Surficial distribution of suspended sediment in Beibu Gulf of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
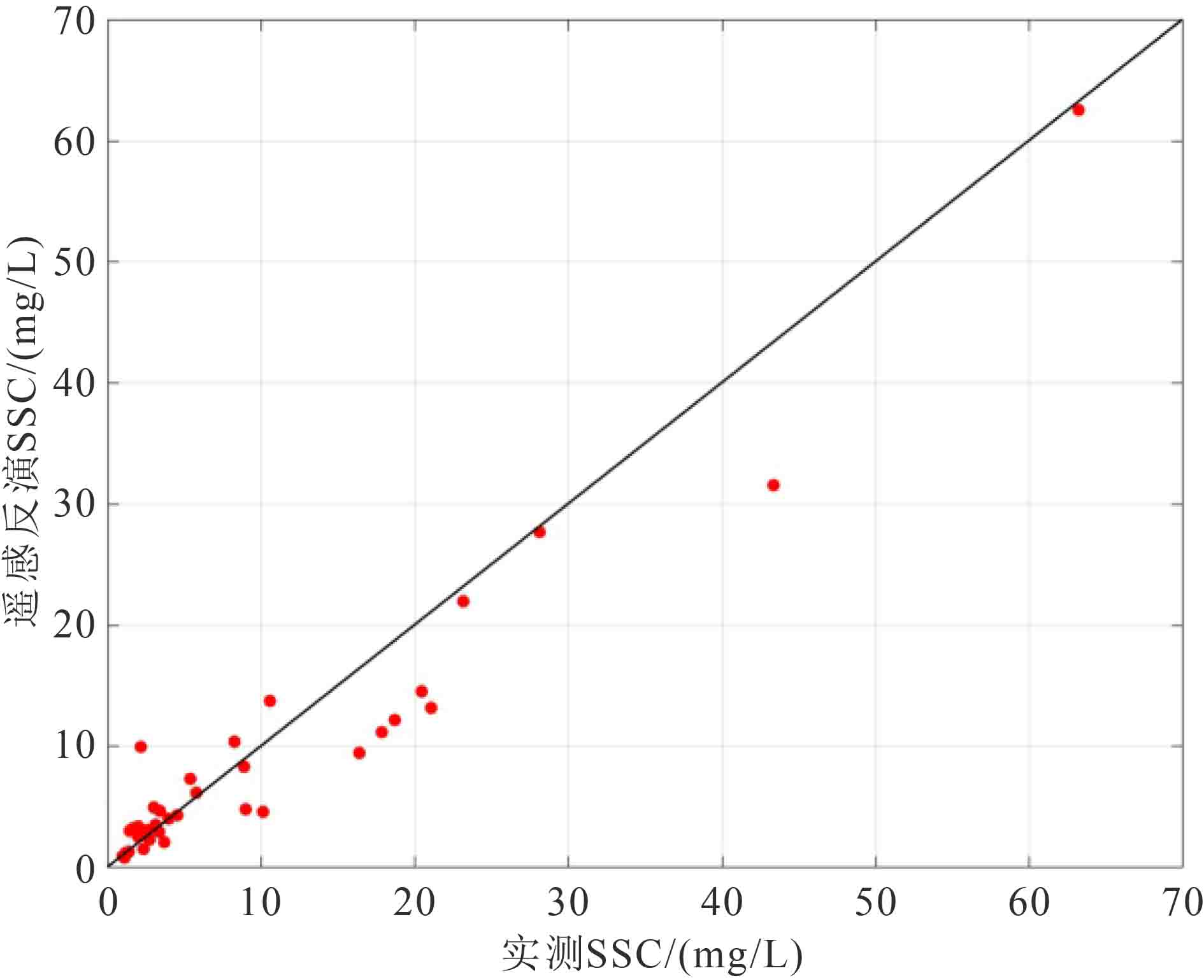
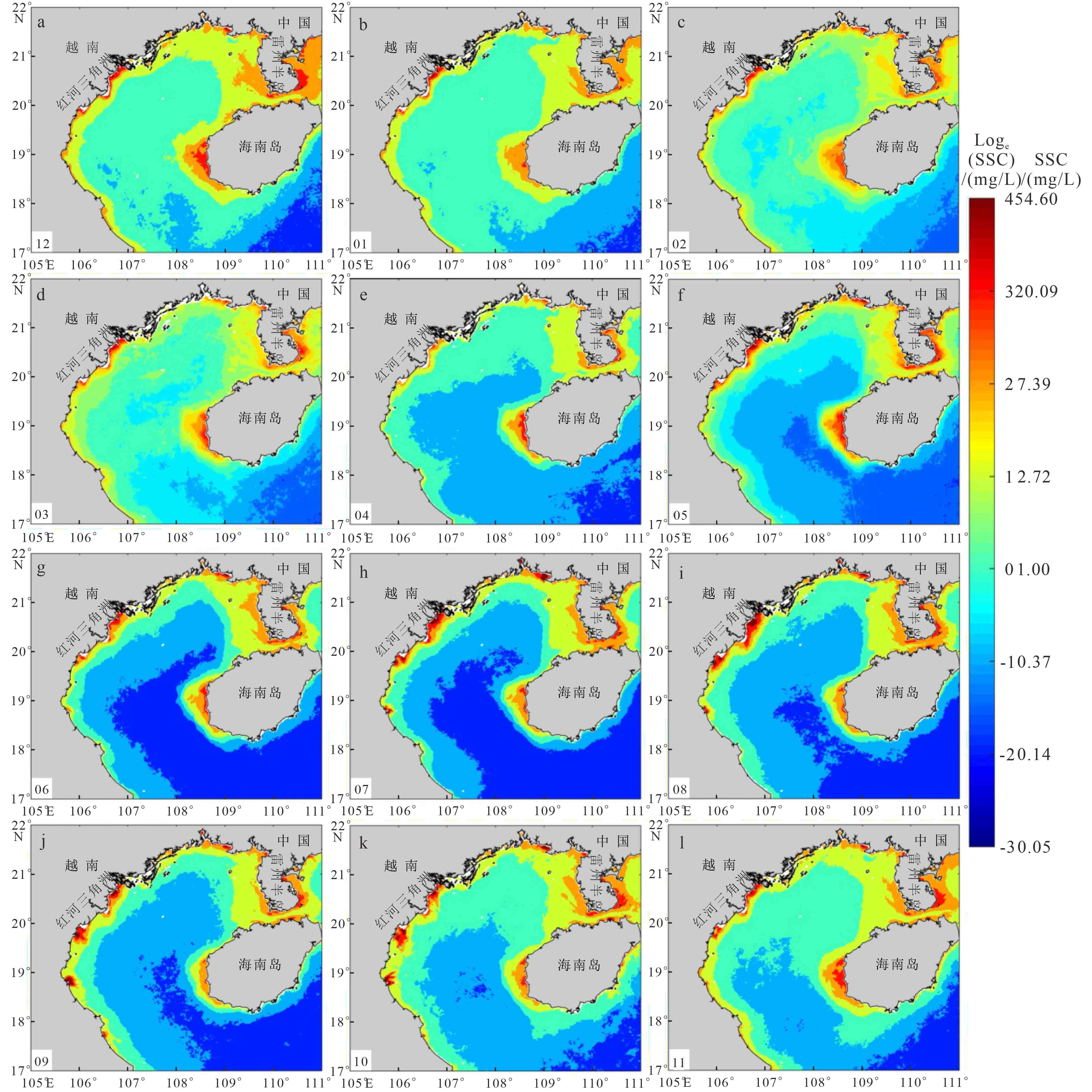
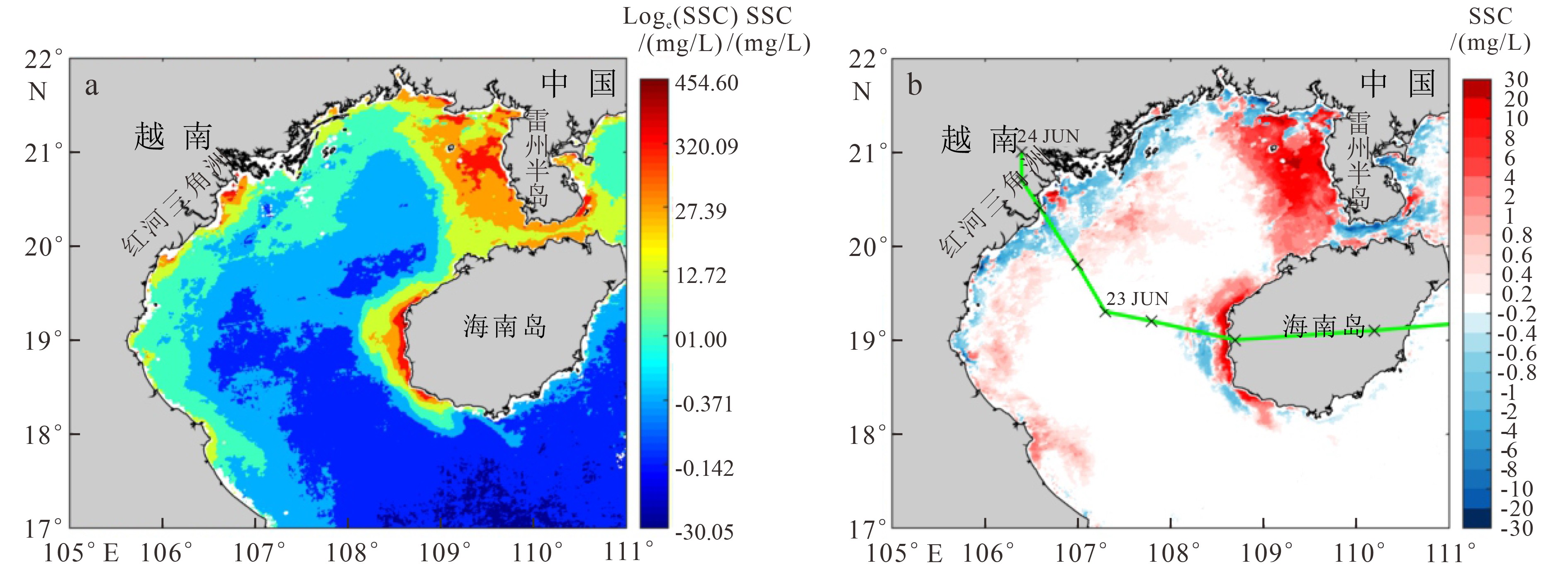
受实测数据海域位置的限制,目前基于遥感手段对北部湾表层悬浮体的研究,在部分海域如海湾西部精度不高,且缺乏对悬浮体浓度(suspended sediment concentration,SSC)季节变化的研究。基于2003—2017年MODIS-Aqua卫星L1B数据,结合海南岛西部、广西沿岸和越南沿岸实测数据,建立表层SSC的反演模型,获得北部湾海域2003—2017年月均表层SSC分布,并对其影响因素进行初步探讨。结果显示:北部湾表层SSC存在3个终年高值区,包括广西沿岸、海南岛西侧和红河三角洲沿岸;受河流输沙和海洋动力季节变化影响,SSC表现为冬季和夏季较高、春季最低的季节变化特征;热带气旋过境导致北部湾海域SSC增高,其中热带风暴“贝碧嘉”过境时位于路径右侧的雷州半岛西部SSC较多年平均值增幅达75%。
Abstract:The study of surficial suspended matter based upon remote sensing is not accurate enough in Beibu Gulf, especially in the western part of the Gulf, due to location constraint. In addition, the data on seasonal variation in suspended sediment concentration (SSC) is lacking in the area. In this paper, a retrieval algorithm for surficial suspended sediment concentration was established by analyzing the images from the MODIS-Aqua satellite in the years from 2003-2017 and the in situ measured data from the Gulf, and thus the distribution of surficial SSC in Beibu Gulf is revealed and carefully studied. The results suggest that the main high-value areas of the surficial suspension are located along the coast of Guangxi, the west side of Hainan Island and the Red River Delta. Under the influence of fluvial sediment transport and ocean dynamics, SSC are higher in winter and summer rather than other seasons in the coastal areas, and reaches the lowest in spring. The transit of tropical cyclones will lead to the increase in SSC. SSC on the west side of Leizhou Peninsula increased by 75% compared with the multi-year average owing to the transit of tropical storm Bebinca.
-
Key words:
- MODIS /
- suspended sediment /
- seasonal variations /
- Beibu Gulf
-

-
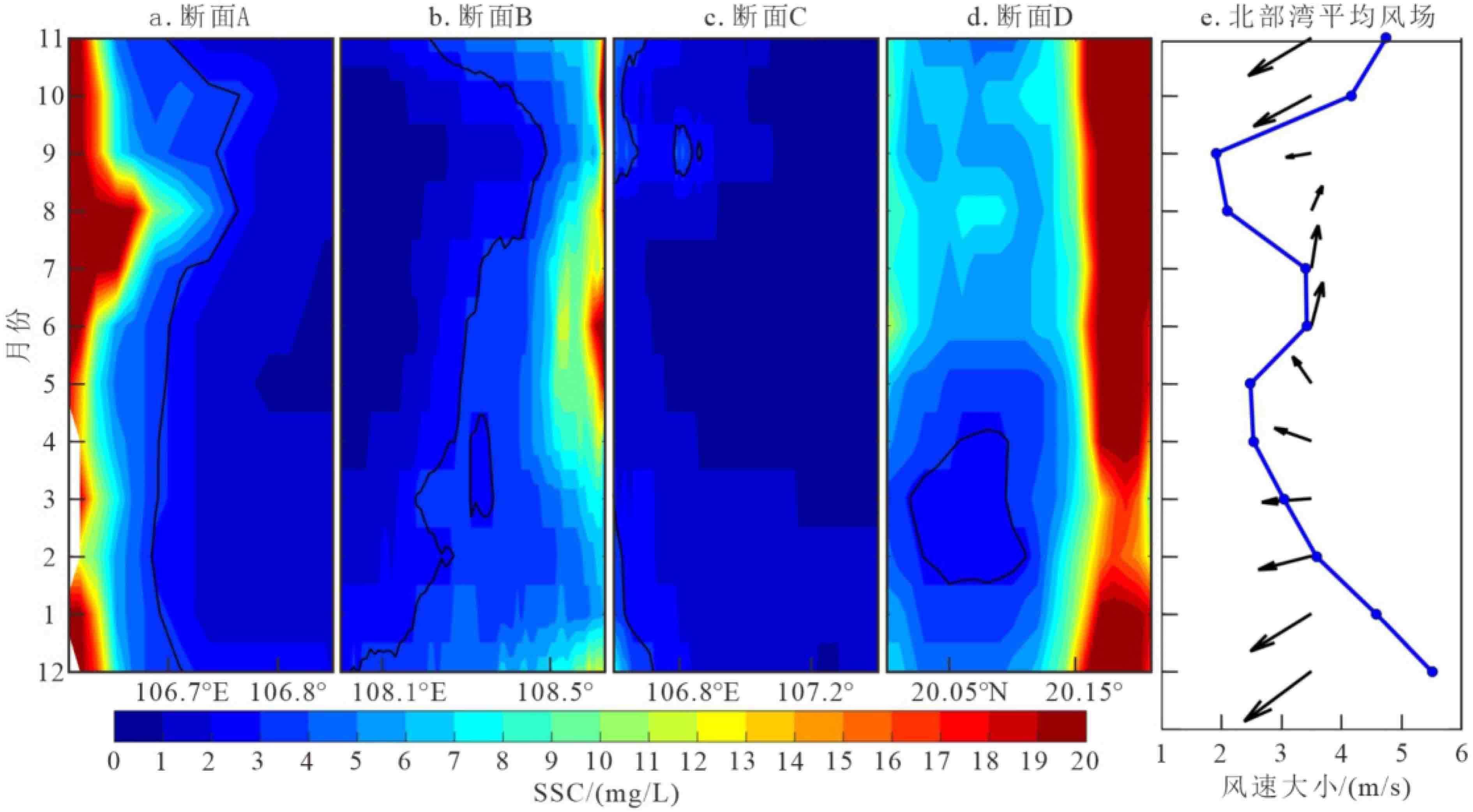
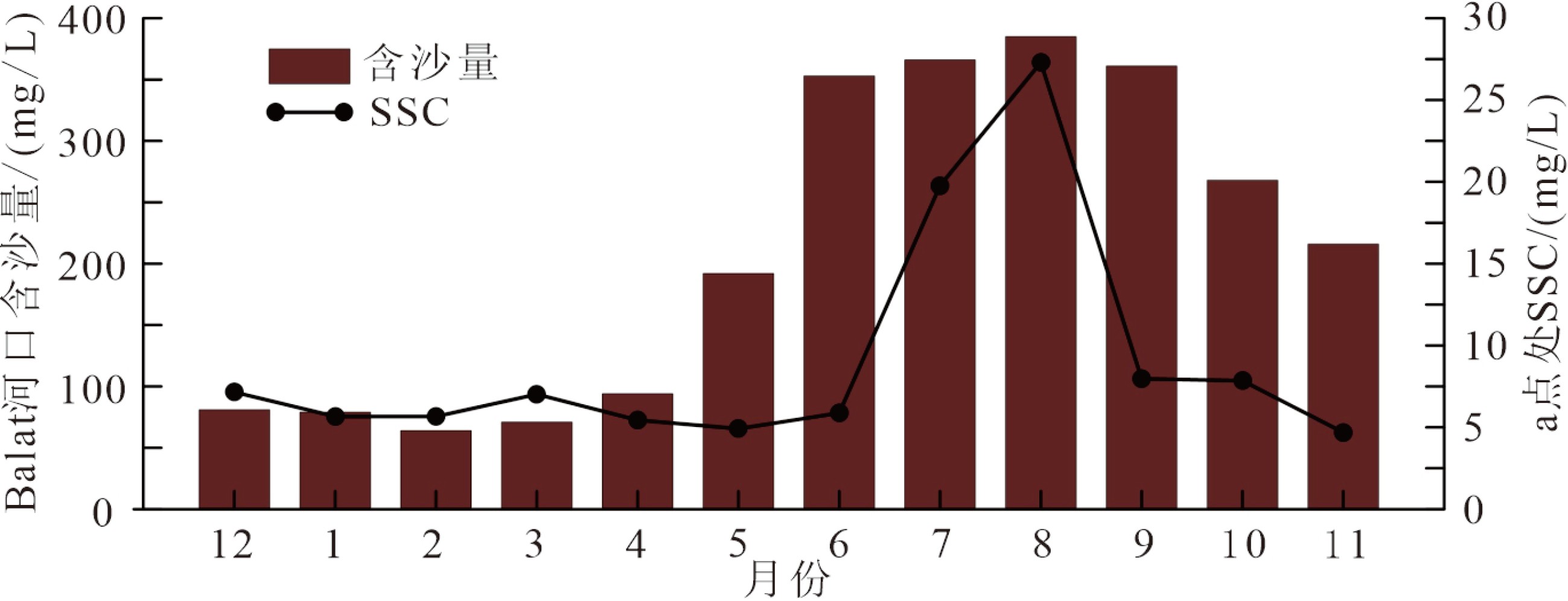
图 8 昌化江下游水体多年月平均含沙量[25]及b站处多年月平均SSC分布
Figure 8.
-
[1] 李高聪, 高抒, 戴晨. 海南岛主要入海河流流域地貌演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(1):121-130 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.12
LI Gaocong, GAO Shu, DAI Chen. Geomorphological evolution of major catchment basins of Hainan Island, southern China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1): 121-130. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.12
[2] 麻德明, 丁绍昆, 谢宜欣. 基于DEM的北部湾入海河流汇水区及子流域划分[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(9):99-103 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.09.020
MA Deming, DING Shaokun, XIE Yixin. Division of river catchment and sub-catchment in Beibu Gulf based on DEM [J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(9): 99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.09.020
[3] 李军, 高抒, 曾志刚, 等. 长江口悬浮体粒度特征及其季节性差异[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(5):499-510 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.005
LI Jun, GAO Shu, ZENG Zhigang, et al. Particle-size characteristics and seasonal variability of suspended particulate matters in the Changjiang River estuary [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(5): 499-510. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.005
[4] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 张东奇, 等. 冬、夏季东海北部悬浮体分布及海流对悬浮体输运的阻隔作用[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(5):71-80
GUO Zhigang, YANG Zuosheng, ZHANG Dongqi, et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended matter in the northern East China Sea and barrier effect of current circulation on its transport [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(5): 71-80.
[5] 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室. 中越合作北部湾海洋综合调查报告[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, 1964.
Scientific and Technical Committee of the People’s Republic of China Ocean Group Integrated Marine Investigation Office. A report of comprehensive marine survey of Beibu gulf and Vietnam[R]. Beijing: Scientific and Technical Committee of the People’s Republic of China Ocean Group Integrated Marine Investigation Office, 1964.
[6] 中越北部湾海洋综合调查队. 中越北部湾海洋综合调查报告[R]. 北京: 国家科委, 1965.
China-Vietnam Joint Oceanic Comprehensive Survey Team. China–Vietnam Beibu Gulf comprehensive survey report[R]. Beijing: State Science and Technology Commission, 1965.
[7] 胡建宇, 杨圣云. 北部湾海洋科学研究论文集[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008.
HU Jianyu, YANG Shengyun. Proceedings of Marine Science Research in Beibu Gulf[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2008.
[8] Chen Z Q, Hu C M, Muller-Karger F. Monitoring turbidity in Tampa Bay using MODIS/Aqua 250-m imagery [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2007, 109(2): 207-220. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2006.12.019
[9] 申力, 许惠平, 吴萍. 基于光谱特征的MODIS影像东海水体类别信息提取[J]. 遥感信息, 2011(3):71-76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2011.03.013
SHEN Li, XU Huiping, WU Ping. Water class extraction of the East China Sea using MODIS data based on spectral characteristics [J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2011(3): 71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2011.03.013
[10] 余佳, 王厚杰, 毕乃双, 等. 基于MODIS L1B数据的黄海悬浮体季节性分布的反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1):1-9
YU Jia, WANG Houjie, BI Naishuang, et al. Seasonal distribution and variation of suspended sediment in the Yellow Sea in 2010 based on retrieved monthly data from MODIS L1B imagery [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 1-9.
[11] 贾丽莉, 张安定, 吴孟泉. 基于MODIS的2013年黄海海域浒苔灾害的时空分布[J]. 鲁东大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 31(2):172-177
JIA Lili, ZHANG Anding, WU Mengquan. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristic of enteromorpha in Shandong Peninsula in 2013 on the basis of MODIS data [J]. Journal of Ludong University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 31(2): 172-177.
[12] 李占海, 柯贤坤, 王倩, 等. 琼州海峡水沙输运特征研究[J]. 地理研究, 2003, 22(2):151-159 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003
LI Zhanhai, KE Xiankun, WANG Qian, et al. Characteristics of water and sediment transport in the Qiongzhou Strait [J]. Geographical Research, 2003, 22(2): 151-159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003
[13] 杨海丽, 郑玉龙, 黄稚. 海南近海海域浊度与悬浮颗粒物粒径的分布特征[J]. 海洋学研究, 2007, 25(1):34-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2007.01.004
YANG Haili, ZHENG Yulong, HUANG Zhi. Characteristics of turbidity and suspended particle size distribution on adjacent area of Hainan [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2007, 25(1): 34-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2007.01.004
[14] 许晟轶. 广西重点港湾流场和悬浮泥沙输移数值模拟[D]. 华东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2010.
XU Shengyi. Numerical simulation for the current and suspended sediment in the key bays of Guangxi offshore area[D]. Master Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2010.
[15] 谷东起, 吴桑云. 廉州湾南部海域泥沙来源及运移趋势分析[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 2001, 19(1):25-31
GU Dongqi, WU Sangyun. Analysis of the sediment sources and the transport tendency in the southern Lianzhou Bay [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 2001, 19(1): 25-31.
[16] Van Maren D S. Water and sediment dynamics in the Red River mouth and adjacent coastal zone [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29(4): 508-522. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.03.012
[17] 王文娟. 东中国海表层悬浮体分布的遥感反演及输运机制研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2008.
WANG Wenjuan. Study on the suspended matter’s distribution from remote sensing retrieval and its movement mechanisms in the surface layer of the East China Seas[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2008.
[18] 肖晓. 南海北部湾底质沉积物粒度和泥沙运移趋势研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
XIAO Xiao. Surface sediment grain size and transport of the Beibu Gulf in South China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[19] 孟凡晓, 陈圣波, 张国亮, 等. 基于Landsat-8数据南海近岸悬浮泥沙与叶绿素a浓度定量反演[J]. 世界地质, 2017, 36(2):616-623, 642 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2017.02.029
MENG Fanxiao, CHEN Shengbo, ZHANG Guoliang, et al. Quantitative inversion of nearshore suspended sediment and chlorophyll-a concentration based on Landsat-8 data in South China Sea [J]. Global Geology, 2017, 36(2): 616-623, 642. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2017.02.029
[20] Tang D L, Kawamura H, Lee M A, et a1. Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 85(4): 475-483. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00049-X
[21] 黄以琛, 李炎, 邵浩, 等. 北部湾夏冬季海表温度、叶绿素和浊度的分布特征及调控因素[J]. 厦门大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 47(6):856-863
HUANG Yichen, LI Yan, SHAO Hao, et al. Seasonal variations of sea surface temperature, chlorophyll-a and turbidity in Beibu Gulf, MODIS imagery study [J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2008, 47(6): 856-863.
[22] 黄以琛. 基于MODIS的北部湾与台湾海峡浊度季节分布及机制研究[D]. 厦门大学硕士学位论文, 2008.
HUANG Yichen. Seasonal distribution and mechanism of turbidity in Beibu Gulf and Taiwan Strait by MODIS[D]. Master Dissertation of Xiamen University, 2008.
[23] 李薛. 基于卫星遥感与再分析资料研究南海上层水体对台风的响应[D]. 广东海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2017.
LI Xue. Studying upper ocean of South China Sea responses to typhoon based on remote-sensing data and reanalysis data[D]. Master Dissertation of Guangdong Ocean University, 2017.
[24] 高婕. 基于遥感分析的海南省昌化江河口泥沙运移模式研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2014.
GAO Jie. Research of sediment transport model of Changhua river estuary in Hainan province based on the analysis of remote sensing[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[25] 张黎明, 魏志远, 曹启民, 等. 近40年来海南省三大河下游水体的含沙量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境, 2006, 15(4):765-769
ZHANG Liming, WEI Zhiyuan, CAO Qimin, et al. Characteristics and impact factors of sediment concentration in lower reaches of three great rivers of Hainan province in the recent 40 years [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2006, 15(4): 765-769.
[26] 王震, 乔璐璐, 王云飞. 东中国海表层悬浮体浓度卫星遥感反演研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(2):292-307
WANG Zhen, QIAO Lulu, WANG Yunfei. Progress on retrieval models of suspended sediment concentration from satellite images in the Eastern China Seas [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(2): 292-307.
[27] Zhang M W, Tang J W, Dong Q, et al. Retrieval of total suspended matter concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS imagery [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2010, 114(2): 392-403. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.09.016
[28] 于向东. 北部湾边界: 海域划界的成功实践[J]. 东南亚纵横, 2005(1):44-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2479.2005.01.010
YU Xiangdong. The Tonkin Bay border, a successful case of solving the dispute over border division of sea area [J]. Around Southeast Asia, 2005(1): 44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2479.2005.01.010
[29] 俎婷婷. 北部湾环流及其机制的分析[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2005.
ZU Tingting. Analysis of the current and its mechanism in the Gulf of Beibu[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2005.
[30] Gao J S, Xue H J, Chai F, et al. Modeling the circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea [J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2013, 63(8): 979-93. doi: 10.1007/s10236-013-0636-y
[31] 陈振华. 北部湾环流季节变化的数值模拟与动力机制分析[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2013.
CHEN Zhenhua. Numerical simulation on seasonal variation of ocean circulation and its dynamic mechanism in the Beibu Gulf[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2013.
[32] 高劲松, 陈波. 北部湾冬半年环流特征及驱动机制分析[J]. 广西科学, 2014, 21(1):64-72
GAO Jingsong, CHEN Bo. Analysis on characteristics and formation mechanism of the winter boreal circulation in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2014, 21(1): 64-72.
[33] 侍茂崇. 北部湾环流研究述评[J]. 广西科学, 2014, 21(4):313-324 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.001
SHI Maochong. Study comments on circulation in Beibu Gulf [J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2014, 21(4): 313-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.001
[34] 高劲松, 陈波, 侍茂崇. 北部湾夏季环流结构及生成机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 58(2):286-299 doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4916-2
GAO Jingsong, CHEN Bo, SHI Maochong. Summer circulation structure and formation mechanism in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(2): 286-299. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4916-2
[35] 丁扬. 南海北部环流和陆架陷波研究[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2015.
DING Yang. Investigation on the circulation and coastal trapped waves in the northern South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[36] 方雪原, 娄安刚, 贺成奇. 北部湾冬季风生环流的数值模拟及其对海洋环境的影响分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2015(1):129-133
FANG Xueyuan, LOU Angang, HE Chengqi. Numerical simulation of wind-driven circulation and its impact on marine environment in winter of the Beibu Gulf [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015(1): 129-133.
[37] 曹振轶, 鲍敏, 管卫兵, 等. 北部湾东北部水团分布及季节变化分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(3):532-542 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190100007
CAO Zhenyi, BAO Min, GUAN Weibing, et al. Water-mass evolution and the seasonal change in northeast of the Beibu Gulf, China [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(3): 532-542. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190100007
[38] 许冬, 初凤友, 李家彪, 等. 粤西-琼东北近海沉积物的运移和沉积[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(3):905-917
XU Dong, CHU Fengyou, LI Jiabiao, et al. Transport and deposition of sediment on the shelf off western Guangdong to northeastern Hainan [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(3): 905-917.
[39] 陈达森, 陈波, 严金辉, 等. 琼州海峡余流场季节性变化特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2006(2):12-17 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003
CHEN Dasen, CHEN Bo, YAN Jinhui, et al. The seasonal variation characteristics of residual currents in the Qiongzhou Strait [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2006(2): 12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003
[40] Shi M C, Chen C S, Xu Q C, et al. The role of Qiongzhou strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation [J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2002, 32(1): 103-121. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2002)032<0103:TROQSI>2.0.CO;2
[41] Le DucCuong. 北部湾海域沉积动力环境对台风“威马逊”响应的数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2019.
Le D C. Numerical Simulation of the Sedimentary Dynamic Changes Response to the Super Typhoon Rammasun in the Gulf of Tonkin[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2019.
[42] 杨亚新, 夏剑东. 西北太平洋热带气旋活动特征[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(2):114-119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.02.022
YANG Yaxin, XIA Jiandong. Characteristics of northwest Pacific tropical cyclones [J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(2): 114-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.02.022
[43] Qiao L L, Liu S D, Xue W J, Liu P, et al. Spatiotemporal variations in suspended sediments over the inner shelf of the east China sea with the effect of oceanic fronts[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106600.
[44] 谷国传, 胡方西. 我国沿海近岸带水域的悬沙分布特征[J]. 地理研究, 1989, 8(2):1-15
GU Guochuan, HU Fangxi. The characteristics of the distribution of the suspended sediments in coastal regions of China [J]. Geographical Research, 1989, 8(2): 1-15.
[45] 黎树式. 南亚热带独流入海河流水沙变化过程研究——以南流江为例[D]. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 2017.
GU Guochuan, HU Fangxi. The characteristics of the distribution of the suspended sediments in coastal regions of China[J]. Geographical Research, 1989, 8(2): 1-15.
[46] 黎树式, 黄鹄. 近50年钦江水沙变化研究[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(4):409-417
LI Shushi, HUANG Hu. Variations of runoff and sediment in Qinjiang River in the past 50 years [J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2018, 25(4): 409-417.
-




 下载:
下载: