Radiolarian assemblages and their distribution characteristics in surface sediments of Prydz Bay
-
摘要:
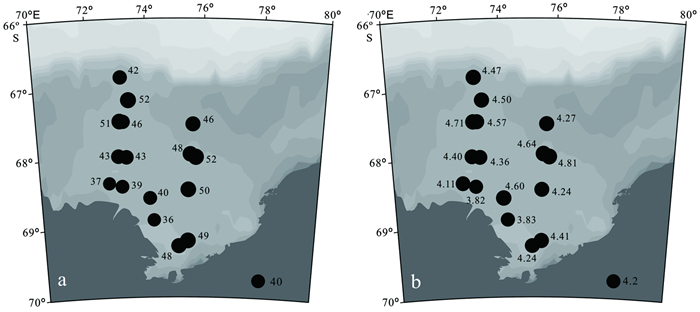
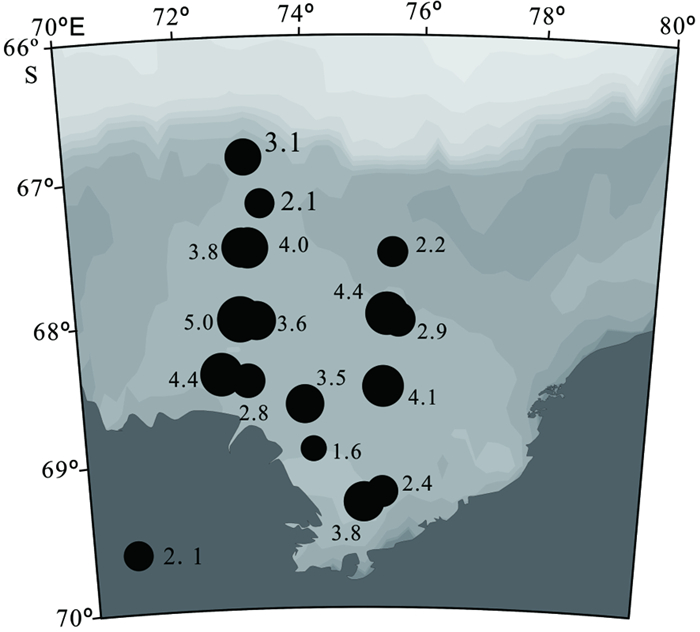
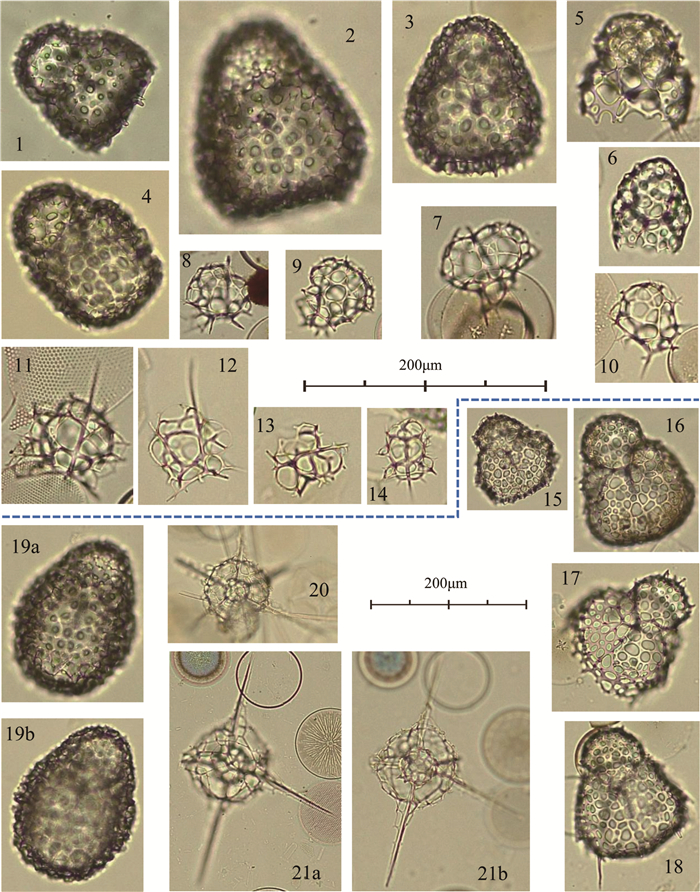
对普里兹湾16个表层沉积物样品中的放射虫动物群进行了全属种鉴定和分析,共检出放射虫2目66属107种,其中罩笼虫目40属71种,泡沫虫目26属36种,前者的属种多样性和个体数量都显著高于后者。研究结果显示:普里兹湾放射虫多样性程度较低,但丰度较高,平均可达3.36万枚/g,呈现出陆架区>湾口区>冰架前缘的趋势,且湾西部高于东部,可能主要受研究区表层生产力、环流结构、沉积物类型和冷水团分布等海洋环境要素的影响。以Antarctissa strelkovi、Antarctissa denticulata为代表的Antarctissa group是该区最典型的优势种组合,平均百分含量高达42.43%,其分布主要受控于水体温度,其高含量具有指示冷水团分布的潜力,而该组合丰度的分布主要受环流和地形的影响; 由Phormacantha hystrix、Plectacantha oikiskos和Rhizoplegma boreale组成的特征种组合平均百分含量为12.54%,其丰度和含量的分布模式主要表征的是与环流结构有关的水团混合作用的强弱,对水深或离岸距离的指示作用并不明显。
Abstract:Radiolarian faunas from 16 surface sediment samples of Prydz Bay are studied by the authors. A total of 2 orders, 66 genera and 107 species are identified, which consists of 71 Nasseillaria species (40 genera) and 36 Spumellaria species (26 genera), of which the former is obviously higher in genus-species diversity and quantity of individuals. Radiolarians in the surface sediments of Prydz Bay are low in diversity but high in abundance, which may reach 3.36×104ind/g (dry sample)on average. The distribution of abundance is in a descending order from the shelf zone, to the mouth of bay and to the front of ice shelf in general, and higher in the west but lower in the east, affected by such environmental factors as surface biological productivity, circulation pattern, sediment type and distribution of cold water mass. The Antarctissa group, mainly composed of Antarctissa strelkovi and Antarctissa denticulata, is the dominating assemblage in Prydz Bay, which may be as high as 42.43% on average depending upon water temperature.Therefore, the high percentage of this assemblage could be used as an indicator of cold water mass. The abundance of the assemblage is also affected by water circulation and subsurface topography. The typical assemblage, which is composed of Phormacantha hystrix, Plectacantha oikiskos and Rhizoplegma boreale, occupies 12.54% in samples. Its distribution pattern of abundance is an indicator to the mixing degree of water mass of concerned circulating currents, but not water depth or the distance to the coast in the bay.
-
Key words:
- surface sediment /
- radiolarian /
- dominant assemblage /
- characteristic assemblage /
- Prydz Bay
-

-
表 1 普里兹湾表层样的站位位置及水深
Table 1. Location and water depth of sampling sites in Prydz Bay
航次 站位 位置 水深/m 环境分区 18 IV-10 67.49°S,73.00°E 587 陆架区 18 IV-08 66.85°S,72.99°E 510 湾口区 21 Ⅲ-13 68.00°S,73.12°E 658 陆架区 21 IS-04 68.90°S,74.08°E 678 冰架前缘 24 IS-02 69.27°S,74.98°E 870 冰架前缘 24 P3-14 67.99°S,72.85°E 647 陆架区 24 P4-11 67.96°S,75.38°E 491 陆架区 24 P4-12 68.47°S,75.32°E 640 陆架区 25 IS-A 68.37°S,72.49°E 828 冰架前缘 27 IS-01 69.20°S,75.31°E 730 冰架前缘 27 IS-06 68.59°S,73.94°E 717 冰架前缘 27 IS-12 68.42°S,72.95°E 748 冰架前缘 27 P3-15 67.49°S,72.94°E 575 陆架区 27 P4-09 67.53°S,75.47°E 421 陆架区 29 M3-old 67.18°S,73.24°E 527 湾口区 29 P6-10 68.00°S,75.57°E 594 陆架区 表 2 普里兹湾表层沉积物中主要放射虫属种百分含量的最大、最小和平均值
Table 2. Maximum, minimum and average percentages of radiolarian species in surface sediments of Prydz Bay
属种名称 最大值/% 最小值/% 平均值/% Antarctissa strelkovi 27.65 13.13 18.86 Antarctissa denticulata 22.32 7.06 14.99 Phormacantha hystrix 9.60 2.53 5.80 Plectacantha oikiskos 10.45 0.00 5.72 Lithomelissa setosa 6.88 2.25 4.42 Antarctissa cylindrica 6.75 1.21 4.07 Arachnocorallium calvata 6.11 1.08 3.80 Eucecryphalus sp. 4.69 0.54 3.22 Antarctissa sp. 6.34 0.85 3.11 Lithomelissa hystrix 4.46 0.63 2.64 Corythospyris sp. 6.02 0.00 2.27 Lithomelissa sp. 3.32 0.32 2.19 Clathrospyris sandellae 3.95 0.96 2.16 Plectacantha sp. 4.26 0.00 2.08 Lithomelissa laticeps 3.92 0.33 1.63 Antarctissa denticulate var. cylindrica 3.57 0.00 1.39 Acrosphaera?labrata 3.41 0.00 1.37 Clathrospyris vogti 3.57 0.27 1.22 Plectacantha group 3.32 0.00 1.06 -
[1] 陈木宏, 谭智源.南海中、北部沉积物中的放射虫[M].科学出版社, 1996.
CHEN Muhong, TAN Zhiyuan. Radiolarians in Sediments of the North and Central of the South China Sea[M]. Science Press, 1996.
[2] 冯庆来.放射虫古生态的初步研究[J].地质科技情报, 1992(2): 41-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000361780
FENG Qinglai. A preliminary study on the radiolarian palaeoecology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1992(2):41-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000361780
[3] 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 向荣, 等.放射虫现代生态学的研究进展及其应用前景——利用放射虫化石揭示古海洋、古环境的基础研究[J].地球科学进展, 2006, 21(5): 474-481. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.05.005
ZHANG Lanlan, CHEN Muhong, XIANG Rong, et al. Progress and prospect in research on living radiolariaecoloy: A basic study of paleoenvironmental and paleoeanographic reconstructions[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(5): 474-481. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.05.005
[4] Abelmann A. Radiolarian taxa from southern-Ocean sediment traps (Atlantic Sector)[J]. Polar Biology, 1992a, 12(3-4): 373-385. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00243108
[5] Goll R M, Bjørklund K R. Radiolaria in surface sediments of the South Atlantic[J]. Micropaleontology, 1974, 20(1): 38-75. doi: 10.2307/1485099
[6] Abelmann A, Brathauer U, Gersonde R, et al. Radiolarian-based transfer function for the estimation of sea surface temperatures in the Southern Ocean (Atlantic Sector)[J]. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14(3): 410-421. doi: 10.1029/1998PA900024
[7] 乐肯堂.普里兹湾及邻近海区水团和环流研究述评[J].海洋科学, 1995, 19(2): 26-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYKX199502013.htm
LE Kentang. Review of the study of water mass and circulation in Prydz Bay and its adjacent sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 1995, 19(2): 26-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYKX199502013.htm
[8] 陈文斌.南极普里兹湾邻近海域表层沉积物中的放射虫[C]//南极科学考察论文集(第二集).北京: 海洋出版社, 1984: 166-179.
CHEN Wenbin. Radiolaria from the surface sediments in adjacent sea of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[C]//A Collection of Antarctic Scientific Explorations(Ⅱ). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984: 166-179.
[9] Nishimura A, Nakaseko K, Okuda Y. A new coastal water radiolarian assemblage recovered from sediment samples from the Antarctic Ocean[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1997, 30(1): 29-44.
[10] 林丽娜.南极普里兹湾及邻近海域水文特征分析[D].国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85301-1014149902.htm LIN Lina. Hydrographic features in the region of Prydz Bay[D]. The First Institute of Oceanography, SOA, 2013.
[11] 史久新.南极冰架-海洋相互作用研究综述[J].极地研究, 2018, 30(3): 287-320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201803005
SHI Jiuxin. A review of ice shelf-ocean interaction in Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2018, 30(3): 287-320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201803005
[12] 董兆乾, 梁湘三.南极海冰, 冰穴和冰川冰及其对水团形成和变性的作用[J].南极研究, 1993, 5(3): 1-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDYZ199303000.htm
DONG Zhaoqian, LIANG Xiangsan. The role of antarctic sea ice, polynyas and glacier ice in formation and modification of the Antarctic water masses[J]. Antarctic Research, 1993, 5(3): 1-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDYZ199303000.htm
[13] 史久新, 乐肯堂.东南极冰-海相互作用研究进展[J].海洋科学, 1999(1): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.1999.01.010
SHI Jiuxin, LE Kentang, A review on studies of ice-ocean interaction in the east Antarctica[J]. Marine Sciences, 1999(1): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.1999.01.010
[14] 蒲书箴, 胡筱敏, 董兆乾, 等.普里兹湾附近绕极深层水和底层水及其运动特征[J].海洋学报, 2002, 24(3): 1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb200203001
PU Shuzhen, HU Xiaomin, DONG Zhaoqian, et al. Features of Circumpolar Deep Water, Antarctic Bottom Water and their movement near the Prydz Bay[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(3): 1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb200203001
[15] Smith N R, Dong Z, Kerry K R, et al. Water masses and circulation in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1984, 31(9): 1121-1147. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(84)90016-5
[16] O'Brien P E, Cooper A K, Richter C, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports Volume 188.R]. Shipboard Scientific Party. Leg 188 Summary: Prydz Bay-Cooperation Sea, Antarctica. 2001.
[17] 侍小兵, 俞光耀, 董兆乾.南极普里兹湾夏季流场诊断分析[J].青岛海洋大学学报, 1995, 25(增刊):293-311. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y131351.aspx
SHI Xiaobing, YU Guangyao, DONG Zhaoqian. Diagnostic analysis ofsummer flow field in Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 1995, 25(Supplement): 293-311. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y131351.aspx
[18] 史久新.南大洋印度洋扇形区南极绕极流和南极沿岸流的相互作用研究[D].中国科学院海洋研究所, 2000.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y360407 SHI Jiuxin. Research of the interaction between Antarctic Circumpolar Current and Antarctic Coastal Current in the Indian Ocean Sector Region of the Southern Ocean[D]. The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2000.
[19] Middleton J H, Hamphries S E. Thermohaline structure and mixing in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Deep Sea Research, 1989, 36(8): 1255-1266. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90104-0
[20] 史久新, 乐肯堂, 于康玲.普里兹湾及其邻近海区冰-海相互作用的数值研究:Ⅱ.环流[J].海洋科学集刊, 2000(1): 22-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKJK200000002.htm
SHI Jiuxin, LE Kentang, YU Kangling. A numerical study of the ice-ocean interaction in the region of Prydz Bay, AntarcticaⅡ.circulation[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 2000(1): 22-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKJK200000002.htm
[21] Shipboard Scientific Party. Leg 188 Summary: Prydz Bay- Cooperation Sea, Antarctica[C]// In: O'Brien P E, Cooper A K, Richter C, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports Volume 188, 2001.
[22] Harris P, Taylor F, Pushina Z, et al.Lithofacies distribution in relation to thegeomorphic provinces of Prydz Bay, East Antarctica[J]. Antarctic Science, 1998, 10(O3):227-235.
[23] 常凤鸣, 庄丽华, 李铁刚, 等.冲绳海槽北部表层沉积物中的放射虫组合[J].海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(2):208-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.02.012
CHANG Fengming, ZHUANG Lihua, LI Tiegang, et al. Modern radiolarian assemblages in surficial sediments of Northern Okinawa Trough[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(2): 208-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.02.012
[24] 王豪壮, 陈志华, 王春娟, 等.普里兹湾陆架表层沉积物粒度特征及其环境指示意义[J].极地研究, 2015, 27(4):421-428. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201504009
WANG Haozhuang, CHEN Zhihua, WANG Chunjuan, et al.Characteristics of grain size in surface sediments from the continental shelf, Prydz Bay, and implications for sedimentary environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2015, 27(4):421-428 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201504009
[25] Martin J H. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: The iron hypothesis[J]. Paleoceanography, 1990, 5(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1029/PA005i001p00001
[26] 刘子琳, 蔡昱明, 宁修仁, 等. 1999/2000年夏季南极普里兹湾及湾口区叶绿素a和初级生产力[J].极地研究, 2001, 13(1): 1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jdyj200101001
LIU Zilin, CAI Yuming, NING Xiuren, et al. Primary productivity and standing stock of phytoplankton in the Prydz Bay and the adjacent northern sea area during the austral summer of 1999/2000[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2001, 13(1): 1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jdyj200101001
[27] 刘子琳, 蔡昱明, 陈中元, 等. 1998/1999年南极夏季普里兹湾及北部海区叶绿素a和初级生产力的分布特征[J].极地研究, 2002, 14(1): 12-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jdyj200201002
LIU Zilin, CAI Yuming, CHEN Zhongyuan, et al. The distribution feature of chlorophyll A and primary productivity in Prydz Bay and its north sea area during the austral summer of 1998/1999[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2002, 14(1): 12-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jdyj200201002
[28] Cai Y M, Ning X R, Zhu G H, Shi J X. Size fractionated biomass and productivity of hytoplankton and new production in the Prydz Bay and the adjacent Indian sector of the outhern Ocean during the austral summer 1998/1999[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 2(4): 651-670.
[29] 刘诚刚, 宁修仁, 孙军, 等. 2002年夏季南极普里兹湾及其邻近海域浮游植物存量、初级生产力粒级结构和新生产力研究[J].海洋学报, 2004, 26(6): 107-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.06.012
LIU Chengang, NING Xiuren, SUN Jun, et al. Size structure of standing stock and productivity and new production of phytoplankton in the Prydz Bay and the adjacent Indian sector of the Southern Ocean during the austral summer of 2001/2002[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(6): 107-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.06.012
[30] 邱雨生, 黄奕普, 刘广山, 等.南极普里兹湾及邻近海域初级生产力的时空变异[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 43(5): 676-681. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xmdxxb200405023
QIU Yusheng, HUANG Yipu, LIU Guangshan, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of primary productivity in Prydz Bay and its adjacent sea area, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2004, 43(5): 676-681. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xmdxxb200405023
[31] 孙维萍, 扈传昱, 韩正兵, 等. 2011年南极夏季普里兹湾营养盐与浮游植物生物量的分布[J].极地研究, 2012, 24(2): 178-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201202010
SUN Weiping, HU Chuanyu, HAN Zhengbing, et al. Distribution of nutrients and Chla in Prydz Bay during the austral summer of 2011[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2012, 24(2): 178-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201202010
[32] 陈际雨, 韩正兵, 扈传昱, 等.南极普里兹湾营养盐分布特征及季节性消耗[J].极地研究, 2017, 29(3): 327-337. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201703003
CHEN Jiyu, HAN Zhengbing. HU Chuanyu, et al. Distribution and seasonal depletion of nutrients in Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2012, 24(2): 178-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201703003
[33] Wang R, Abelmann A. Radiolarian responses to paleoceanographic events of the southern South China Sea during the Pleistocene[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2002, 46(1): 25-44. http://openurl.ebscohost.com/linksvc/linking.aspx?stitle=Marine%20Micropaleontology&volume=46&issue=1&spage=25
[34] 王汝建, 陈荣华, 肖文申.白令海表层沉积物中放射虫的深度分布特征及其海洋学意义[J].微体古生物学报, 2005, 22(2): 127-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2005.02.002
WANG Rujian, CHEN Ronghua, XIAO Wenshen. Depth distribution pattern of radiolarians in surface sediments of the Bering Sea and their oceanographic implications[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2005, 22(2): 127-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2005.02.002
[35] Abelmann A, Gowing M M. Spatial distribution pattern of living polycystine radiolarian taxa — baseline study for paleoenvironmental reconstructions in the Southern Ocean (Atlantic sector)[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1997, 30(1-3): 3-28. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8398(96)00021-7
[36] 沈国英, 施并章.海洋生态学(第二版)[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002.
SHEN Guoying, SHI Bingzhang. Marine Ecology(Second Edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002.
[37] 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 陆钧, 等.南海南部上层水体中多孔放射虫的组成与分布特征[J].热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(3):55-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.008
ZHANG Lanlan, CHEN Muhong, LU Jun, et al. Living polycystine radiolarian fauna in upper water column of southern South China sea and its distribution[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(3): 55-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.008
[38] Shannon C E, Winner W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication[M]. Urbana: Universit y of Illinois Press, 1949.
[39] 许新雨.夏季极地海洋的初级生产力[D].厦门大学, 2014.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2401822 XU Xinyu. Primary productivity of the polar ocean in summer[D]. Xiamen University, 2014.
[40] 于培松.南极普里兹湾海洋沉积记录及其对气候变化的响应[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80068-1013299963.htm YU Peisong. Ocean sedimental records and their respones to climate change in Prydz Bay, Antarctica[D]. Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Institute of Oceanology), 2013.
[41] Abelmann A. Radiolarian flux in Antarctic waters (Drake Passage, Powell Basin, Bransfield Strait)[J]. Polar Biology, 1992b, 12(3-4): 357-372.
[42] Popofsky A. Die Radiolarien der Antarktis (mitAusnahme der Tripyleen). Deutsche Südpolar-Exped. 1901-1903[R]. 1908, 10 (Zool. 2). 3: 183-105.
[43] Petrushevskaya M G. Radiolarii otryadov Spumellaria i Nassellaria Antarkticheskoi oblasti (po materialam Sovetskoi, Antarkticheskoi Ekspeditsii)[J]. Issled Fauny Morei, 1967, 4(3): 2-186.
[44] Abelmann A, Nimmergut A. Radiolarians in the Sea of Okhotsk and their ecological implication for paleoenvironmental reconstructions[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2005, 52(16): 2302-2331. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8772e876e1ea8ceb5efb85801d10187b
[45] Itaki T, Kim S, Rella S F, et al. Millennial-scale variations of late Pleistocene radiolarian assemblages in the Bering Sea related to environments in shallow and deep waters[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part Ⅱ, 2012, 61-64: 127-144. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2011.03.002
[46] Jorgensen E. Protophyten und Protozoenim plankton aus der norwegischen Westktiste[Z]. Bergens Museums Aarbog, 1899, 6: 5l-95.
[47] Jergensen E. The protist plankton and the diatoms in bottom samples[Z]. Bergen Museum Skrifter, 1905, 7: 49-225.
[48] Bjorklund K R. Radiolaria from the Norwegian sea, Leg 38 of the Deep Sea Drilling Project[C]//Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, 38. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington D C, 1976: 1101-1168.
[49] Cleve P T. Plankton collected by Swedish Expedition to Spitzbergen in 1898[Z]. Kongl Svensk Vetensk Akad Handl, 1898, 32: 3-47.
[50] Swanberg N R, Bjørklund K R. The radiolarian fauna of western Norwegian fjords: Patterns of abundance in the plankton[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1986, 11(1): 231-241. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0377839886900174
[51] 严金辉, 李锐祥, 侍茂崇, 等. 2011年1月普里兹湾埃默里冰架附近水文特征[J].极地研究, 2012, 24(2): 101-109. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201202001
YAN Jinhui, LI Ruixiang, SHI Maochong, et al. Oceanographic features near the Amery Ice Shelf in Prydz Bay, Antarctica, January 2011[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2012, 24(2): 101-109. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdyj201202001
[52] Ikenoue T, Takahashi K, Tanaka S. Fifteen year time-series of radiolarian fluxes and environmental conditions in the Bering Sea and the central subarctic Pacific, 1990-2005[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part Ⅱ, 2012, 61-64: 17-49. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2011.12.003
[53] Nishimura A, Nakaseko K. Characterization of radiolarian assemblages in the surface sediments of the Antarctic Ocean[J]. Palaeoworld, 2011, 20(2): 232-251. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1871174X11000205/pdfft?md5=5c602d54650a658fb9c3e83caf39997e&pid=1-s2.0-S1871174X11000205-main.pdf
-




 下载:
下载: