Sediment pore-structure and permeability variation induced by hydrate formation: Evidence from low field nuclear magnetic resonance observation
-
摘要:
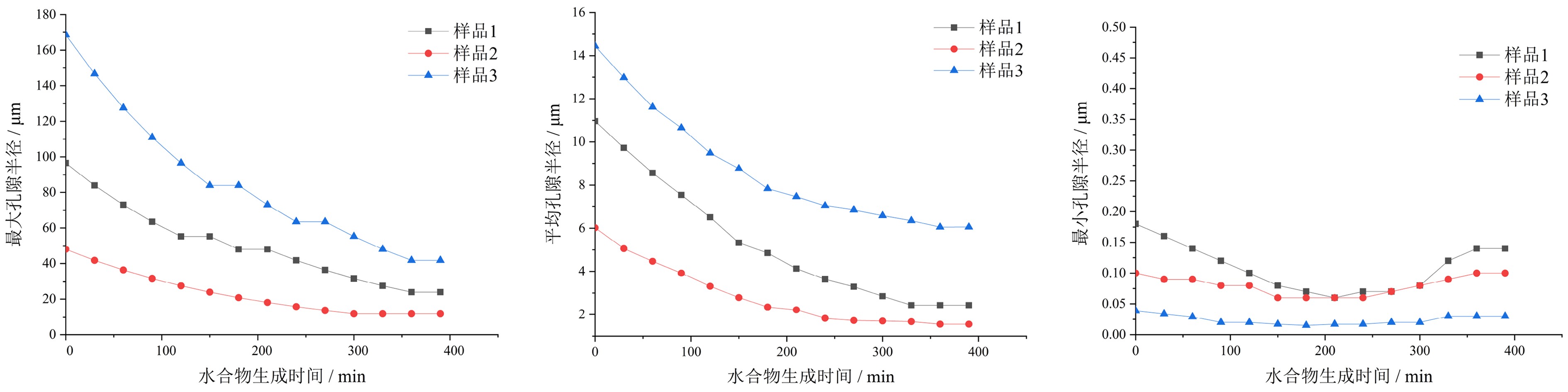
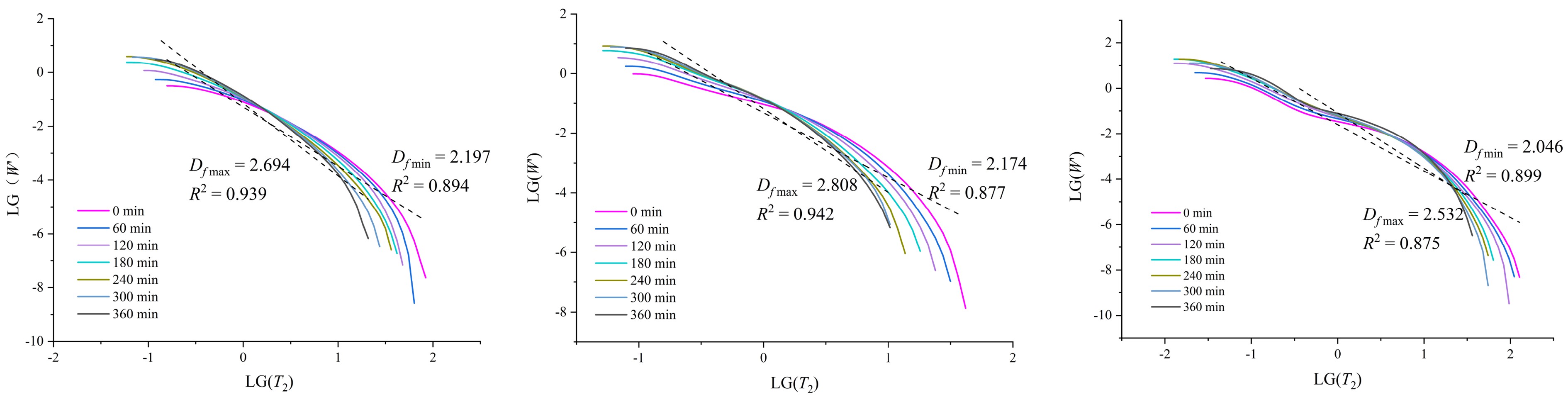
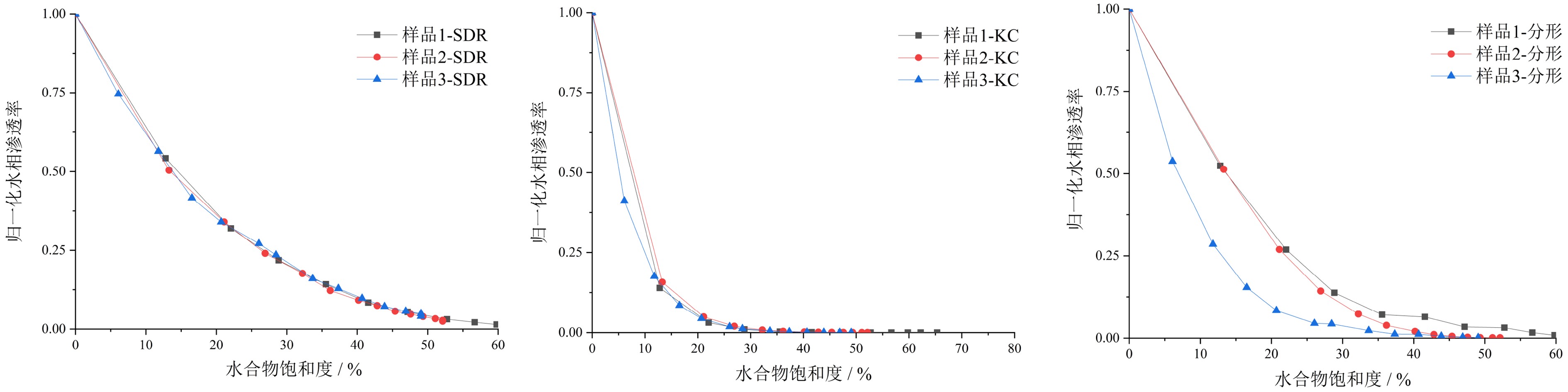
含水合物储层的宏观物性表现是由储层沉积物的微观孔隙特征所控制的。理解沉积物在水合物生成过程中微观孔隙结构特征变化对于其物性特征的预测和分析有重要意义。本文利用低场核磁共振(LFNMR)技术监测了不同砂样中氙气水合物的生成过程,利用横向弛豫时间(T2)谱对生成过程中的微观孔隙结构及水相渗透率演化规律进行了分析。研究表明,水合物优先生成于沉积物较大孔隙中,在半径较小的孔隙中水合物很难生成;生成前期水合物的生长速率较快,后期逐渐减缓;水合物的生成导致沉积物孔隙尺寸和分布的变化,表现为随着水合物的生成,沉积物水相孔隙空间的最大孔隙半径和平均孔隙半径逐渐减小,孔隙空间的分形系数逐渐增大;沉积物水相渗透率随水合物生成过程中水合物饱和度的增加,先迅速减小后缓慢减小;具有不同孔隙结构特征的样品水相渗透率变化规律存在差异;相较于SDR模型和Kozeny-Carman模型,分形方法能够更好地体现孔隙结构变化对渗透率的影响。
Abstract:The macro-scale physical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments is in fact controlled by their micro-scale pore-structures. Understanding the changes in pore-structure characteristics of the sediments during the process of hydrate formation is essential to the analyzing and predicting of the sediment properties. In this paper, the formation processes of Xenon hydrate in different sandy samples are measured with the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LFNMR) method. The obtained transverse relaxation time (T2) spectra are interpreted for study of the changes in pore-structure and physical properties of the sediments during the hydrate formation. The results show that Xenon hydrates preferentially form in larger pores and only little amount of hydrates formed in smaller pores; the forming rate of hydrate is higher at the early stage of formation but decrease slowly at the later stage; the hydrate formation process also leads to the changes in pore size and pore-size distribution patterns, for examples, the maximum radius and mean radius of the water-phase pores decrease with increasing hydrate saturation, while the fractal dimension of the effective water-phase pores increases with the increasing hydrate saturation; the water-phase permeability decreases rapidly in the early stage of hydrate formation, but slowly decrease since then; the changes of water-phase permeability during hydrate formation are affected by the pore-structures of the sediment; compared to the SDR model and the Kozeny-Carman model, the fractal model of permeability performs better in showing the influences of pore-structure characteristics on the changes of water-phase permeability during the hydrate formation.
-

-
表 1 测量沉积物样品基础物性参数
Table 1. Physical properties of sedimentary samples for testing
样品编号 样品组成 样品粒径分布/μm 样品尺寸/cm2 样品1 不规则石英砂颗粒 150~250 ϕ 2.5×4.2 样品2 不规则石英砂颗粒 100~150 ϕ 2.5×4.9 样品3 不规则石英砂颗粒 75~250 ϕ 2.5×4.6 -
[1] Boswell R, Collett T S. Current perspectives on gas hydrate resources [J]. Energy Environmental Science, 2011, 4(4): 1206-1215. doi: 10.1039/C0EE00203H
[2] Ruppel C D, Kessler J D. The interaction of climate change and methane hydrates [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2017, 55(1): 126-168. doi: 10.1002/2016RG000534
[3] 吴能友, 黄丽, 胡高伟, 等. 海域天然气水合物开采的地质控制因素和科学挑战[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):1-11
WU Nengyou, HUANG Li, HU Gaowei, et al. Geological controlling factors and scientific challenges for offshore gas hydrate exploitation [J]. Marine Geology & Quantenary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 1-11.
[4] 吴能友. 天然气水合物运聚体系: 理论、方法与实践[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 2020: 2-17.
WU Nengyou. Gas Hydrate Migartion and Accumulation System Theory, Method and Practice[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 2020: 2-17.
[5] 叶建良, 秦绪文, 谢文卫, 等. 中国南海天然气水合物第二次试采主要进展[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(3):557-568
YE Jianliang, QIN Xuwen, XIE Wenwei, et al. Main progress of the second gas hydrate trial production in the South China Sea [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(3): 557-568.
[6] 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 陆敬安, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征及主控因素新认识[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):1-14
YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, LU Jing’an, et al. New understandings on the characteristics and controlling factors of gas hydrate reservoirs in the Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 1-14.
[7] 吴能友, 李彦龙, 万义钊, 等. 海域天然气水合物开采增产理论与技术体系展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):100-115 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.008
WU Nengyou, LI Yanlong, WAN Yizhao, et al. Prospect of marine natural gas hydrate stimulation theory and technology system [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 100-115. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.008
[8] 刘乐乐, 刘昌岭, 吴能友, 等. 天然气水合物储层岩心保压转移与测试进展[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3):408-422
LIU Lele, LIU Changling, WU Nengyou, et al. Advances in pressure core transfer and testing technology of offshore hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3): 408-422.
[9] Kneafsey T J, Tomutsa L, Moridis G J, et al. Methane hydrate formation and dissociation in a partially saturated core-scale sand sample [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 56(1-3): 108-126. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2006.02.002
[10] Lei L, Liu Z C, Seol Y, et al. An investigation of hydrate formation in unsaturated sediments using X-ray computed tomography [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2019, 124(4): 3335-3349. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016125
[11] 王代刚, 魏伟, 孙静静, 等. 水合物降压分解过程中沉积物孔隙结构动态演化规律[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(21):2292-2302 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0010
WANG Daigang, WEI Wei, SUN Jingjing, et al. Dynamic evolution of pore structures of hydrate-bearing sediments induced by step-wise depressurization [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(21): 2292-2302. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0010
[12] 张永超, 刘昌岭, 吴能友, 等. 含水合物沉积物孔隙结构特征与微观渗流模拟研究[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(9):23-33
ZHANG Yongchao, LIU Changling, WU Nengyou, et al. Advances in the pore-structure characteristics and microscopic seepage numerical simulation of the hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(9): 23-33.
[13] 刘昌岭, 郝锡荦, 孟庆国, 等. 气体水合物基础特性研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(9):1-10
LIU Changling, HAO Xiluo, MENG Qingguo, et al. Research progress in basic characteristics of gas hydrate [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(9): 1-10.
[14] 李承峰, 刘乐乐, 孙建业, 等. 基于数字岩心的含水合物石英砂微观渗流有限元分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(9):68-72
LI Chengfeng, LIU Lele, SUN Jianye, et al. Finite element analysis of micro-seepage in hydrate-bearing quartz sands based on digital cores [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(9): 68-72.
[15] Kleinberg R L. Nuclear magnetic resonance [J]. Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences, 1999, 35: 337-385.
[16] Kleinberg R L, Flaum C, Griffin D D, et al. Deep sea NMR: Methane hydrate growth habit in porous media and its relationship to hydraulic permeability, deposit accumulation, and submarine slope stability [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B10): 2508.
[17] 陈合龙, 韦昌富, 田慧会, 等. CO2水合物在砂中生成和分解的核磁共振弛豫响应[J]. 物理化学学报, 2017, 33(8):1599-1604 doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201704194
CHEN Helong, WEI Changfu, TIAN Huihui, et al. NMR relaxation response of CO2 hydrate formation and dissociation in sand [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2017, 33(8): 1599-1604. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201704194
[18] Waite W F, Santamarina J C, Cortes D D, et al. Physical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2009, 47(4): RG4003.
[19] Ge X M, Liu J Y, Fan Y R, et al. Laboratory investigation into the formation and dissociation process of gas hydrate by low-field NMR technique [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(5): 3339-3346. doi: 10.1029/2017JB014705
[20] Ji Y K, Hou J, Zhao E M, et al. Study on the effects of heterogeneous distribution of methane hydrate on permeability of porous media using low-field NMR technique [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2020, 125(2): e2019JB018572.
[21] Tinni A, Odusina E, Sulucarnain I, et al. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance response of brine, oil, and methane in organic-rich shales [J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 2015, 18(3): 400-406.
[22] Kenyon W E. Nuclear magnetic resonance as a petrophysical measurement [J]. Nuclear Geophysics, 1992, 6(2): 153-171.
[23] Civan F. Predictability of porosity and permeability alterations by geochemical and geomechanical rock and fluid interactions[C]//Proceedings at the SPE International Symposium on Formation Damage Control. Lafayette, Louisiana, USA: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2000.
[24] Zhang Y C, Liu L L, Wang D G, et al. Application of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LFNMR) in characterizing the dissociation of gas hydrate in a porous media [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(3): 2174-2182.
[25] Liu L L, Zhang Z, Liu C L, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse surface relaxivity in quartzitic sands containing gas hydrate [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(7): 6144-6152. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c00225
[26] 陈光进, 孙长宇, 马庆兰. 气体水合物科学与技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2020: 80-90.
CHEN Guangjin, SUN Changyu, MA Qinglan. Gas Hydrate Science and Technology[M]. 2nd ed. Bejing: Chemical Indistry Press, 2020: 80-90.
[27] Takeya S, Hachikubo A. Structure and density comparison of noble gas hydrates encapsulating Xenon, Krypton and Argon [J]. ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20(19): 2518-2524. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201900591
[28] Linga P, Clarke M A. A review of reactor designs and materials employed for increasing the rate of gas hydrate formation [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(1): 1-13.
[29] Kim H C, Bishnoi P R, Heidemann R A, et al. Kinetics of methane hydrate decomposition [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1987, 42(7): 1645-1653. doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(87)80169-0
[30] Yin Z Y, Chong Z R, Tan H K, et al. Review of gas hydrate dissociation kinetic models for energy recovery [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 35: 1362-1387. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.04.050
[31] 李彦龙, 孙海亮, 孟庆国, 等. 沉积物中天然气水合物生成过程的二维电阻层析成像观测[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(10):132-138 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.10.017
LI Yanlong, SUN Hailiang, MENG Qingguo, et al. 2-D electrical resistivity tomography assessment of hydrate formation in sandy sediments [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(10): 132-138. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.10.017
[32] 魏纳, 周守为, 崔振军, 等. 南海北部天然气水合物物性参数评价与分类体系构建[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):59-67 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.004
WEI Na, ZHOU Shouwei, CUI Zhenjun, et al. Evaluation of physical parameters and construction of a parameter classification system for natural gas hydrate in the northern South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 59-67. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.004
[33] Yu B M, Li J H. Some fractal characters of porous media [J]. Fractals, 2001, 9(3): 365-372. doi: 10.1142/S0218348X01000804
[34] 蔡建超, 胡祥云. 多孔介质分形理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 2-22.
CAI Jianchao, HU Xiangyun. Fractal Theory in Porous Media and its Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 2-22.
[35] Liu L L, Zhang Z, Li C F, et al. Hydrate growth in quartzitic sands and implication of pore fractal characteristics to hydraulic, mechanical, and electrical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 75: 103-109.
[36] Cai J C, Xia Y, X Lu C, et al. Creeping microstructure and fractal permeability model of natural gas hydrate reservoir [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 115: 104282. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104282
[37] 蔡建超, 夏宇轩, 徐赛, 等. 含水合物沉积物多相渗流特性研究进展[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(1):208-223 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-362
CAI Jianchao, XIA Yuxuan, XU Sai, et al. Advances in multiphase seepage characteristics of natural gas hydrate sediments [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2020, 52(1): 208-223. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-362
[38] Zhang Z, Li C F, Ning F L, et al. Pore fractal characteristics of hydrate-bearing sands and implications to the saturated water permeability. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2020, 125(3): e2019JB018721.
[39] Lei G, Liao Q Z, Lin Q L, et al. Stress dependent gas-water relative permeability in gas hydrates: a theoretical model [J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4(3): 326-338. doi: 10.46690/ager.2020.03.10
[40] 刘乐乐, 刘昌岭, 孟庆国, 等. 分形理论在天然气水合物研究领域的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(9):11-22
LIU Lele, LIU Changing, MENG Qingguo, et al. Application of fractal theory to natural gas hydrate researches [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(9): 11-22.
[41] Ghanbarian B, Hunt A G, Ewing R P, et al. Tortuosity in porous media: a critical review [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2013, 77(5): 1461-1477. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2012.0435
[42] Cai J C, Yu B M. Prediction of maximum pore size of porous media based on fractal geometry [J]. Fractals, 2010, 18(4): 417-423. doi: 10.1142/S0218348X10005123
[43] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 廖华林, 等. 泥质粉砂沉积物: 天然气水合物混合体系的力学特性[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):159-168 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.013
LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIAO Hualin, et al. Mechanical properties of the mixed system of clayey-silt sediments and natural gas hydrates [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 159-168. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.013
[44] 张辉, 卢海龙, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部神狐海域沉积物颗粒对天然气水合物聚集的主要影响[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(3):388-397 doi: 10.1360/N972014-01395
ZHANG Hui, LU Hailong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. The methane hydrate accumulation controlled compellingly by sediment grain at Shenhu, northern South China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. doi: 10.1360/N972014-01395
-



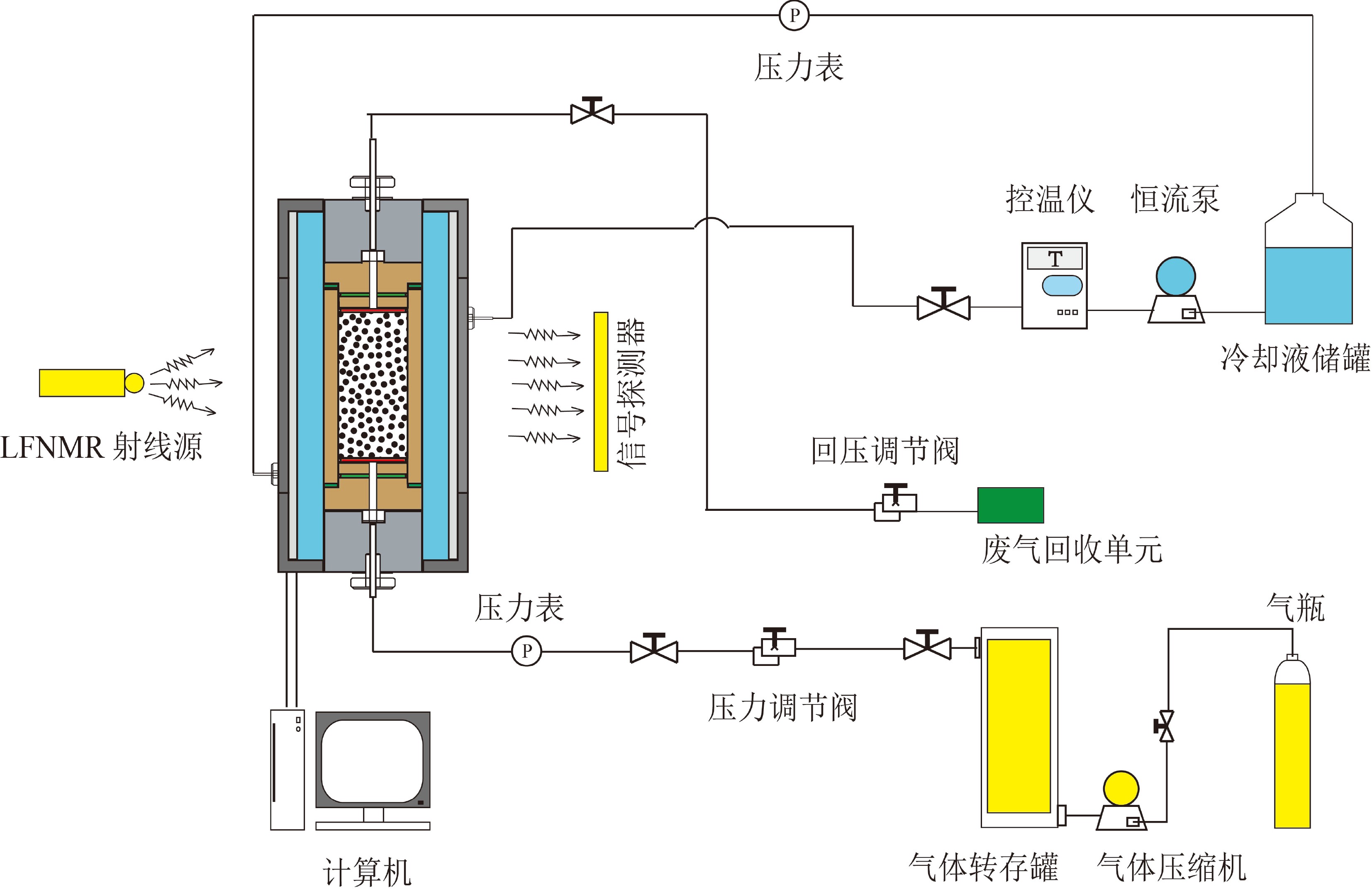
 下载:
下载:

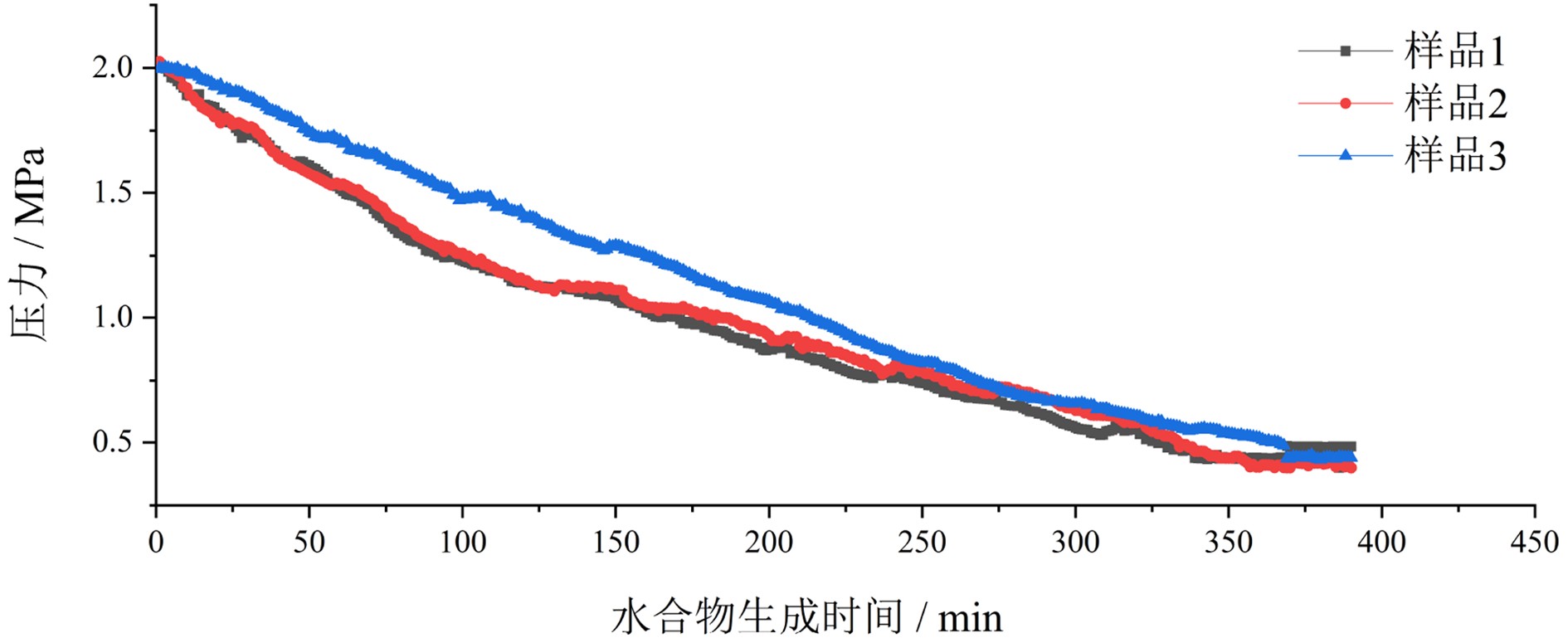

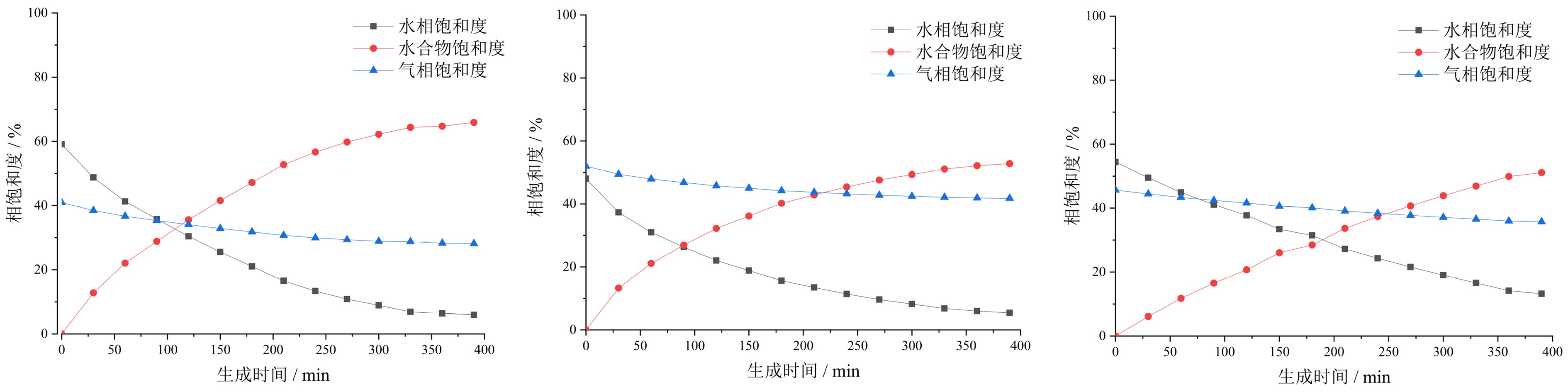
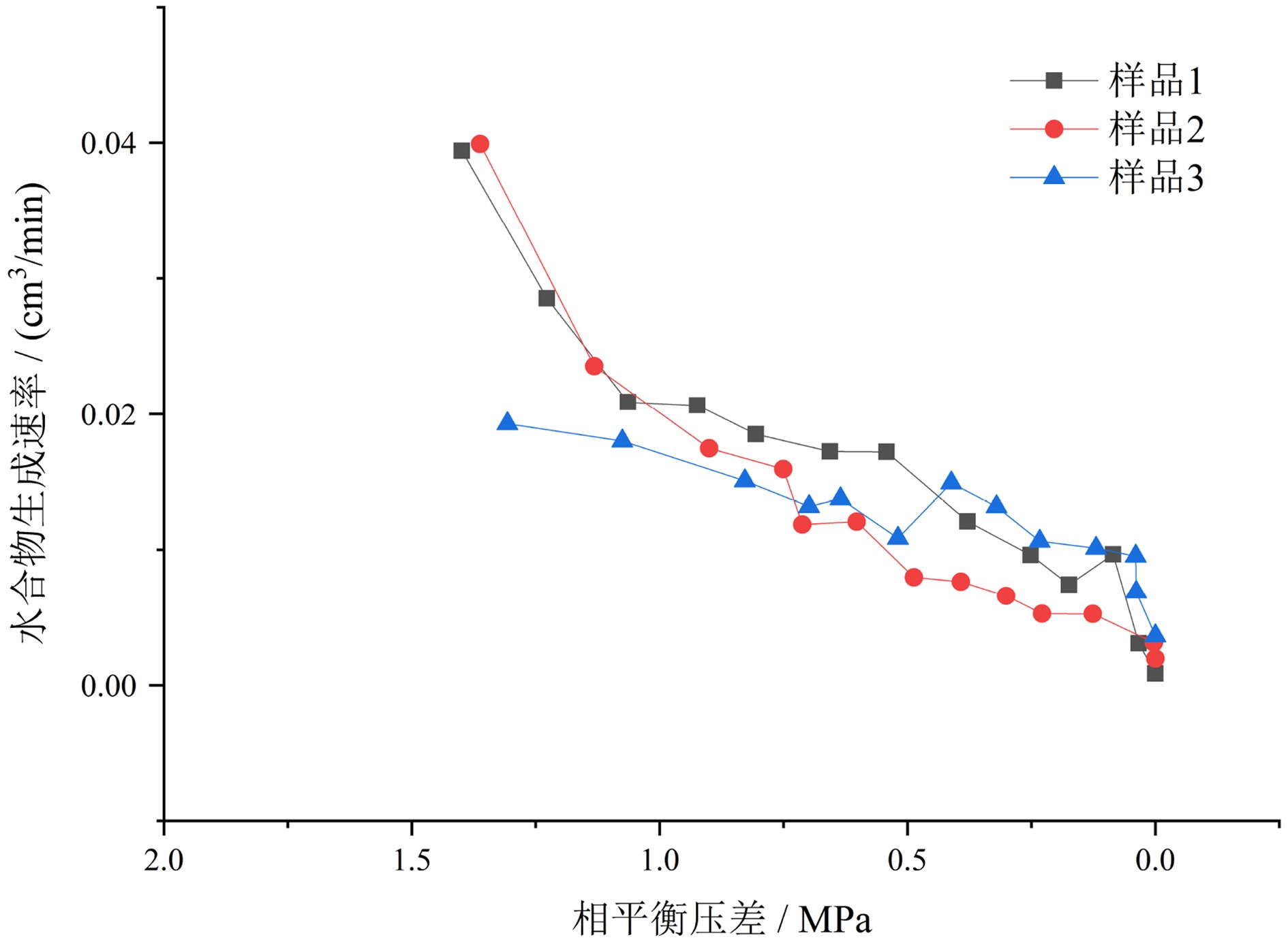
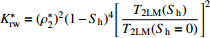
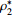 为横向表面弛豫率,T2LM为T2特征谱的对数平均值。
为横向表面弛豫率,T2LM为T2特征谱的对数平均值。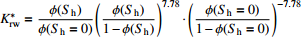
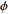 为样品有效孔隙度
为样品有效孔隙度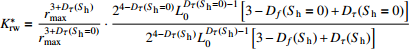
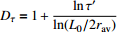
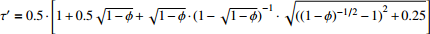
 为迂曲度系数,
为迂曲度系数,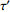 为平均迂曲度,
为平均迂曲度, 为平均孔隙半径,
为平均孔隙半径,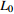 为样品的长度
为样品的长度