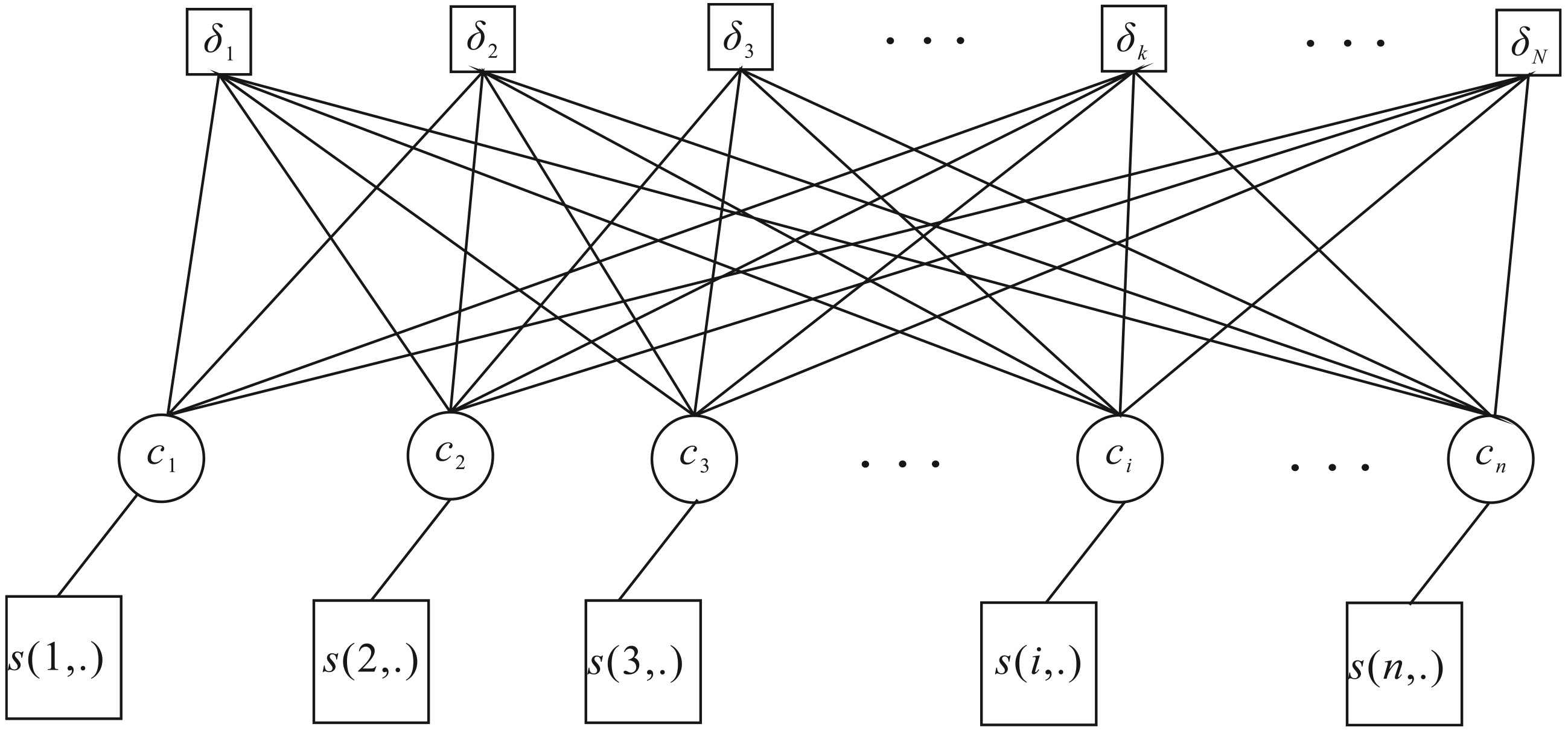
Application of the affinity propagation clustering algorithm based on grain-size distribution curve to discrimination of sedimentary environment——A case study in Baiyangdian area
-
摘要:
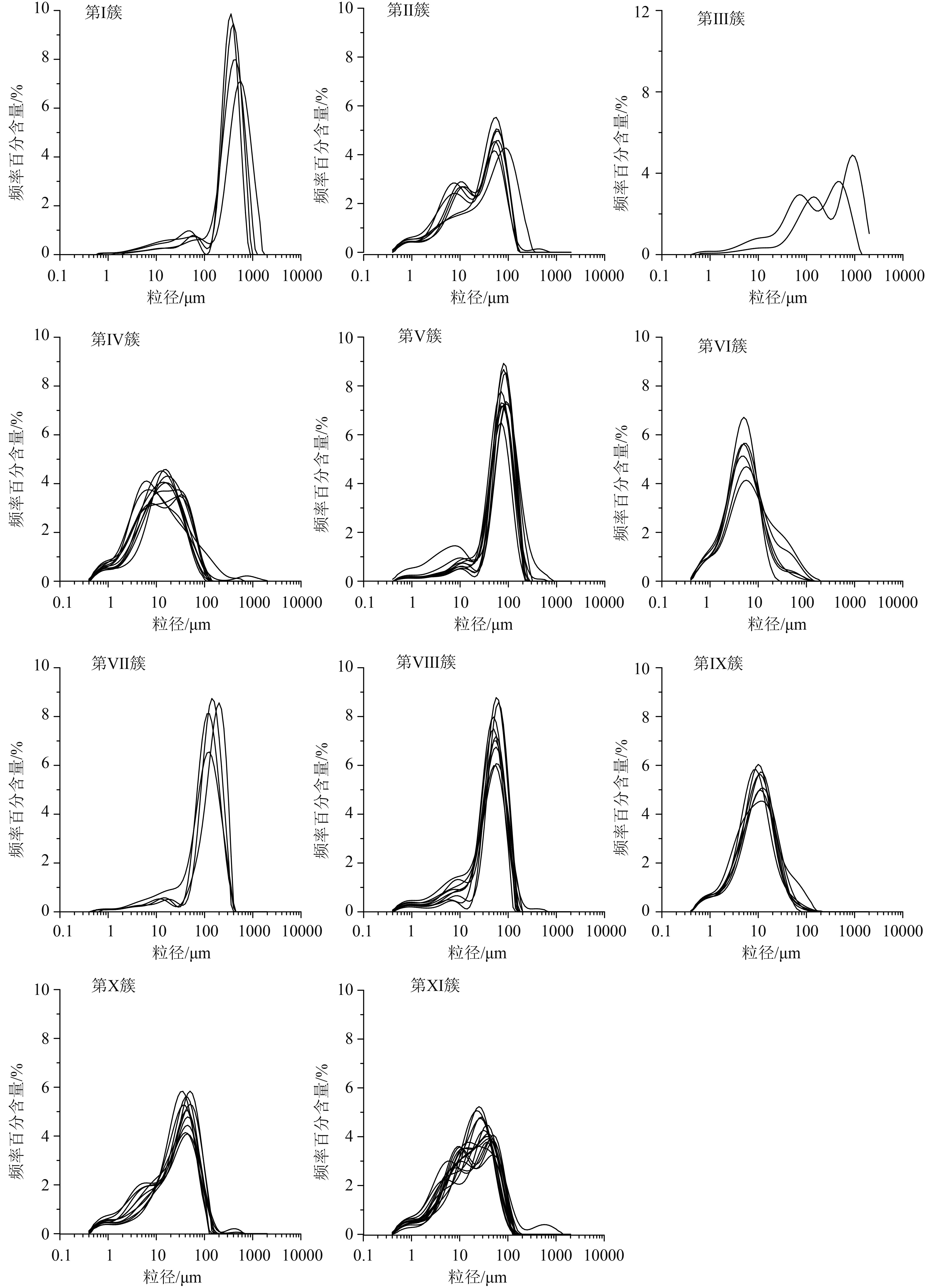
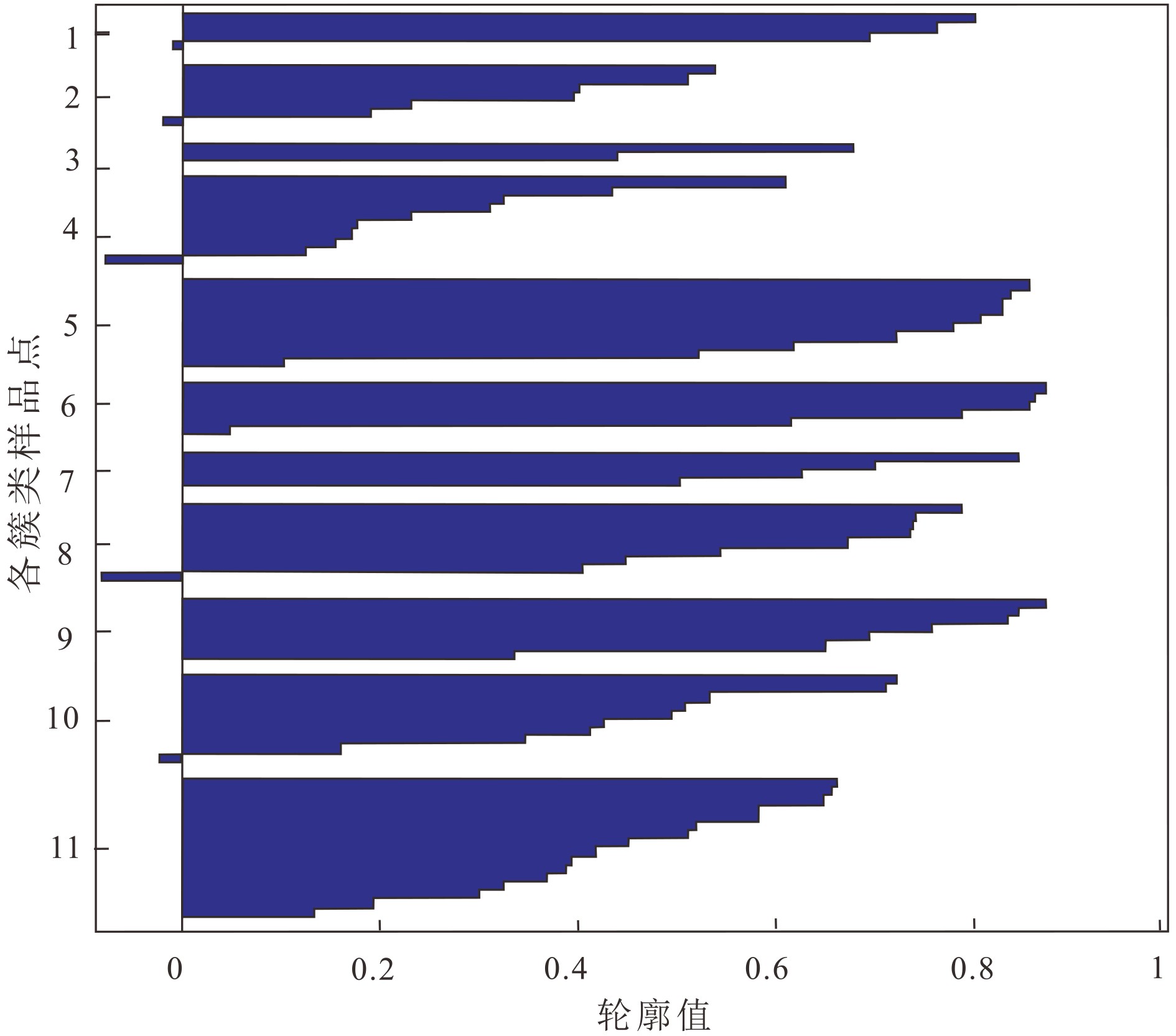
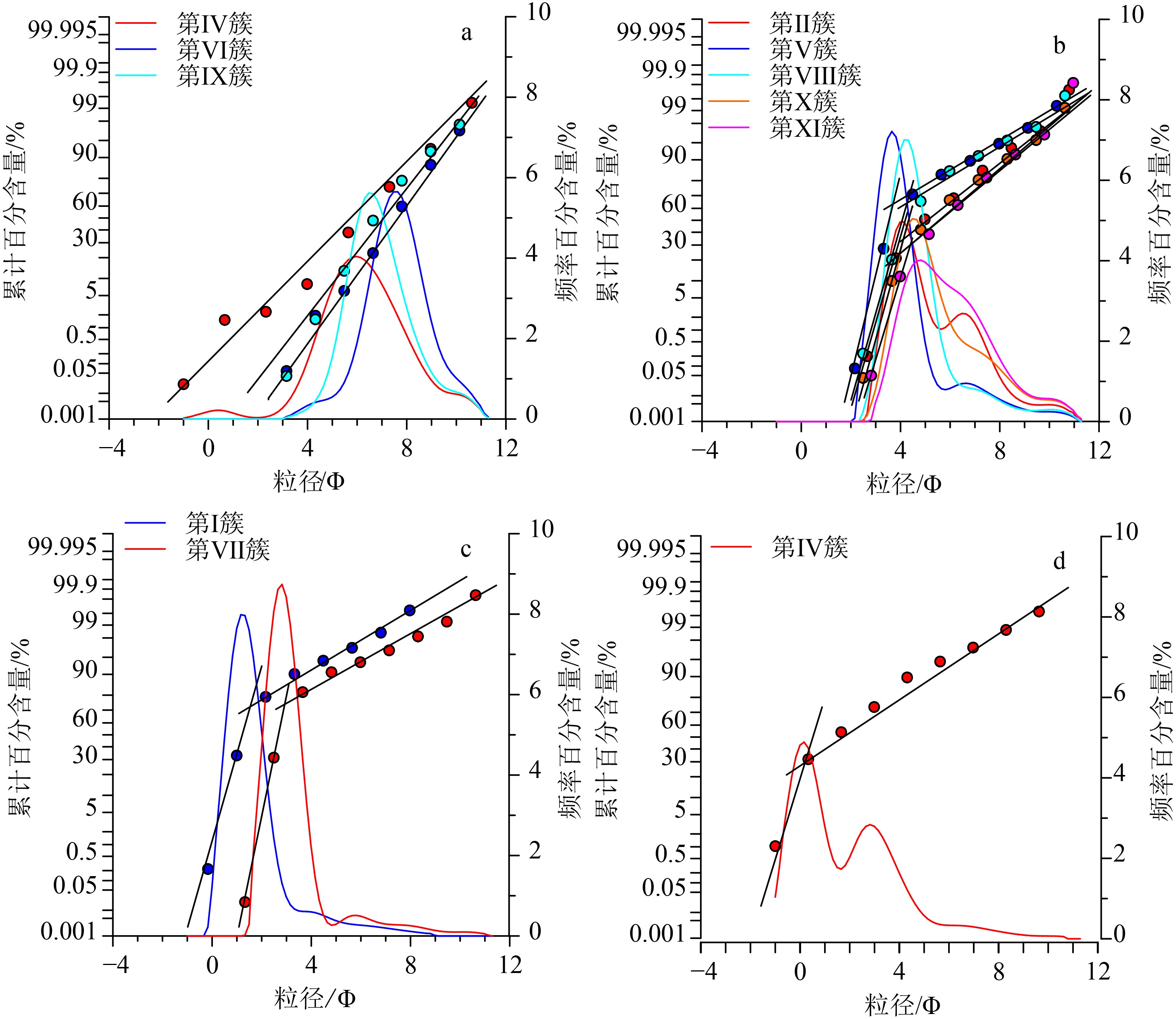
以白洋淀地区出露的22个沉积剖面中沉积物的粒度数据为研究对象,利用邻近传播聚类算法(AP聚类算法)进行聚类分析,并与已知典型沉积环境形成的沉积物粒度频率分布曲线进行对比,探讨了基于沉积物粒度特征的邻近传播聚类算法在沉积环境识别中应用的可行性以及白洋淀地区不同沉积环境的粒度特征。结果表明:邻近传播聚类算法能够将相同或者相近动力条件下形成的沉积物聚为一类,挖掘沉积物粒度数据中蕴含的沉积动力信息;所有样品的沉积物粒度频率分布曲线划分为11类簇;考虑到同一沉积环境中动力条件的变化,将聚类结果得到的分布范围、形状相近的11簇曲线进一步合并为4组曲线,并与已知典型沉积环境粒度曲线进行对比,识别出湖沼相、湖相、河流相、洪积相等4种主要的沉积相。其中,湖沼相与湖心相沉积环境、湖滨相与河漫滩相沉积环境形成的沉积物粒度组分相近。湖沼相与湖心相、湖滨相与漫滩相、河床相的沉积物粒度主要组分分别为细粉砂、粗粉砂、细砂或粗砂,洪积物中粗粉砂、中砂、粗砂含量相近,呈多峰态。邻近聚类传播算法可为沉积环境动力条件反演、分区等提供潜在的新手段。
Abstract:In the paper, 22 sedimentary sections are selected from the Baiyangdian region as research carriers. The affinity propagation (AP) clustering algorithm is adopted to cluster the similar grain size distribution of sediment into clusters. The results are then compared with the characteristics of grain size distribution which are known in typical sedimentary environments. The grain size distribution patterns in different sedimentary environments in Baiyangdian area are concluded and the feasibility of application of the affinity propagation clustering algorithm based on sediment grain characteristics to environmental interpretation discussed. The results suggests that the AP clustering algorithm can gather the sediments formed under the same or similar dynamical conditions into groups, and dig out the sedimentary dynamical information contained in the grain size data; The distribution curves of grain size for all samples are subdivided into 11 clusters. Considering the change in dynamic conditions in the same sedimentary environment, the 11 cluster curves are further categorized into 4 sets of curves, which could be compared with the grain size curves from known environment. 4 sedimentary facies i.e. the lacustrine-swamp facies, lacustrine facies, fluvial facies and alluvial facies are recognized. Among them, in terms of sedimentary dynamics, the lacustrine-swamp facies are similar with the central lake facies, while the lake shore facies similar with alluvial flat facies. The lacustrine-swamp facies and central lake facies are mainly composed of fine silty sand, whereas the lake shore facies and alluvial flat facies composed of coarse silt. River bed facies consist of sand or coarse sand. The contents of coarse silt, medium sand and coarse sand are similar in the flooding deposits, characterized by multi-peak curves. The performance proves that the AP clustering algorithm can provide a new mean for inversion and zonation of sedimentary environment conditions.
-

-
表 1 采样点描述
Table 1. Description of sampling sites
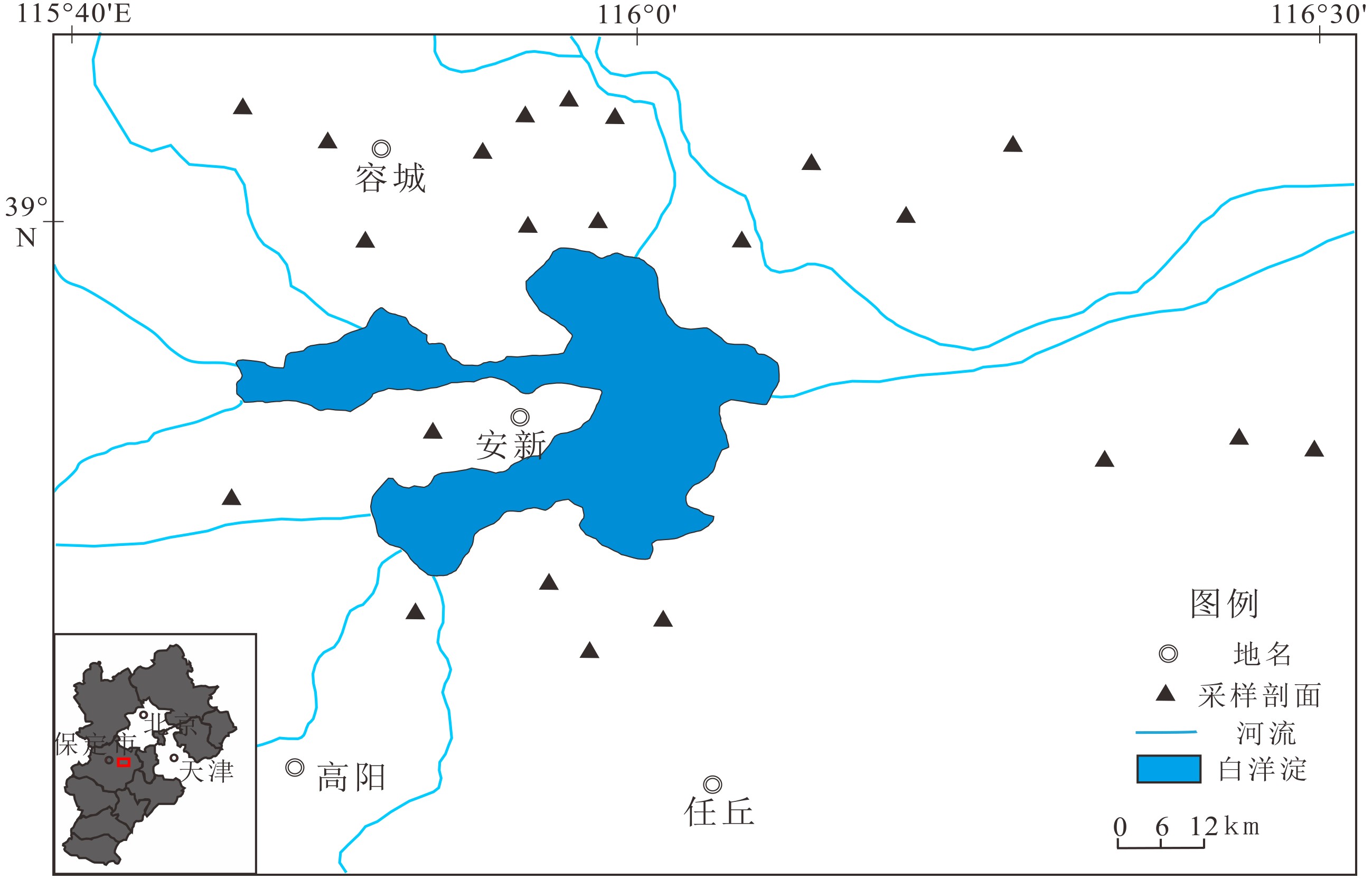
采样剖面名称 剖面位置 剖面描述 采样数/个 新庄窠村 38°59′31.56″N,115°50′54.04″E 沉积物以灰黄色黏土质粉砂、灰黑色或灰色粉砂质黏土和浅黄色细砂为主,沉积环境主要为湖滨相、湖沼相和河床相 3 段庄村剖面 39°03′20.44″N,115°49′30.28″E 沉积物为灰黑色粉砂质黏土、灰黄色黏土质粉砂,沉积环境为湖沼相、湖滨相 3 北张村剖面 39°04′40.23″N,115°46′32.13″E 沉积物以灰黑色、棕黄色粉砂质黏土和灰黄色细砂为主,沉积环境为湖沼相以及河床相 4 向村剖面 39°00′05.42″N,115°56′46.51″E 沉积物以灰黄色、浅灰色黏土质粉砂、灰褐色粉砂质黏土、灰色细砂以及灰黄色粉砂质中砂为主,沉积环境主要为湖滨相、湖沼相和河床相、洪积相 4 大阳村 39°00′18.32"N,115°59′19.28"E 沉积物为灰黑色粉砂质黏土、浅黄色黏土质粉砂以及具有水平层理的灰黄色粉砂,沉积环境主要有湖沼相、漫滩相以及河床相 3 李庄头村 38°59′33.60"N,116°04′48.67"E 沉积物以细砂、中砂为主,沉积环境主要为河流相 3 晾马台村 39°04′14.65"N,115°59′05.65"E 沉积物具有典型的“二元结构”,沉积环境为漫滩相 1 北剧村 09°04′56.42"N,115°58′16.81"E 沉积物以浅灰色中砂为主,沉积环境为河床相 1 南文村 39°04′19.98"N,115°56′42.30"E 沉积物以黄褐色、灰黄色黏土质粉砂以及含有黑色碳屑的灰黄色粉砂质粗砂为主,沉积环境主要有洪积相、湖相 4 马家庄村 39°02′53.77"N,115°55′07.67"E 沉积物为灰黄色黏土质粉砂,沉积环境为湖滨相 2 胡家台村 39°02′25.71"N,116°07′02.92"E 沉积物以灰黄色粗粉砂、细砂为主,发育交错层理,沉积环境为漫滩相 3 大步村 39°00′31.04"N,116°10′27.99"E 沉积物为灰褐色、黑色黏土、褐黄色黏土质粉砂以及浅灰色中细砂,沉积环境为湖沼相、湖滨相、河床相 8 邢岗村 39°03′0 8.65"N,116°14′18.92"E 沉积物以棕红色、灰黄色粉砂质黏土以及灰色、灰黄色黏土质粉砂为主,沉积环境为湖沼相、湖滨相 10 袁郭村 38°51′03.40"N,116°25′15.25"E 沉积物以灰黑色粉砂质黏土、浅黄色黏土质粉砂、灰黄色中细砂为主,沉积环境为湖沼相、湖滨相 4 胡屯村 38°51′59.62"N,116°22′34.97"E 沉积物以灰褐色、灰黑色粉砂质黏土以及灰黄色粉砂为主,沉积环境主要为湖沼相、湖滨相 5 小务村 38°51′8.86"N,116°17′39.73"E 沉积物以棕黄色亚砂土、细粉砂、灰黑色粉砂质黏土为主,沉积环境为湖滨相、湖沼相 6 双塔村 38°45′26.20"N,116°1′44.33"E 沉积物以灰黄色细粉砂、灰黑色黏土质粉砂为主,沉积环境为湖滨相、湖沼相 4 东良淀村 38°44′5.70"N,
115°59′7.99"E沉积物为棕红色粉砂质黏土,沉积环境为湖相 2 北队村 38°46′22.53"N,115°57′27.94"E 沉积物为浅灰色细砂土、棕黄色黏土质粉砂,沉积环境为漫滩相、湖滨相 3 韩堡村 38°46′23.07"N,115°53′24.07"E 沉积物为灰黄色黏土质粉砂,沉积环境为湖滨相 2 东垒头村 38°52′16.08"N,115°54′02.73"E 沉积物以灰黑色、棕红色粉砂质黏土、灰黄色黏土质粉砂为主,沉积环境为漫滩相、湖滨相、湖沼相 7 董庄村 38°49′32.73"N,
115°46′06.36"E棕红色、灰黑色粉砂质黏土,沉积环境为湖沼相 3 表 2 Folk&Ward 图解法公式
Table 2. Formulas of Folk-Ward graphic methods
粒度参数 计算公式 平均粒径(Mz) 
分选系数(Sd) 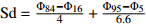
偏态(SK) 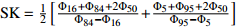
峰态(Ku) 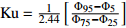
式中,粒径为  值粒径,
值粒径,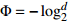 ,
, 为毫米直径;
为毫米直径;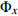 为x%累积含量的
为x%累积含量的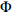 值粒径。
值粒径。表 3 各簇代表性样品粒度组成成分及粒度参数
Table 3. The size composition and size parameters of representative samples in each cluster
簇类 类代表性样品 沉积相 粒度成分/% 平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 偏态 峰态 黏土 细粉砂 粗粉砂 细砂 中砂 粗砂 Ⅰ SITE01-01 河流相 1.27 3.72 6.95 18.33 45.34 24.38 1.462 1.155 0.344 1.584 Ⅱ SITE03-03 湖滨相 12.72 25.35 40.23 21.47 0.2 0.02 5.255 1.75 0.32 0.887 Ⅲ SITE04-06 洪积相 2.85 6.15 15.43 29.62 16.16 29.8 1.582 1.976 0.319 0.908 Ⅳ SITE12-02 湖沼相 19.67 41.22 34.45 4.33 0.14 0.13 6.227 1.722 0.096 1.066 Ⅴ SITE13-08 漫滩相 4.72 7.81 34.25 52.54 0.58 0.09 4.213 1.515 0.467 1.561 Ⅵ SITE13-09 湖沼相 40.67 47.21 10.66 1.46 0 0 7.537 1.301 0.019 1.158 Ⅶ SITE14-04 河流相 2.58 5.38 12.08 72.54 7.42 0 2.919 1.108 0.343 1.797 Ⅷ SITE17-04 漫滩相 6.68 10.46 55.59 27.18 0.08 0.01 4.577 1.343 0.363 1.485 Ⅸ SITE18-01 湖心相 20.74 55.49 22.38 1.4 0 0 6.819 1.329 0.175 1.123 Ⅹ SITE21-06 湖滨相 12.75 22.99 50.4 13.71 0.13 0.02 5.507 1.799 0.374 1.014 Ⅺ SITE18-02 湖滨相 15.1 33.35 43.32 7.98 0.11 0.12 5.841 1.745 0.209 0.981 表 4 沉积环境识别过程中存在差异的沉积物样品
Table 4. Sediment samples with differences in the process of sedimentary environment identification
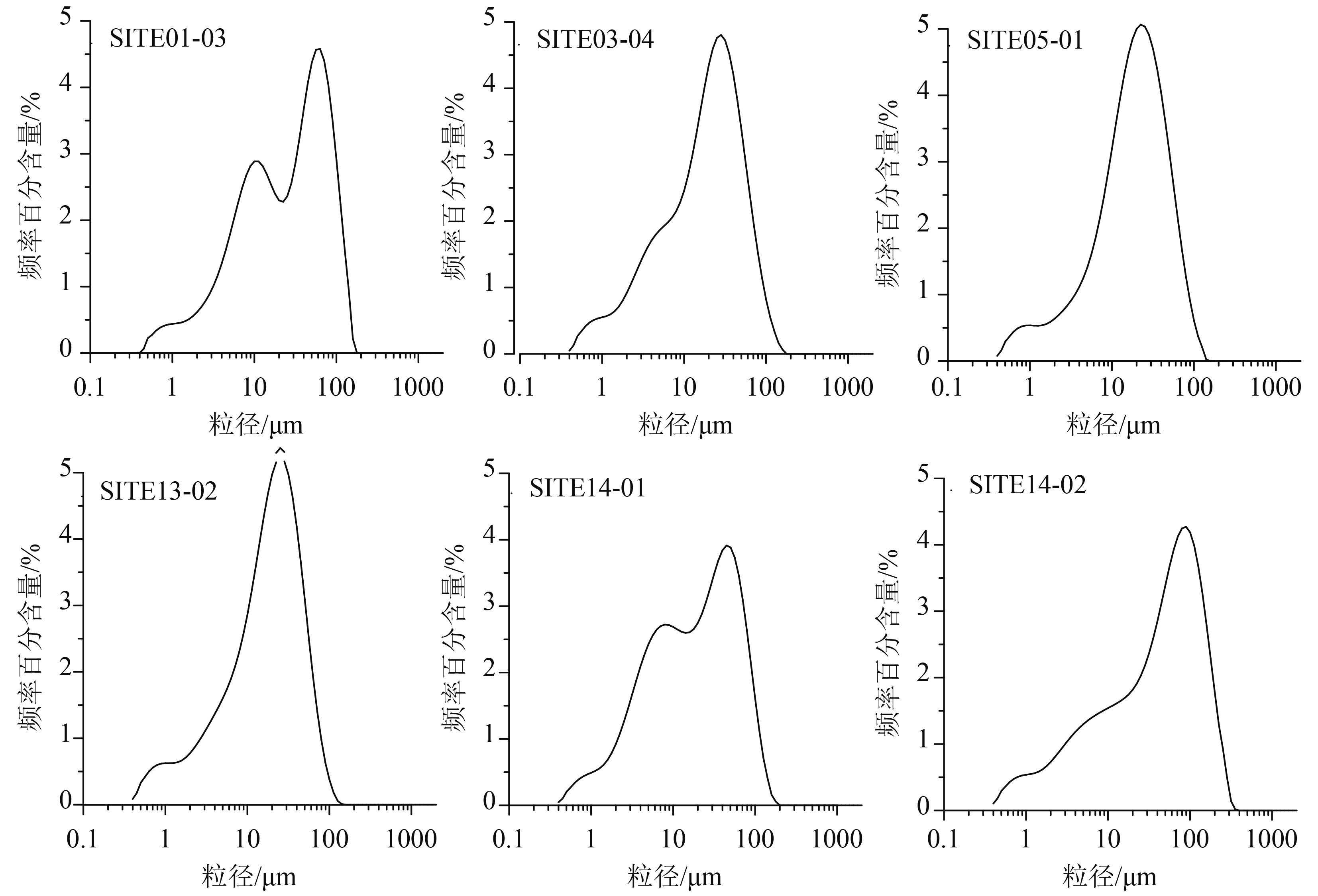
样品编号 簇类 野外人为识别 粒度分布曲线对比识别 SITE01-03 Ⅱ 灰黑色粉砂质黏土,湖沼相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 SITE03-04 Ⅱ 灰黑色黏土,湖沼相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 SITE05-01 Ⅺ 灰黄色粉砂,河流相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 SITE13-02 Ⅺ 灰黄色粉砂,河流相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 SITE14-01 Ⅺ 灰黑色粉砂质黏土,湖相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 SITE14-02 Ⅱ 湖沼相沉积 湖滨相或漫滩相 -
[1] Weltje G J, Prins M A. Muddled or mixed? Inferring palaeoclimate from size distributions of deep-sea clastics [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162(1-2): 39-62. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(03)00235-5
[2] 范天来, 范育新. 频率分布曲线和概率累积曲线在沉积物粒度数据分析中应用的对比[J]. 甘肃地质, 2010, 19(2):32-37
FAN Tianlai, FAN Yuxin. A comparison of grain size expression methods: A case study [J]. Gansu Geology, 2010, 19(2): 32-37.
[3] 曲政. 沉积物粒度数据表征方法的研究[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2001, 7(4):24-31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5548.2001.04.008
QU Zheng. A study on characterization methods of grain-size data of sediment [J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2001, 7(4): 24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5548.2001.04.008
[4] 孙东怀, 鹿化煜, David R, et al. 中国黄土粒度的双峰分布及其古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 18(3):327-335 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.03.002
SUN Donghuai, LU Huayu, David R, et al. Bimode grain-size distribution of Chinese loess and its paleoclimate implication [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 18(3): 327-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.03.002
[5] Weltje G J. End-member modeling of compositional data: Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem [J]. Mathematical Geology, 1997, 29(4): 503-549. doi: 10.1007/BF02775085
[6] 孙吉贵, 刘杰, 赵连宇. 聚类算法研究[J]. 软件学报, 2008, 19(1):48-61 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2008.00048
SUN Jigui, LIU Jie, ZHAO Lianyu. Clustering algorithms research [J]. Journal of Software, 2008, 19(1): 48-61. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2008.00048
[7] 李玉中, 陈沈良. 系统聚类分析在现代沉积环境划分中的应用——以崎岖列岛海区为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(3):487-494 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.019
LI Yuzhong, CHEN Shenliang. Application of system cluster analysis to classification of modern sedimentary environment: A case study in Qiqu Archipelago Area [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(3): 487-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.019
[8] 杨传慧, 吉根林, 章志刚. AP算法在图像聚类中的应用研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2012, 40(10):119-121 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2012.10.036
YANG Chuanhui, JI Genlin, ZHANG Zhigang. Research on application of algorithm AP in images clustering [J]. Computer and Digital Engineering, 2012, 40(10): 119-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2012.10.036
[9] 吴娱, 钟诚, 尹梦晓. 基因表达数据的分层近邻传播聚类算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2016, 37(11):2961-2966
WU Yu, ZHONG Cheng, YIN Mengxiao. Gene expression data clustering algorithm using hierarchical affinity propagation [J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2016, 37(11): 2961-2966.
[10] 肖宇, 于剑. 基于近邻传播算法的半监督聚类[J]. 软件学报, 2008, 19(11):2803-2813
XIAO Yu, YU Jian. Semi-supervised clustering based on affinity propagation algorithm [J]. Journal of Software, 2008, 19(11): 2803-2813.
[11] 许清海, 陈淑英, 孔昭宸, 等. 白洋淀地区全新世以来植被演替和气候变化初探[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1988, 12(2):143-151
XU Qinhai, CHEN Shuying, KONG Zhaochen, et al. Preliminary discussion of vegetation succession and climate change since the Holocene in the Baiyangdian lake district [J]. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 1988, 12(2): 143-151.
[12] 王永, 闵隆瑞, 董进, 等. 河北白洋淀全新统沉积特征与地层划分[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(5):575-582 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.05.07
WANG Yong, MIN Longrui, DONG Jin, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and stratigraphic division of Holocene series in Baiyang Dian, Hebei Provence [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(5): 575-582. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.05.07
[13] 杨慧君, 王永, 迟振卿, 等. 河北白洋淀老河头剖面25.5 kaBP以来气候环境变化的沉积记录[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2):291-298 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.011
YANG Huijun, WANG Yong, CHI Zhenqing, et al. Sedimentary record of climate change during the past 25.5 ka of Laohetou profile from Baiyangdian, Hebei Province [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 291-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.011
[14] 高彦春, 王金凤, 封志明. 白洋淀流域气温、降水和径流变化特征及其相互响应关系[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(4):467-477
GAO Yanchun, WANG Jinfeng, FENG Zhiming. Variation trend and response relationship of temperature, precipitation and runoff in Baiyangdian Lake Basin [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(4): 467-477.
[15] 何乃华, 朱宣清. 白洋淀地区近3万年来的古环境与历史上人类活动的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1992, 12(2):79-88
HE Naihua, ZHU Xuanqing. Palaeoenvironment changes since 30000 aBP and effects of human activities in the Baiyangdian area [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1992, 12(2): 79-88.
[16] Frey B J, Dueck D. Clustering by passing messages between data points [J]. Science, 2007, 315(5814): 972-976. doi: 10.1126/science.1136800
[17] Brusco M J, Köhn H F. Comment on "Clustering by passing messages between data points" [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 726.
[18] Nelson P A, Bellugi D, Dietrich W E. Delineation of river bed-surface patches by clustering high-resolution spatial grain size data [J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 205: 102-119. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.06.008
[19] Baxter M J, Beardah C C, Cool H E M, et al. Compositional data analysis of some alkaline Glasses [J]. Mathematical Geology, 2005, 37(2): 183-196. doi: 10.1007/s11004-005-1308-3
[20] Ordóñez C, Ruiz-Barzola O, Sierra C. Sediment particle size distributions apportionment by means of functional cluster analysis (FCA) [J]. Catena, 2016, 137: 31-36. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.09.006
[21] 朱连江, 马炳先, 赵学泉. 基于轮廓系数的聚类有效性分析[J]. 计算机应用, 2010, 30(2):139-141
ZHU Lianjiang, MA Bingxian, ZHAO Xuequan. Clustering validity analysis based on silhouette coefficient [J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 30(2): 139-141.
[22] 张晋, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 南海南部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):1-10
ZHANG Jin, LI Anchun, WAN Shiming, et al. Grain size distribution of surface sediments in the southern South China Sea and influencing factors [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 1-10.
[23] 殷志强, 秦小光, 吴金水, 等. 中国北方部分地区黄土、沙漠沙、湖泊、河流细粒沉积物粒度多组分分布特征研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2):343-351
YIN Zhiqiang, QIN Xiaoguang, WU Jinshui, et al. The multimodal grain-size distribution characteristics of loess, desert, lake and river sediments in some areas of Northern China [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(2): 343-351.
[24] 孙东怀, 安芷生, 苏瑞侠, 等. 古环境中沉积物粒度组分分离的数学方法及其应用[J]. 自然科学进展, 2001, 11(3):269-276 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2001.03.008
SUN Donghuai, AN Zhisheng, SUN Ruixia, et al. Mathematics method and its application of grain size distribution of Paleoenvironment Sediments [J]. Progress in Natural Sciences, 2001, 11(3): 269-276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2001.03.008
[25] 张平, 宋春晖, 杨用彪, 等. 稳定湖相沉积物和风成黄土粒度判别函数的建立及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(3):501-507
ZHANG Ping, SONG Chunhui, YANG Yongbiao, et al. The significance and establishment of discriminant function with grain size of stable lacustrine sediment and eolian loess [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(3): 501-507.
[26] 卢连战, 史正涛. 沉积物粒度参数内涵及计算方法的解析[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2010, 35(6):54-60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
LU Lianzhan, SHI Zhengtao. Analysis for sediment grain size parameters of connotations and calculation method [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2010, 35(6): 54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
[27] Blott S J, Pye K. GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2001, 26(11): 1237-1248. doi: 10.1002/esp.261
-



 下载:
下载: