Constraints of slope break belt on oil and gas trapping−An example from the Pinghu Formation in the Kongqueting area of Pinghu Slope
-
摘要:
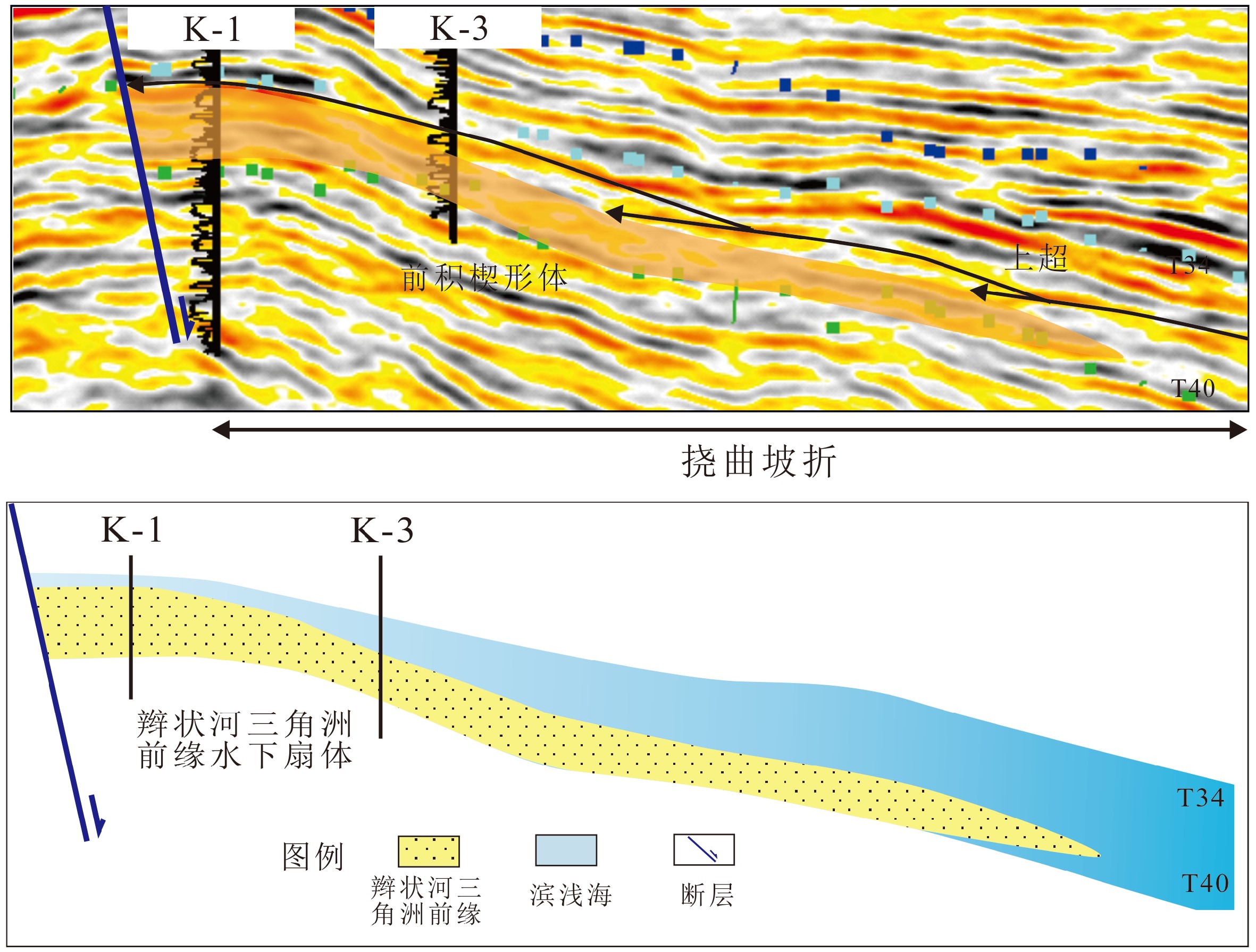
坡折带对复合岩性圈闭的发育具有重要控制作用。平湖斜坡带孔雀亭地区具备坡折带发育的古地貌背景,研究其类型和对沉积砂体、相带发育及成圈模式的控制,对下一步勘探开发具有重要意义。根据研究区坡折带发育的构造位置及与洼陷的匹配关系,可将研究区划分为高区坡折带、中区坡折带与低区坡折带。按成因机制不同,可在坡折区内进一步细分出三种类型,即断裂坡折、挠曲坡折和侵蚀坡折。高区坡折带以发育侵蚀坡折为主,控制辫状河三角洲平原沉积体系,形成侵蚀沟谷圈闭;中区坡折带以发育断裂坡折和挠曲坡折为主,控制辫状河三角洲平原与前缘沉积体系,发育辫状河道与扇体,形成断块-河道侧向尖灭复合岩性圈闭;低区坡折带发育断裂坡折,控制复合砂坝,形成断块-砂坝复合岩性圈闭。
Abstract:Slope break belt plays critical controlling roles in the formation of complex lithologic traps. The Kongqueting area on the Pinghu slope was a typical slope break belt in terms of paleogeomorphogy. To reveal the tectonic type of the slope break and its control over sand body sedimentation, depositional facies and trapping formation process is very important for the next cycle of oil and gas exploration of the region. According to the structural position of the slope break belt and its matching relationship with depressions, there are three types of slope break belts in the study area including the high stand slope break, the middle stand slope break and the low stand slope break. According to the genetic mechanism, it can be subdivided into faulting slope-break, flexure slope break and erosional slope break. In the high stand slope breaks, the erosional one dominates, which controls the formation of depositional systems of braided river and deltaic plain as well as the erosional valley traps. The middle slope break is dominated by fault slope break and flexure slope break, which controls the formation of the depositional systems of braided river, deltaic plain and deltaic front, and the compound lithologic traps such as braided river channels and fan bodies, and the fault block-river channel laterally pinched sandbodies. The low slope break is developed along the fault steps, where composite sand bar deposits occur, forming the fault block-sand bar composite lithologic traps.
-
Key words:
- slope break belt /
- sedimentary facies /
- lithologic trap /
- Pinghu Formation /
- Kongqueting area
-

-
[1] 周祥林, 高伟中, 张建培, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平北断裂特征及其对油气成藏的控制[J]. 上海国土资源, 2014(4):54-57
ZHOU Xianglin, GAO Weizhong, ZHANG Jianpei, et al. Fractures in the Pingbei area and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea [J]. Shanghai Land and Resourse, 2014(4): 54-57.
[2] 张国华, 刘金水, 秦兰芝, 等. 西湖凹陷渐新统花港组大型辫状河沉积体系特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(3):10-18
ZHANG Guohua, LIU Jinshui, QIN Lanzhi, et al. Characteristics of the large braided river depositional system of the Oligocene Huagang Formation in the Xihu sag [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(3): 10-18.
[3] 舒志国, 何希鹏, 邓世新. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起南坡上奥陶统礁滩相带的发现及油气勘探意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):80-85
SHU Zhiguo, HE Xipeng, DENG Shixin. Discovery of Ordovician reef flat belt and significant for hydrocarbon exploration in the southern slope of the Tazhong Uplift of Tarim Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(6): 80-85.
[4] 杜学斌, 解习农, 任建业, 等. 松辽坳陷湖盆环状坡折带发育特征及对沉积过程控制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):163-170
DU Xuebin, XIE Xinong, REN Jianye, et al. Characteristics of double-circular slope break and the control on sedimentary process in the Songliao Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 163-170.
[5] Vail P R. Seismic Stratigraphy Interpretation Using Sequence Stratigraphy Part I : Seismic Stratigraphy Interpretation Procedure[M]. 1987.
[6] 陈启林. 大型咸化湖盆地层岩性油气藏有利条件与勘探方向——以柴达木盆地柴西南古近纪为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(1):46-51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.008
CHEN Qilin. Favorable condition and exploration prospecting of lithologic hydrocarbon reservoir in large-scale saline basin—Case study on the Eogene in the Southwest of Qaidam Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(1): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.008
[7] 王英民, 金武弟, 刘书会, 等. 断陷湖盆多级坡折带的成因类型、展布及其勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(3):5-9,20
WANG Yingmin, JIN Wudi, LIU Shuhui, et al. Genetic types, distribution and exploration signification of multistage slope breaks in rift lacustrine basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(3): 5-9,20.
[8] 李相博, 刘化清, 陈启林, 等. 大型坳陷湖盆沉积坡折带特征及其对砂体与油气的控制作用——以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(4):75-87
LI Xiangbo, LIU Huaqing, CHEN Qilin, et al. Characteristics of slope break belt in large depression lacustrine basin and its controlling effect on sandbody and petroleum: taking the triassicyanchang formation in the ordos basin as an example [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(4): 75-87.
[9] 黄胜兵, 叶加仁, 朱红涛, 等. 渤中西环古沟谷与坡折带特征及其对储层的控制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(1):119-124
HUANG Shengbin, YE Jiaren, ZHU Hongtao, et al. Characteristics of valley-slope break zone in the western circle of the Bozhong Depression and its control over reservoir distribution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(1): 119-124.
[10] 冉怀江, 林畅松, 代一丁, 等. 陆架坡折带识别及其对沉积层序的控制作用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(A1):125-128
RAN Huaijiang, LIN Changsong, DAI Yiding, et al. Shelf break zone identification and its control on sedimentary sequence formations [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(A1): 125-128.
[11] 施和生, 柳保军, 颜承志, 等. 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区油气成藏条件与勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2010, 22(6):19-24
SHI Heshen, LIU Baojun, YAN Chengzhi, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area, Pearl River Month Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2010, 22(6): 19-24.
[12] 谢玉洪, 王振峰, 解习农, 等. 莺歌海盆地坡折带特征及其对沉积体系的控制[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(5):569-574
XIE Yuhong, WANG Zhenfeng, XIE Xinong, et al. Patterns of slope-break zone and their depositional models in the Yinggehai Basin [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(5): 569-574.
[13] 胡望水, 胡芳, 李瑞生, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡区坡折带发育及特征研究[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2010, 24(3):5,11-14
HU Wangshui, HU Fang, LI Ruisheng, et al. Slope break zone development and characteristics in Pinghu Slope zone around Xihu Sag of East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2010, 24(3): 5,11-14.
[14] 赵洪, 蒋一鸣, 常吟善, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖组基于沉积相标志的沉积特征研究[J]. 上海国土资源, 2018, 39(1):94-98
ZHAO Hong, JIANG Yiming, CHANG Yinshan, et al. Study on sedimentary characteristics of the Pinghu Formation based on sedimentary facies markers in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Shanghai Land and Resources, 2018, 39(1): 94-98.
[15] 周心怀, 高顺莉, 高伟中, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡型岩性油气藏形成与分布预测[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2):153-164
ZHOU Xinhuai, GAO Shunli, GAO Weizhong, et al. Formation and distribution of marine- continental transitional lithologic reservoirs in Pingbei slope belt, Xihu sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(2): 153-164.
[16] 刘金水, 许怀智, 蒋一鸣, 等. 东海盆地中、新生代盆架结构与构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3):675-691
LIU Jinshui, XU Huaizhi, JIANG Yiming, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic Basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China Sea Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 675-691.
[17] 蔡华, 秦兰芝, 刘英辉. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡相源-汇系统差异性及其耦合模式[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3):880-897 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.025
CAI Hua, QIN Lanzhi, LIU Yinghui, et al. Differentiation and coupling model of source-to-sink systems with transitional facies in Pingbei Slope of Xihu Sag [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2019, 44(3): 880-897. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.025
[18] 刘金水, 邹玮, 李宁, 等. “储保耦合”控藏机制与西湖凹陷大中型油气田勘探实践[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):11-19
LIU Jinshui, ZOU Wei, LI Ning, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation control mechanism of reservoir-conservation coupling and its large and medium-sized fields exploration practice in Xihu sag, East China Sea basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(3): 11-19.
[19] 蔡华, 张建培, 唐贤君. 西湖凹陷断裂系统特征及其控藏机制[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(10):18-26 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.10.003
CAI Hua, ZHANG Jianpei, TANG Xianjun. Characteristics of the fault systems and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(10): 18-26. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.10.003
[20] 刘金水, 赵洪. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带差异性气侵的成藏模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 46(4):487-496
LIU Jinshui, ZHAO Hong. Characteristics of differential gas invasion on Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2019, 46(4): 487-496.
-




 下载:
下载: