.78~0.84 0.91~1.08 平均值 0.91 1.06 0.82 0.91 CEM1/% 平均值 / 1.1 16.6 44.3 CEM2/% 平均值 / 8 11.5 47.2 CEM3/% 平均值 / 7.1 66.6 7.8 CEM4/% 平均值 / 83.8 5.3 0.7 -
[1] 董欣欣, 杨石岭, 唐自华, 等.基于黄土粒度估算粉尘源区-沉积区距离的新方法[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2016, 46(10):1406-1412. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201610011
DONG Xinxin, YANG Shiling, TANG Zihua, et al. A grain-size-based model for dust source-to-sink distance reconstruction: A case study from Chinese loess (in Chinese)[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2016, 46(10):1406-1412. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201610011
[2] 王斌, 曾琳, 赵万苍, 等.对黄土高原风尘搬运动力与沉积控制因素的新认识[J].中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2):237-246. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201702005
WANG Bin, ZENG Lin, ZHAO Wancang, et al. A new progress of the transport dynamics and the accumulation factors of the aeolian dust in Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Deserts Research, 2017, 37(2):237-246. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201702005
[3] Sun M, Zhang X, Tian M, et al. Loess deposits since early Pleistocene in northeast China and implications for desert evolution in east China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 155(2):164-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=29014f62f286f5ba26277098ea047a76
[4] Sun D H, Zhang Y B, Yan F H, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and paleoenvironmental records for a Late Cenozoic sedimentary sequence from Lanzhou, Northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Global and Planetary Change, 2011, 76 (2011):106-116.
[5] 徐树建, 丁新潮, 倪志超.山东埠西黄土剖面沉积特征及古气候环境意义[J].地理学报, 2014, 69(11):1707-1717. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201411011
XU Shujian, DING Xinchao, NI Zhichao. The sedimentary characteristics of Buxi Loess profile in Shandong Province and their paleoclimatic and paleoenvironment significance[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(11):1707-1717. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201411011
[6] 李腾飞, 李金凤, 鲁瑞洁, 等.青海湖东岸沙地风成沉积物粒度敏感组分及其古气候意义[J].中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5):878-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201705008
LI Tengfei, LI Jinfeng, LU Ruijie, et al. Extraction of grain-size components with environmentally sensitivity of aeolian sediments in eastern shore of Qinghai Lake and their paleoclimatic implications[J]. Journal of Deserts Research, 2017, 37(5):878-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201705008
[7] 王琳栋, 杨太保, 梁烨, 等.会宁地区全新世黄土沉积粒度特征及其古气候意义[J].干旱区研究, 2016, 33(6):1150-1156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj201606002
WANG Lindong, YANG Taibao, LIANG Ye, et al. Grain size characteristics in the loess-paleosol at Huining Section and its signification to paleoclimate during Holocene[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(6):1150-1156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj201606002
[8] 陈洪云, 孙有斌.黄土高原风尘沉积的物质来源研究:回顾与展望[J].第四纪研究, 2008, 28(5):892-900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.012
CHEN Hongyun, SUN Youbin. Study on provenance of eolian dust deposits on the Chinses Loess Plateau: Retrospects and prospects[J].Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(5):892-900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.012
[9] 何继山, 梁杏, 李静, 等.天津滨海平原区深孔沉积物环境敏感粒度提取及其意义[J].地球科学, 2015, 40(7):1215-1225. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201507009
HE Jishan, LIANG Xi, LI Jing, et al. Environmentally sensitive grain-size extraction of deep hole sediment from Tianjin coastal plain and its significance[J].Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(7):1215-1225. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201507009
[10] 周烨, 蒋富清.南青云, 等.奄美三角盆地晚更新世以来碎屑沉积物粒度特征及其物源和古气候意义[J].地球科学进展, 2016, 31(3):298-309. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603008
ZHOU Ye, JIANG Fuqing, NAN Qinyun, et al.Grain-size distribution of detrital sediment in the AmamiSankaku Basin since late Pleistocene and its provenance and paleoclimate implications[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(3): 298-309. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603008
[11] 葛本伟, 刘安娜.天山北麓黄土沉积的光释光年代学及环境敏感粒度组分研究[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(2):110-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201702019
GE Benwei, LIU Anna. Optically stimulated luminescence dating and analysis of environmentally sensitive grain—size component of Loess in the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(2):110-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201702019
[12] Zhang X N, Zhou A F, Xie H C, et al. Unmixing grain-size distributions in lake sediments: a new method of endmember modeling using hierarchical clustering[J].Quaternary Resesch, 2017:1-9.
[13] Weltje G J, Prins M A, Muddled or mixed? Inferring paleoclimate from size distributions of deep-sea clastics[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162:39-62. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(03)00235-5
[14] Yu S Y, Steven M. Colman, Li L X. BEMMA: A hierarchical bayesian end-member modeling analysis of sediment grain-size distributions[J]. Math Geosci, 2016, 48:723-741. doi: 10.1007/s11004-015-9611-0
[15] 张晓东, 季阳, 杨作升, 等.南黄海表层沉积物粒度端元反演及其对沉积动力环境的指示意义[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(10):1515-1523. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201510009
ZHANG Xiaodong, JI Yang, YANG Zuosheng, et al. End member inversion of surface sediment grain size in the South Yellow Sea and its implications for dynamic sedimentary environments[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 45(10):1515-1523. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201510009
[16] 赵松, 常凤鸣, 李铁刚, 等.粒度端元法在东海内陆架古环境重建中的应用[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):187-196. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a71fbe9a-df1f-49bc-a093-8af7f3722857
ZHAO Song, CHANG Fengming, LI Tiegang, et al. The application of grain-size end member algorithm to paleoenvironmental reconstruction on inner shelf of East China Sea[J].Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3):187-196. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a71fbe9a-df1f-49bc-a093-8af7f3722857
[17] 李志文, 李保生, 孙丽, 等.柳夼剖面末次冰期层段Rb/Sr的不稳定变化及其揭示的气候特征[J].热带地理, 2015, 35(4):592-600. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rddl201504018
LI Zhiwen, LI Baosheng, SUN Li, et al.Climatic characteristics indicated by the variations of Rb/Sr in the Liukuang Section during the Last Glacial Period[J].Tropical Geography, 2015, 35(4):592-600. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rddl201504018
[18] 程振波, 傅命佐, 鞠小华.渤海海峡和辽东半岛海岸带黄土中的古生物化石的地质意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(1):85-94. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=589d743a-23a7-4354-95ab-668b2bf7b76e
CHENG Zhenbo, FU Mingzuo, JU Xiaohua. Geological significance of paleontological fossils in coastal loess in the Bohai Strait and Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(1):85-94. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=589d743a-23a7-4354-95ab-668b2bf7b76e
[19] 刘恩峰, 张祖陆, 沈吉.莱州湾南岸滨海平原晚更新世以来古环境演变的孢粉记录[J].古地理学报, 2004, 6(1):78-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.01.009
LIU Enfeng, ZHANG Zulu, SHEN Ji. Spore-pollen records of environmental change on south coast plain of Laizhou Bay since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2004, 6(1):78-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.01.009
[20] 王箫风, 郑祥民, 许健, 等.山东长岛黄土沉积物的磁性与碳酸盐特征及其环境意义初探[J].云南地理环境研究, 2007, 19(4):133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7852.2007.04.026
WANG Xiaofeng, ZHENG Xiangmin, XU Jian, et al.The primary research on magnetic measurements and CaCo3 from loess sediments of Changdao in Shandong[J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2007, 19(4):133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7852.2007.04.026
[21] 彭淑贞, 朱丽君, 肖国桥, 等.山东青州黄土的地层年代及其物质来源研究[J].干旱区地理, 2010, 33(6):947-953. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqdl201006014
PENG Shuzhen, ZHU Lijun, XIAO Guoqiao, et al. Magnetostraigraphy and provenance of the Qingzhou Loess in Shandong Province[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2010, 33(6):947-953. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqdl201006014
[22] 徐树建, 王涛.蓬莱黄土剖面光释光年代学及其沉积特征研究[J].中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2):295-301. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7449570
XU Shujian, WANG Tao. Optically stimulated luminescence dating and sedimentary characteristics of loess section at Penglai in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Deserts Research, 2011, 31(2):295-301. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7449570
[23] 丁新潮, 曹文, 徐树建, 等.山东砣矶岛大口北黄土剖面的沉积特征及其古环境意义[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(10):192-197. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201610032
DING Xinchao, CAO Wen, XU Shujian, et al. The sedimentary characteristics of Dakoubei loess profile in Tuoji island and their paleoenvironment significance[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(10):192-197. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201610032
[24] Grootes P M, Stulver M, Whlte J W C, et al. Comparison of oxygen isotope records from the GISP2 and GRIP Greenland ice cores[J]. Nature, 1993, 366:552-554. doi: 10.1038/366552a0
[25] Wang Q S, Song Y G, Zhao Z J, et al. Color characteristics of Chinese loess and its paleoclimatic significance during the last glacial-interglacial cycle[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 116 :132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.013
[26] Guo Z T, A Berger, Yin Q Z, et al. Strong asymmetry of hemispheric climates during MIS-13 inferred from correlating China loess and Antarctica ice records[J]. Climate of the Past, 2009, 5:21-31. doi: 10.5194/cp-5-21-2009
[27] 李小艳, 赵泉鸿, 姚政权, 等.渤海百万年以来的海侵记录:BH08孔有孔虫和介形类证据[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(6):93-108. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c8d6bfd7-8e07-4854-9bbf-eabe63ce06b9
LI Xiaoyan, ZHAO Quanhong, YAO Zhenquan, et al. Transgressive records of last million years in the Bohai Sea, China: Evidence from foraminifera and ostracoda of Core BH08[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(6):93-108. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c8d6bfd7-8e07-4854-9bbf-eabe63ce06b9
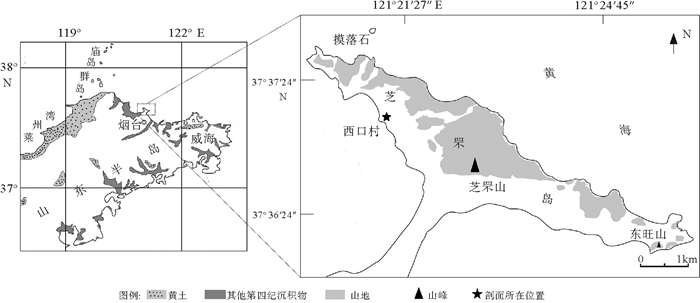
[28] 蔡爱智.论芝罘连岛沙坝的形成[J].海洋与湖沼, 1987, 9(1):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197801000.htm
CAI Aizhi. On the formation of Zhifu Tombolo[J]. Oceanologic et Limnologic Sinica, 1987, 9(1):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197801000.htm
[29] 邢秀臣, 杜国云, 魏新华, 等.芝罘岛北岸海湾砾滩侵蚀研究[J], 湖沼海洋通报, 2009(1):73-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhztb200901012
XING Xiuchen, DU Guoyun, WEI Xinhua, et al. The erosion of gravel beaches in northern coast of Zhifu Island[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009(1):73-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhztb200901012
[30] Folk R L, Ward W C.Brazos River Bar:A study in the signification of grain size parameter[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1957(27):3-27.
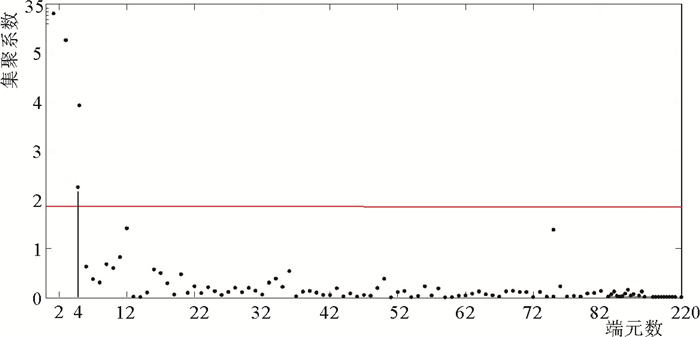
[31] Salvador S, Chan P. Determining the number of clusters/segments in hierarchical clustering/segmentation algorithms[J]. In: Proceedings 16th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Boca Raton, FL, 2004: 576-584.
[32] 郭正堂.黄土高原见证季风和荒漠的由来[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47, (4):421-437. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201704005
GUO Zhengtang. Loess Plateau attests to the onsets of monsoon and deserts (in Chinese)[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2017, 47(4): 421-437. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201704005
[33] 朱显谟.我国黄土性沉积物中的古土壤[J].第四纪研究, 1965, 4:9-19.
ZHU Xianmo. Paleosol in the Loess sediments of China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1965, 4:9-19.
[34] 曹家欣, 李培英, 石宁.山东庙岛群岛的黄土[J].中国科学(B辑), 1987, 10(10):1117-1122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200812010
CAO Jiaxin, LI Peiying, SHI Ning. Loess of Miaodao Islands in Shandong Province[J]. Science China(Series B), 1987, 10(10):1117-1122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200812010
[35] Du S H, Li B S, Chen M H, et al. Paleotempestology evidence recorded by eolian deposition in the Bohai Sea coastal zone during the last interglacial period[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 379: 78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.05.013
[36] 孙东怀, 鹿化煜, David Rea, 等.中国黄土粒度的双峰分布及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18(3):327-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.001
SUN Donghuai, LU Huayu, David Rea, et al. Bimode grain-size distribution of Chinese Loess and its paleoclimate implication[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3):327-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.001
[37] 管清玉, 潘保田, 高红山.等.粘粒含量—夏季风的良好替代指标[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2004, 18(8):17-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH2004S2003.htm
GUAN Yuqing, PAN Baotian, GAO Hongshan, et al. A good proxy of east Asian monsoon-fine grain size[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2004, 18(8):17-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH2004S2003.htm
[38] 董光荣, 靳鹤龄, 陈惠忠.末次间冰期以来沙漠-黄土边界带移动与气候变化[J].第四纪研究, 1997, 17(2):158-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.008
DONG Guangrong, JIN Heling, CHEN Huizhong. Desert-loess boundary belt shift and climatic change since the Last Interglacial period[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1997, 17(2):158-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.008
[39] 孙继敏, 丁仲礼, 刘东生, 等.末次间冰期以来沙漠一黄土边界带的环境演变[J].第四纪研究, 1995, 15(2):117-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.02.003
SUN Jimin, DING Zhongli, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Environmental changes in the desert-loess transitional zone of north china since beginning of the last interglacial[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1995, 15(2):117-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.02.003
[40] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Richard J, et al. The suspended sediment concentration distribution in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Oceanic and Coastal Sea Research, 2013, 12 (3): 345-354.
[41] 徐树建, 潘保田, 高红山, 等.末次间冰期-冰期旋回黄土环境敏感粒度组分的提取及意义[J].土壤学报, 2006, 43(2):183-189. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.02.002
XU Shujian, PAN Baotian, GAO Hongshan, et al.Analysis of grain-size populations with environmentally sensitive components of loess during the Last Interglacial-glacial cycle and their implications[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(2):183-189. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.02.002
[42] 刘厚敏, 吴世迎, 王永吉.黄海晚第四纪沉积[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1987.
LIu Houmin, WU Shiying, WANG Yongjie.Late Quaternary Sediments in the Yellow Sea[M].Beijing: Ocean Press, 1987.
[43] 刘东生.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.
LIU Dongsheng. Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[44] 姚政权, 石学法.渤海湾沿岸第四纪海侵研究进展[J].海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(2):9-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201502002
YAO Zhengquan, SHI Xuefa. A review of Quaternary transgression researches along the Bohai Bay[J].Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(2):9-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201502002
-



 下载:
下载: