Quantitative characterization of the depositional system in Gas field A, Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag and its bearing on periodicity of sea level changes
-
摘要:
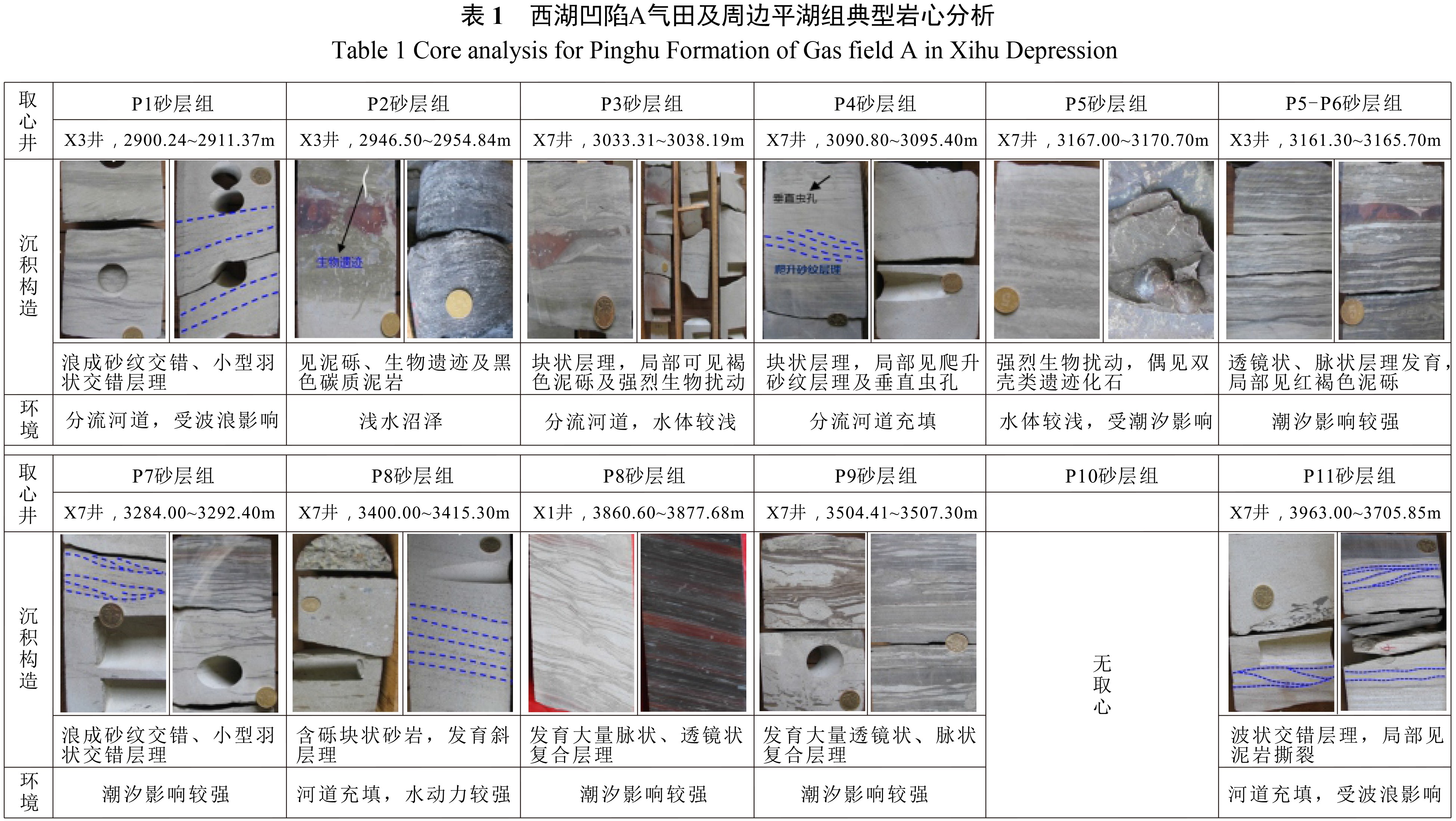
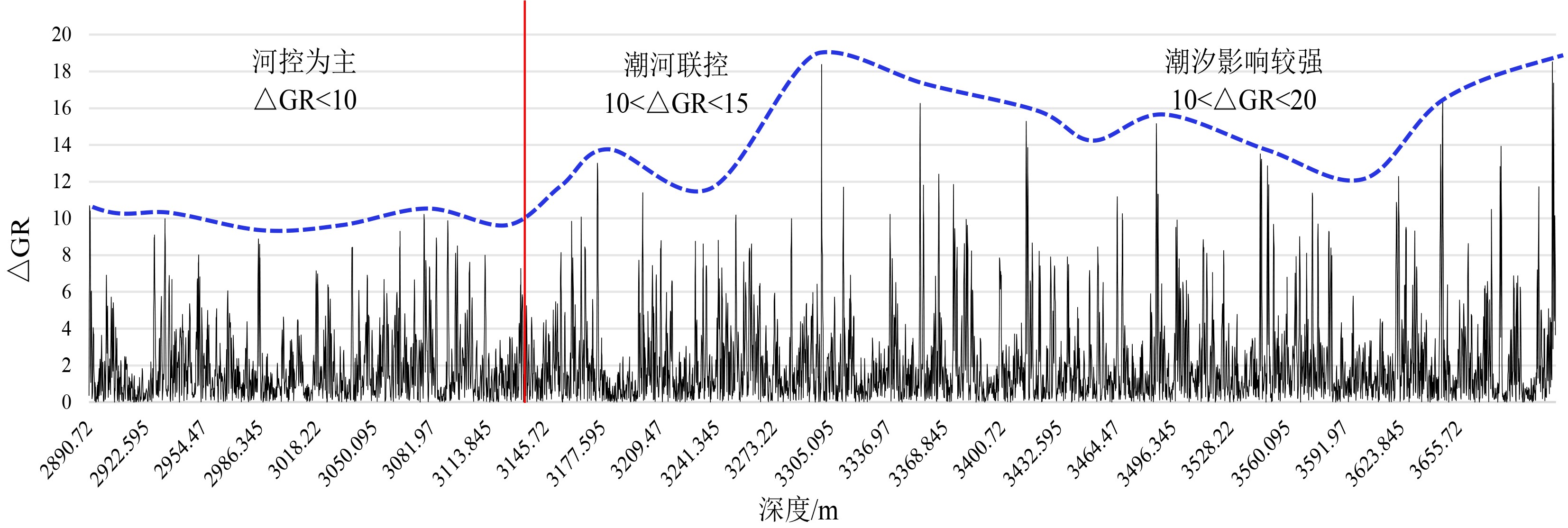
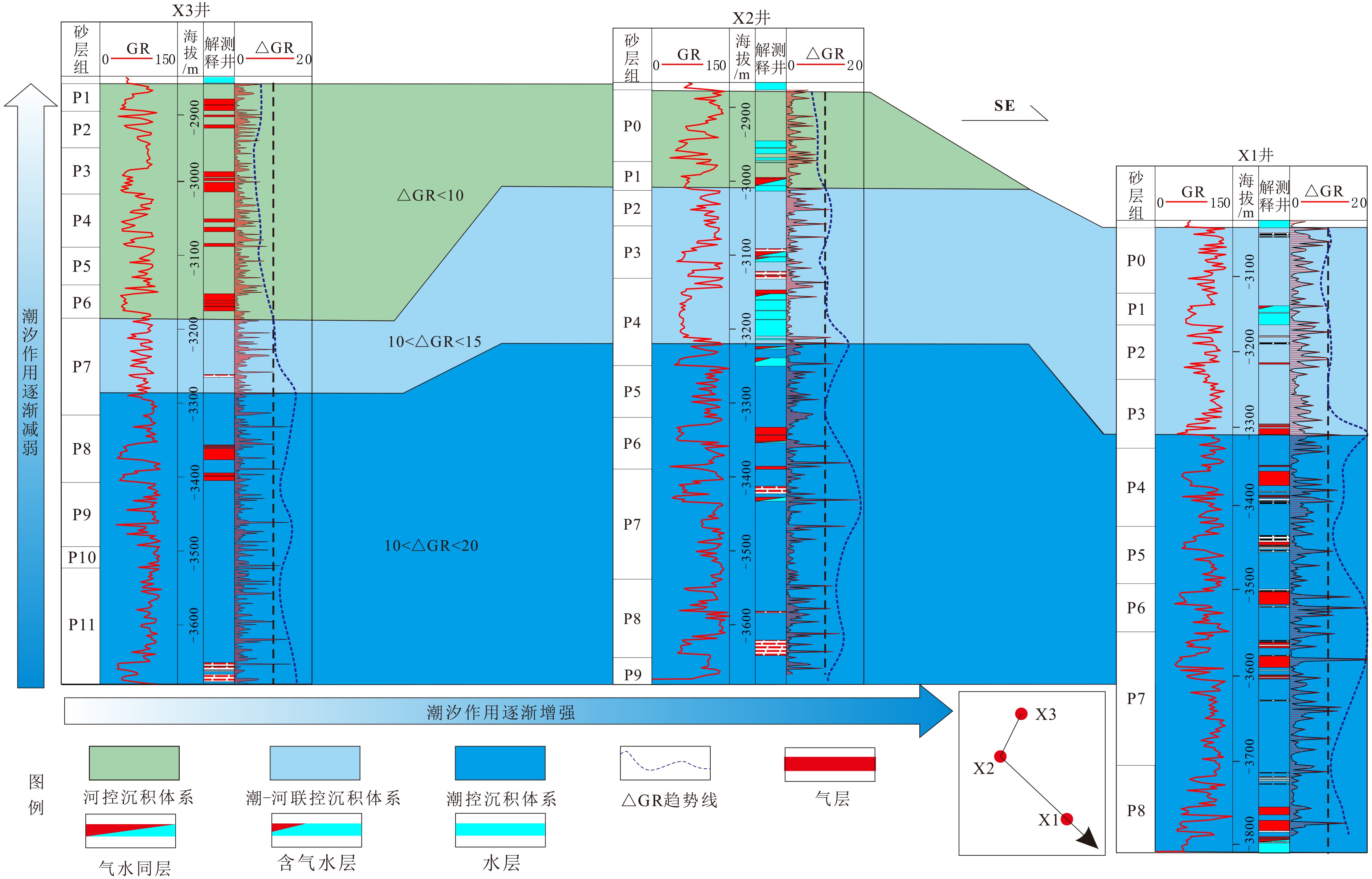
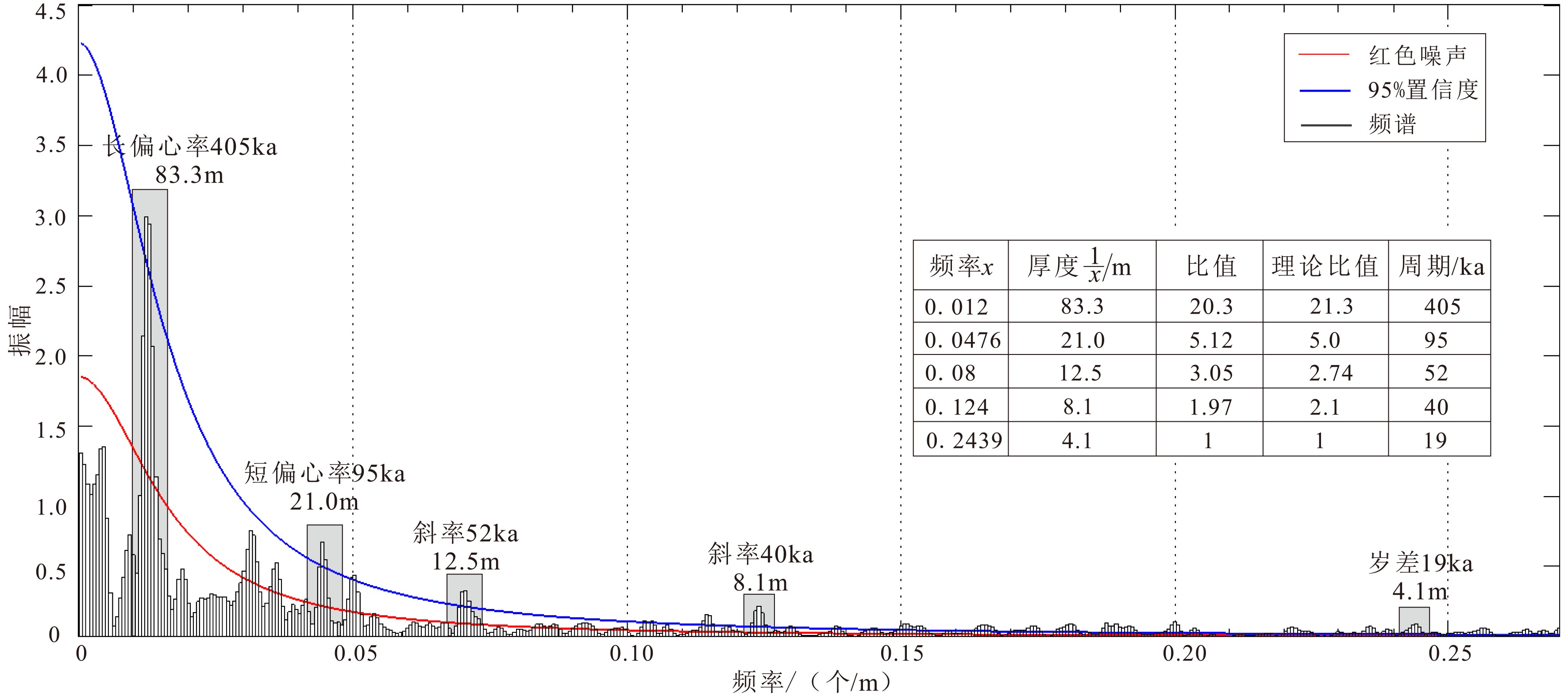
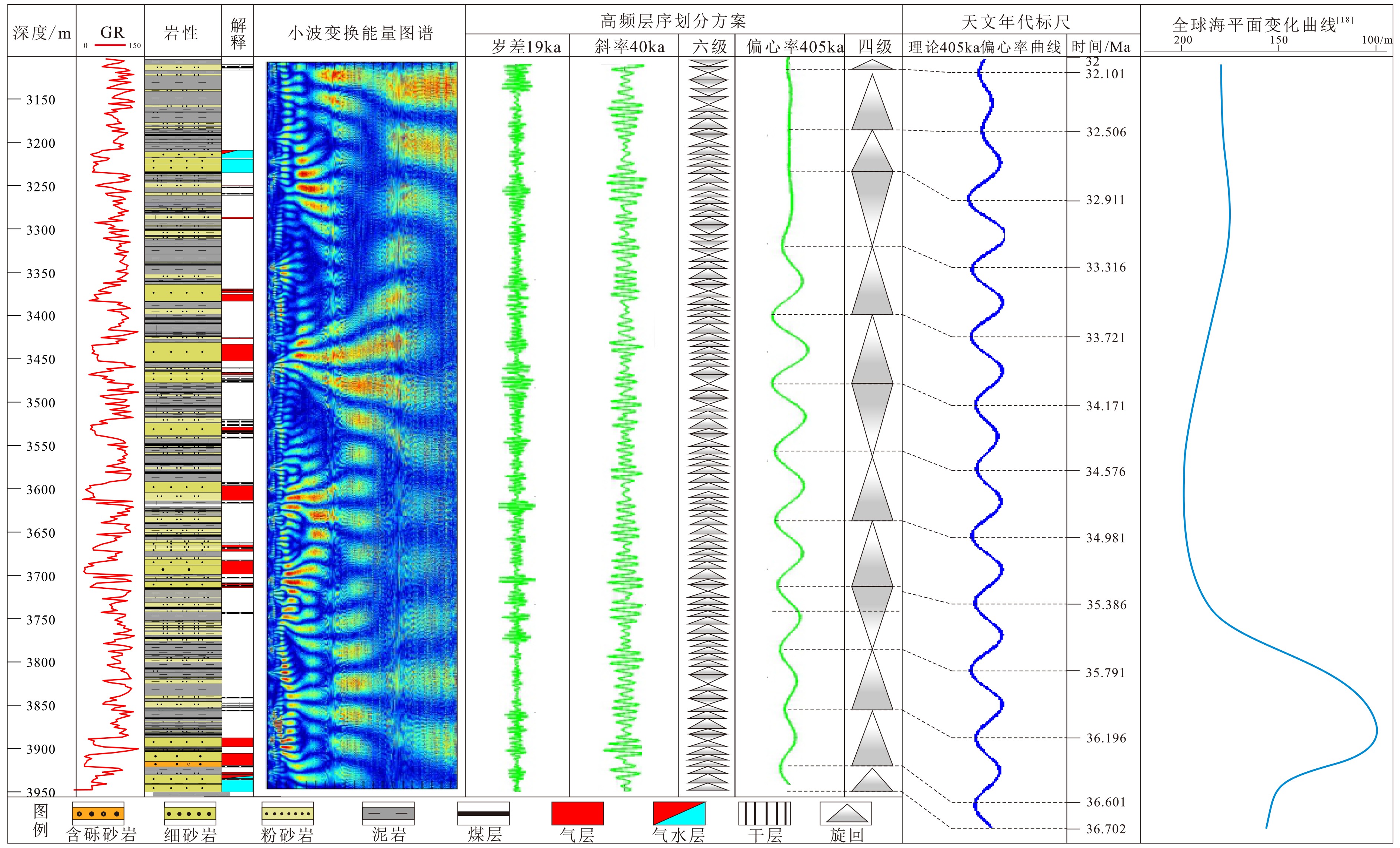
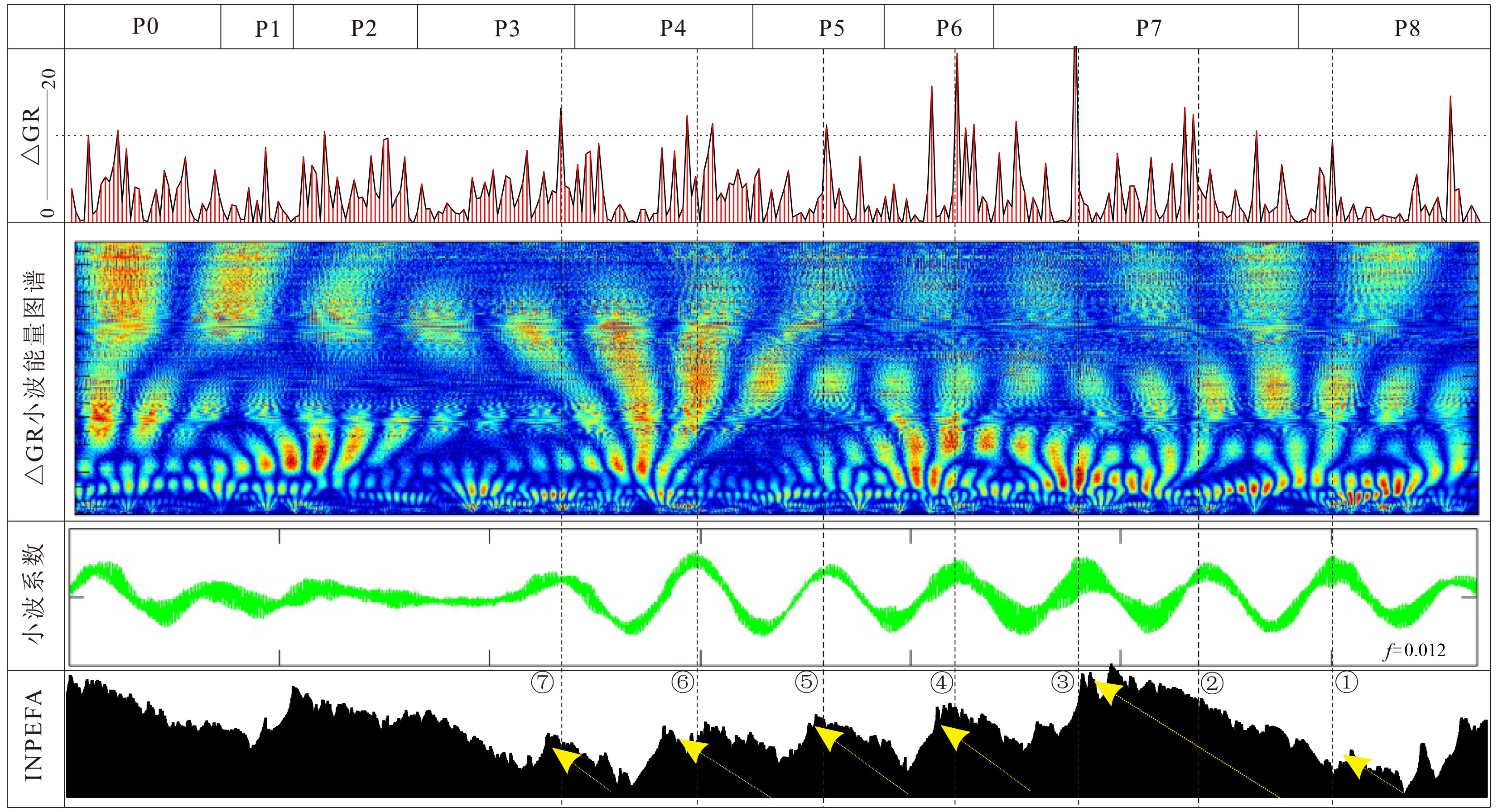
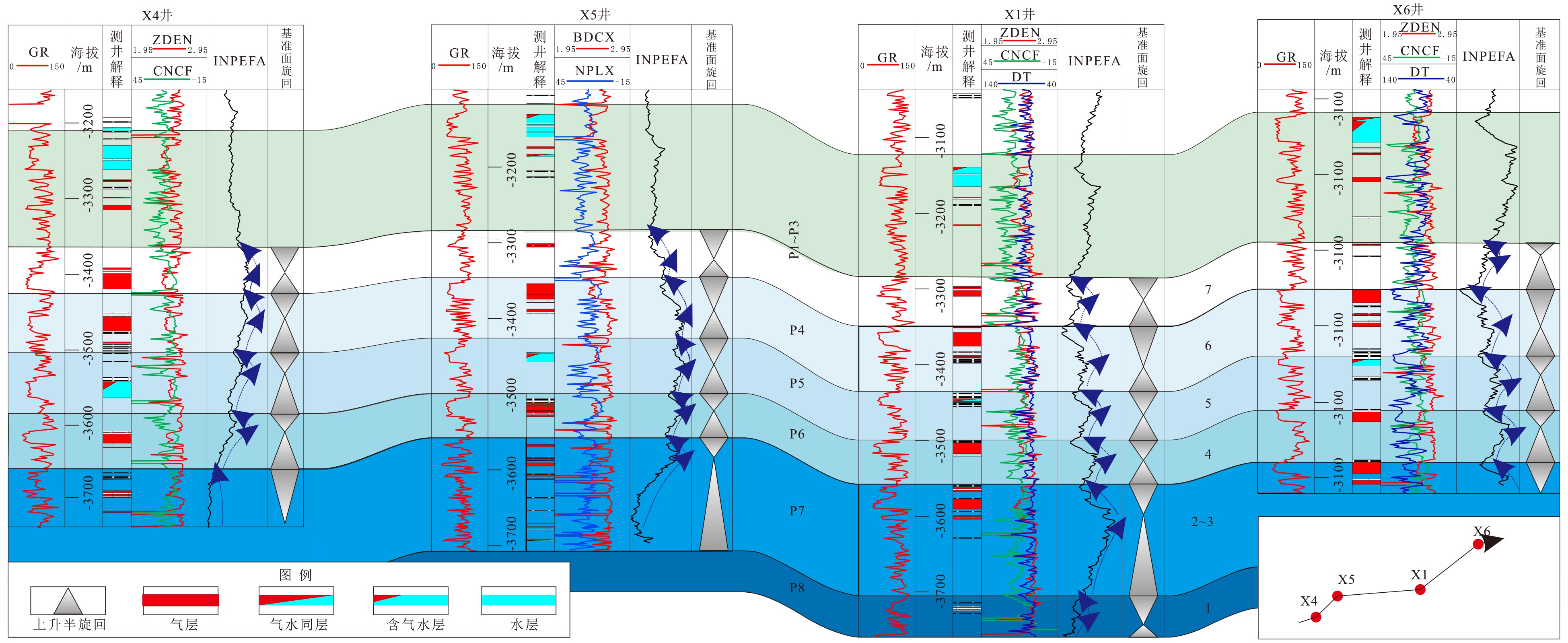
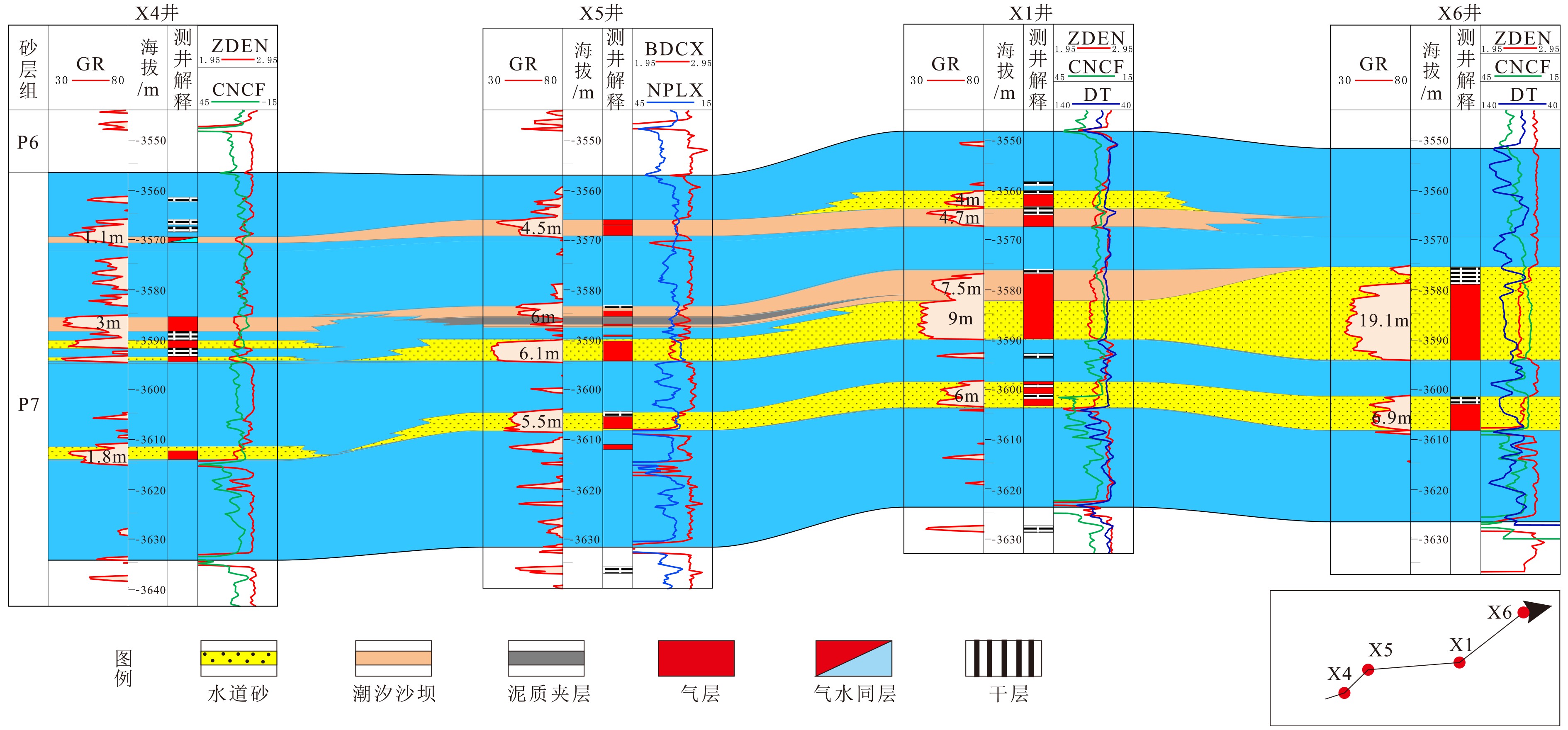
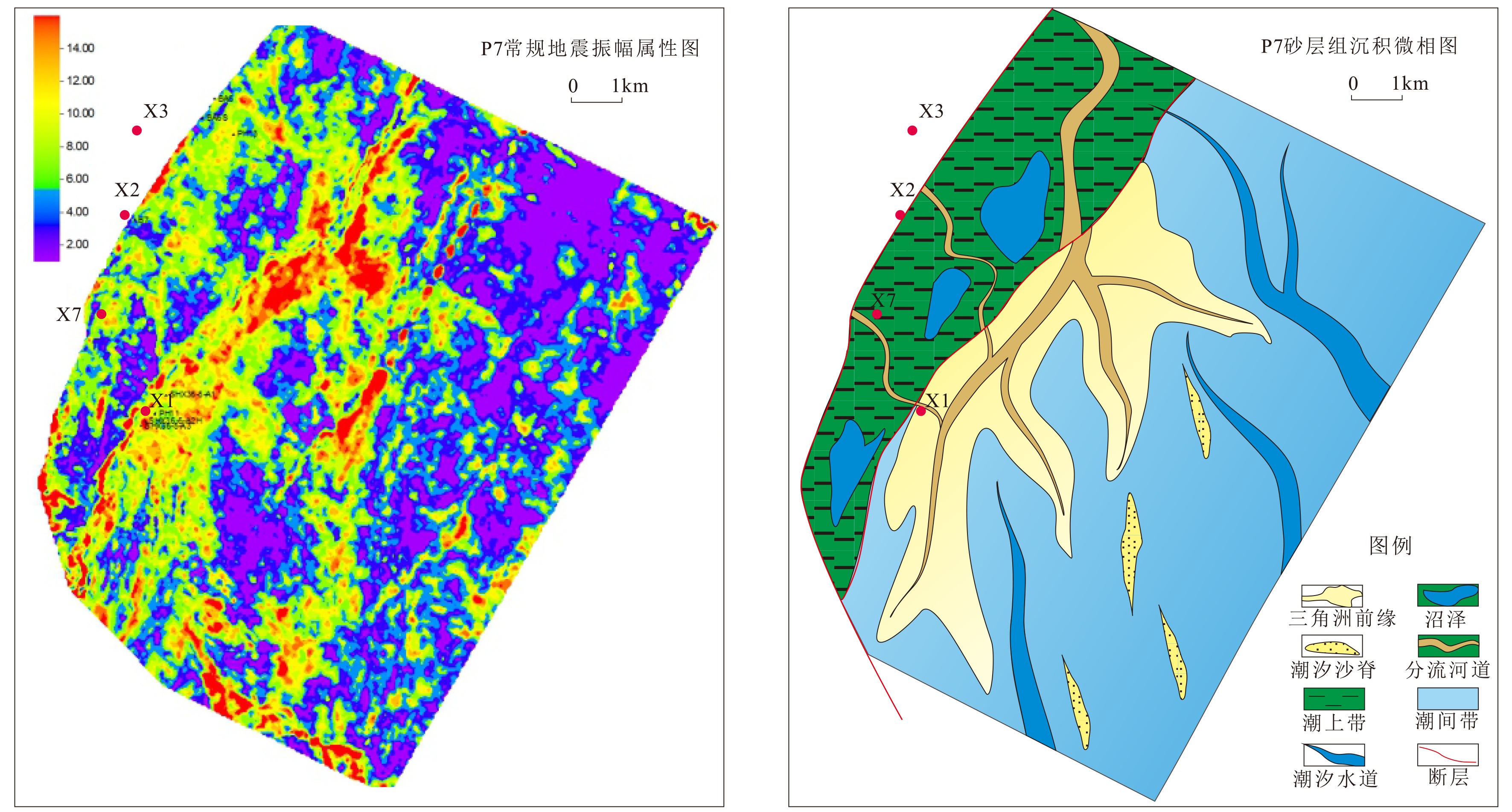
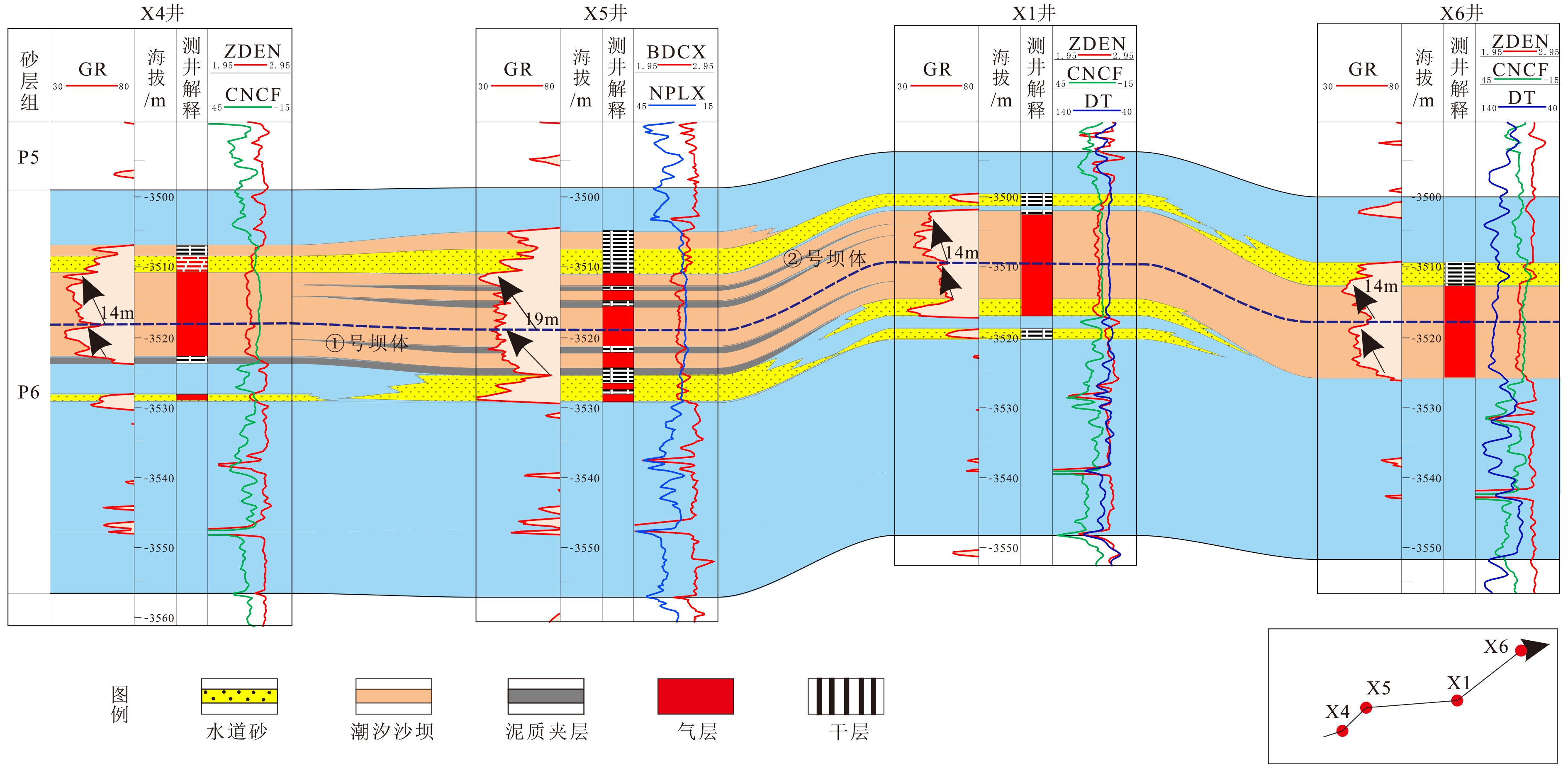
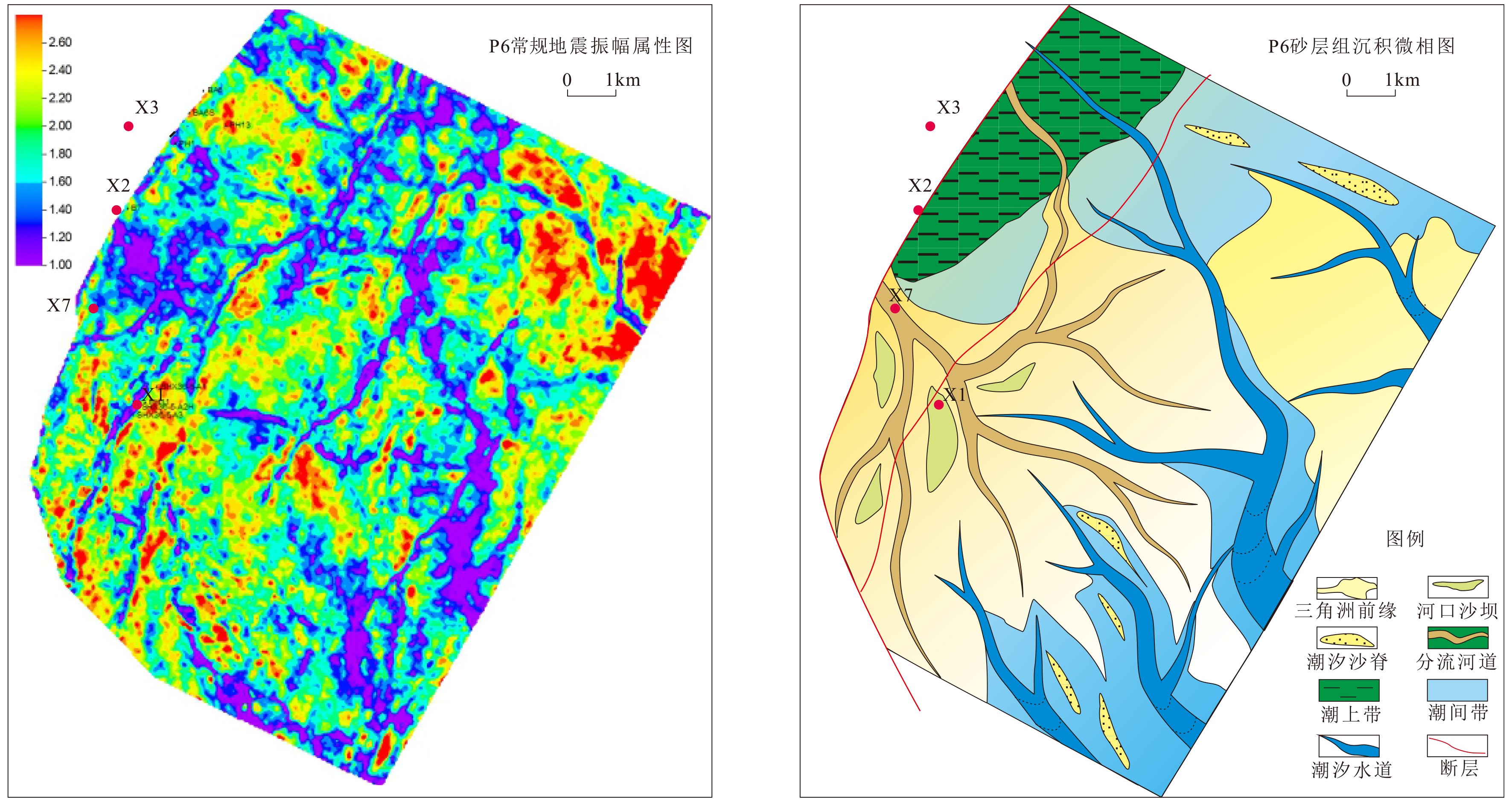
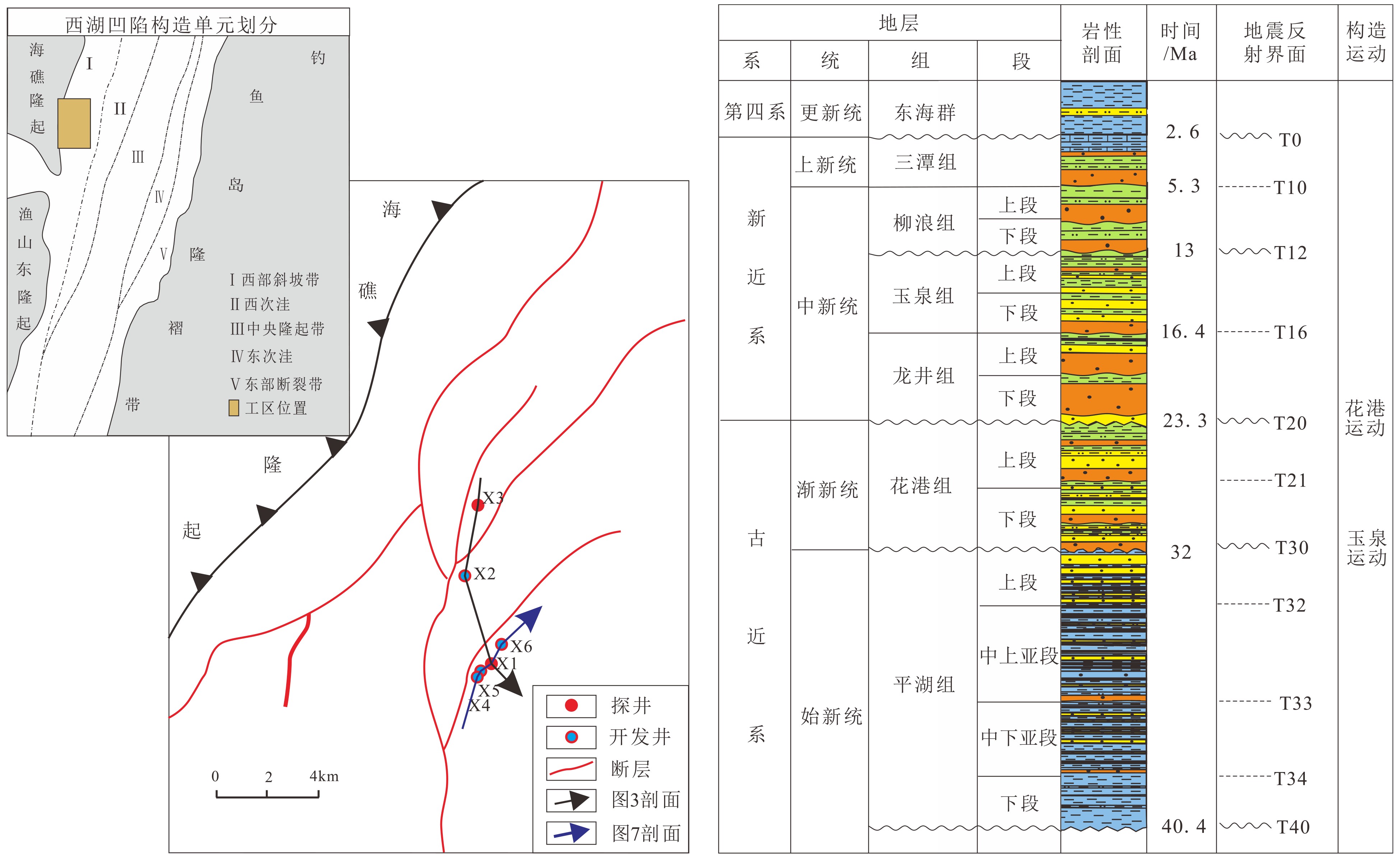
西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组是西湖凹陷重要的油气勘探开发层系之一,明确其沉积背景、演化规律、探讨深层储层保存机制是提高地质油藏预测准确率的关键。综合利用岩心、测井(△GR)等资料对A气田沉积体系进行定量表征,并基于米兰科维奇旋回理论,通过小波变换、频谱分析等手段,结合全球海平面变化规律,对A气田平湖组海平面变化周期性进行探讨分析。结果表明,A气田平湖组沉积体系自下而上可分为潮控三角洲沉积体系、潮-河联控三角洲沉积体系及河控三角洲沉积体系。同时在潮控三角洲沉积体系及潮河联控三角洲沉积体系中共识别7次大规模海平面升降事件,其中以P7海平面升降规模最大,每次海平面升降周期约405ka。最后基于7次海平面升降事件指导气田内高频层序划分,且重点对P7—P6层砂体发育规律、展布特征进行分析,结合储层物性纵向变化规律认为,潮汐作用对研究区内砂体具有一定的改造作用,有利于纯净砂岩的发育,预测A气田潮下带潮汐改造砂体是未来有利勘探开发方向。
Abstract:The Pinghu Formation in the Pinghu slope zone is one of the most important oil and gas exploration targets and gas producers in the Xihu Depression of the East China Sea. The key to improve the accuracy of reservoir prediction should be put on the right clarification of sedimentary background, evolution pattern and the mechanism of deep reservoir preservation. In this paper, the depositional systems of the Gas field A are quantitatively characterized with coring and well logging data. Our results suggest that the Pinghu Formation of the Gas field A consists of three depositional systems, i.e. the tidal delta system, tidal-river delta system and river delta system in ascending order. In addition to it, the periodicity of sea level fluctuation of the Pinghu Formation is analyzed by means of wavelet transform and spectrum analysis upon the global sea level changes or so-called Milankovitch cycles. Seven transgression events are identified, among which the P7 is the largest, and each cycle lasted for a time span of about 405 ka. Based on this, the isochronal sequence stratigraphic frameworks of the gas field are established. Finally, on the basis of high-frequency sequence framework and evolutionary pattern, the distribution characteristics of sand bodies in the layers of P7-P5 are carefully analyzed. Combined with the vertical variation in reservoir physical properties, it is considered that the reworking of sand bodies by tidal activities is critical important to the enhancement of the physical properties of the sandstone reservoirs. Therefore, the tidal sand bodies in the subtidal zone are the most favorable targets for oil and gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- depositional system /
- quantitative characterization /
- sea level change /
- Gas field A
-

-
[1] 彭伟欣, 刘金水. 东海西湖凹陷保俶斜坡平湖组层序地层分析[J]. 上海地质, 1995(4):15-24, 32
PENG Weixin, LIU Jinshui. Sequence stratigraphic analysis of Pinghu Formation in Baoshu slope of Xihu sag in the East China Sea [J]. Shanghai Geology, 1995(4): 15-24, 32.
[2] 刘成鑫. 东海平湖油气田平湖组沉积相研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2010, 30(2):9-13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.009
LIU Chengxin. Study on sedimentary facies for Pinghu Formation in Pinghu oil and gas field in East China Sea Basin [J]. Offshore Oil, 2010, 30(2): 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.009
[3] 杨彩虹, 高兆红, 蒋一鸣, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组碎屑沉积体系再认识[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(9):11-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2013.09.003
YANG Caihong, GAO Zhaohong, JIANG Yiming, et al. Recognition of the clastic sedimentary system of the Eocene Pinghu Formation in the Pinghu slope zone of the Xihu Depression [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(9): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2013.09.003
[4] 顾惠荣, 贾健谊, 叶加仁. 东海西湖凹陷含油气系统特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):295-297, 306 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.021
GU Huirong, JIA Jianyi, YE Jiaren. Characteristics of oil and gas bearing system in Xihu lake depression in the East China Sea [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(3): 295-297, 306. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.021
[5] 须雪豪, 陈琳琳, 汪企浩. 东海陆架盆地中生界地质特征与油气资源潜力浅析[J]. 海洋石油, 2004, 24(3):1-7, 55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2004.03.001
XU Xuehao, CHEN Linlin, WANG Qihao. Analysis of mesozoic geological characteristics and resource potential in the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Offshore Oil, 2004, 24(3): 1-7, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2004.03.001
[6] 武法东, 张燕梅, 周平, 等. 东海陆架盆地第三系沉积-构造动力背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 1999, 13(2):37-41
WU Fadong, ZHANG Haiyan, ZHOU Ping, et al. Tertiary basin setting analysis and sedimentary dynamics of the East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Geoscience, 1999, 13(2): 37-41.
[7] 胡惠娟. 东海平湖构造带地质构造特征及含油气条件[J]. 海洋石油, 2003, 23(1):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2003.01.001
HU Huijuan. Geological features and hydrocarbon-bearing condition of the Pinghu tectonic belt, the East China Sea [J]. Offshore Oil, 2003, 23(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2003.01.001
[8] 徐伟. 东营凹陷沙河街组三段、四段高频旋回识别及其地质意义[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)硕士学位论文, 2011.
XU Wei. High-frequency cycles of the 3rd and 4th member of Shahejie formation in Dongying depression and its geological significance[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2011.
[9] 薛年喜. MATLAB在数字信号处理中的应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2008.
XUE Nianxi. Application of MATLAB in Digital Signal Processing[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2008.
[10] 常吟善, 覃军, 赵洪, 等. 基于米氏旋回理论的高频层序识别与划分: 以东海陆架盆地平湖斜坡带宝云亭地区平三段为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):51-60
CHANG Yinshan, QIN Jun, ZHAO Hong, et al. Identification and division of high-frequency sequence based on Milakovitch cycle: A case of the 3rd member of Pinghu Formation in Baoyunting Area, Pinghu Slope Zone, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3): 51-60.
[11] 张运波, 赵宗举, 袁圣强, 等. 频谱分析法在识别米兰科维奇旋回及高频层序中的应用: 以塔里木盆地塔中-巴楚地区下奥陶统鹰山组为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(2):400-410
ZHANG Yunbo, ZHAO Zongju, YUAN Shengqiang, et al. Application of spectral analysis to identify Milankovitch cycles and high-frequency sequences: Take the lower Ordovician Yingshan formation of Mid-Tarim Basin as an example [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(2): 400-410.
[12] 黄春菊. 旋回地层学和天文年代学及其在中生代的研究现状[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(2):48-66
HUANG Chunju. The current status of cyclostratigraphy and astrochronology in the Mesozoic [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(2): 48-66.
[13] Osleger D. Subtidal carbonate cycles: Implications for allocyclic vs. autocyclic controls [J]. Geology, 1991, 19(9): 917-920. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0917:SCCIFA>2.3.CO;2
[14] 赵宗举, 陈轩, 潘懋, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中-巴楚地区上奥陶统良里塔格组米兰科维奇旋回性沉积记录研究[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(4):518-536
ZHAO Zongju, CHEN Xuan, PAN Mao, et al. Milankovitch cycles in the upper ordovician Lianglitage formation in the Tazhong-Bachu Area, Tarim Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(4): 518-536.
[15] Torrence C, Compo G P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis [J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1998, 79(1): 61-78. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0061:APGTWA>2.0.CO;2
[16] 姚益民, 徐道一, 李保利, 等. 东营凹陷牛38井沙三段高分辨率旋回地层研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2007, 31(3):229-239 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2007.03.004
YAO Yimin, XU Daoyi, LI Baoli, et al. High resolution cyclostratigraphic study on the third member of Shahejie formation of drill core Niu38 in the Dongying depression, Shandong province [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2007, 31(3): 229-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2007.03.004
[17] 毛凯楠, 解习农, 徐伟, 等. 基于米兰科维奇理论的高频旋回识别与划分: 以琼东南盆地梅山组和三亚组地层为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(6):641-647 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201206641
MAO Kainan, XIE Xinong, XU Wei, et al. Identification and division of high-frequency cycles based on Milakovitch theory: a case study on Miocene Sanya and Meishan Formations in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2012, 34(6): 641-647. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201206641
[18] Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. Mesozoic and Cenozoic chronostratigraphy and cycles of sea-level change[M]//Sea-Level Changes: An Integrated Approach. Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA: SEPM Special Publication, 1988.
[19] 路顺行, 张红贞, 孟恩, 等. 运用INPEFA技术开展层序地层研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(6):703-708 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2007.06.017
LU Shunxing, ZHANG Hongzhen, MENG En, et al. Application of INPEFA technique to carry out sequence-stratigraphic study [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(6): 703-708. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2007.06.017
[20] 薛欢欢, 李景哲, 李恕军, 等. INPEFA在高分辨率层序地层研究中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地油房庄地区长4+5油组为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2015, 45(7):101-106
XUE Huanhuan, LI Jingzhe, LI Shujun, et al. Application of INPEFA technique to research high resolution sequence stratigraphy: as an example of Youfangzhuang area Chang 4+5 in Ordos Basin [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(7): 101-106.
-



 下载:
下载: