Unparallel MIS13 climate evolution between western and eastern Chinese Loess Plateau
-
摘要:
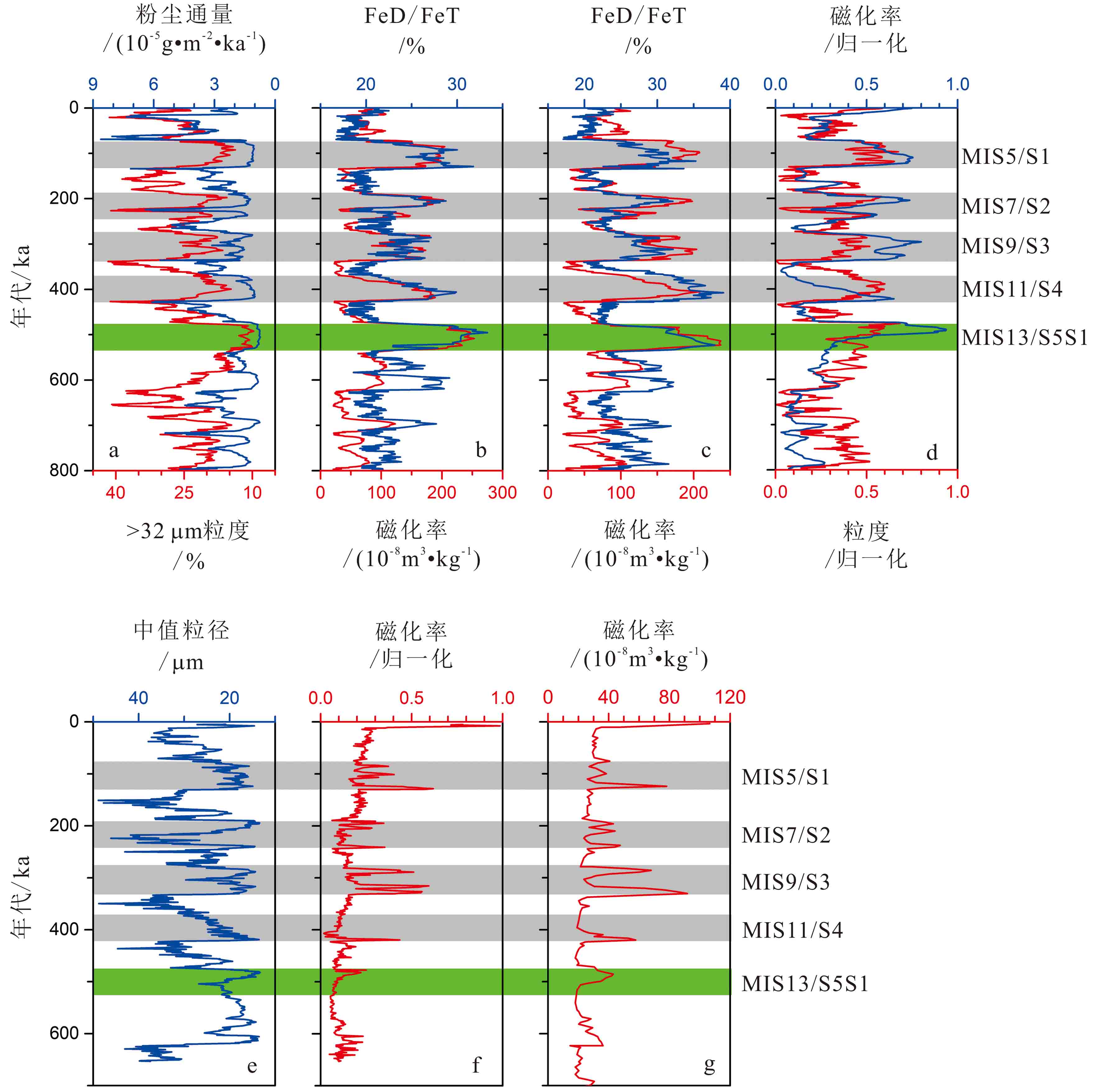
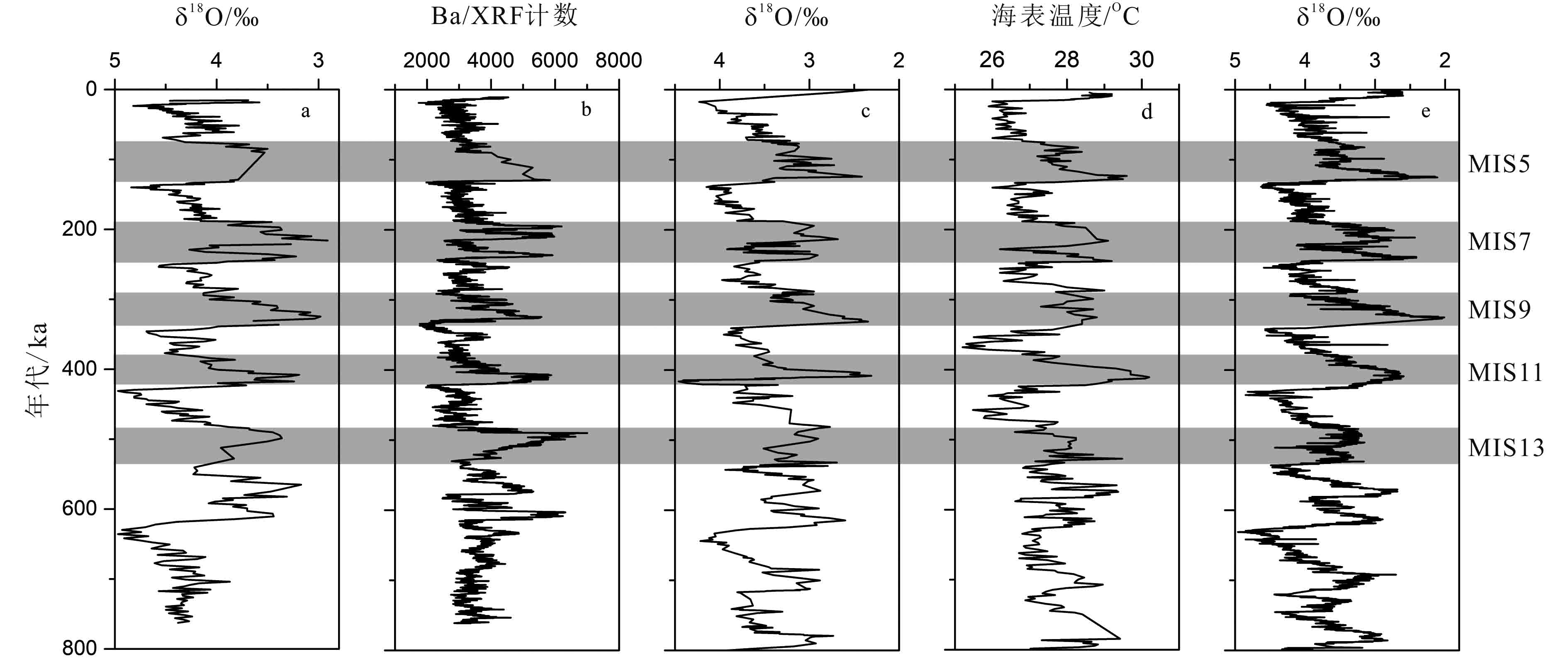
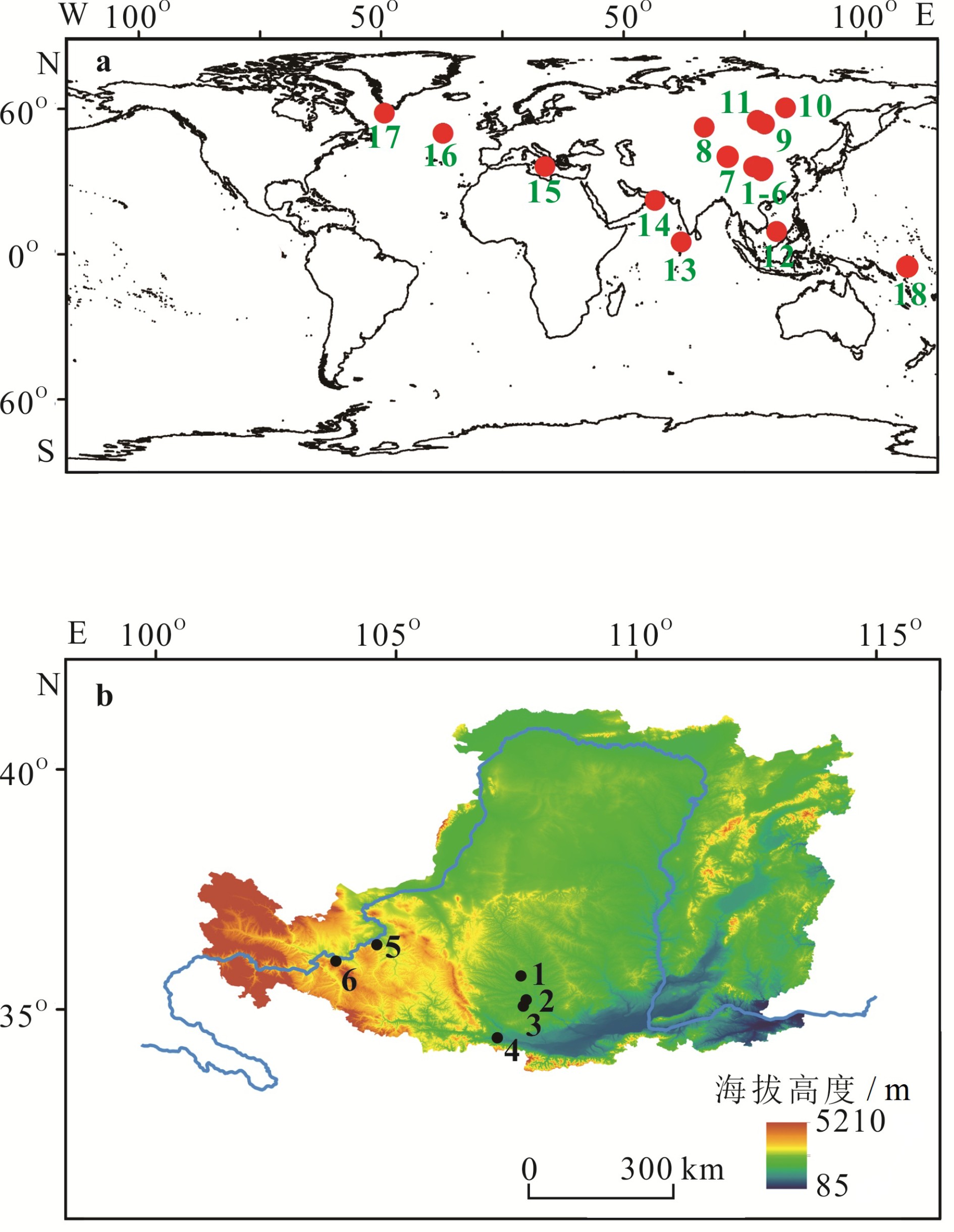
根据黄土高原中东部地区黄土沉积物的地质记录,前人研究推断MIS13时期北半球气候为高温高湿环境,然而,这似乎与黄土高原西部黄土沉积物的地质记录存在差别。本研究通过综合前人的研究结果,对比黄土高原东西部地区MIS13时期的古气候及古土壤风化强度在空间上的梯度分布,发现两地的古气候演化存在不对称性。对比MIS13时期低纬度的亚非季风区和北半球中高纬度地区气候状况得出:高降水量环境仅存在于亚非季风区大部分地区,但当时是否呈现高温环境值得商榷;北半球中高纬地区则显著不同,呈现相对较干冷的间冰期气候。由此推断,MIS13时期黄土高原东西部地区之间气候演化的不对称现象可能是季风缺少动力因素,对黄土高原西部影响较小,且长时间停留在黄土高原中东部地区所致;而在此之后的间冰期,由于季风的扩展和加深可能进一步加剧黄土高原西部地区S5S1古土壤风化强度与年轻古土壤层的差别。
Abstract:The quasi-continuously deposited Chinese loess is widely recognized as one of the most important paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental archive for Quaternary climate. The paleosol layer S5S1, corresponding to the Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 13, is the most prominent paleosol layer in the central Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). According to the pedogenesis evidence there, previous studies suggested that the North Hemisphere was then dominated by humid and warm climate under the strong East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM). It seems contradicted with the common understanding that the period was prevailed by large global ice volumes in the past interglacials. Recently, it is found that in some of the CLP loess sequences, the phenomenon is lacking. Then a question is raised if the EASM is really strong at that time. In this study, we made a thorough review of previous studies, and discovered that the strongly pedogenic S5S1 units are located in the East and Central CLP only, while the pedogenesis was weak in the West CLP. Comparing the Africa-Asian monsoon records with those in the region of mid- and high latitudes in the North Hemisphere, it is found that the abnormal MIS13 climate occurred only in the Africa-Asian monsoon region, but not the high latitude region of the North Hemisphere. In addition, the abnormal climate on CLP is possibly characterized by humidity, but not temperature. Based on the facts mentioned above, it is proposed that the EASM did not cover the region of West CLP during MIS13 benefited from the atmosphere dynamics, which caused the unparallel pedogenesis of loess-paleosol sequences between the West and East CLP.
-
Key words:
- MIS13 /
- paleoclimatic /
- out-of-phase pattern of climate variation /
- Chinese Loess Plateau
-

-
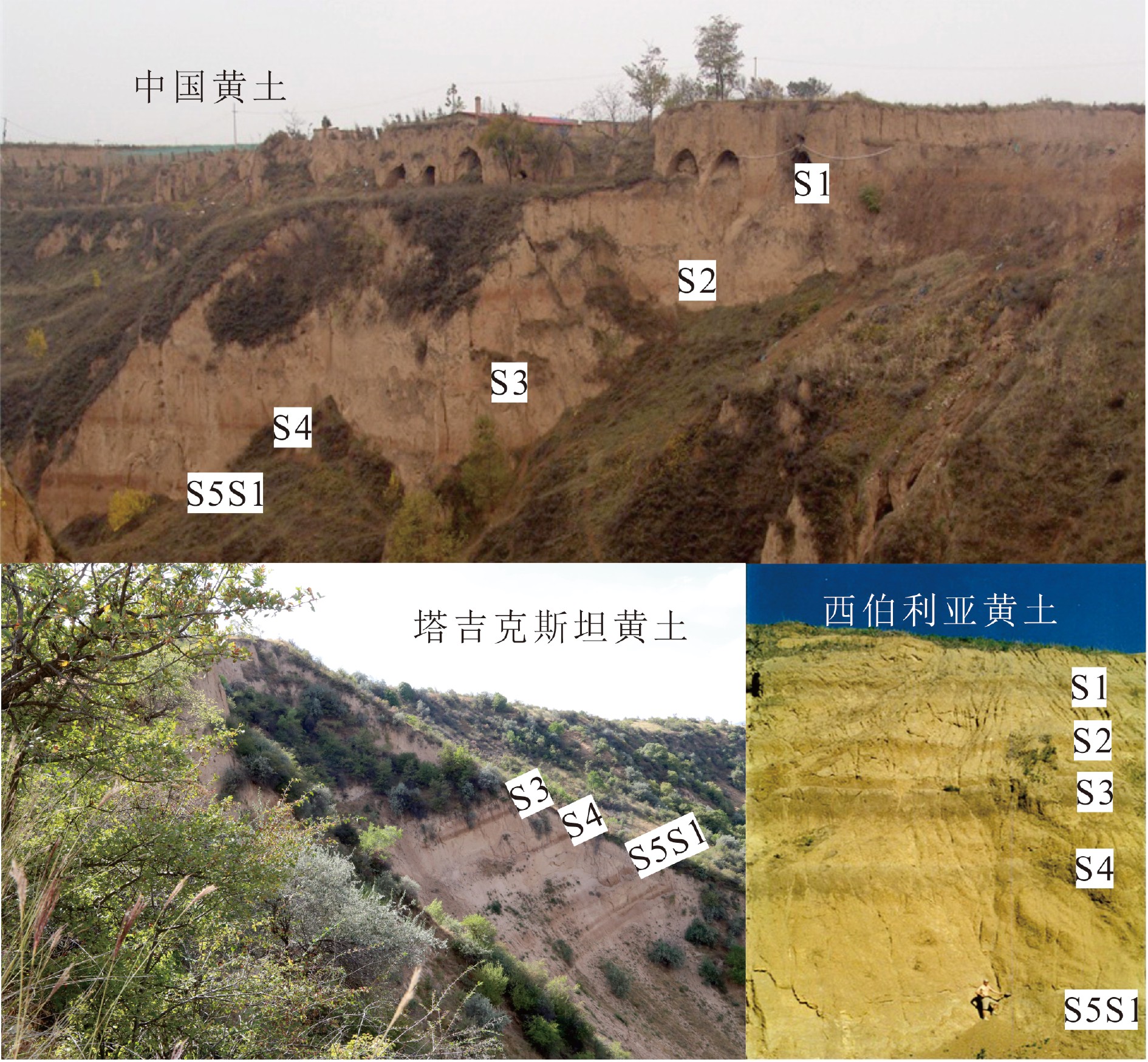
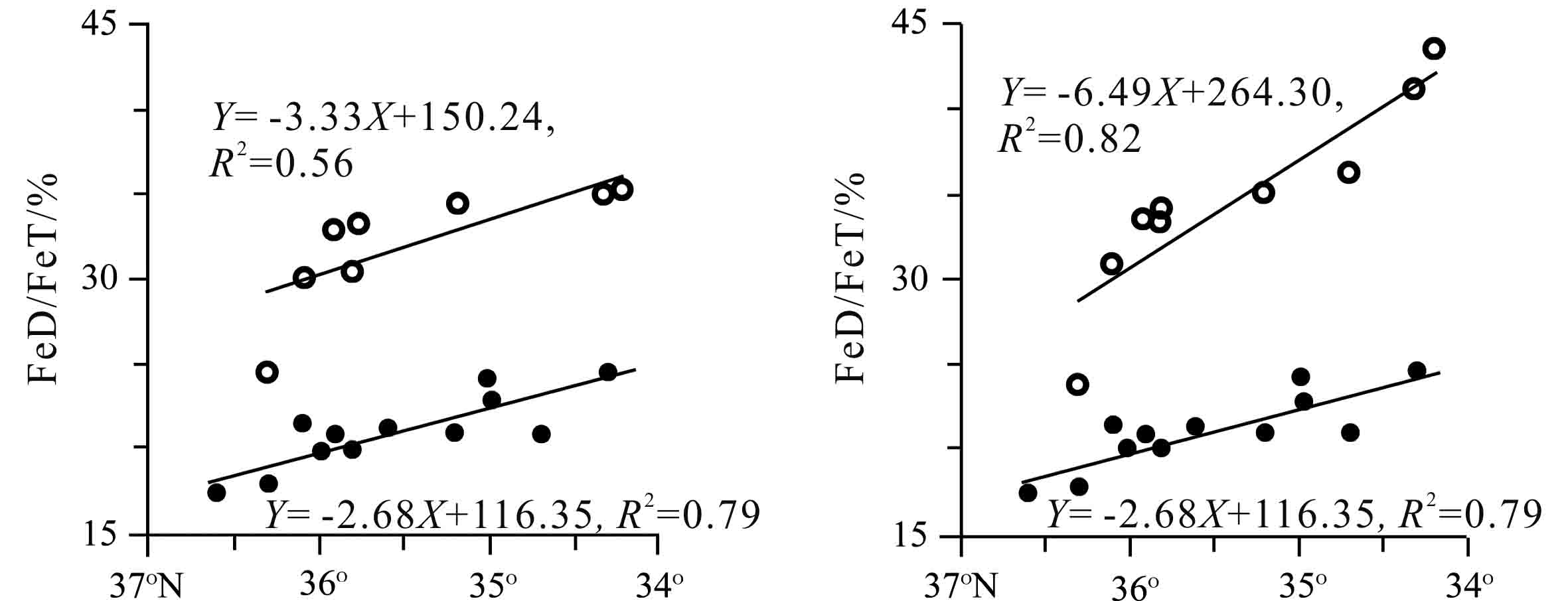
图 3 黄土高原古风化强度沿纬向变化特征 (引自文献[6])
Figure 3.
-
[1] Lüthi D, Le Floch M, Bereiter B, et al. High-resolution carbon dioxide concentration record 650 000-800000 years before present [J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7193): 379-382. doi: 10.1038/nature06949
[2] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A pliocene-pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[3] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T. Spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility of Chinese loess for the last 600 kyr: Implications for monsoon evolution [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2005, 110(B12): B12101. doi: 10.1029/2005JB003765
[4] Yin Q Z, Guo Z T. Strong summer monsoon during the cool MIS-13 [J]. Climate of the Past, 2008, 4(1): 29-34. doi: 10.5194/cp-4-29-2008
[5] Guo Z T, Berger A, Yin Z, et al. Strong asymmetry of hemispheric climates during MIS-13 inferred from correlating China loess and Antarctica ice records [J]. Climate of the Past, 2009, 5(1): 21-31. doi: 10.5194/cp-5-21-2009
[6] 葛俊逸, 郭正堂, 郝青振. 特征时期黄土高原风化成壤强度的空间特征与气候梯度[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(6):962-968 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.011
GE Junyi, GUO Zhengtang, HAO Qingzhen. Spatial variations of weathering intensity of the Loess Plateau and the climate gradients within characteristic timeslices [J]. Quaternary Science, 2006, 26(6): 962-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.011
[7] Ziegler M, Louren L J, Tuenter E, et al. High Arabian Sea productivity conditions during MIS13-odd monsoon event or intensified overturning circulation at the end of the Mid-Pleistocene transition? [J]. Climate of the Past, 2010, 6(1): 63-76. doi: 10.5194/cp-6-63-2010
[8] Caley T, Malaizé B, Bassinot F, et al. The monsoon imprint during the ‘atypical’ MIS 13 as seen through north and equatorial Indian Ocean records [J]. Quaternary Research, 2011, 76(2): 285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.07.001
[9] Rossignol-Strick M, Paterne M, Bassinot F C, et al. An unusual mid-Pleistocene monsoon period over Africa and Asia [J]. Nature, 1998, 392(6673): 269-272. doi: 10.1038/32631
[10] Bassinot F C, Labeyrie L D, Vincent E, et al. The astronomical theory of climate and the age of the Brunhes-Matuyama magnetic reversal [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 126(1-3): 91-108. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90244-5
[11] Tramp K L, Soreghan G S, Elmore R D. Paleoclimatic inferences from paleopedology and magnetism of the Permian Maroon Formation loessite, Colorado, USA [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2004, 116(5-6): 671-686.
[12] 周晓霞, 丁一汇, 王盘兴. 夏季亚洲季风区的水汽输送及其对中国降水的影响[J]. 气象学报, 2008, 66(1):59-70
ZHOU Xiaoxia, DING Yihui, WANG Panxing. Moisture transpotr in Asian summer monsoon region and its relationship with summer precipitation in China [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2008, 66(1): 59-70.
[13] 周兵, 文继芬. 1998年夏季我国东部降水与大气环流异常及其低频特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2007, 18(2):129-136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2007.02.001
ZHOU Bing, WEN Jifen. Abnormality of summertime precipitation of eastern china and general circulation with LFO in 1998 [J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2007, 18(2): 129-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2007.02.001
[14] Guo X L, Liu X M, Li P Y, et al. The magnetic mechanism of paleosol S5 in the Baoji section of the southern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 306: 129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.02.033
[15] Liu Q S, Bloemendal J, Torrent J, et al. Contrasting behavior of hematite and goethite within paleosol S5 of the Luochuan profile, Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(20): L20301. doi: 10.1029/2006GL027172
[16] Liu Q S, Barrón V, Torrent J, et al. Magnetism of intermediate hydromaghemite in the transformation of 2-line ferrihydrite into hematite and its paleoenvironmental implication [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2008, 113(B1): B01103. doi: 10.1029/2007JB005207
[17] Sun Y B, Lu H Y, An Z S. Grain size of loess, palaeosol and Red Clay deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau: Significance for understanding pedogenic alteration and palaeomonsoon evolution [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 241(1): 129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.06.018
[18] Sun Y B, Chen J, Clemens S C, et al. East Asian monsoon variability over the last seven glacial cycles recorded by a loess sequence from the northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(12): Q12Q02. doi: 10.1029/2006GC001287
[19] Shi P H, Yang T B, Tian Q C, et al. Loess record of climatic changes during MIS 12-10 in the Jingyuan section, northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 296: 149-159. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.08.2102
[20] Zhang J, Li J J, Guo B H, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age and monsoonal evolution recorded by the thickest Quaternary loess deposit of the Lanzhou region, western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 139: 17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.025
[21] Ding Z L, Liu T S, Rutter N W, et al. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800,000 years [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 149-159. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1059
[22] Feng Z D, Wang H B. Geographic variations in particle size distribution of the last interglacial pedocomplex S1 across the Chinese Loess Plateau: Their chronological and pedogenic implications [J]. CATENA, 2006, 65(3): 315-328. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2006.01.002
[23] Balsam W, Ji J F, Chen J. Climatic interpretation of the Luochuan and Lingtai loess sections, China, based on changing iron oxide mineralogy and magnetic susceptibility [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(3-4): 335-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.04.023
[24] 陈发虎, 张维信. 甘青地区的黄土地层学与第四纪冰川问题[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 18-19.
CHEN Fahu, ZHANG Weixin. The Loess Stratigraphy and Quaternary Glacial in Gan-Qing Region[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 18-19.
[25] 卢玉东, 孙建中, 李佩成. 用洛川黄土中碳同位素重建140万年以来古气候[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2008, 22(1):60-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2008.01.012
LU Yudong, SUN Jianzhong, LI Peicheng. Predicting Paleo-climate since 140 Ma BP by experiment of carbon isotope in loess [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2008, 22(1): 60-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2008.01.012
[26] 石培宏, 杨太保, 田庆春, 等. 靖远黄土-古土壤色度变化特征分析及古气候意义[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 48(2):15-23
SHI Peihong, YANG Taibao, TIAN Qingchun, et al. Chroma charcteristics in the loess-paleosol at Jingyuan section and its signification to paleocliamete [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Sciences, 2012, 48(2): 15-23.
[27] Sun Y B, Yin Q Z, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition [J]. Nature Communication, 2019, 10: 352. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08257-9
[28] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu cave, China [J]. Science, 2001, 294(5550): 2345-2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[29] Berger A, Loutre M F. Intertropical latitudes and precessional and half-precessional cycles [J]. Science, 1997, 278(5342): 1476-1478. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5342.1476
[30] Tian J, Wang P X, Chen X R, et al. Astronomically tuned plio-pleistocene benthic 18O record from South China Sea and Atlantic-Pacific comparison [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 203(3-4): 1015-1029. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00923-8
[31] Medina-Elizalde M, Lea D W, Fantle M S. Implications of seawater Mg/Ca variability for Plio-Pleistocene tropical climate reconstruction [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 269(3-4): 585-595. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.03.014
[32] Hodell D A, Channell J E T, Curtis J H, et al. Onset of “Hudson Strait” heinrich events in the eastern north atlantic at the end of the middle pleistocene transition (~640 ka)? [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2008, 23(4): PA4218. doi: 10.1029/2008PA001591
[33] Prokopenko A A, Karabanov E B, Williams D F, et al. Biogenic silica record of the lake Baikal response to climatic forcing during the Brunhes [J]. Quaternary Research, 2001, 55(2): 123-132. doi: 10.1006/qres.2000.2212
[34] Vaks A, Gutareva O S, Breitenbach S F M, et al. Speleothems reveal 500 000-year history of Siberian permafrost [J]. Science, 2013, 340(6129): 183-186. doi: 10.1126/science.1228729
[35] Jia J, Lu H, Wang Y J, et al. Variations in the iron mineralogy of a loess section in Tajikistan during the Mid-Pleistocene and Late Pleistocene: implications for the climatic evolution in central Asia [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2018, 19(4): 1244-1258. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007371
[36] Ding Z L, Ranov V, Yang S L, et al. The loess record in southern Tajikistan and correlation with Chinese loess [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 200(3-4): 387-400. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00637-4
[37] De Vernal A, Hillaire-Marcel C. Natural variability of Greenland climate, vegetation, and ice volume during the past million years [J]. Science, 2008, 320(5883): 1622-1625. doi: 10.1126/science.1153929
-



 下载:
下载: