Paleoclimatic evidence inferred from soluble salt deposits in the Pleistocene sediments at Jijiazhuang site, Nihewan Basin
-
摘要:
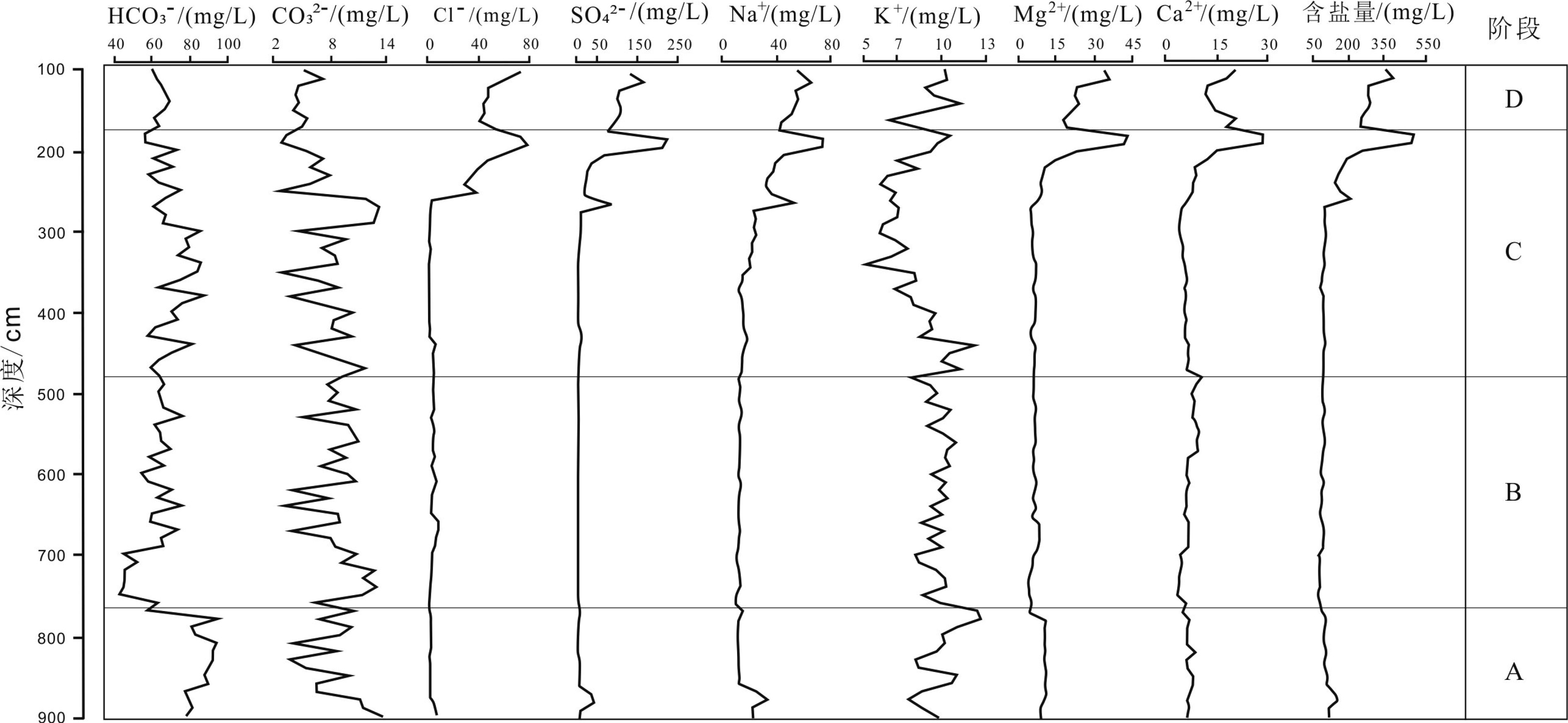
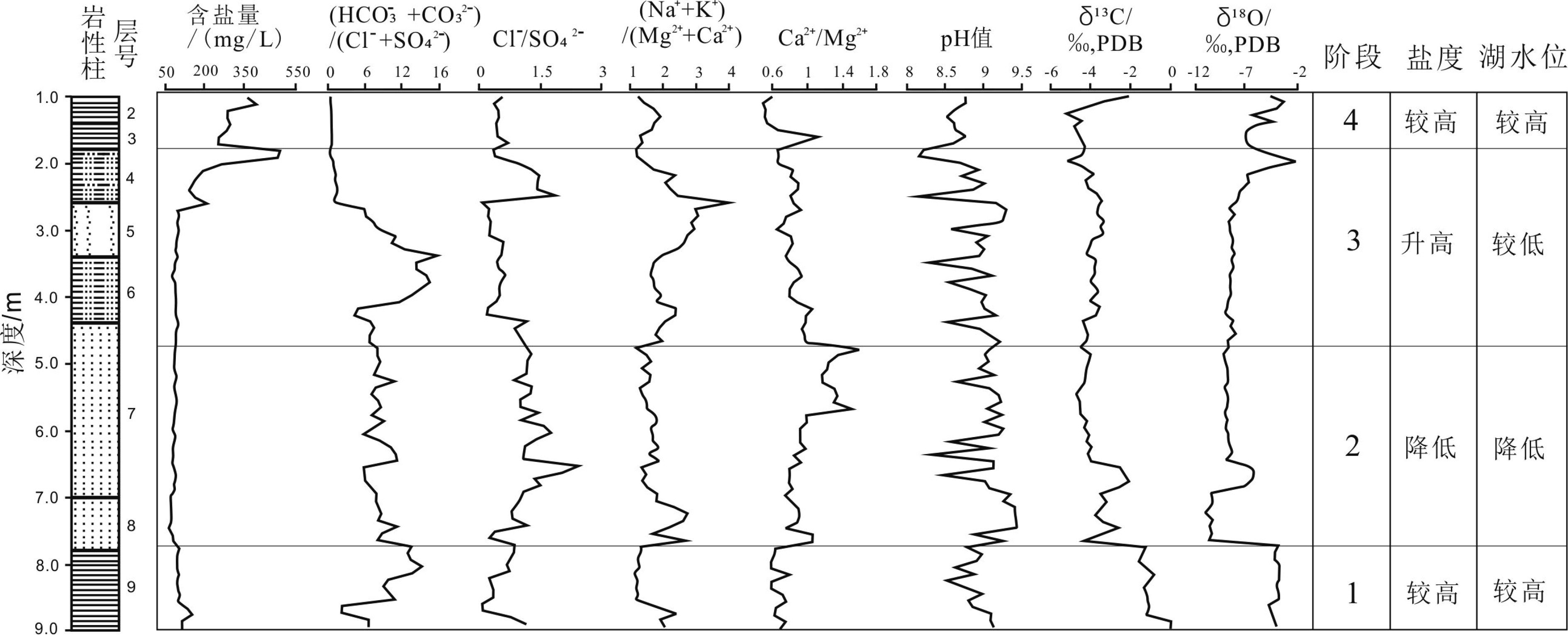
泥河湾盆地发育晚新生代河湖相沉积并记录了华北更新世人类活动历史。近年来的发现表明,作为盆地重要组成部分,蔚县盆地是解读中更新世古人类行为演化与环境适应的关键区域。吉家庄遗址地处蔚县盆地东部吉家庄-黄梅台地古人类活动集中区,是近年来新发现和发掘的中更新世古人类活动遗址之一。对遗址湖滨相沉积物易溶盐的测试和分析表明,此剖面代表的泥河湾古湖易溶盐为HCO3--SO42--Na+型,pH值平均为8.93,偏碱性;剖面平均含盐量为0.67‰,属于半咸水湖,指示半干旱区湖泊演化由碳酸盐湖向硫化物湖过渡阶段。SO42-、Cl-、Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+等5类离子的变化曲线与剖面沉积物易溶盐总含量变化大体一致。依据易溶盐主要离子比值和碳酸盐碳、氧稳定同位素含量,并结合沉积物特点将湖泊气候演化划分为4个阶段,记录了气候由相对冷湿→凉干→相对温暖湿润的变化过程,古人类在该遗址活动时期对应于湖泊演化的第2阶段早期,处在古湖水位降低且气候向干凉转变的湖滨环境。该项研究对探讨泥河湾古湖的演化以及蔚县盆地吉家庄遗址利用者的生存行为与气候关系具有重要意义。
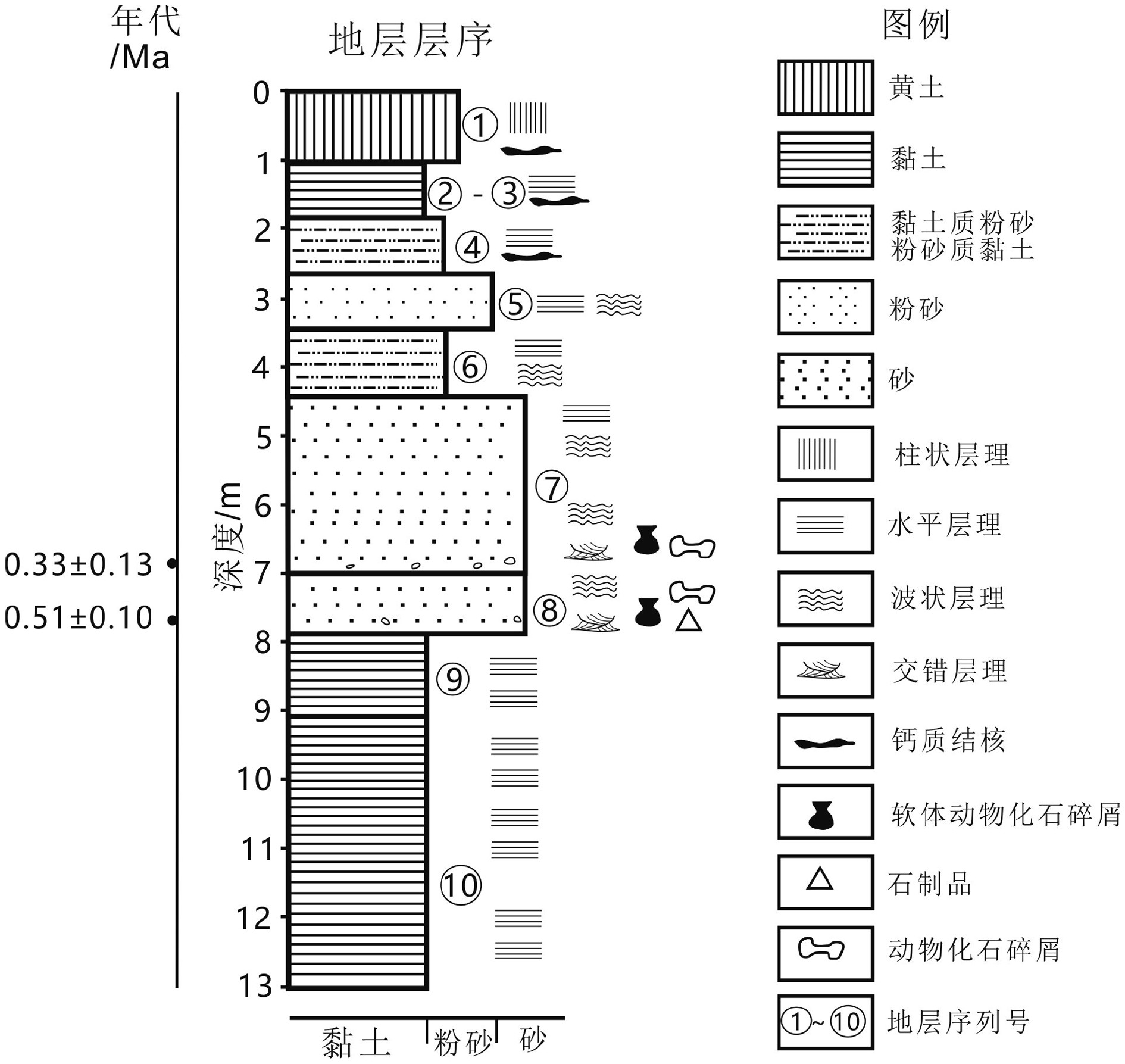
Abstract:The Nihewan Basin, a Late Cenozoic basin in North China filled by fluvio-lacustrine deposits, preserves a large number of Pleistocene archaeological sites, which well recorded the occupation history of early hominins. The Yuxian Basin, as a major part of the Nihewan Basin (senso lato), is a key region for study of such a relationship between early hominin evolution and climatic changes during Middle Peistocene. The Jijiazhuang site is a newly discovered site complex of human occupation, located in the center of the Jijiazhuang-Huangmei fluvio-lacustrine platform in the northeast Yuxian Basin. It was discovered in 2003 and excavated three years later. The Jijiahzuang-B section (JJZ-B), a key section of the Jijiazhuang site complex, is located along a lake shore. The section includes the fluvio-lacustrine fine sand, silt, and clay of brown-grey, brown-yellow, grey-green, dark-grey in color, capped by loess, with a total thickness of more than 20 m. Based on the soluble salts and stable C-O isotopes from carbonate deposits of the section, the studies of hydro-chemical and climatic evolution as well as human activities are carried out by the author. The results suggest that the Paleo-Nihewan lake at the section of JJZ-B site is characterized by HCO3−-SO42−-Na+ions, and the average content of the total soluble salts is around 0.67‰, which indicate a brackish paleo-lake in a carbonate and sulphate phase of lake evolution in a semi-arid area. The variation and distribution patterns of SO42−, Cl−, Na+, Ca2+and Mg2+are well correlated with the total content of soluble salts. Upon the basis and by the changes in total soluble salt and soluble salt indicators as well as the content of carbonate δ13C and δ18O, four paleo-climatic stages corresponding to paleohydro-climatic changes of the lake were recognized: 1) the stage relatively cold and humid with a high lake water level; 2-3) the stages relatively cool and dry with a low lake water level and 4) the warm and humid stage with relatively high lake water level. The period occupied by early hominins corresponds to the early episode of stage 2 after the recession of the lake level evidenced by the sporadic lithic artifacts discovered, and the possible behaviors of animal dismemberment and utilization. In conclusion, the results bear great significance to the research of the adaptive environment and behaviors adopted by early hominins at the Jijiazhuang site and even the Yuxian Basin.
-
Key words:
- soluble salt /
- human occupation /
- Middle Pleistocene /
- Jijiahzuang site /
- Nihewan Basin
-

-
表 1 吉家庄B地点地层剖面易溶盐各离子含量
Table 1. Dominant ions in soluble salt from JJZ-B site
主要离子 最小值/
(mg/L)最大值/
(mg/L)平均值/
(mg/L)标准偏差 HCO3- 43.1 96.2 69.1 4.7 CO32- 2.5 13.65 7.95 3.1 Cl- 1.5 78.15 13.0 8.9 SO42- 2.2 225.0 24.9 80.6 Na+ 9.9 73.1 22.3 28.1 K+ 5.1 12.6 9.2 0.8 Ca2+ 3.7 28.1 8.2 5.9 Mg2+ 4.4 42.6 10.4 3.7 含盐量 66.7 490.0 133.4 135.3 -
[1] 周廷儒, 李华章, 刘清泗, 等. 泥河湾盆地新生代古地理研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991: 1-162.
ZHOU Tingru, LI Huazhang, LI Rongquan, et al. Study on the Cenzoic Paleogeography of the Nihewan Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991: 1-162.
[2] 袁宝印, 同号文, 温锐林, 等. 泥河湾古湖的形成机制及其与早期古人类生存环境的关系[J]. 地质力学学报, 2009, 15(1):77-87
YUAN Baoyin, TONG Haowen, WEN Ruilin, et al. The formation mechanism of the Nihewan paleo-lake and its relationship with living environment for early ancient humen [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(1): 77-87.
[3] 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地考证[J]. 文物春秋, 2016(2):3-11
WEI Qi. Examination on the Nihewan Basin [J]. Stories of Relics, 2016(2): 3-11.
[4] 裴树文. 泥河湾盆地南部(蔚县盆地)发现一处重要古人类活动遗址群[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(1):26
PEI Shuwen. A newly discovered Paleolithic site complex in the south part of the Nihewan basin (Yuxian basin) [J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2017, 36(1): 26.
[5] 裴树文, 马东东, 贾真秀, 等. 蔚县盆地吉家庄旧石器遗址发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(4):510-528
PEI Shuwen, MA Dongdong, JIA Zhenxiu, et al. A preliminary report on excavation of the Jijiazhuang Paleolithic site in the Yuxian Basin, North China [J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4): 510-528.
[6] 白振平. 对蔚县盆地发育过程的初步认识[M]//卫奇, 谢飞. 泥河湾研究论文选编. 北京: 文物出版社, 1989: 466-474.
BAI Zhenping. Preliminary understanding of the development history of Yuxian basin[M]//WEI Qi, XIE Fei. Selected Publications of Nihewan. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 1989: 466-474.
[7] 夏正楷. 大同-阳原盆地的新生代沉积和环境演变[M]//王乃樑, 杨景春, 夏正楷, 等. 山西地堑系新生代沉积与构造地貌. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 1-72.
XIA Zhengkai. Cenozoic geology and environmental change of Datong-Yangyuan Basin[M]//WANG Nailiang, YANG Jingchun, XIA Zhengkai, et al. Cenozoic deposits and Tectonic Geomorphology of Shanxi Graben. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 1-72.
[8] 夏正楷, 刘锡清. 泥河湾层古地理环境的初步认识[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(3):101-110
XIA Zhengkai, LIU Xiqing. On paleogeography of the Nihewan basin during the accumulation of Nihewan series [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1984, 4(3): 101-110.
[9] 吉云平, 王贵玲. 泥河湾盆地第四纪古湖最终消亡过程研究[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(S1):38-42
JI Yunping, WANG Guiling. Final disappearing process of ancient lake during Quaternary in Nihewan Basin [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(S1): 38-42.
[10] Håkanson L, Jansson M. Principles of Lake Sedimentology[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1983: 1-174.
[11] 王晓蓉. 环境化学[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 1993.
WANG Xiaorong. Environmental Chemistry[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1993: 1-360.
[12] 吴敬禄, 王苏民. 若尔盖盆地RM孔自生碳酸盐δ18O、δ13C记录所揭示的环境演化特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(4):63-71
WU Jinglu, WANG Sumin. Environmental characteristics showed by δ18O and δ13C of authicarbonate in core RM from Zoige basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(4): 63-71.
[13] Bowen R. Isotopes and Climates[M]. London: Elsevier Applied Science, 1991: 140-175.
[14] Björck S, Olsson S, Ellis-Evans C, et al. Late Holocene palaeoclimatic records from lake sediments on James Ross Island, Antarctica [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1996, 121(3-4): 195-220. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(95)00086-0
[15] 翟秋敏. 全新世安固里淖易溶盐沉积与环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2001, 3(1):91-96
ZHAI Qiumin. Holocene soluble salt sediments of Angulinao lake and its environment [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2001, 3(1): 91-96.
[16] 张洪, 靳鹤龄, 肖洪浪, 等. 东居延海易溶盐沉积与古气候环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2004, 24(4):409-415
ZHNAG Hong, JIN Heling, XIAO Honglang, et al. Soluble salt sediments of East Juyan Lake and its indicating palaeoclimate environment Changes [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2004, 24(4): 409-415.
[17] 李容全, 乔建国, 邱维理, 等. 泥河湾层内易溶盐沉积及其环境意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 43(5):464-479 doi: 10.1007/BF02875308
LI Rongquan, QIAO Jianguo, QIU Weili, et al. Soluble salt deposit in the Nihewan beds and its environmental significance [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2000, 43(5): 464-479. doi: 10.1007/BF02875308
[18] 李潇丽, 裴树文, 马宁, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址剖面易溶盐沉积及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(3):307-314
LI Xiaoli, PEI Shuwen, MA Ning, et al. Soluble salt sediments and its environmental significance at the Donggutuo site, Nihewan Basin [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(3): 307-314.
[19] 李潇丽, 贾真秀, 裴树文, 等. 泥河湾盆地麻地沟遗址地层易溶盐沉积及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(3):151-159
LI Xiaoli, JIA Zhenxiu, PEI Shuwen, et al. Soluble salt in the sediments at the Madigou site, Nihewan basin and its environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(3): 151-159.
[20] 中国科学院南京土壤研究所. 土壤理化分析[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1978: 1-161.
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Soil Physico-chemical Properties Analysis[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1978: 1-161.
[21] 刘东生. 中国第四纪环境概要[M]//WILLIAMS M A J, DUNKERLEY D L, DE DECKKER P, 等. 第四纪环境. 刘东生, 等译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 189-239.
LIU Dongsheng. Outline of the Quaternary environment in China[M]//WILLIAMS M A J, DUNKERLEY D L, DE DECKKER P, et al. Quaternary Environment. LIU Dongsheng, et al., trans. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 189-239.
[22] 陈茅南. 泥河湾层的研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988: 1-145.
CHEN Maonan. Study on the Nihewan Beds[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Science Press, 1988: 1-145.
[23] 奚晓霞, 穆德芬, 方小敏, 等. 早更新世东山古湖氯离子含量变化与季风演化[J]. 冰川冻土, 1996, 18(2):125-133
XI Xiaoxia, MU Defen, FANG Xiaomin, et al. Variation of Cl- content in Paleo-Dongshan lake during Early Pleistocene and monsoonal evolution [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1996, 18(2): 125-133.
[24] 李徐生, 杨达源, 鹿化煜. 皖南风尘堆积序列氧化物地球化学特征与古气候记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(4):75-82
LI Xusheng, YANG Dayuan, LU Huayu. Oxide-geochemistry features and paleoclimatic record of the aeolian-dust depositional sequence in southern Anhui [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(4): 75-82.
[25] 吴立, 王心源, 莫多闻, 等. 巢湖东部含山凌家滩遗址地层元素地球化学特征研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2015, 39(4):443-453
WU Li, WANG Xinyuan, MO Duowen, et al. Elemental geochemistry of the Lingjiatan site in Hanshan, East Chaohu Lake Basin [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2015, 39(4): 443-453.
[26] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 238-256.
LIU Dongsheng. Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 238-256.
[27] 蓝江湖, 徐海, 刘斌, 等. 湖泊沉积中碳酸盐、有机质及其同位素的古气候意义[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(5):1326-1334
LAN Jianghu, XU Hai, LIU Bin, et al. Paleoclimate implications of carbonate, organic matter, and their stable isotopes in lacustrine sediments: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(5): 1326-1334.
[28] 沈吉, 吴瑞金, 羊向东, 等. 大布苏湖沉积剖面碳酸盐含量、氧同位素特征的古气候意义[J]. 湖泊学报, 1997, 9(3):217-222 doi: 10.18307/1997.0304
SHEN Ji, WU Ruijin, YANG Xiangdong, et al. Paleoclimatic change inferred from δ18O and carbonate content of the section in Dabusu lake [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1997, 9(3): 217-222. doi: 10.18307/1997.0304
[29] 雷国良, 张虎才, 朱云, 等. 湖泊沉积碳酸盐氧同位素影响因素的定量评估[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(1):143-151
LEI Guoliang, ZHANG Hucai, ZHU Yun, et al. Quantitative evaluation for driving factors of carbonate Oxygen isotope composition in lake sediments [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(1): 143-151.
[30] 曾承. 湖泊自生碳酸盐碳同位素在环境变化中的应用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2010, 18(2):1-6
ZENG Cheng. Carbon isotopic records from lacustrine authigenic carbonates as environmental change indicators [J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2010, 18(2): 1-6.
[31] Maslin M A, Brierley C M, Milner A M, et al. East African climate pulses and early human evolution [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 101: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.06.012
[32] Lepre C J. Early Pleistocene lake formation and hominin origins in the Turkana-Omo rift [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 102: 181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.08.012
[33] 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地考古地质学框架[C]//童永生, 张银运, 吴文裕, 等. 演化的实证: 纪念杨钟健教授百年诞辰论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1997: 193-208.
WEI Qi. The framework of archaeological geology of the Nihewan Basin[C]//TONG Yongsheng, ZHANG Yinyun, WU Wenyu, et al. Evidence for Evolution Essays in Honor of Prof. Chungchien Young on the Hundredth Anniversary of His Birth. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1997: 193-208.
[34] 袁宝印, 夏正楷, 牛平山. 泥河湾裂谷与古人类[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 1-257.
YUAN Baoyin, XIA Zhengkai, NIU Pingshan. Nihewan Rift and Early Man[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011: 1-257.
[35] 朱日祥, 邓成龙, 潘永信. 泥河湾盆地磁性地层定年与早期人类演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2002, 27(6):922-944
ZHU Rixiang, DENG Chenglong, PAN Yongxin. Magnetochronology of the fluvio-lacustrine sequences in the Nihewan basin and its implications for early human colonization of Northeast Asia [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2002, 27(6): 922-944.
[36] Deng C L, Zhu R X, Zhang R, et al. Timing of the Nihewan formation and faunas [J]. Quaternary Research, 2008, 69(1): 77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.10.006
[37] Ao H, Dekkers M J, An Z S, et al. Magnetostratigraphic evidence of a mid-Pliocene onset of the Nihewan Formation - implications for early fauna and hominid occupation in the Nihewan Basin, North China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 59: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.10.025
[38] 唐锐枰, 葛俊逸, 庞海娇, 等. 泥河湾黑土沟剖面磁组构特征及古湖水文环境变化[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(11):1027-1045 doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0737
TANG Ruiping, GE Junyi, PANG Haijiao, et al. Paleohydro-climatic changes revealed by anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility at the Heitugou section, Nihewan Basin, and its influences on human’s occupation [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(11): 1027-1045. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0737
[39] 吴文祥. 试论早期人类占据泥河湾盆地的时代[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(3):249-253
WU Wenxiang. A tentative discussion on the age of the ancient human occupation of the Nihewan Basin [J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(3): 249-253.
[40] 卫奇, 裴树文, 贾真秀, 等. 泥河湾盆地黑土沟遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(1):43-62
WEI Qi, PEI Shuwen, JIA Zhenxiu, et al. Heitugou Paleolithic site from the Lower Pleistocene in the Nihewan Basin, Northern China [J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2016, 35(1): 43-62.
[41] Yang S X, Deng C L, Zhu R X, et al. The Paleolithic in the Nihewan Basin, China: Evolutionary history of an Early to Late Pleistocene record in Eastern Asia [J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2020, 29(3): 125-142. doi: 10.1002/evan.21813
[42] 夏正楷. 大同-阳原盆地古泥河湾湖的岸线变化[J]. 地理研究, 1992, 11(2):52-59
XIA Zhengkai. The study of the change of ancient lake shore in the Datong-Yangyuan basin [J]. Geographical Research, 1992, 11(2): 52-59.
[43] 裴树文, 李潇丽, 刘德成, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址古人类生存环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(21):3896-3904 doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0646-9
PEI Shuwen, LI Xiaoli, LIU Decheng, et al. Preliminary study on the living environment of hominids at the Donggutuo site, Nihewan Basin [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(21): 3896-3904. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0646-9
[44] Li X L, Pei S W, Jia Z X, et al. Paleoenvironmental conditions at Madigou (MDG), a newly discovered Early Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China [J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 400: 100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.07.071
[45] 武仙竹, 哈连维奇•弗拉基米尔, 阿给莫娃•伊莲娜. 西伯利亚特罗伊茨卡亚季节性古营地遗址研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4):805-812
WU Xianzhu, Харевич B M, Акимовa E B. Research on an seasonal ancient camp site at ТРОИЦКАЯ, Siberia [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(4): 805-812.
-




 下载:
下载: