Characteristics of quartz grains in the red clay of Tongling City and their environmental implications
-
摘要:
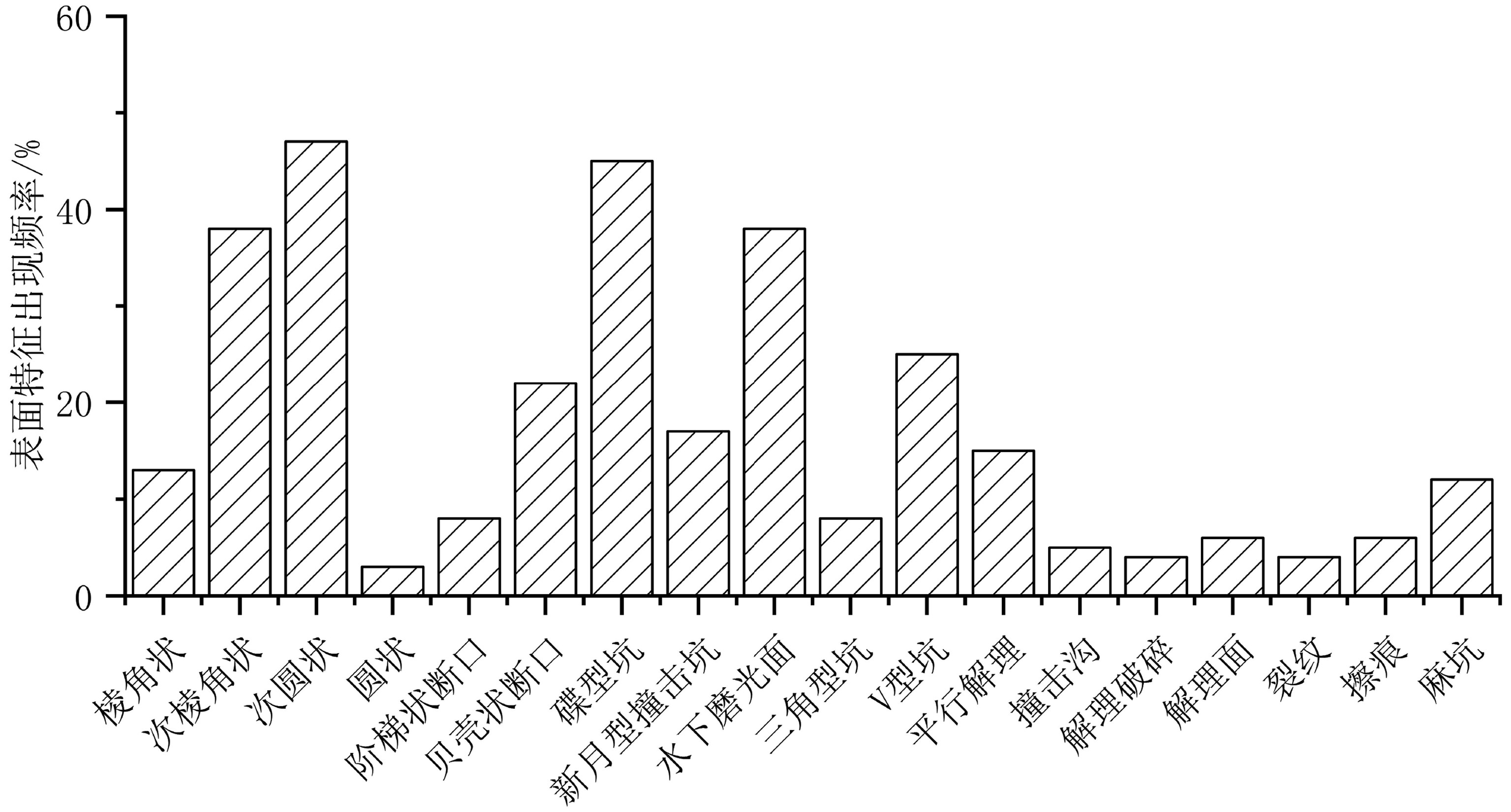
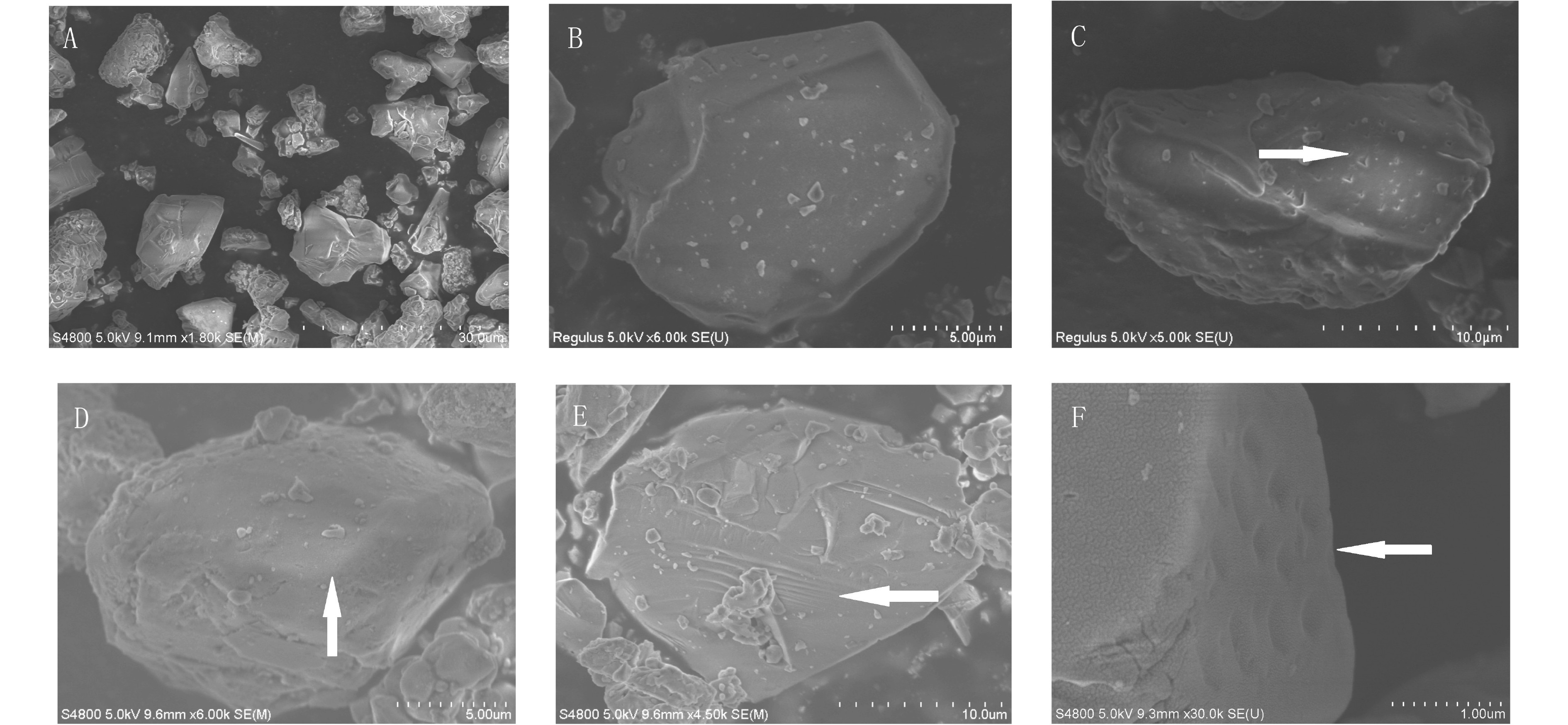
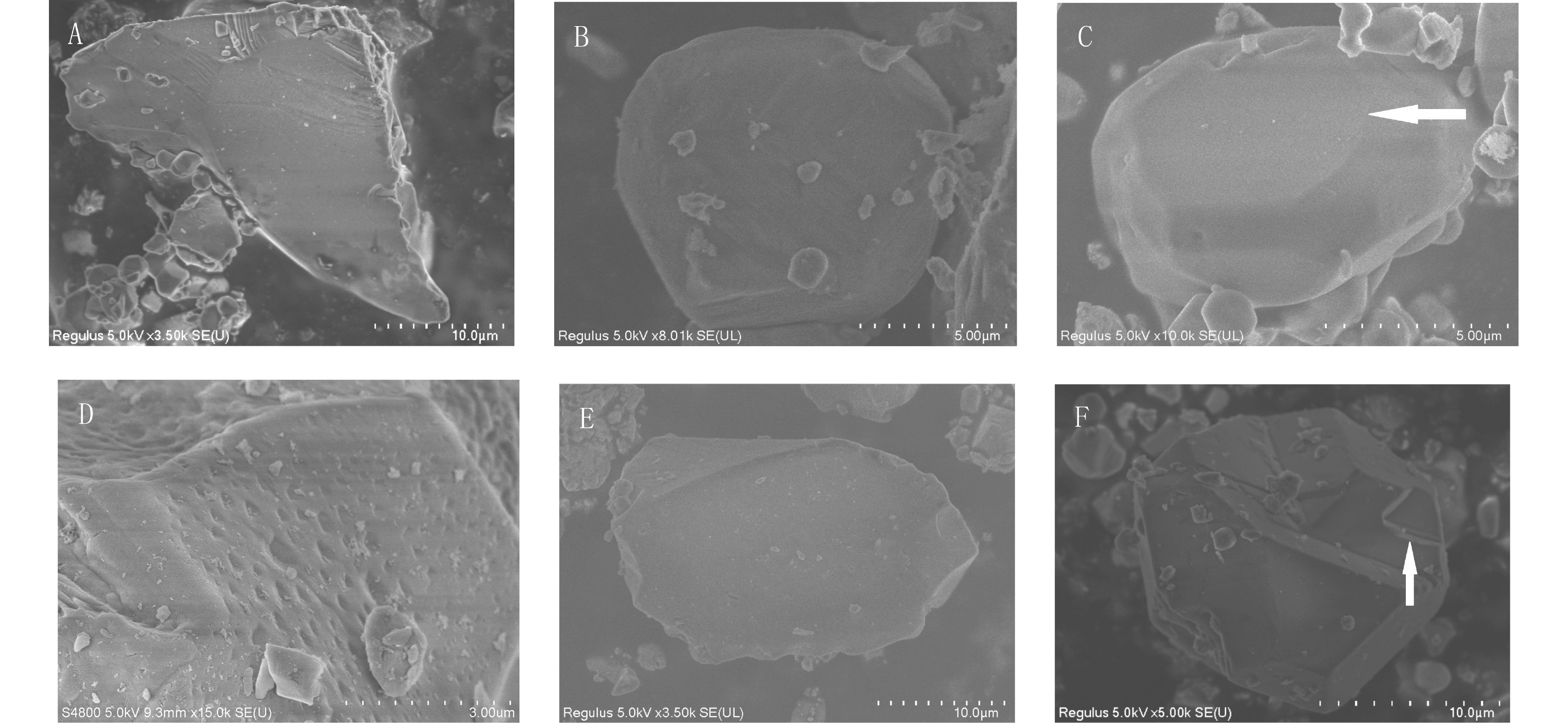
目前我国南方网纹红土的成因、物源存在争议,通过分析铜陵红土剖面石英粒度和石英颗粒表面形态特征,并结合已发表年代数据探讨了红土沉积物的搬运动力和物质来源。结果表明,铜陵剖面石英粒度表现出明显的风力搬运特征,粒径整体偏细,剖面自下而上粒径变粗,粗粉砂(10~50 μm)组分为众数粒组,粒度频率分布曲线总体呈现出双峰且主峰明显的特征,并在粗粒端含有隐峰,颗粒总体分选较差,呈正偏态,峰态尖锐;石英颗粒大多呈次棱角状或次圆状,颗粒表面既出现水下磨光面、V型坑、三角型坑等水成特征,也出现碟型坑、新月型坑、麻坑等风成特征,还具有两种特征叠加的现象。剖面自上而下颗粒磨圆度逐渐变好,风成特征更加明显。综合分析推测铜陵网纹红土是风力搬运近源与远源物质共同沉积,并随着东亚季风的变化,不同物源区物质的贡献程度也发生转变。
Abstract:Hot debate has been occurred for long concerning the origin and provenance of the vermicular red clay in South China. In this paper, transportation mechanism and provenance of the vermicular red clay were studied by means of grain size and surface textures of the quartz grains from the red clay in Tongling city in the south of Anhui province. The quartz grains from the Tongling section show some obvious characteristics of wind transportation. The grains are fine in general and gradually coarsen up from bottom to top. The vermicular red clay is dominated by silt (10~50 μm), ranging from 40.62% to 60.37%. The frequency curves of the quartz grains are essentially bimodal with a low hidden peak in the coarse fraction. And the frequency curves of different layers in the profile shows good consistency. Microscopic images of quartz grains show that they are, in fact, the mixture of rounded and poorly rounded grains. Some particles have obvious hydrodynamic effects remained on the surface, such as underwater polished surfaces, V-shaped pits, etc., some have obvious traces of wind action, such as dish-shaped pits, crescent-shaped pits, etc., while the others show some surface texture jointly formed by hydrodynamic and wind actions, suggesting a mixture of distant and nearby sources. The near-source sediments may come from the floodplain of surrounding rivers, where the hydrological characteristics are retained due to the short-distance of wind transport. The surface of the quartz particles at the bottom of the profile has obvious features of hydrogenic origin, and the aeolian features increase upwards. Finally, it is confirmed that the red vermicular clay in Tongling city is a kind of mixed deposits composed of the particles from near and distant wind sources, and the contribution of the materials of different sources depends upon the change of East Asian monsoon.
-

-
表 1 铜陵剖面石英粒度组成、粒度参数
Table 1. Quartz grain size composition and grain size parameters in Tongling section
层位描述 样品属性 粒度组成/% 粒度参数 <5 μm 5~10 μm 10~50 μm >50 μm 平均粒径Mz 偏度Sk 峰态Kg 分选系数Sd 层I 棕黄色网纹红土层 最大值 35.27 23.80 50.82 5.41 18.20 0.81 1.32 1.75 最小值 26.40 18.17 40.62 0.31 9.87 0.61 1.25 1.51 平均值 29.66 20.40 47.02 2.92 14.26 0.71 1.29 1.63 层II 典型网纹红土层 最大值 27.49 18.11 56.00 7.32 20.82 0.87 1.33 1.77 最小值 22.56 14.32 49.82 3.16 14.78 0.56 1.27 1.65 平均值 24.93 16.48 53.21 5.36 17.97 0.77 1.30 1.70 层III 紫红色网纹红土层 最大值 28.86 17.35 57.19 9.37 23.49 0.83 1.33 1.83 最小值 22.26 14.58 50.66 3.13 14.34 0.66 1.26 1.66 平均值 24.29 15.58 53.89 6.24 19.37 0.76 1.30 1.74 层IV 网纹化下蜀黄土层 最大值 25.39 15.37 60.37 13.22 24.48 0.95 1.32 1.84 最小值 19.43 12.38 52.93 4.48 16.66 0.72 1.29 1.64 平均值 22.75 13.99 55.71 7.55 20.22 0.84 1.30 1.73 表 2 铜陵剖面石英颗粒表面各特征统计
Table 2. Surface characteristics of quartz particles, Tongling section
层I 层II 层III 层IV 编号 形貌特征 粒数/颗 频率/% 粒数/颗 频率/% 粒数/颗 频率/% 粒数/颗 粒数/颗 1 棱角状 13 21 29 15 16 13 7 10 2 次棱角状 26 43 72 37 48 38 23 33 3 次圆状 22 36 93 47 60 47 37 53 4 圆状 0 0 3 2 4 3 3 4 5 阶梯状断口 6 10 16 8 11 8 1 1 6 贝壳状断口 7 11 32 16 28 22 6 8 7 碟型坑 9 15 40 20 58 45 24 33 8 新月型撞击坑 5 8 30 15 22 17 10 14 9 水下磨光面 31 51 90 46 49 38 26 36 10 三角型坑 8 13 44 22 11 8 6 8 11 V型坑 23 38 71 36 32 25 27 38 12 平行解理 4 7 17 9 19 15 11 15 13 撞击沟 1 2 8 4 7 5 1 1 14 解理破碎 1 2 3 2 5 4 0 0 15 解理面 1 2 1 1 8 6 6 8 16 裂纹 3 5 8 4 5 4 1 1 17 擦痕 2 3 9 5 8 6 6 8 18 麻坑 2 3 21 11 15 12 6 8 -
[1] 刘良梧, 龚子同. 古红土的发育与演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(3):37-42
LIU Liangwu, GONG Zitong. Development and evolution of red paleosols [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(3): 37-42.
[2] 赵其国, 杨浩. 中国南方红土与第四纪环境变迁的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1995, 15(2):107-116 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.02.002
ZHAO Qiguo, YANG Hao. A preliminary study on red earth and changes of quaternary environment in South China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1995, 15(2): 107-116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.02.002
[3] 胡雪峰, 朱煜, 沈铭能. 南方网纹红土多元成因的粒度证据[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(9):918-925 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.09.014
HU Xuefeng, ZHU Yu, SHEN Mingneng. The granularity evidence of multi-cause formation of vermicular red clay [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(9): 918-925. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.09.014
[4] 彭红霞, 詹成, 马瑞元, 等. 江西九江红土生物标志化合物的分布特征及其古气候环境意义[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(3):447-455 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.120501
PENG Hongxia, ZHAN Cheng, MA Ruiyuan, et al. Characteristics of biomarkers in Pleistocene Red earth of Jiujiang, Jiangxi Province and its Paleoclimatic and environmental significance [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2019, 40(3): 447-455. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.120501
[5] 胡雪峰, 龚子同, 夏应菲, 等. 安徽宣州黄棕色土和第四纪红土的比较研究及其古气候意义[J]. 土壤学报, 1999, 36(3):301-307 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1999.03.002
HU Xuefeng, GONG Zitong, XIA Yingfei, et al. Comparative study of yellow-brown earth and Quaternary Red Clay in Xuanzhou, Anhui Province and its palaeo-climate significance [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1999, 36(3): 301-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1999.03.002
[6] 杨达源, 韩辉友, 周旅复, 等. 安徽宣城地区中晚更新世风成堆积与环境变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 11(2):97-104
YANG Dayuan, HAN Huiyou, ZHOU Lvfu, et al. Eolian deposit and environmental change of middle-late Pleistocene in Xuancheng, Anhui Province south of the lower reaches of the Changjiang river [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1991, 11(2): 97-104.
[7] 李徐生, 杨达源, 鹿化煜, 等. 皖南第四纪风尘堆积序列粒度特征及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(4):73-81
LI Xusheng, YAGN Dayuan, LU Huayu, et al. The grain-size features of Quaternary aeolian-dust deposition sequence in South Anhui and their significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(4): 73-81.
[8] 杜丹丹, 郑祥民, 邓黄月, 等. 安徽郎溪县十字镇第四纪红土理化性质及其古环境意义[J]. 热带地理, 2017, 37(2):258-268
DU Dandan, ZHEN Xiangmin, DENG Huangyue, et al. Physical and chemical properties of the Quaternary red clay in Shizi town of Langxi county, Anhui Province and its paleo-environmental significance [J]. Tropical Geography, 2017, 37(2): 258-268.
[9] 胡雪峰, 龚子同. 江西九江泰和第四纪红土成因的比较研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2001, 38(1):1-9 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2001.01.001
HU Xuefeng, GONG Zitong. Comparative study on the origin of Quaternary red earth in Jiujiang and Taihe, Jiangxi Province [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2001, 38(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2001.01.001
[10] 夏应菲, 杨浩. 安徽宣城第四纪红土剖面石英颗粒扫描电镜研究[J]. 南京师大学报: 自然科学版, 1998(1):124-128
XIA Yingfei, YANG Hao. SEM scanning of quartz of the Quaternary Red Earth in Xuancheng, Anhui [J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 1998(1): 124-128.
[11] 魏骥, 胡雪峰, 许良峰, 等. 长江中游地区第四纪红土的二元结构及古环境意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(5):826-835 doi: 10.11766/trxb200901210033
WEI Ji, HU XueFeng, XU Liangfeng, et al. Dualistic structure of the Quaternary red clay in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river and its paleo-environmental implication [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(5): 826-835. doi: 10.11766/trxb200901210033
[12] Hu X F, Wei J, Du Y, et al. Regional distribution of the Quaternary Red Clay with aeolian dust characteristics in subtropical China and its paleoclimatic implications [J]. Geoderma, 2010, 159(3-4): 317-334. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.08.008
[13] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, Qiao Y S, et al. Geochemical evidence for the provenance of middle Pleistocene loess deposits in southern China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(23-24): 3317-3326. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.004
[14] 黄颖, 朱丽东, 张晓, 等. 庐山北麓JL红土剖面粉砂粒级元素地球化学特征及其物源意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5):1092-1102 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2019.05.03
HUANG Ying, ZHU Lidong, ZHANG Xiao, et al. Geochemical characteristics and their provenance implications of the silt fraction from JL red earth section in Lushan region, Jiujiang, South China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5): 1092-1102. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2019.05.03
[15] 谢又予. 中国石英砂表面结构特征图谱[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984.
XIE Youyu. Micrograph Atlas of Surface Textural Features of Quartz Sand in China[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1984.
[16] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China [J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[17] 刘进峰, 郭正堂, 乔彦松, 等. 秦安中新世黄土-古土壤序列石英颗粒形态特征、粒度分布及其对成因的指示意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(1):117-120 doi: 10.1007/s11434-005-0811-8
LIU Jinfeng, GUO Zhengtang, Qiao Yansong, et al. Eolian origin of the Miocene loess-soil sequence at Qin’an, China: Evidence of quartz morphology and quartz grain-size [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(1): 117-120. doi: 10.1007/s11434-005-0811-8
[18] 孙有斌, 鹿化煜, 安芷生. 黄土-古土壤中石英颗粒的粒度分布[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(19):2094-2097 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.19.014
SUN Youbin, LU Huayu, AN Zhisheng. Particle size distribution of quartz particles in loess-paleosol [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(19): 2094-2097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.19.014
[19] Xiao J L, Porter S C, An Z S, et al. Grain size of quartz as an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130,000 yr [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 43(1): 22-29. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1003
[20] 侯圣山. 灵台剖面石英颗粒表面形态初步研究及其古气候意义[J]. 中国科学院研究生院学报, 2002, 19(1):59-68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1175.2002.01.008
HOU Shengshan. Preliminary SEM study of quartz surface features from Lingtai section and its Palaeoclimatic significance [J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2002, 19(1): 59-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1175.2002.01.008
[21] 陈钰, 刘兴起. 青藏高原可可西里库赛湖年纹层石英颗粒表面形态特征研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(5):1123-1133 doi: 10.18307/2016.0523
CHENG Yu, LIU Xingqi. Surface textural analysis of quartz grains from varved sediments of Lake Kusai in the Hoh Xil area, Xizang Plateau [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(5): 1123-1133. doi: 10.18307/2016.0523
[22] 王彩霞. 铜陵第四纪网纹红土的风化特征及其环境意义[D]. 浙江师范大学硕士学位论文, 2017.
WANG Caixia. Weathering characteristics and environmental significance of quaternary reticulated red clay in Tongling[D]. Master Dissertation of Zhejiang Normal University, 2017.
[23] 孙有斌. 黄土样中石英单矿物的分离[J]. 岩矿测试, 2001, 20(1):23-26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.01.006
SUN Youbin. Separation of quartz minerals from loess samples [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2001, 20(1): 23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.01.006
[24] 谷喜吉. 洞庭湖周边地区第四纪红土物源初探[D]. 浙江师范大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
GU Xiji. Preliminary research on provenance of Quaternary red earth in Dongting lake area[D]. Master Dissertation of Zhejiang Normal University, 2014.
[25] 安福元, 马海州, 樊启顺, 等. 粒度在沉积物物源判别中的运用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2012, 20(1):49-56
AN Fuyuan, MA Haizhou, FAN Qishun, et al. The application of grain size analysis in sediments provenance discriminance [J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2012, 20(1): 49-56.
[26] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 191-208.
LIU Dongsheng. Loess and the Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 191-208.
[27] 胡兆国, 冯金良, 鞠建廷. 成都粘土中石英的粒度分布及其表面微结构特征[J]. 山地学报, 2010, 28(4):392-406 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.04.002
HU Zhaoguo, FENG Jinliang, JU Jianting. Grain-size distribution and micro-structure of Quartz in the Chengdu Clay [J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2010, 28(4): 392-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.04.002
[28] 成都地质学院陕北队. 沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 1-105.
North Shanxi Team of Chengdu Institute of Geology. Grain Size Analysis of Sedimentary Rock and its Application[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1978: 1-105.
[29] 刘冬雁, 李巍然, 彭莎莎, 等. 粒度分析在中国第四纪黄土古气候研究中的应用现状[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 40(2):79-84
LIU Dongyan, LI Weiran, PENG Shasha, et al. Current application of grain size analysis in Chinese loess paleoclimatic study [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(2): 79-84.
[30] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1957, 27(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[31] 范庆斌, 叶玮, 陈渠. 江西南昌横岗“砂山”石英颗粒表面形态特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 2014, 37(5):1170-1181
FAN Qinbin, YE Wei, CHEN Qu. Surface morphology of quartz grains from the Henggang “sand dune” at Nanchang County, Jiangxi Province [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 37(5): 1170-1181.
[32] 韩建恩, 余佳, 孟庆伟, 等. 西藏札达盆地沉积物的石英砂表面特征及其环境意义[J]. 地球学报, 2009, 30(5):651-658 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.05.011
HAN Jianen, YU Jia, MENG Qingwei, et al. Quartz grain surface characteristics of sediments from the Zanda Basin of Xizang and their environmental significance [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(5): 651-658. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.05.011
[33] 王颖, 迪纳芮尔B. 石英砂表面结构模式图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 1-134.
WANG Ying, DEONARINE B. Atlas of Surface Structure Patterns of Quartz Sand[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 1-134.
[34] 程涌, 文义明, 吴伟, 等. 场发射扫描电镜在现代河流沉积石英颗粒表面形态特征研究中的应用[J]. 电子显微学报, 2017, 36(5):457-465 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2017.05.006
CHENG Yong, WEN Yiming, WU Wei, et al. The application of field emission scanning electron microscopy to the study of surface textures of quartz grains from modern fluvial deposits [J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2017, 36(5): 457-465. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2017.05.006
[35] 徐洪阳, 郑祥民, 周立旻, 等. 南京周家山下蜀黄土石英颗粒特征及其物源意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(6):1176-1186
XU Hongyang, ZHENG Xiangmin, ZHOU Limin, et al. Characteristics of quartz grains of the Xiashu loess in Zhoujiashan Nanjing and its provenance significance [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(6): 1176-1186.
[36] 王永焱, 滕志宏, 岳乐平. 黄土中石英颗粒表面结构与中国黄土的成因[J]. 地理学报, 1982, 49(1):35-40 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1982.01.005
WANG Yongyan, TENG Zhihong, YUE Leping. Surface texture of quartz grains under the scaning electron microscope and the genesis of loess in China [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1982, 49(1): 35-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1982.01.005
[37] Pye K. Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits[M]. London: Academic Press, 1987: 1-165.
[38] 乔彦松, 郭正堂, 郝青振, 等. 皖南风尘堆积-土壤序列的磁性地层学研究及其古环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(19):2088-2093 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.19.017
QIAO Yansong, GUO Zhengtang, HAO Qingzhen, et al. Loess-soil sequences in Southern Anhui Province: magnetostratigraphy and paleoclimatic significance [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(19): 2088-2093. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.19.017
[39] 徐树建. 晚第四纪我国风尘堆积的区域对比研究[M]. 济南: 山东人民出版社, 2012: 1-248.
XU Shujian. The Research of Dust Accumulation in China and its Regional Contrast during Late Quaternary[M]. Ji’nan: People’s Publishing House in Shandong, 2012: 1-248.
[40] Shackleton N J. The 100,000-year ice-age cycle identified and found to lag temperature, carbon dioxide, and orbital eccentricity [J]. Science, 2000, 289(5486): 1897-1902. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5486.1897
[41] Ding Z L, Yu Z, Rutter N W, et al. Towards an orbital time scale for Chinese loess deposits [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1994, 13(1): 39-70. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(94)90124-4
[42] 石磊, 张跃, 陈艺鑫, 等. 贡嘎山海螺沟冰川沉积的石英砂扫描电镜形态特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 46(1):96-102
SHI Lei, ZHANG Yue, CHEN Yixin, et al. Quartz grain SEM microtextures analyses of Sub-Glacial deposits at Hailuogou Glacier [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2010, 46(1): 96-102.
[43] 陈方, 朱大奎. 海岸、内陆沙漠与大陆架砂质沉积石英颗粒表面结构的对比研究[J]. 地理学报, 1999, 54(2):134-141 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1999.02.005
CHEN Fang, ZHU Dakui. A critical evaluation of the hypothesis of Chinese continental shelf desertification [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1999, 54(2): 134-141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1999.02.005
[44] 吴正. 我国内陆沙漠与海岸沙丘石英颗粒表面结构的对比研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 1995, 15(3):201-206
WU Zheng. A comparative study of the surface texture of quartz sand in inland deserts and that in coastal dune, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1995, 15(3): 201-206.
[45] 范庆斌. 中国南方风成沉积石英颗粒表面形态特征及环境意义[D]. 浙江师范大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
FAN Qingbin. Surface features of quartz grains of aeolian deposit in south China and its environmental significance[D]. Master Dissertation of Zhejiang Normal University, 2014.
[46] 李越, 宋友桂, 赵井东. 伊犁尼勒克黄土石英颗粒微形态特征及其成因与物源意义[J]. 地球环境学报, 2016, 7(4):366-379 doi: 10.7515/JEE201604005
LI Yue, SONG Yougui, ZHAO Jingdong. Micromorphological characters of quartz grain from Nilke loess-paleosol sequences and their implications of origin and provenance [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(4): 366-379. doi: 10.7515/JEE201604005
[47] 刘东生, 郑绵平, 郭正堂. 亚洲季风系统的起源和发展及其与两极冰盖和区域构造运动的时代耦合性[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998(3):194-204 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.002
LIU Dongsheng, ZHENG Mianping, GUO Zhengtang. Initiation and evolution of the Asian monsoon system timely coupled with the ice-sheet growth and the tectonic movements in Asia [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998(3): 194-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.002
[48] 熊尚发, 丁仲礼, 刘东生. 赣北红土与北京邻区黄土及沙漠砂的粒度特征对比[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(11):1216-1219 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.11.022
XIONG Shangfa, DING Zhongli, LIU Dongsheng. The comparison of particle characteristics among laterite in Northern Jiangxi Province, loess near Beijing and sand of desert [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(11): 1216-1219. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.11.022
[49] Liu F, Li G J, Chen J. U-Pb ages of zircon grains reveal a proximal dust source of the Xiashu loess, Lower Yangtze River region, China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(20): 2391-2395. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0318-2
[50] 邬光剑, 潘保田, 管清玉, 等. 中更新世全球最大冰期与中国沙漠扩张[J]. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(5):544-549 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.05.012
WU Guangjian, PAN Baotian, GUAN Qingyu, et al. The maximum glaciation and desert expansion in China during MIS16 [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2002, 24(5): 544-549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.05.012
[51] 陈骏, 李高军. 亚洲风尘系统地球化学示踪研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(9):1279-1301 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4269-z
CHEN Jun, LI Gaojun. Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(9): 1279-1301. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4269-z
[52] 杨立辉. 长江中下游地区第四纪红土沉积特征与成因机制研究[D]. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 2017.
YANG Lihui. The study of sedimentary characteristics and red clay in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze river[D]. Doctor Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2017.
-




 下载:
下载: