Second-order climatic cycles in the Chinese Loess Plateau and their bearing on precession driving
-
摘要:
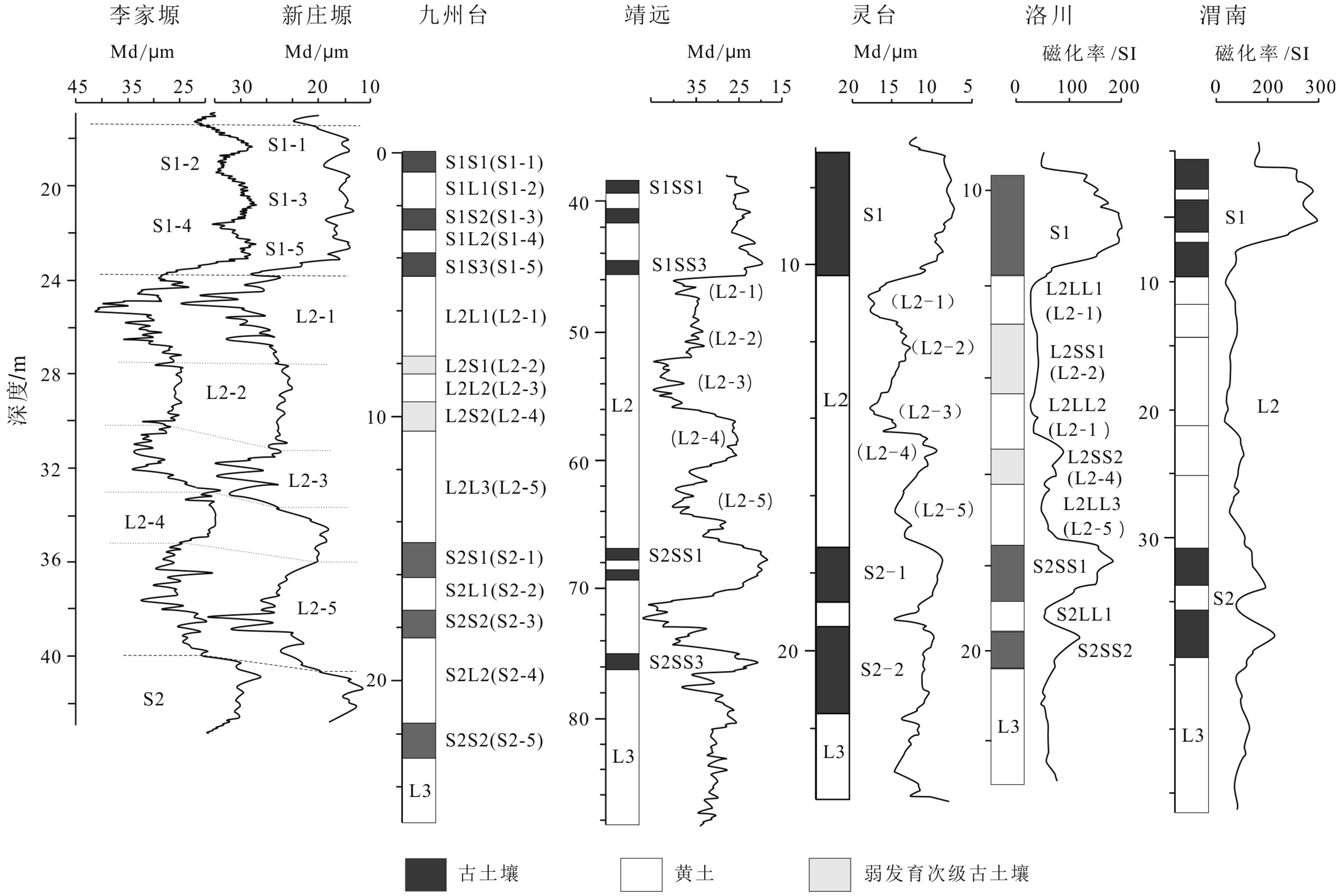
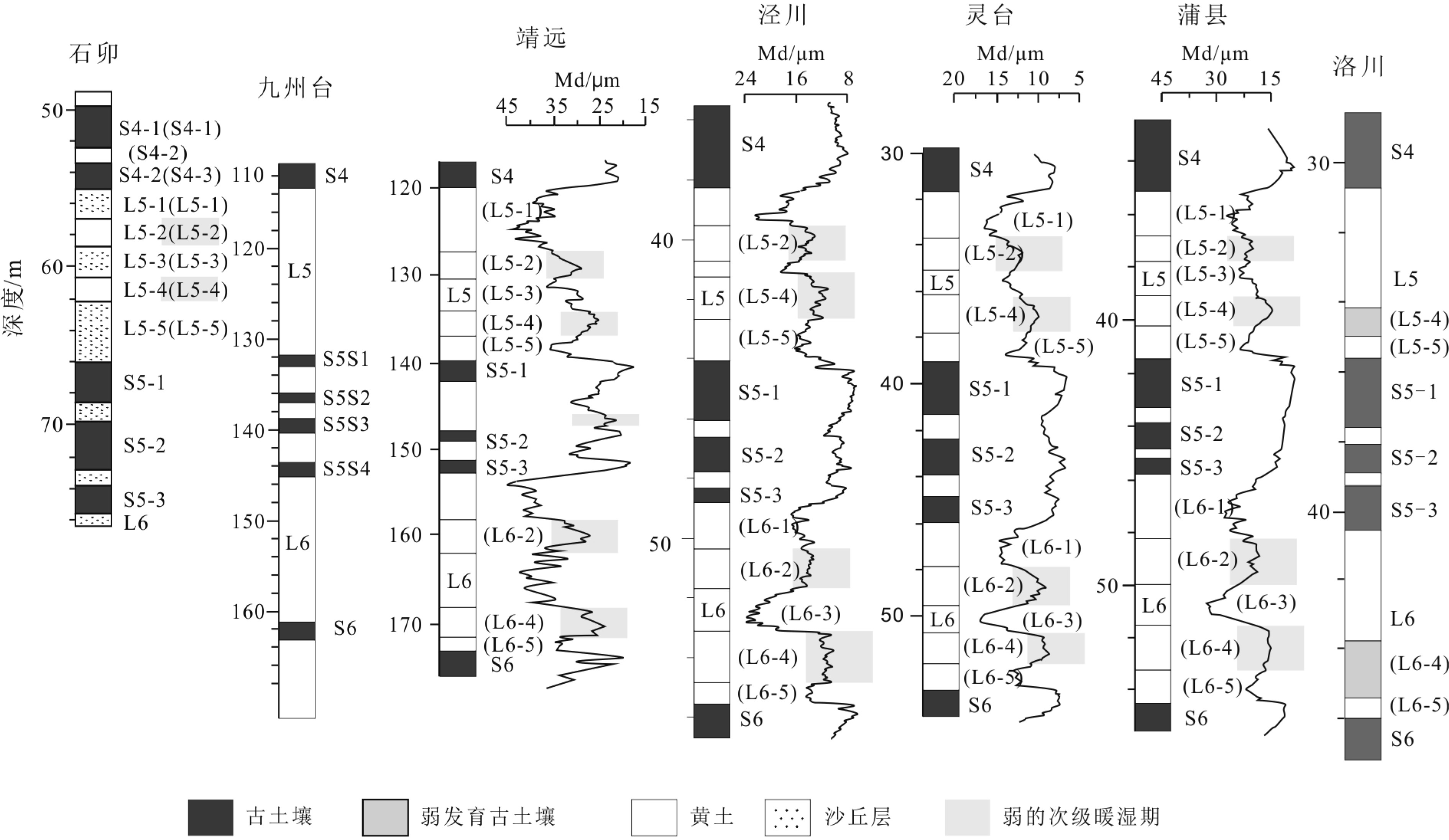
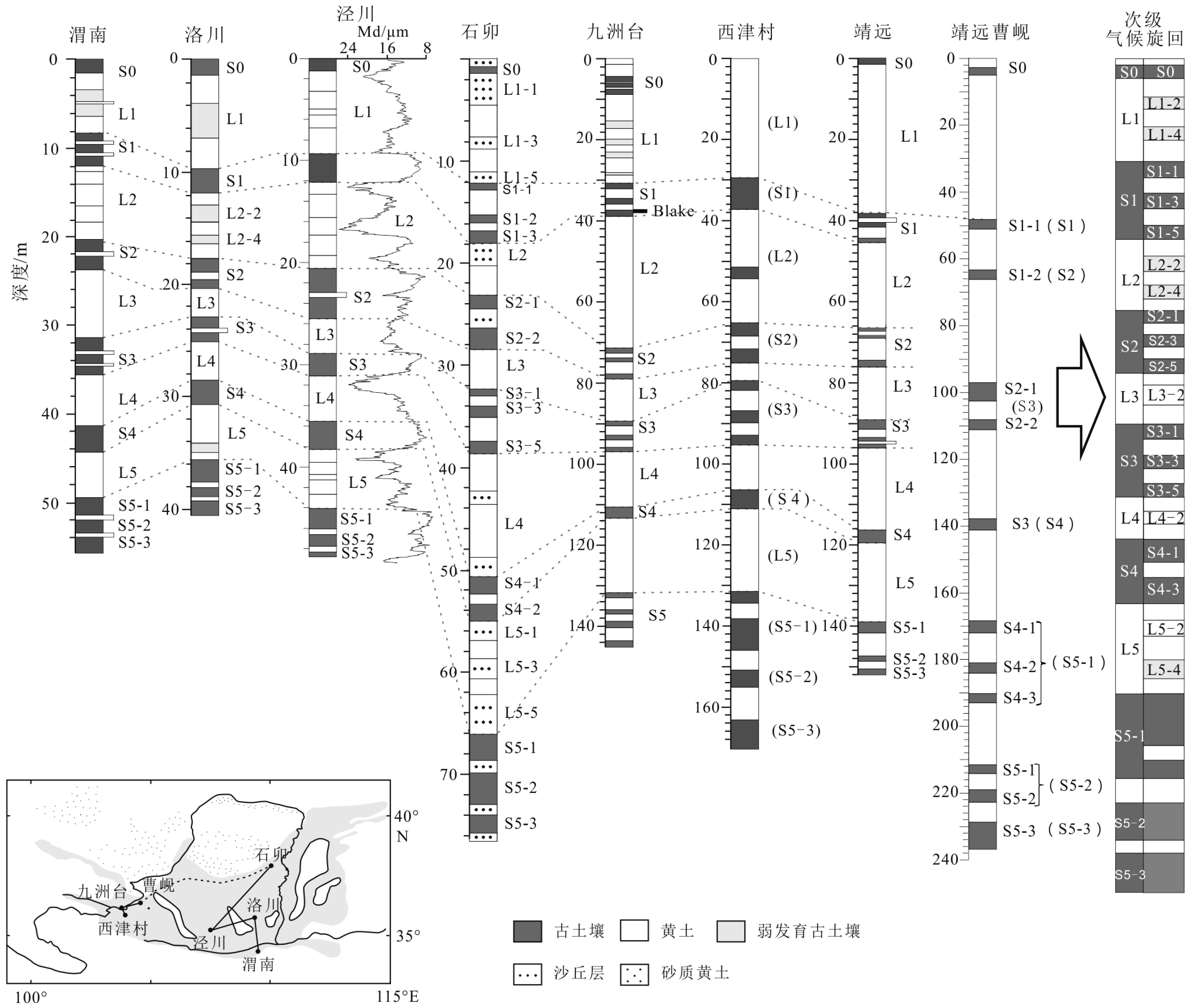
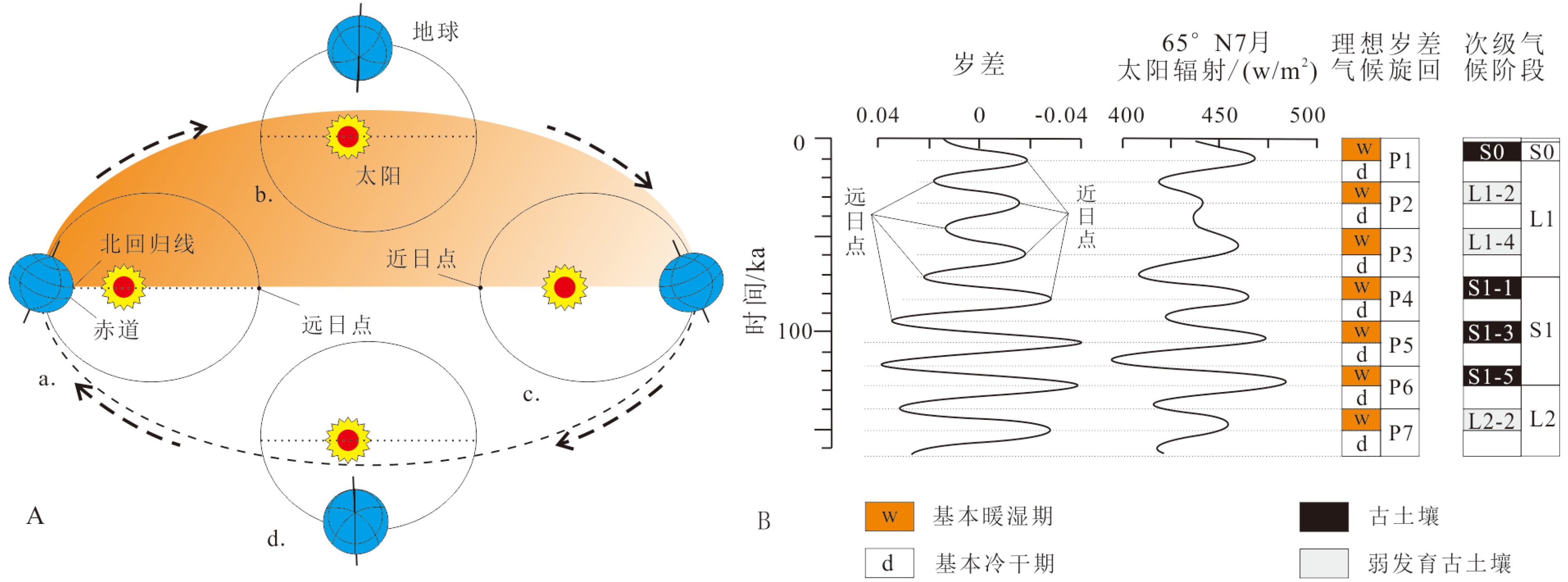
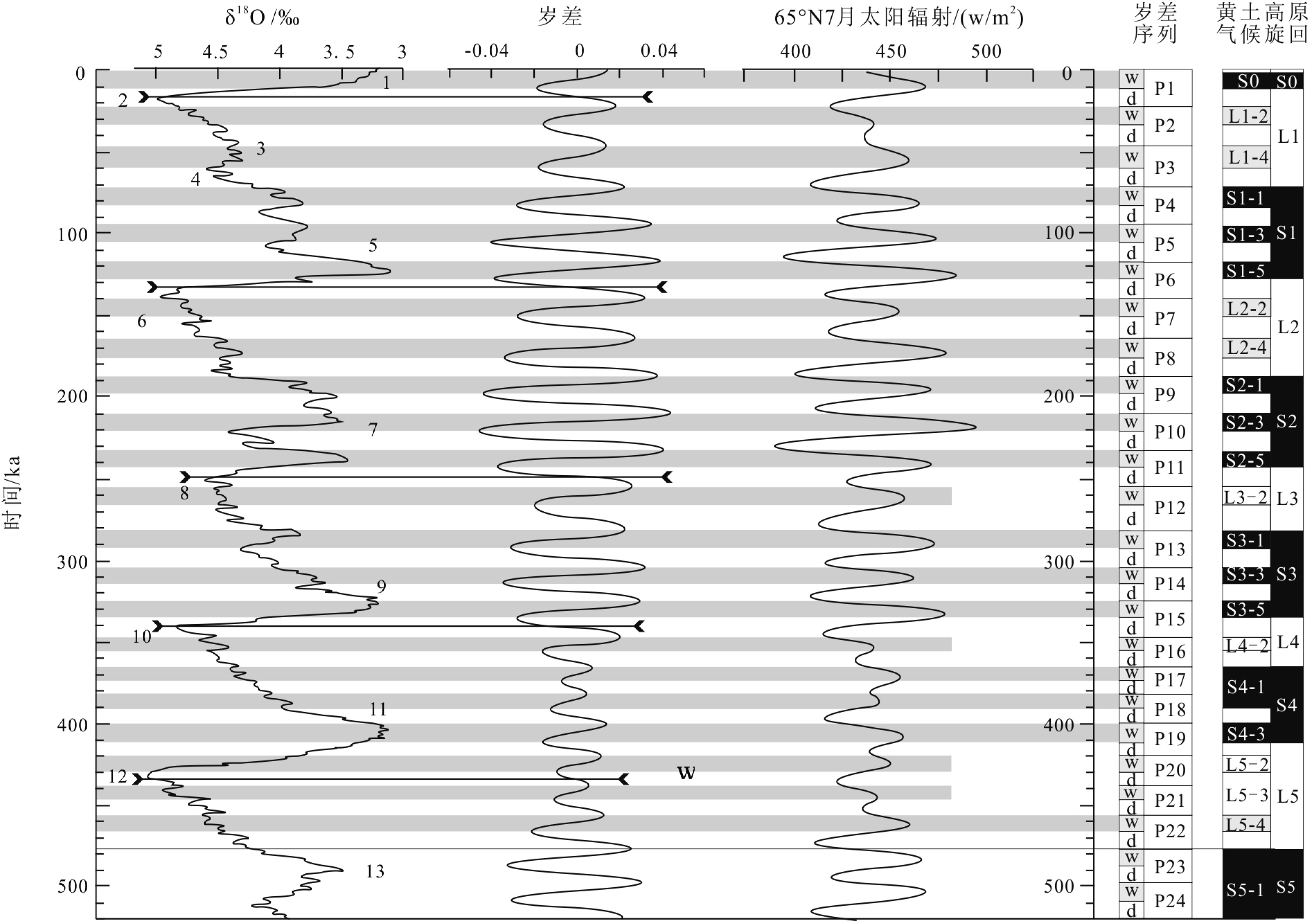
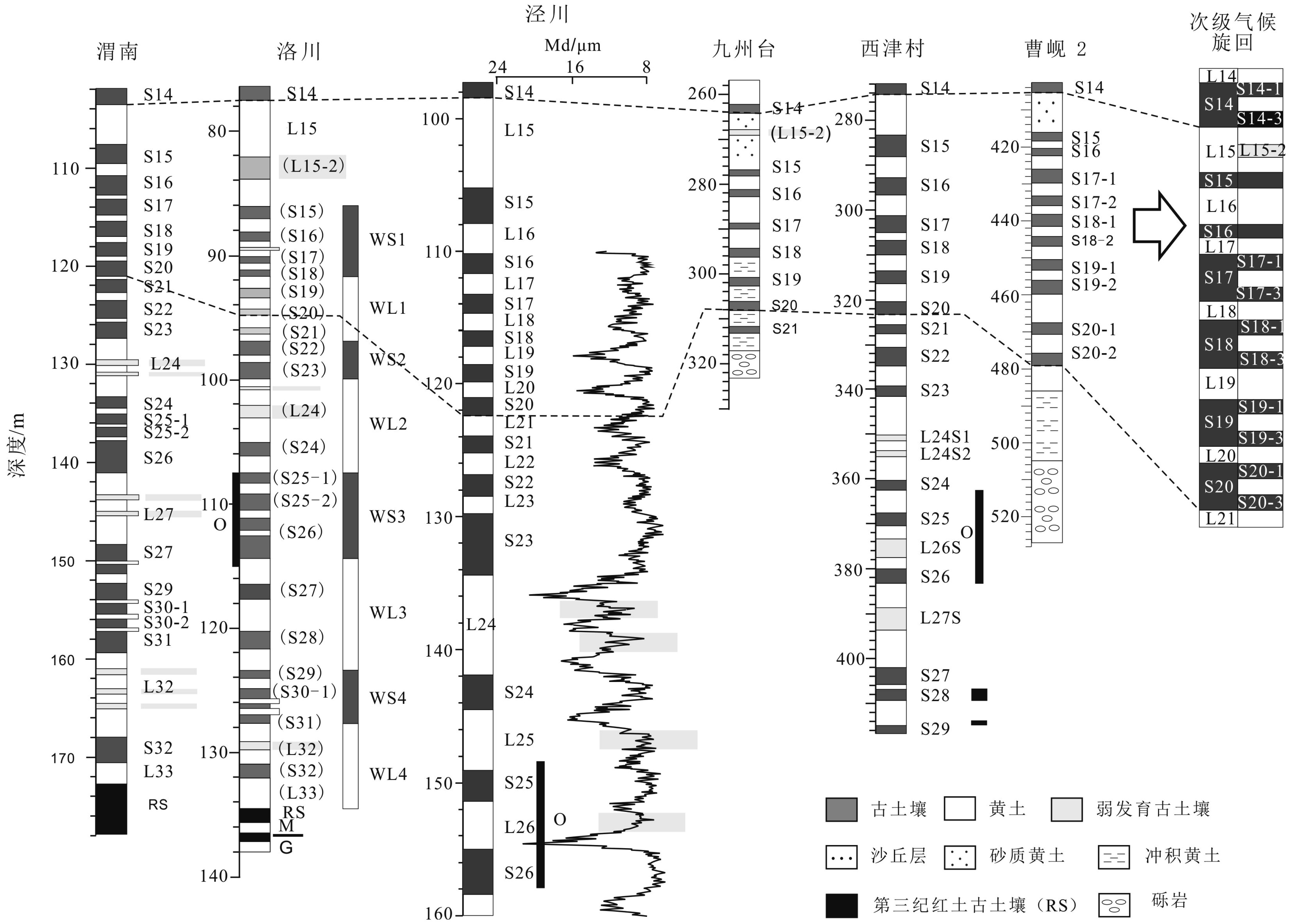
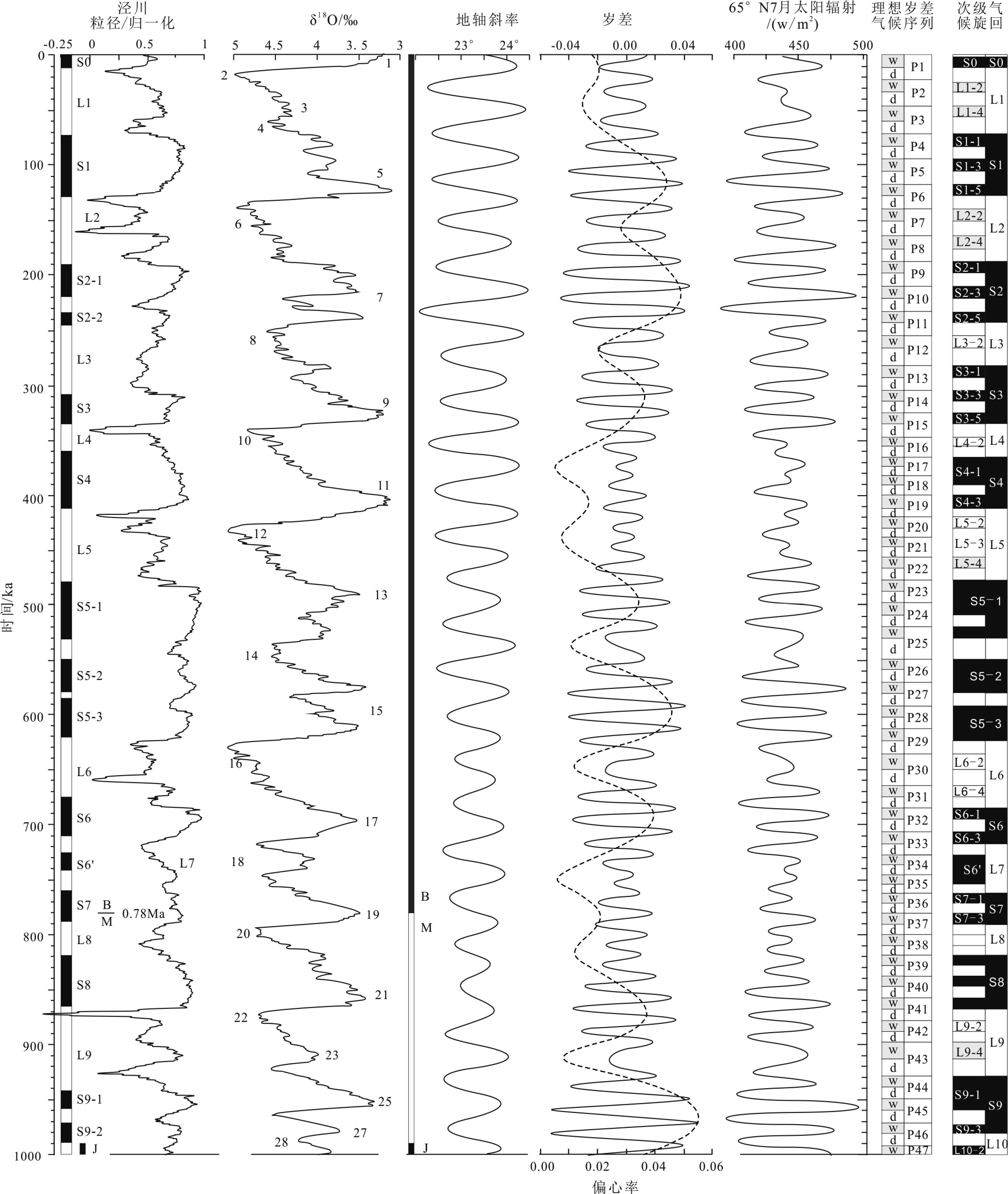
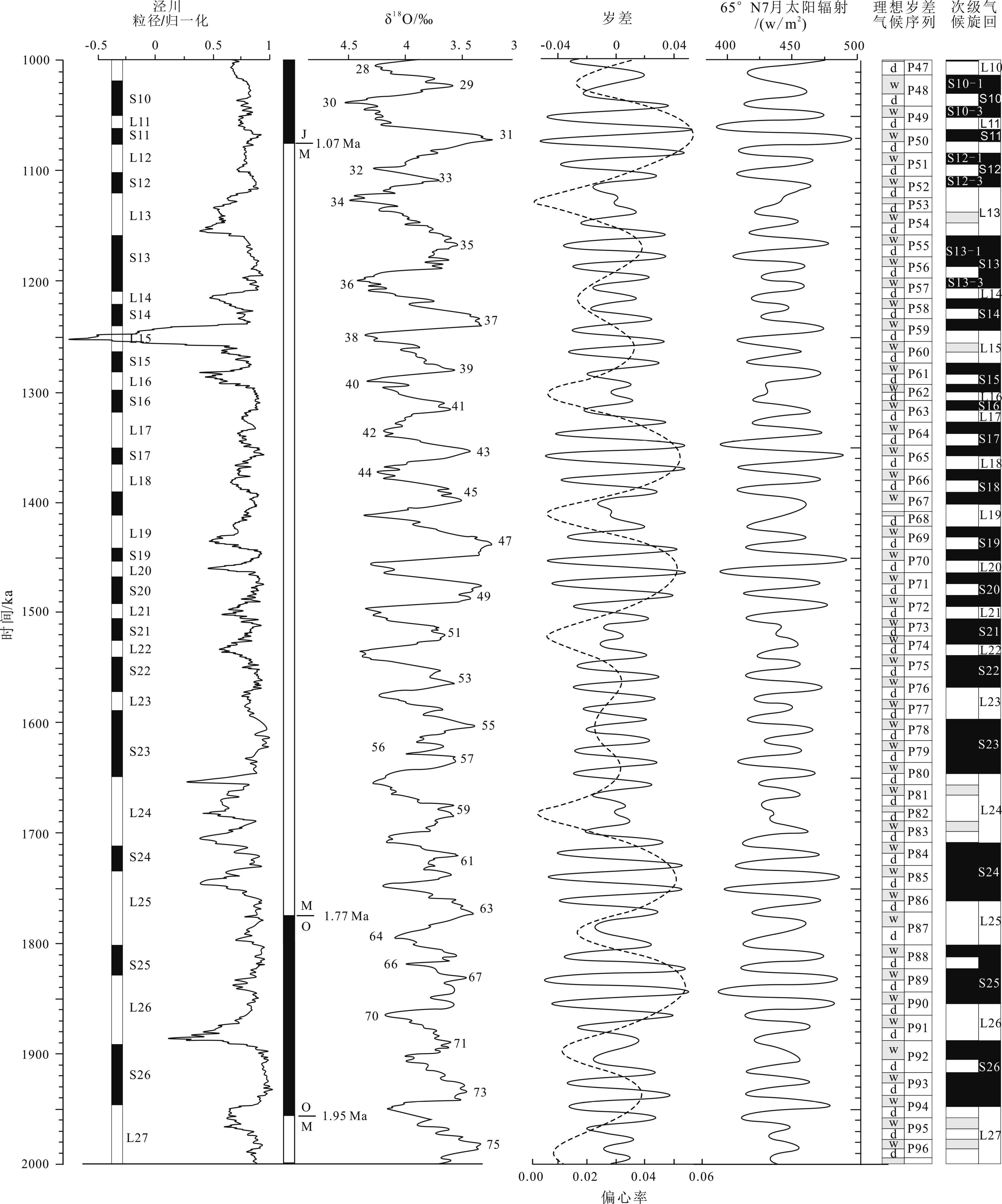
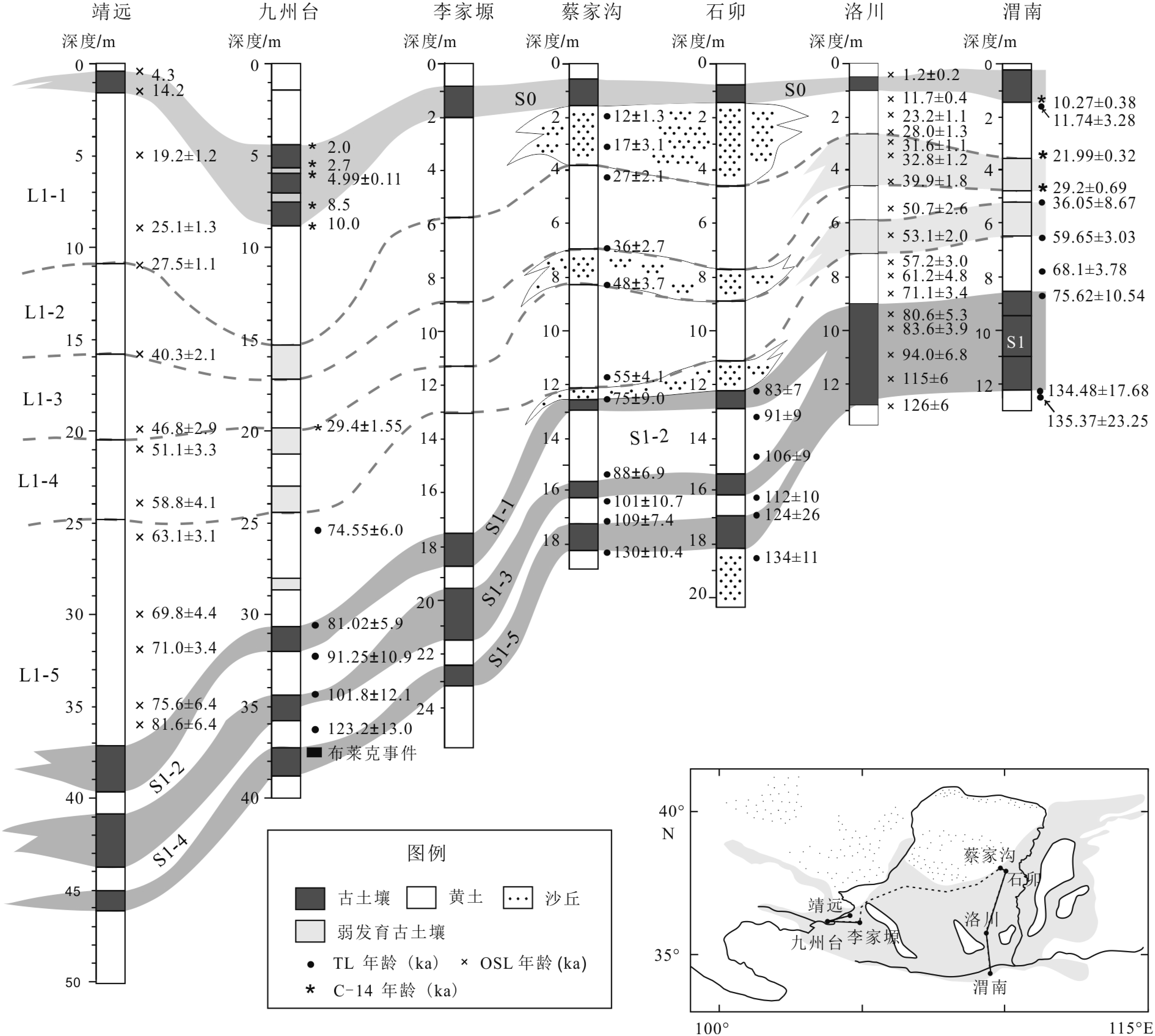
以黄土高原普遍存在的次级古土壤为基础,结合粒度资料和磁化率资料,对黄土高原的次级气候阶段进行了划分与对比,初步建立了黄土高原L21以来的次级气候旋回序列。以北半球夏至日在近日点和远日点为界,将岁差旋回转变为北半球"理想岁差气候旋回",并与黄土高原次级气候旋回逐一对比,发现L21以来的72个岁差旋回中,共发育了122个次级气候阶段,合61个次级气候旋回。除去岁差变化微弱的时段,黄土高原次级气候旋回与理想岁差旋回间几乎是一一对应的关系。从而认为,黄土高原的次级气候旋回主要由岁差旋回驱动。与反映全球变化的一级气候旋回相比,黄土高原的次级气候旋回凸显了具有半球效应的岁差旋回在黄土高原气候变化中的作用。黄土高原的次级气候旋回一定程度上受到冰期旋回的遮掩,需要在高原各地往复追索才能清楚揭示。黄土高原的次级气候旋回不仅可以作为地层划分与对比的基本单元,也由于岁差的约束而在一定程度上具有了绝对年代的意义,在地层划分和古气候研究中应引起足够的重视。
Abstract:Sub-palaeosols are commonly observed in the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). Based on the grain size and magnetic susceptibility data, second-order climatic stages (SOCC) of the CLP are further divided and correlated, and the sequence of SOCC after L21 is preliminarily established in this paper. Taking the Northern Hemisphere summer solstice at perihelion and apohelion as boundaries, precession cycles are transformed into the “Ideal precession climatic cycle” (IPCC) for the Northern Hemisphere. Correlated with the SOCC established in the Loess Plateau, it is found that there are 122 second order climatic stages, corresponding to 61 secondary climatic cycles, could be identified in the 72 precession cycles since L21. Except for the stages which are too weak in precession variation, there is almost a one-to-one correspondent relationship between the SOCC and the IPCC. It is, therefore, concluded that the SOCC in the CLP are mainly driven by precession cycles. Compared with the first-order climatic cycle which reflect global climatic change, the SOCC of the CLP highlights the role of the precession cycle with hemispheric effect in the climatic change of the Loess Plateau. The SOCC have been partly obscured by the glacial-interglacial cycles. It is needed to trace back and forth across the plateau to reveal the pattern clearly. SOCC in the CLP not only serves as the basic unit for stratigraphic classification, but also has some absolute chronological significance to some extent due to the constraints of precession. Enough attention should be paid to its paleoclimatic implication in addition to stratigraphic significance.
-
Key words:
- Chinese Loess Plateau /
- second-order climatic cycles /
- precession /
- subpaleosol
-

-
[1] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
LIU Tungsheng. The Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985
[2] 郭正堂, Fedoroff N, 刘东生. 130ka来黄土-古土壤序列的典型微形态特征与古气候事件[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 1996, 26(5):392-398
GUO Zhengtang, Fedoroff N, LIU Tungsheng. Typical micromorphological characteristics of loess -paleosol sequences and paleoclimatic events since 130 ka [J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 1996, 26(5): 392-398.
[3] 孙继敏, 丁仲礼. 近13万年来黄土高原干湿气候的时空变迁[J]. 第四纪研究, 1997, 17(2):168-175 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.009
SUN Jimin, DING Zhongli. Spatial and temporal changes of dry and wet climate during the last 130, 000 years in the Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1997, 17(2): 168-175. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.009
[4] 葛俊逸, 郭正堂, 郝青振. 特征时期黄土高原风化成壤强度的空间特征与气候梯度[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(6):962-968 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.011
GE Junyi, GUO Zhengtang, HAO Qingzhen. Spatial variations of weathering intensity of the Loess Plateau and the climate gradients within characteristic timeslices [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(6): 962-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.011
[5] Sun J M, Ding Z L, Liu T S, et al. 580 000-year environmental reconstruction from aeolian deposits at the Mu Us Desert margin, China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1999, 18(12): 1351-1364. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(98)00086-9
[6] Ding Z L, Liu T S, Rutter N W, et al. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800, 000 Years [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 149-159. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1059
[7] Sun Y B, Chen J, Clemens S C, et al. East Asian monsoon variability over the last seven glacial cycles recorded by a loess sequence from the northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(12): Q12Q02.
[8] 丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 余志伟, 等. 黄土高原过去130ka来古气候事件年表[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(6):567-574 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.06.002
DING Zhongli, SUN Jimin, YU Zhiwei, et al. Chronology of past 130 ka climatic events over the Loess Plateau [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(6): 567-574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.06.002
[9] 吴乃琴, 裴云鹏, 吕厚远, 等. 黄土高原35万年来冬、夏季风变化周期的差异——陆生蜗牛化石的证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(6):540-550 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.06.010
WU Naiqin, PEI Yunpeng, LÜ Houyuan, et al. Orbital forcing of East Asian summer and winter monsoon variations in the past 35 000 years [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(6): 540-550. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.06.010
[10] 刘东生, 丁仲礼. 中国黄土研究新进展(二)古气候与全球变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, 10(1):1-9 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.01.001
LIU Tungsheng, DING Zhongli. Progresses of loess research in China (Part 2): Paleoclimatology and global change [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1990, 10(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.01.001
[11] 郭正堂, 丁仲礼, 刘东生. 黄土中的沉积-成壤事件与第四纪气候旋回[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41(1):56-59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.01.017
GUO Zhengtang, DING Zhongli, LIU Tungsheng. The depositional-pedogenic events in the loess deposit and the Quaternary climatic cycles [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41(1): 56-59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.01.017
[12] Ding Z L, Sun J M, Yu Z W, et al. Chronology of environmental events over East Asia during the past 130 ka [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(21): 1761-1769. doi: 10.1007/BF02883368
[13] Ding Z L, Ren J Z, Yang S L, et al. Climate instability during the penultimate glaciation: Evidence from two high-resolution loess records, China [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B9): 20123-20132. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900183
[14] 安芷生, 吴锡浩, 汪品先, 等. 最近130ka中国的古季风-Ⅰ. 古季风记录[J]. 中国科学B辑: 化学 生命科学 地学, 1991, 21(10):1076-1081
AN Zhisheng, WU Xihao, WANG Pinxian, et al. The Paleomonsoon of China since 130 ka-I. Paleomonsoon records [J]. Science in China Series B: Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 1991, 21(10): 1076-1081.
[15] 安芷生, 吴锡浩, 汪品先, 等. 最近130ka中国的古季风-Ⅱ. 古季风变迁[J]. 中国科学B辑: 化学 生命科学 地学, 1991, 21(11):1209-1215
AN Zhisheng, WU Xihao, WANG Pinxian, et al. The paleomonsoon of China since 130 ka-II. Paleomonsoon Variations [J]. Science in China Series B: Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 1991, 21(11): 1209-1215.
[16] 郭正堂, 刘东生, 安芷生. 渭南黄土沉积中十五万年来的古土壤及其形成时的古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 1994, 14(3):256-269 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.007
GUO Zhengtang, LIU Tungsheng, AN Zhisheng. Paleosols of the last 0.15 Ma in the Weinan loess section and their paleoclimatic significance [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1994, 14(3): 256-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.007
[17] 安芷生, Kukla G, 刘东生. 洛川黄土地层学[J]. 第四纪研究, 1989, 9(2):155-168 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1989.02.006
AN Zhisheng, Kukla G, LIU Tungsheng. Loess stratigraphy in Luochuan of China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1989, 9(2): 155-168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1989.02.006
[18] 陈发虎, 张维信. 甘青地区的黄土地层学与第四纪冰川问题[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 9-34.
CHEN Fahu, ZHANG Weixin. The Loess Stratigraphy and Quaternary Glaciation Problems of Ganshu-Qinghai Areas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 9-34
[19] 刘嘉麒, 陈铁梅, 聂高众, 等. 渭南黄土剖面的年龄测定及十五万年来高分辨时间序列的建立[J]. 第四纪研究, 1994, 14(3):193-202 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.001
LIU Jiaqi, CHEN Tiemei, NIE Gaozhong, et al. Datings and reconstruction of the high resolution time series in the Weinan loess section in the last 150 000 years [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1994, 14(3): 193-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.001
[20] 聂高众, 刘嘉麒, 郭正堂. 渭南黄土剖面十五万年以来的主要地层界线和气候事件——年代学方面的证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 1996, 16(3):221-231 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.03.004
NIE Gaozhong, LIU Jiaqi, GUO Zhengtang. The major stratigraphic boundaries and climatic events in Weinan loess section since 0.15 MaBP: Based on chronological evidences [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1996, 16(3): 221-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.03.004
[21] 王文远, 刘嘉麒, 潘懋, 等. 末次间冰期以来渭南黄土剖面高分辨率古气候时间标尺[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25(1):98-102 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.01.018
WANG Wenyuan, LIU Jiaqi, PAN Mao, et al. Reconstruction of the high resolution timescale in the Weinan loess section of the late Quaternary [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 25(1): 98-102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.01.018
[22] 孙湘君, 宋长青, 王琫瑜, 等. 黄土高原南缘最近10万年来的植被[J]. 植物学报, 1996, 38(12):982-988
SUN Xiangjun, SONG Changqing, WANG Fengyu, et al. Vegetation history of the southern Loess Plateau of China during the last 100 000 years based on pollen data [J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1996, 38(12): 982-988.
[23] Chen F H, Bloemendal J, Wang J M, et al. High-resolution multi-proxy climate records from Chinese loess: evidence for rapid climatic changes over the last 75 kyr [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1997, 130(1-4): 323-335. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(96)00149-6
[24] Sun J M, Ding Z L. Deposits and soils of the past 130, 000 years at the desert-loess transition in northern China [J]. Quaternary Research, 1998, 50(2): 148-156. doi: 10.1006/qres.1998.1989
[25] Li B, Li S H, Sun J M. Isochron dating of sand-loess-soil deposits from the Mu Us Desert margin, central China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6(6): 556-563. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.08.004
[26] Li S H, Chen Y Y, Li B, et al. OSL dating of sediments from deserts in northern China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1-4): 23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.034
[27] 唐克丽, 贺秀斌. 黄土高原全新世黄土-古土壤演替及气候演变的再研讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(2):129-139 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.02.002
TANG Keli, HE Xiubin. Re-discussion on loess-paleosol evolution and climatic change on the Loess-Plateau during the Holocene [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(2): 129-139. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.02.002
[28] Forman S L. Late Pleistocene chronology of loess deposition near Luochuan, China [J]. Quaternary Research, 1991, 36(1): 19-28. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90014-V
[29] Lu Y C, Wang X L, Wintle A G. A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130, 000yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1): 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
[30] 岳乐平, 屈红军, 杨永利, 等. 兰州九洲台黄土剖面古地磁研究[J]. 西北大学学报, 1992, 22(1):87-94
YUE Leping, QU Hongjun, YANG Yongli, et al. Paleomagnetic research of loess section from Jiuzhoutai, Lanzhou [J]. Journal of Northwest University, 1992, 22(1): 87-94.
[31] Sun Y B, Wang X L, Liu Q S, et al. Impacts of post-depositional processes on rapid monsoon signals recorded by the last glacial loess deposits of northern China [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 289(1-2): 171-179.
[32] Chen F H, Li J J, Zhang W X. Loess stratigraphy of the Lanzhou profile and its comparison with deep-sea sediment and ice core record [J]. GeoJournal, 1991, 24(2): 201-209.
[33] Sun J M. Origin of eolian sand mobilization during the past 2300 years in the Mu Us Desert, China [J]. Quaternary Research, 2000, 53(1): 78-88. doi: 10.1006/qres.1999.2105
[34] 何忠, 周杰, 赖忠平, 等. 石英光释光测年揭示的晚第四纪毛乌素沙地演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29(4):744-754 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.04.10
HE Zhong, ZHOU Jie, LAI Zhongping, et al. Late Pleistocene sand dune development and climatic changes in the Mu Us Desert, China based on luminescence dating [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29(4): 744-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.04.10
[35] 王丰年, 李保生, 牛东风, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域MGS1层段粒度与CaCO3记录的全新世千年尺度的气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(2):331-339
Wang Fengnian, Li Baosheng, Niu Dongfeng, et al. Holocene millennial scale climate variations from records of grain size and CaCO3 in MGS1 segment of Milanggouwan section in the Salawusu River Valley, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2012, 32(2): 331-339.
[36] Niu D F, Li B S, Du S H, et al. Cold events of Holocene indicated by primary elements distribution of the high-resolution sand dunes in the Salawusu River Valley [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2008, 18(1): 26-36. doi: 10.1007/s11442-008-0026-4
[37] Li S H, Sun J M, Li B. Holocene environmental changes in central Inner Mongolia revealed by luminescence dating of sediments from the Sala Us River valley [J]. Holocene, 2012, 22(4): 397-404. doi: 10.1177/0959683611425543
[38] 庞奖励, 黄春长, 陈宝群. 黄土高原南部全新世土壤微结构形成机理探讨[J]. 地理研究, 2002, 21(4):487-494 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.04.011
PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, CHEN Baoqun. Genetic and micromorphological studies of the Holocene soil complex on the southern Loess Plateau [J]. Geographical Research, 2002, 21(4): 487-494. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.04.011
[39] 吴锡浩, 安芷生, 王苏民, 等. 中国全新世气候适宜期东亚夏季风时空变迁[J]. 第四纪研究, 1994, 14(1):24-37 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.01.003
WU Xihao, AN Zhisheng, WANG Sumin, et al. The temporal and spatial variation of East-Asian summer monsoon in Holocene optimum in China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1994, 14(1): 24-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.01.003
[40] 靳鹤龄, 董光荣, 苏志珠, 等. 全新世沙漠-黄土边界带空间格局的重建[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(12):969-974 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.12.001
JIN Heling, DONG Guangrong, SU Zhizhu, et al. Reconstruction of the spatial patterns of desert/loess boundary belt in North China during the Holocene [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(12): 969-974. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.12.001
[41] Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3. 5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(1-2): 45-55.
[42] Lü H Y, Wu N Q, Liu T S, et al. Seasonal climatic variation recorded by phytolith assemblages from the Baoji loess sequence in central China over the last 150000 a [J]. Science in China (Series D), 1996, 39(6): 629-639.
[43] 董光荣, 李保生, 高尚玉, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原的第四纪古风成沙[J]. 地理学报, 1983, 38(4):341-347 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1983.04.002
DONG Guangrong, LI Baosheng, GAO Shangyu, et al. The Quaternary ancient eolian sands in the Ordos Plateau [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1983, 38(4): 341-347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1983.04.002
[44] Fang X M, Li J J, van der Voo R, et al. A record of the Blake Event during the last interglacial paleosol in the western Loess Plateau of China [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 146(1-2): 73-82.
[45] Ding Z L, Rutter N W, Liu T S, et al. Correlation of Dansgaard-Oeschger cycles between Greenland ice and Chinese loess [J]. Paleoclimates, 1998, 2(4): 281-291.
[46] 陈发虎, 张宇田, 张维信, 等. 兰州九洲台黄土沉积年代的综合研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1989, 7(3):105-111
CHEN Fahu, ZHANG Yutian, ZHANG Weixin, et al. The comprehensive study on depositional age of Jiuzhoutai loess, Lanzhou [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1989, 7(3): 105-111.
[47] Chen F H, Feng Z D, Zhang J W. Loess particle size data indicative of stable winter monsoons during the last interglacial in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Catena, 2000, 39(4): 233-244. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(00)00083-7
[48] Chen F H, Qiang M R, Feng Z D, et al. Stable East Asian monsoon climate during the Last Interglacial (Eemian) indicated by paleosol S1 in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Global & Planetary Change, 2003, 36(3): 171-179.
[49] Zhang J, Li J J, Guo B H, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age and monsoonal evolution recorded by the thickest Quaternary loess deposit of the Lanzhou region, western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 139: 17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.025
[50] 岳乐平, 雷祥义, 屈红军. 靖远黄土剖面磁性地层的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1991, 11(4):349-353 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.006
YUE Leping, LEI Xiangyi, QU Hongjun. A magnetostratigraphic study on the Jingyuan loess section, Gansu, China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1991, 11(4): 349-353. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.006
[51] Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record [J]. Paleoceanography, 2002, 17(3): 5-1-5-21. doi: 10.1029/2001PA000725
[52] Kukla G, An Z S. Loess stratigraphy in Central China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1989, 72: 203-225. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(89)90143-0
[53] Kalm V E, Rutter N W, Rokosh C D. Clay minerals and their paleoenvironmental interpretation in the Baoji loess section, southern Loess Plateau, China [J]. Catena, 1996, 27(1): 49-61. doi: 10.1016/0341-8162(96)00008-2
[54] Rutter N, Ding Z L, Evans M E, et al. Baoji-type pedostratigraphic section, Loess Plateau, north-central China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(1): 1-22. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90028-S
[55] Guo Z T, Biscaye P, Wei L Y, et al. Summer monsoon variations over the last 1.2 Ma from the weathering of loess-soil sequences in China [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(12): 1751-1754. doi: 10.1029/1999GL008419
[56] Stevens T, Buylaert J P, Thiel C, et al. Ice-volume-forced erosion of the Chinese Loess Plateau global Quaternary stratotype site [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 983. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03329-2
[57] 鹿化煜, Stevens T, 弋双文, 等. 高密度光释光测年揭示的距今约15~10 ka黄土高原侵蚀事件[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(23):2767-2772 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.23.011
LU Huayu, Thomas Stevens, Ge Shuangwen, et al. Erosion events in the Loess Plateau revealed by high density OSL dating in about 15~10 ka [J]. Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(23): 2767-2772. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.23.011
[58] 白凤龙, 朱文中. 兰州西津村黄土剖面及磁性年代的确定[J]. 长安大学学报: 地球科学版, 1986, 8(2):71-75
BAI Fenglong, ZHU Wenzhong. The loess section and magnetic ages of Xijin Village, Lanzhou [J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Earth Science Edition, 1986, 8(2): 71-75.
[59] 雷祥义. 靖远曹岘黄土的形成时代及显微结构特征[J]. 地理学报, 1995, 50(6):521-533 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.06.008
LEI Xiangyi. Formation age and microfabric characteristics of loess in Chaoxian, Jingyuan, Gansu, China [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1995, 50(6): 521-533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.06.008
[60] Berger A, Loutre M F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(4): 297-317. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q
[61] Grossman E L. Oxygen isotope stratigraphy[M]//The Geologic Time Scale. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012: 181-206.
[62] 丁仲礼, 余志伟. 第四纪时期东亚季风变化的动力机制[J]. 第四纪研究, 1995, 15(1):63-74 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.01.007
DING Zhongli, YU Zhiwei. Forcing mechanisms of paleomonsoons over East Asia [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1995, 15(1): 63-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.01.007
[63] Kukla G. Loess stratigraphy in central China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1987, 6(3-4): 191-219. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(87)90004-7
[64] Cheng H, Sinha A, Wang X F, et al. The Global Paleomonsoon as seen through speleothem records from Asia and the Americas [J]. Climate Dynamics, 2012, 39(5): 1045-1062. doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1363-7
[65] An Z S, Liu T S, Zhou Y Z, et al. The paleosol complex S5 in the China Loess Plateau-A record of climatic optimum during the last 1.2 Ma [J]. GeoJournal, 1987, 15(2): 141-143.
[66] 李珍, 李玲琴, 曾永年, 等. 西宁的黄土研究[J]. 青海地质, 1996(2):1-10
LI Zhen, LI Lingqin, ZENG Yongnian, et al. The studies of Xining loess [J]. Geology of Qinghai, 1996(2): 1-10.
[67] Liu L W, Chen J, Ji J F, et al. Variation of Zr/Rb ratios in the Chinese loess deposits during the past 1.8 Myr and its implication for the change of East Asian monsoon intensity [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(10): Q10006.
[68] Lu H Y, Liu X D, Zhang F Q, et al. Astronomical calibration of loess-paleosol deposits at Luochuan, central Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 154(3): 237-246. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00113-3
-



 下载:
下载: