Environmental magnetic characteristics and influencing factors on the west coast of Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica
-
摘要:
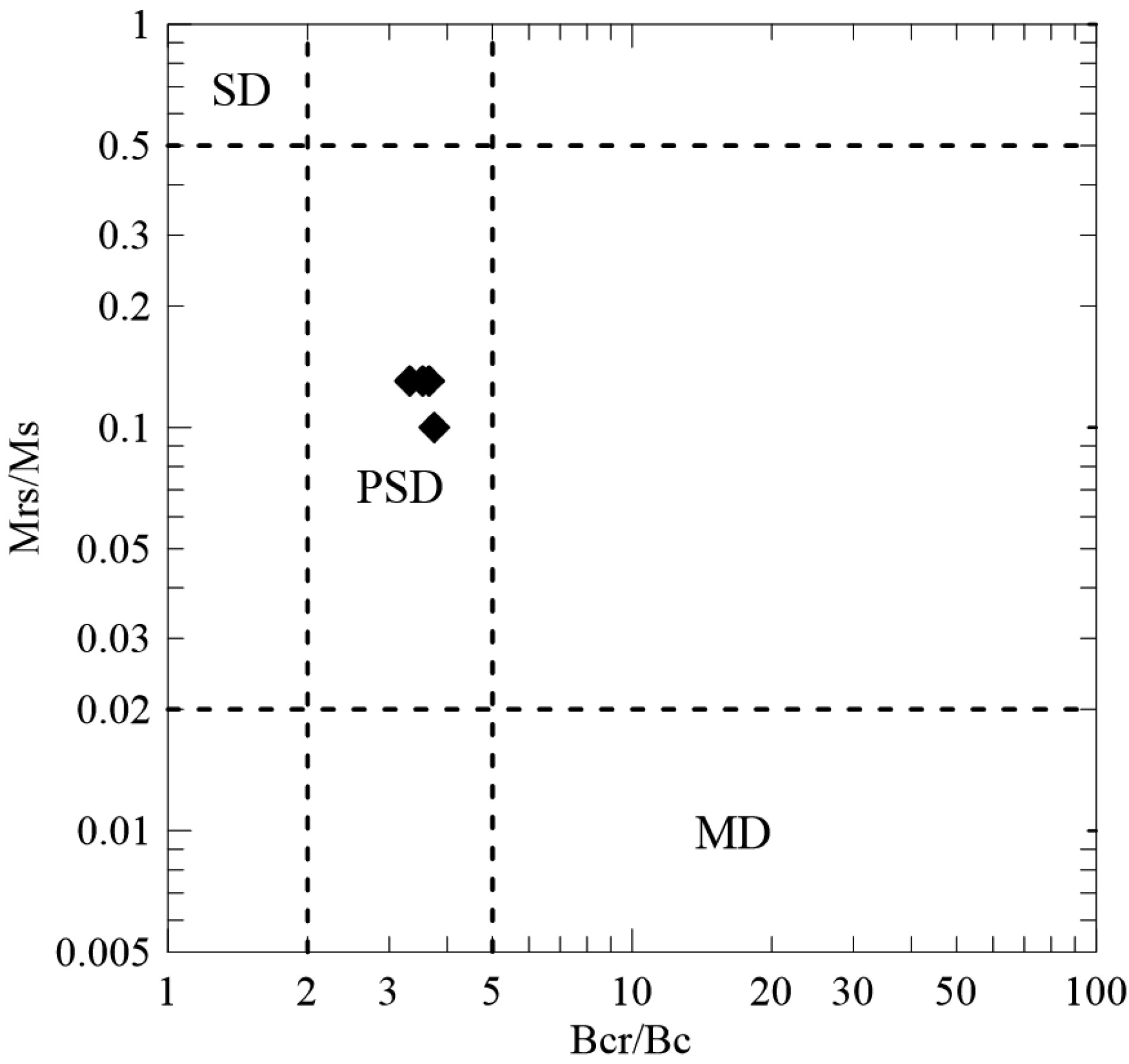
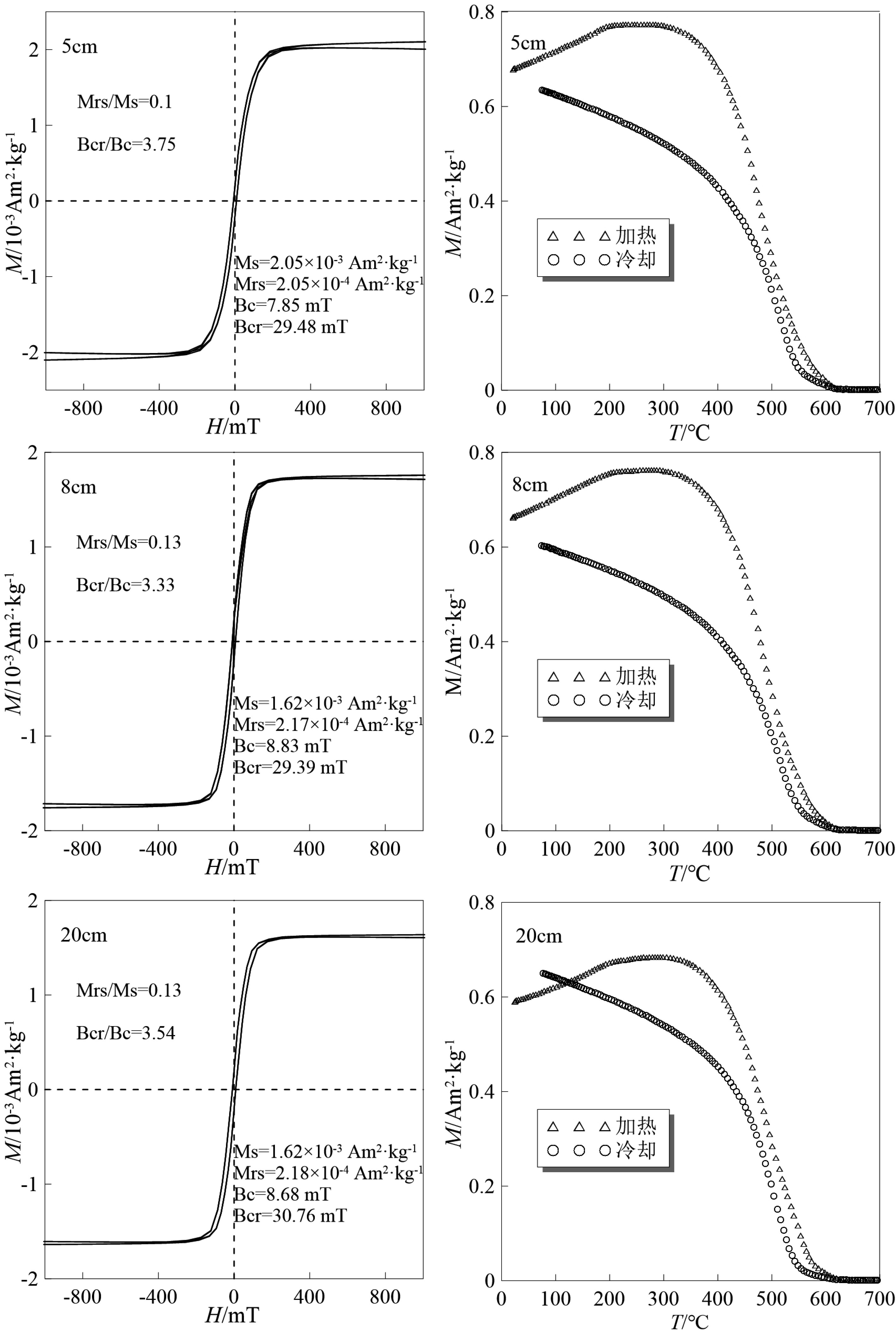
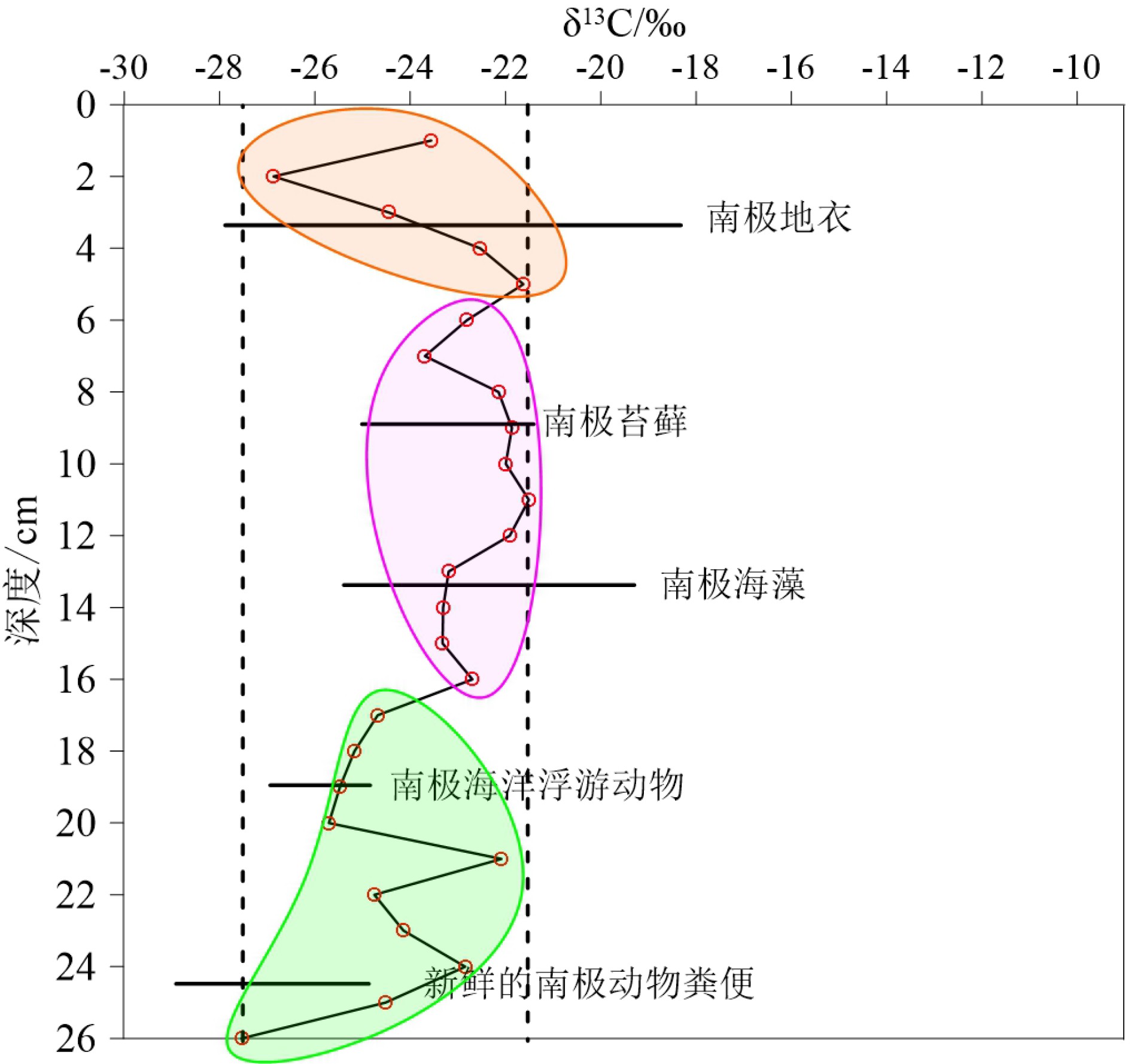
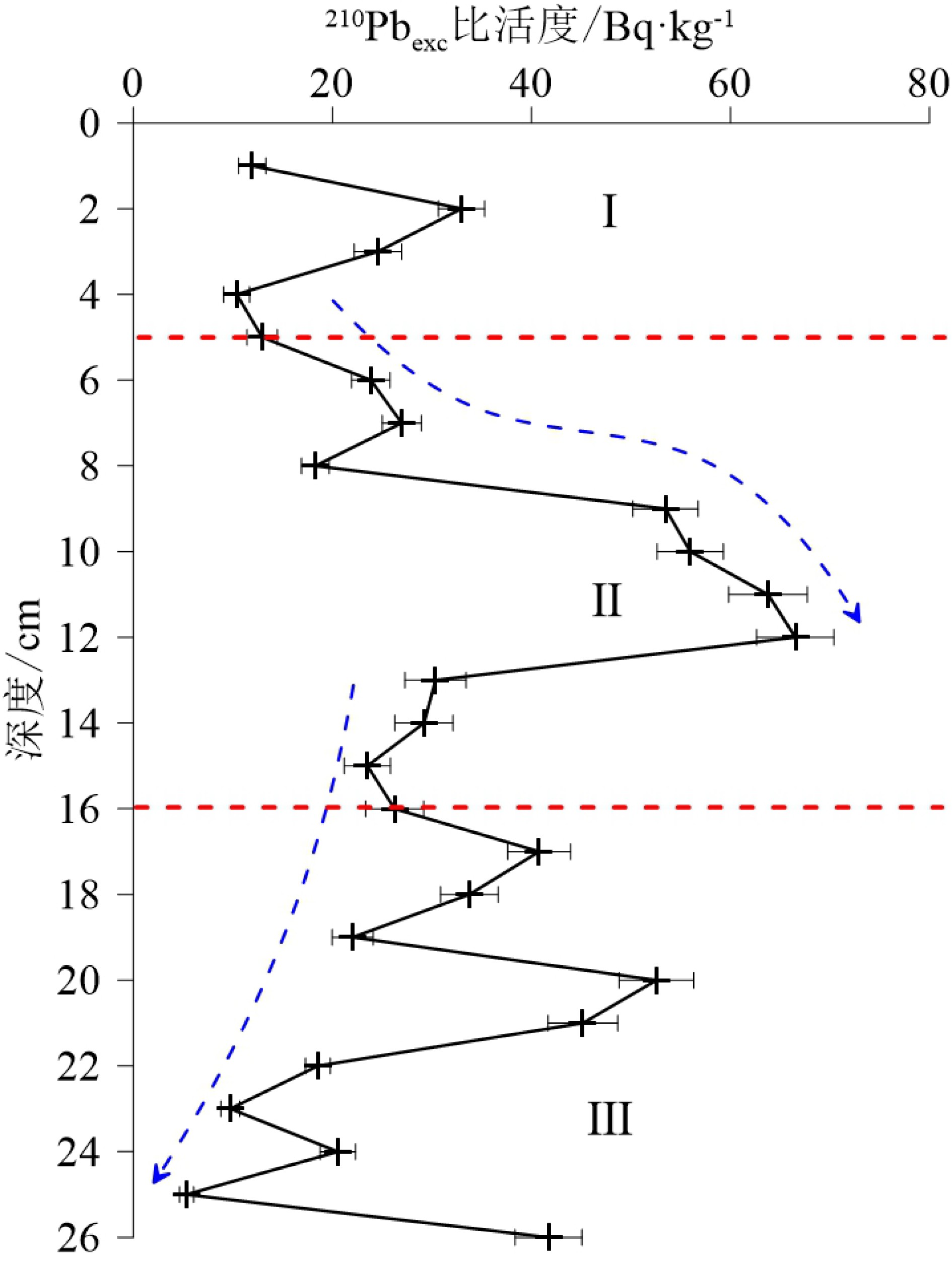
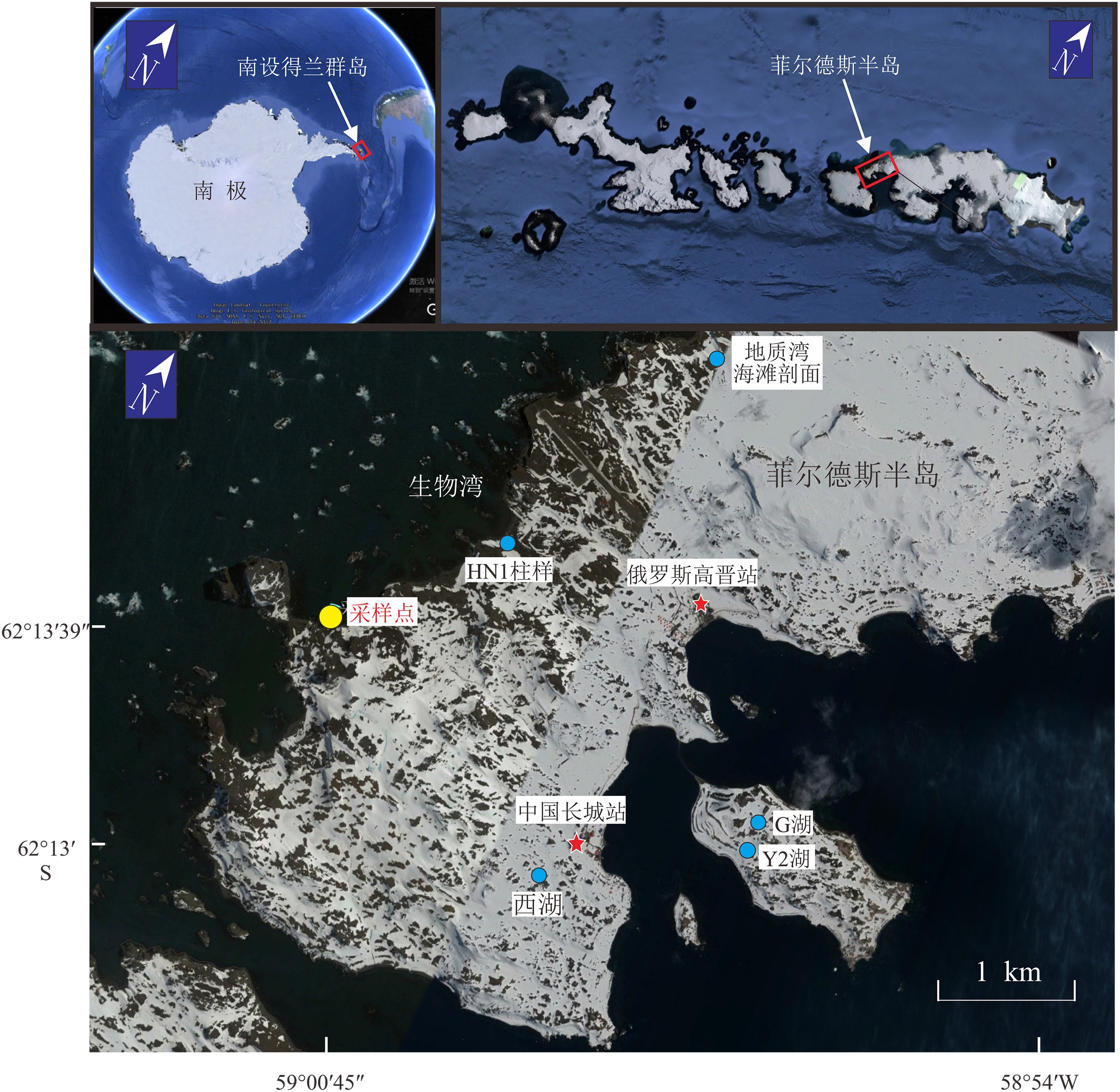
南极无冰区独特的环境系统近几十年来被广泛地关注和研究,同时环境磁学方法在环境变化研究中也被越来越多的应用。本文通过对2015年采自南极菲尔德斯半岛西海岸一根长26 cm的柱样进行环境磁学、粒度、210Pb和稳定碳同位素测试分析发现,由于海岸基岩为安山质玄武岩,所以沉积柱样整体的磁性矿物含量较高,表现出较强的磁性,其磁化率均值(χlf)高达1597×10−8 m3·kg−1,约为一般海滩磁化率值的3~4倍。其磁性矿物类型主要是假单畴的亚铁磁性矿物颗粒(磁铁矿)且含有少量的反铁磁性矿物颗粒(赤铁矿)。垂向上210Pb和粒度结果显示,柱样上段沉积物粒度较细,水动力较弱使得细粒磁性矿物颗粒被快速保存下来,而随着深度的增加粒度逐渐变粗,岸滩水动力相对增强,而且底部受到生物有机质溶解作用的影响导致柱样上段磁学参数值高于下段。
Abstract:The unique environmental system of the Antarctic ice-free region has been widely studied in recent decades, and environmental magnetism is doubtlessly the method most commonly used in the study. In the year of 2015, a 26 cm long core was collected by the authors from the west coast of the Antarctic peninsula for environmental magnetism, granularity, 210Pb and stable carbon isotope testing and analysis. The bedrock of the coast is dominated by andesitic basalt, so the sediments of the core samples are high in magnetic minerals in general, that resulted in high magnetism. The average susceptibility (χlf) is about 1597×10−8 m3·kg−1, almost 3~4 times higher than the beach magnetic susceptibility. The magnetic minerals mainly consist of ferromagnetic particles (magnetite) with small amount of antiferromagnetic particles (hematite). The vertical changes in 210Pb and granularity data suggest that the sediment particle size is too fine for water movement, and therefore, the movement of pore water is weak. Under such a circumstance, the fine magnetic mineral grains are easily to be preserved. With the increase in depth, the sediments gradually become coarser, and the movement of water is thus enhanced. Plus the influence of biological organic dissolution, magnetism parameters of the lower part of the core is decreased accordingly.
-
Key words:
- environmental magnetism /
- beach sediment /
- 210Pb dating /
- stable carbon isotope /
- Fildes Peninsula
-

-
表 1 柱样各段测试参数结果
Table 1. Test parameters for each section of the core
测试参数 第I段 第II段 第III段 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 χlf /(10−8m3·kg−1) 1702~1754 1727 1627~1781 1709 1315~1518 1418 χARM /(10−8m3·kg−1) 3208~3526 3343 2722~3666 3145 1693~2481 2091 SIRM /(10−6Am2·kg−1) 173813~199122 190423 170772~212543 197464 156705~215261 177939 χfd% 0.1~0.8 0.5 0.1~1.4 0.6 0.1~0.8 0.4 χARM/χlf 1.9~2.0 1.9 1.5~2.2 1.8 1.2~1.7 1.5 χARM/SIRM /(m·A−1) 16.3~19.7 17.6 13.8~19.3 16 9.8~13.9 11.9 HIRM /(10−6Am2·kg−1) 3337~30204 16697 5456~28867 15009 5569~18502 11838 S−300 /% 98.5~99.8 99.1 98.6~99.7 99.2 98.9~99.7 99.3 HIRM/% 0.4~3.1 1.7 0.6~2.9 1.5 0.6~2.1 1.3 中值粒径/mm 0.2~0.3 0.3 0.3~0.5 0.3 0.5~1.4 1 砾石含量/% 1.6~8.8 5.2 1.0~17.8 6.2 8.8~43.6 27.6 砂含量/% 75.3~89.1 82.8 71.3~87.4 81.5 55.2~98.0 74.4 粉砂和黏土含量/% 9.4~16.0 12.0 9.5~15.6 12.5 1.0~7.1 2.6 表 2 不同类型沉积物的磁学参数
Table 2. Magnetic parameters of different types of sediments
沉积物 物源类型 χlf
/10−8m3·kg−1χARM
/10−8m3·kg−1SIRM
/10−6 Am2·kg−1HIRM
/10−6 Am2·kg−2S−300/% 数据来源 黄河 黄土 范围 20~100 23~509 1942~11982 139~956 86.4~99.7 文献[43] 平均值±标准差 43±13 164±80 5574±1445 372±101 93.3±2.3 长江 中酸性火成岩 范围 43~220 84~662 5551~16763 241~671 92.4~96.3 文献[43] 平均值±标准差 73±20 286±130 10900±2505 525±111 95.0±0.7 南极摩西岛土壤 片岩、砾岩 范围 9~339.6 − 1000~39000 − 81.5~98.5 文献[44] 平均值±标准差 55.1±75.8 − 6700±6900 − 90±4.2 东南极
Sandy湖长英质片麻岩 范围 20.96~66.19 60~410 − − − 文献[22] 平均值±标准差 − − − − − 印度西部
海滩片岩、花岗岩 范围 1.2~60.3 − 48.7~6908.4 222.9~74989.2 9~82 文献[45] 平均值±标准差 9.1±19.2 − 940.7±2243 8938.6±24774.2 52.8±22.1 印度尼西亚东部熔岩 玄武岩、安山岩 范围 734.87~1795.17 − − − − 文献[46] 平均值±标准差 1471.53 − − − − 中国东海
北部陆架黄河长江入海物质 范围 15~50 30~130 − − 0.84~0.88 文献[47] 平均值±标准差 − − − − − 南极菲尔德斯半岛海滩 玄武岩、安山岩 范围 1314.8~1780.8 1692.8~3666.3 156705.7~215260.6 333.7~3020.4 98.5~99.8 本文 平均值±标准差 1600.9±152.7 2772.4±592.5 188732.4±16370.1 1392.8±685.4 99.3±0.3 -
[1] 黄婧, 孙立广, 王新明, 等. 西南极菲尔德斯半岛海豹粪土沉积物有机地球化学特征[J]. 极地研究, 2011, 23(1):35-41
HUANG Jing, SUN Liguang, WANG Xinming, et al. Organic geochemistry of seal excrement sediment from Fildes Peninsula, Western Antarctica [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar research, 2011, 23(1): 35-41.
[2] 刘晓收, 王晓晓, 王璐, 等. 南极菲尔德斯半岛潮间带小型底栖动物初步研究[J]. 极地研究, 2020, 32(3):281-289
LIU Xiaoshou, WANG Xiaoxiao, WANG Lu, et al. A preliminary study of intertidal Meiofauna in Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2020, 32(3): 281-289.
[3] Sun L G, Xie Z Q, Zhao J L. A 3, 000-year record of penguin populations [J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6806): 858. doi: 10.1038/35038163
[4] Wang J J, Wang Y H, Wang X M, et al. Penguins and vegetations on Ardley Island, Antarctica: evolution in the past 2400 years [J]. Polar Biology, 2007, 30(11): 1475-1481. doi: 10.1007/s00300-007-0308-9
[5] Lu Z B, Cai M H, Wang J, et al. Baseline values for metals in soils on Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctica: the extent of anthropogenic pollution [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2011, 184(11): 7013-7021.
[6] Fabri-Jr R, Krause M, Dalfior B M, et al. Trace elements in soil, lichens, and mosses from Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica: spatial distribution and possible origins [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(4): 124.
[7] Na G S, Liu C Y, Wang Z, et al. Distribution and characteristic of PAHs in snow of Fildes Peninsula [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(9): 1445-1451. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60605-5
[8] Na G S, Gao Y Z, Li R J, et al. Occurrence and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmosphere and soil from 2013 to 2019 in the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 156: 111173.
[9] Li H J, Fu J J, Zhang A Q, et al. Occurrence, bioaccumulation and long-range transport of short-chain chlorinated paraffins on the Fildes Peninsula at King George Island, Antarctica [J]. Environment International, 2016, 94: 408-414. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.05.005
[10] 谢周清, 孙立广, 刘晓东, 等. 近2000年来南极菲尔德斯半岛西湖沉积物中稀土元素1/δEu特征与气候演变[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(2):303-306 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.02.019
XIE Zhouqing, SUN Liguang, LIU Xiaodong, et al. The characteristic of 1/δEu in the sediments of west lake with respect to climate change during the past 2000 Years, Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(2): 303-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.02.019
[11] 李小梅, 袁宝印, 赵俊琳. 南极菲尔德斯半岛全新世以来湖泊沉积的环境演变研究[J]. 极地研究, 2002, 14(1):35-43
LI Xiaomei, YUAN Baoyin, ZHAO Junlin. Holocene environmental change delivered from lake core in Fildes Peninsula of King George island, Antarctic [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2002, 14(1): 35-43.
[12] Liu Q, Roberts A P, Larrasoana J C, et al. Environmental magnetism: principles and applications[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2012, 50(4): 1-50.
[13] Evans M E, Heller F. Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics [M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2003.
[14] 邓成龙, 袁宝印, 胡守云, 等. 环境磁学某些研究进展评述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(2):93-101
DENG Chenglong, YUAN Baoyin, HU Shouyun, et al. Environmental magnetism: a review [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(2): 93-101.
[15] Oldfield F. Toward the discrimination of fine-grained ferrimagnets by magnetic measurements in lake and near-shore marine sediments [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(B5): 9045-9050. doi: 10.1029/93JB03137
[16] Watkins S J, Maher B A. Magnetic characterization of present-day deep-sea sediments and sources in the North Atlantic [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 214(3-4): 379-394. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00422-9
[17] 霍城, 李盼盼, 葛林科, 等. 南极南设得兰群岛附近海域表层沉积物中有色溶解有机物的分布特征及来源分析[J]. 极地研究, 2016, 28(4):484-490
HUO Cheng, LI Panpan, GE Linke, et al. Distribution and source of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the surface sediment from the sea area surrounding the South Shetland islands, Antarctica [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2016, 28(4): 484-490.
[18] 孙立广, 谢周清, 刘晓东, 等. 西南极乔治王岛和东南极拉斯曼丘陵典型无冰区概述-南极无冰区生态地质学 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
SUN Liguang, XIE Zhouqing, LIU Xiaodong, et al. An Overview of Typical Ice-free Areas in the Geowang Island and Lasman Hills in the Southwest Pole and the Southeast Pole, Ecological Geology of Ice-free Areas in Antarctica[M]. Beijing: science press, 2006.
[19] 王自磐, Peter H U, Pfeiffer S. 南极菲尔德斯半岛海鸟与种群分布[J]. 极地研究, 2004, 16(4):271-280
WANG Zipan, Peter H U, Pfeiffer S. Species and distribution of the birds on Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctica [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2004, 16(4): 271-280.
[20] 赵烨. 南极乔治王岛菲尔德斯半岛土壤与环境 [M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999.
ZHAO Ye. The Soil and Environment in the Fildes Peninsula of King George Island, Antarctica[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1999.
[21] 张凯棣, 李安春, 卢健, 等. 东海陆架沉积物环境磁学特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(2):246-257
ZHANG Kaidi, LI Anchun, LU Jian, et al. Magnetic property of the East China Sea sediment: indication to the provenance [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(2): 246-257.
[22] Warrier A K, Mahesh B S, Mohan R, et al. Glacial–interglacial climatic variations at the Schirmacher Oasis, East Antarctica: The first report from environmental magnetism [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 412: 249-260. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.08.007
[23] Zhang Q, Liu Q, Li J, et al. An integrated study of the eolian dust in pelagic sediments from the North Pacific Ocean based on environmental magnetism, transmission electron microscopy, and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(5): 3358-3376. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014951
[24] 吕双燕, 金秉福, 贺世杰, 等. 莱州湾-龙口湾表层沉积物有机质特征及来源分析[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(3):650-658
LV Shuangyan, JIN Bingfu, HE Shijie, et al. Characteristics and sources of organic matter in surface sediments of Laizhou Bay and Longkou Bay [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(3): 650-658.
[25] 孙萱, 宋金明, 于颖, 等. 元素分析仪快速测定海洋沉积物TOC和TN的条件优化[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(7):14-19
SUN Xuan, SONG Jinming, YU Ying, et al. A rapid method for determing the total organic carbon and total nitrogen in marine sediments with an elemental analyzer [J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(7): 14-19.
[26] 夏威岚, 薛滨. 吉林小龙湾沉积速率的210Pb和137Cs年代学方法测定[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(1):124-125 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.01.017
XIA Weilan, XUE Bin. The 210Pb and 137Cs chronological meansurement on sedimentation rate of Xiaolongwan, Jilin [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(1): 124-125. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.01.017
[27] Hoffmann V, Knab M, Appel E. Magnetic susceptibility mapping of roadside pollution [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 66(1-2): 313-326. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(99)00014-X
[28] 彭俊, 陈洪全, 马随随, 等. 黄河三角洲潮滩沉积物磁性特征与沉积环境分析[J]. 地理科学, 2014, 34(10):1262-1269
PENG Jun, CHEN Hongquan, MA Suisui, et al. Magnetic properties of sediment and sedimentary environment in tidal flat of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(10): 1262-1269.
[29] 刘青松, 邓成龙. 磁化率及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(4):1041-1048 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021
LIU Qingsong, DENG Chenglong. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021
[30] Maher B A, Taylor R M. Formation of ultrafine-grained magnetite in soils [J]. Nature, 1988, 336(6197): 368-370. doi: 10.1038/336368a0
[31] Day R, Fuller M, Schmidt V A. Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1977, 13(4): 260-267. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(77)90108-X
[32] Dunlop D J. Theory and application of the day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc). 1. Theoretical curves and tests using titanomagnetite data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2002, 107(B3): 4-22.
[33] Dunlop D J. Theory and application of the day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc). 2. Application to data for rocks, sediments, and soils [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2002, 107(B3): 5-15.
[34] 李波, 王艳, 钟和贤, 等. 花东海盆浊流沉积的磁性特征及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9):3330-3342 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160917
LI Bo, WANG Yan, ZHONG Hexian, et al. Magnetic properties of turbidites in the Huatung Basin and their environmental implications [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(9): 3330-3342. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160917
[35] 朱日祥, 李春景, 吴汉宁, 等. 中国黄土磁学性质与古气候意义[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1994, 24(9):992-997
ZHU Rixiang, LI Chunjing, WU Hanning, et al. Magnetic properties and paleoclimatic significance of loess in China [J]. Science in China: B, 1994, 24(9): 992-997.
[36] 李萍. 冲绳海槽沉积物磁性特征及其与环境的关系 [D]. 中国海洋大学, 2005.
LI Ping. Magnetic properties of sediments from the Okinawa trough and their relationship to sedimentary environment[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean university of China, 2005.
[37] Roberts A P. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite(Fe3S4) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 134(3-4): 227-236.
[38] Liu X D, Li H C, Sun L G, et al. δ13C and δ15N in the ornithogenic sediments from the Antarctic maritime as palaeoecological proxies during the past 2000 yr [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 243(3-4): 424-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2006.01.018
[39] Thompson R, Oldfield F. Environmental Magnetism [M]. London: Oldfield, 1986.
[40] 潘永信, 邓成龙, 刘青松, 等. 趋磁细菌磁小体的生物矿化作用和磁学性质研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(24):2563-2568
PAN Yongxin, DENG Chenglong, LIU Qingsong, et al. Biomineralization and magnetism of bacterial magnetosomes [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(24): 2563-2568.
[41] 谢又予. 中国南极长城站地区(菲尔德斯半岛)地貌与沉积 [M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993.
XIE Youyu. Geomorphology and Deposition in the Great Wall Station Area (Fildes Peninsula) in Antarctica, China[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1993.
[42] 卢良兆, 许文良. 岩石学 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
LU Liangzhao, XU Wenliang. Petrology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011.
[43] Zhang W G, Xing Y, Yu L Z, et al. Distinguishing sediments from the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China: a mineral magnetic approach [J]. The Holocene, 2008, 18(7): 1139-1145. doi: 10.1177/0959683608095582
[44] Chaparro M A E, Nuñez H, Lirio J M, et al. Magnetic screening and heavy metal pollution studies in soils from Marambio Station, Antarctica [J]. Antarctic Science, 2007, 19(3): 379-393. doi: 10.1017/S0954102007000454
[45] Bandaru V L, Gawali P B, Hanamgond P T, et al. Heavy metal monitoring of beach sands through environmental magnetism technique: a case study from Vengurla and Aravali beaches of Sindhudurg district, Maharashtra, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(8): 678. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5477-9
[46] Pratama A, Bijaksana S, Abdurrachman M, et al. Rock Magnetic, Petrography, and Geochemistry Studies of Lava at the Ijen Volcanic Complex (IVC), Banyuwangi, East Java, Indonesia [J]. Geosciences, 2018, 8(5): 183. doi: 10.3390/geosciences8050183
[47] Kim W, Doh S J, Yu Y, et al. Magnetic evaluation of sediment provenance in the northern East China Sea using fuzzy c-means cluster analysis [J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 337: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.01.001
[48] Wang Y H, Huang Q H, Lemckert C, et al. Laboratory and field magnetic evaluation of the heavy metal contamination on Shilaoren Beach, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 117(1-2): 291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.080
[49] 张卫国, 俞立中. 长江口潮滩沉积物的磁学性质及其与粒度的关系 [J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2002, (9): 783-792.
ZHANG Weiguo, YU Lizhong. Magnetic properties of tidal flat sediments in the Yangtze Estuary and their relationship with grain size[J]. Scientia Sinica(Series D: Earth Sciences), 2002, (9): 954-966.
[50] 刘健. 磁性矿物还原成岩作用述评[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(4):103-107
LIU Jian. Reductive diagenesis of magnetic minerals: a review [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(4): 103-107.
-



 下载:
下载: