Characteristics of grain size and magnetic susceptibility of the Late Quaternary sediments from core 07SR01 in the middle Jiangsu coast and their paleoenvironmental significances
-
摘要:
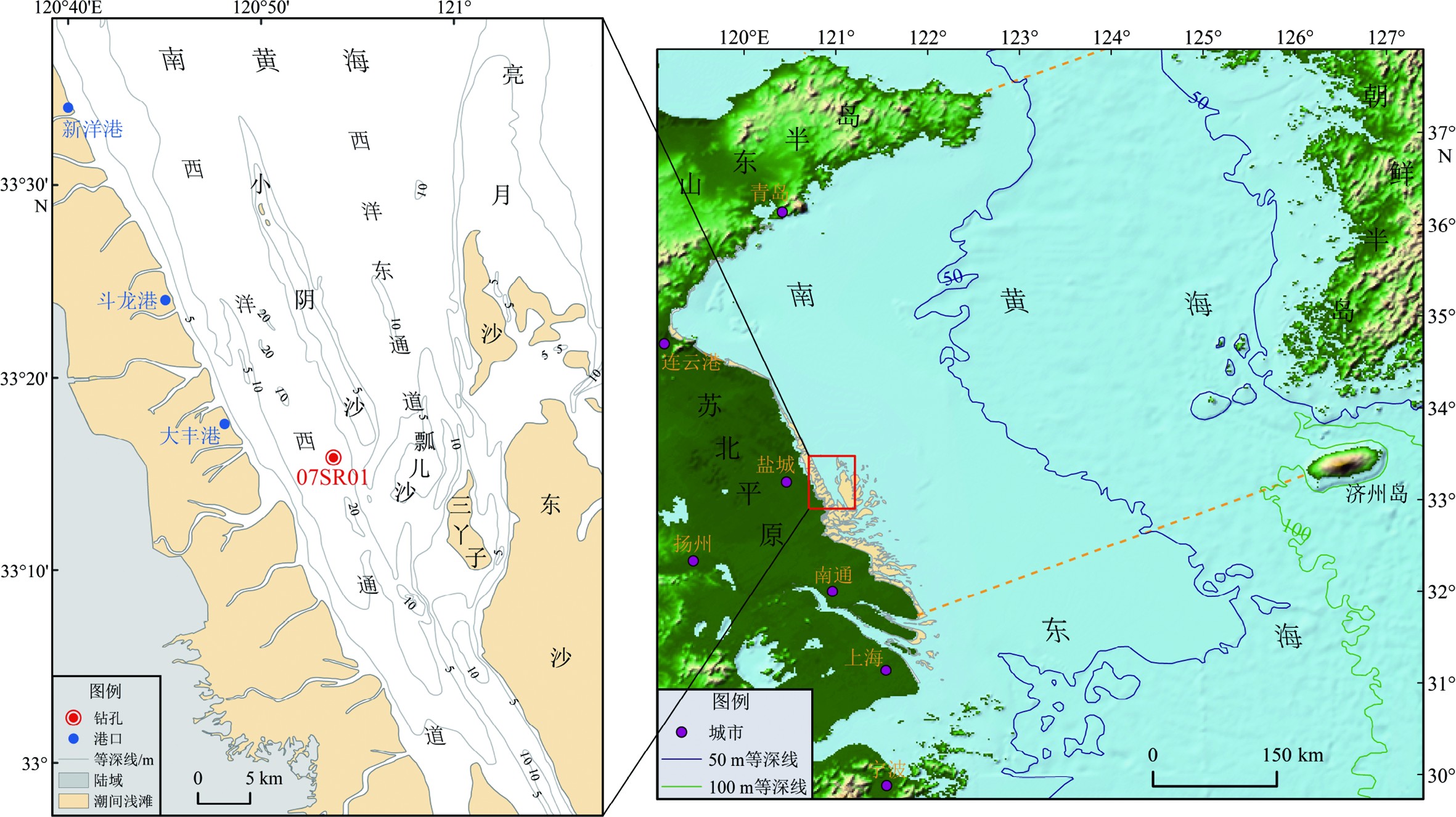
对位于江苏中部海岸的07SR01钻孔沉积物进行了粒度和磁化率测量,分析了粒度与磁化率的变化特征及其两者间的相关关系,并结合北半球晚更新世气候与相对海面变化以及该孔年代框架和沉积相的研究认识,进一步揭示了研究区的古环境变化。研究表明,MIS 5晚期至MIS 3时期,江苏中部海岸先后经历了3个阶段的环境演化:① MIS 5晚期为较高海面、较强水动力的潮汐河口(边滩、河床)阶段(36.10~26.65 m),该阶段沉积物主要受古长江物源影响,粒度粗,分选性波动大(0.55~2.35),粒度频率分布曲线呈极正偏的窄峰(主峰位于3 Φ附近)且“拖细尾”,磁化率较高且波动小[(5.81~42.16)×10−8 m3·kg−1],与砂组分(<4 Φ)呈强正相关;② MIS 4-3时期为冷干转为暖湿、海面先下降后上升和较弱水动力的淡水与滨岸湖沼阶段(26.65~15.77 m),该阶段沉积物细,分选性稳定(1.51~3.03),粒度频率分布曲线呈正偏的宽峰(主峰位于4.75 Φ附近),磁化率低且稳定[(6.46~20.04)×10−8 m3·kg−1],主要与粗粉砂组分(4~5 Φ)呈弱正相关;③ MIS 3时期为较高海面、较强水动力的潮汐河口(分流河道)阶段(15.77~0 m),该阶段沉积物受MIS 3苏北古黄河的影响增强,粒度较粗,分选性波动大(0.94~2.82),粒度频率分布曲线呈极正偏的窄峰(主峰位于3.75 Φ附近)且“拖细尾”,磁化率较高且波动大[(10.21~57.25)×10−8 m3·kg−1],与砂和粗粉砂组分(<5 Φ)呈弱正相关。揭示海岸沉积物粒度和磁化率组合指标的古环境指示意义,将为进一步深入研究这一指示意义的形成机理提供必要的基础。
Abstract:The grain size and magnetic susceptibility of sediments from core 07SR01 in the middle Jiangsu coast were measured, as well as their variation and correlation were analyzed. Combined with the chronological framework and sedimentary facies data from the core, plus the research results of the Northern Hemisphere climate and relative sea level changes since the Late Pleistocene, the paleoenvironmental evolution of the study area was further established. It is found that the study area has experienced three periods of environmental changes from late MIS 5 to MIS 3: (1) The period of marginal bank and riverbed developed in the tidal estuary during late MIS 5 (36.10~26.65 m) which was under relatively high sea level and strong hydrodynamic conditions, the sediments deposited during this period were mainly affected by the provenance of old Yangtze River and characterized by coarse grain size, dramatical variations in sorting coefficients (0.55~2.35), extremely positive deviation with a high-narrow peak near 3 Φ and a thin tail in the frequency curve, and high magnetic susceptibilities with small fluctuations in the range of (5.81~42.16)×10−8 m3·kg−1 and strongly and positively correlated with sand (<4 Φ); (2) The period dominated by fluviolacustrine and littoral environments with weak hydrodynamics during MIS 4-3, in which the climate changed from cold and dry to warm and humid as the sea level rose after a drop (26.65~15.77 m), the sediments deposited at this period are characterized by fine grain size, stable sorting coefficients (1.51~3.03), positive deviation with a low-broad peak near 4.75 Φ in the frequency curve, low values and small variations of magnetic susceptibilities [(6.46~20.04)×10−8 m3·kg−1], which are weakly and positively correlated with coarse silt (4~5 Φ); (3) The period of distributary channel in the tidal estuary with relatively high sea level and strong hydrodynamics during MIS 3 (15.77~0 m), the sediments deposited at this period were strongly influenced by the old Yellow River of North Jiangsu and characterized by relatively coarse grain size and large variations in sorting coefficients (0.94~2.82), extremely positive deviation with a high-narrow peak near 3.75 Φ and a thin tail in the frequency curve, and relatively high magnetic susceptibilities with great fluctuations in the range of (10.21~57.25)×10−8 m3·kg−1 and weakly and positively correlated with sand and coarse silt (<5 Φ). To reveal the paleoenvironmental significances for combination of grain size and magnetic susceptibility of coastal sediments, will provide a necessary basis for further study on their genetic mechanisms.
-

-
表 1 07SR01孔沉积物粒度参数
Table 1. Grain size parameters of core 07SR01 sediments
深度/m 平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 偏态 峰态 样品数/个 0~36.10(全岩心) 最小值 2.70 0.55 −0.20 0.69 229 最大值 6.66 3.03 0.64 2.52 平均值 4.76 1.71 0.26 1.14 26.65~36.10(潮汐河口边滩、河床相) 最小值 2.70 0.55 0.02 0.71 65 最大值 5.81 2.35 0.64 2.53 平均值 4.02 1.56 0.35 1.32 21.67~26.65(淡水湖沼相) 最小值 2.83 1.51 −0.12 0.75 22 最大值 6.50 2.69 0.50 1.59 平均值 4.66 1.95 0.23 1.08 20.50~21.67(洪泛平原相) 最小值 4.78 1.54 0.11 0.88 11 最大值 6.24 1.94 0.48 1.42 平均值 5.48 1.71 0.32 1.09 15.77~20.50(滨岸沼泽相) 最小值 4.14 1.65 −0.15 0.70 36 最大值 6.55 3.03 0.53 1.24 平均值 5.66 1.98 0.12 0.87 0~15.77(潮汐河口分流河道相) 最小值 2.88 0.94 −0.20 0.69 95 最大值 6.66 2.82 0.45 1.68 平均值 4.86 1.65 0.25 1.14 表 2 07SR01孔沉积物粒度组分与磁化率的相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between grain size and magnetic susceptibility of core 07SR01 sediments
岩心分段
(深度/沉积相)粒度/Φ >8 6~8 5~6 4~5 <4 0~36.10 m −0.544 −0.407 −0.207 0.126 0.280 26.65~36.10 m −0.600 −0.514 −0.633 −0.817 0.712 15.77~26.65 m 0.018 −0.024 −0.025 0.145 −0.030 0~15.77 m −0.500 −0.304 −0.087 0.118 0.254 潮汐河口边滩、河床相 −0.600 −0.514 −0.633 −0.817 0.712 淡水湖沼相 0.084 0.141 0.187 0.164 −0.163 洪泛平原相 −0.935 −0.690 −0.028 0.620 0.581 滨岸沼泽相 −0.058 −0.112 −0.177 0.066 0.109 潮汐河口分流河道相 −0.500 −0.304 −0.087 0.118 0.254 -
[1] Prins M A, Postma G, Weltje G J. Controls on terrigenous sediment supply to the Arabian Sea during the late Quaternary: the Makran continental slope [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 169(3-4): 351-371. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00087-6
[2] 舒强, 李才林, 赵志军, 等. 苏北盆地浅钻沉积物磁化率与粒度记录的末次冰消期以来的环境变化[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(1):111-117
SHU Qiang, LI Cailin, ZHAO Zhijun, et al. The records of mass susceptibility and grain size for climate changes in Subei basin during the last deglaciation [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(1): 111-117.
[3] 蔡廷禄, 贾建军, 汪亚平. 河口海岸和近海沉积物的粒度资料同化技术[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1):185-193
CAI Tinglu, JIA Jianjun, WANG Yaping. Techniques for particle size data standardization: an example form estuarine and coastal sediments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 185-193.
[4] 邓程文, 张霞, 林春明, 等. 长江河口区末次冰期以来沉积物的粒度特征及水动力条件[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(6):185-198
DENG Chengwen, ZHANG Xia, LIN Chunming, et al. Grain-size characteristics and hydrodynamic conditions of the Changjiang estuarine deposits since last glacial [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(6): 185-198.
[5] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海陆架中北部沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6):1039-1049 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206003003
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. The grain size compositions of the surface sediments in the East China Sea: Indication for sedimentary environments [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1039-1049. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206003003
[6] 丁大林, 张训华, 于俊杰, 等. 长江三角洲北翼后缘晚第四纪以来的沉积粒度特征及环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(4):34-45
DING Dalin, ZHANG Xunhua, YU Junjie, et al. Sediment grain size distribution patterns of the late Quaternary on the back side of northern Yangtze River Delta and their environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(4): 34-45.
[7] 周连成, 李军, 高建华, 等. 长江口与舟山海域柱状沉积物粒度特征对比及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5):21-27
ZHOU Liancheng, LI Jun, GAO Jianhua, et al. Comparison of core sediment grain-size characteristics between Yangtze River estuary and Zhoushan Islands and its significance to sediment source analysis [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 21-27.
[8] 李红军, 刘月, 程岩, 等. 鸭绿江口沉积粒度特征及其对沉积环境演化的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):58-66
LI Hongjun, LIU Yue, CHENG Yan, et al. Characteristics of sediment grain size at Yalu River estuary and implications for depositional environment [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3): 58-66.
[9] 潘峰, 林春明, 李艳丽, 等. 钱塘江南岸SE2孔晚第四纪以来沉积物粒度特征及环境演化[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(2):236-244 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2011.02.012
PAN Feng, LIN Chunming, LI Yanli, et al. Sediments grain-size characteristics and environmental evolution of core SE2 in southern bank of Qiangtang River since the late Quaternary [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2011, 13(2): 236-244. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2011.02.012
[10] Thompson R, Oldfield F. Environmental Magnetism[M]. London: Allen & Unwin, 1986: 1-227.
[11] Verosub K L, Roberts A P. Environmental magnetism: Past, present, and future [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1995, 100(B2): 2175-2192. doi: 10.1029/94JB02713
[12] 贾海林, 刘苍字, 张卫国, 等. 崇明岛CY孔沉积物的磁性特征及其环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(1):117-123 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.01.018
JIA Hailin, LIU Cangzi, ZHANG Weiguo, et al. Magnetic properties of core CY from Chongming island, the Yangtze estuary and its environmental significance [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(1): 117-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.01.018
[13] 张瑞虎, 谢建磊, 刘韬, 等. 长江口水下三角洲沉积物记录的古环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(1):1-10
ZHANG Ruihu, XIE Jianlei, LIU Tao, et al. Palaeoenvironmental evolution of subaqueous Yangtze delta inferred from sedimentary records [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(1): 1-10.
[14] 葛宗诗. 南黄海QC2孔磁化率研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(4):35-42
GE Zongshi. Study on magnetic susceptibility on hole QC2 in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(4): 35-42.
[15] 姚菁. 渤海南岸LZ908孔海陆交互相地层气候代用指标及沉积环境研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2014: 1-119.
YAO Jing. Climatic indicators and sedimentary environment studies inferred from transgressive and regressive sediments of core LZ908, south Bohai Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014: 1-119.
[16] Maher B A. Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1988, 94(1): 83-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1988.tb03429.x
[17] 王建, 刘泽纯, 姜文英, 等. 磁化率与粒度、矿物的关系及其古环境意义[J]. 地理学报, 1996, 51(2):155-163 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1996.02.009
WANG Jian, LIU Zechun, JIANG Wenying, et al. A relationship between susceptibility and grain-size and minerals, and their paleo-environmental implications [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1996, 51(2): 155-163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1996.02.009
[18] Wang L S, Hu S Y, Yu G, et al. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the radial sand ridge field in the South Yellow Sea (east China) since 45 ka using the sediment magnetic properties and granulometry [J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015, 122: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.08.002
[19] Zhou X, Sun L G, Huang W, et al. Relationship between magnetic susceptibility and grain size of sediments in the China Seas and its implications [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 72: 131-137. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.07.011
[20] 卫蕾华, 蒋汉朝, 何宏林, 等. 末次冰期山西洪洞高分辨率粒度和磁化率记录的H5事件及其气候演化意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4):193-202
WEI Leihua, JIANG Hanchao, HE Honglin, et al. Heinrich-5 Event revealed by high-resolution grain-size and magnetic susceptibility records and its significance of climate evolution in the last glacial at Hongtong, Shanxi, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 193-202.
[21] Hilton J. A simple model for the interpretation of magnetic records in lacustrine and ocean sediments [J]. Quaternary Research, 1987, 27(2): 160-166. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(87)90074-3
[22] 刘健, 朱日祥, 李绍全. 南黄海北部末次冰期棕黄色细粒沉积物的磁学特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(4):15-20
LIU Jian, ZHU Rixiang, LI Shaoquan. Magnetic properties of the last glacial brown-yellow fine-grained sediment in the northern south Yellow Sea: implication for its origin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(4): 15-20.
[23] 刘健, 朱日祥, 李绍全, 等. 南黄海东南部冰后期泥质沉积物中磁性矿物的成岩变化及其对环境变化的响应[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(6):583-592 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.06.013
LIU Jian, ZHU Rixiang, LI Shaoquan, et al. Magnetic mineral diagenesis in the post-glacial muddy sediments from the southeastern South Yellow Sea: Response to marine environmental changes [J]. Science in China (Series D), 2003, 33(6): 583-592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.06.013
[24] 刘庚, 韩喜彬, 陈燕萍, 等. 南黄海沉积物磁性特征及其对物源变化的指示——以南黄海中部泥质区YSC-10孔为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(2):383-394
LIU Geng, HAN Xibin, CHEN Yanping, et al. Magnetic characteristics of core YSC-10 sediments in the central Yellow Sea mud area and implications for provenance changes [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(2): 383-394.
[25] 夏非, 殷勇, 王强, 等. MIS 3晚期以来江苏中部海岸的层序地层[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(10):1696-1712 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.10.009
XIA Fei, YIN Yong, WANG Qiang, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the central part of North Jiangsu coasts since late MIS 3, eastern China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(10): 1696-1712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.10.009
[26] Xia F, Zhang Y Z, Wang Q, et al. Evolution of sedimentary environments of the middle Jiangsu coast, South Yellow Sea since late MIS 3 [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013, 23(5): 883-914. doi: 10.1007/s11442-013-1051-5
[27] 夏非. 辐射沙脊群西洋潮流通道的浅部层序地层与沉积环境演化[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2016: 1-187.
XIA Fei. Shallow sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary evolution of the Xiyang tidal channel in the Radial Sand Ridge Field[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2016: 1-187.
[28] 夏非, 张永战, 刘德政. 南黄海辐射沙脊群西洋潮流通道的浅部沉积层序及其形成演化再认识[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4):13-26
XIA Fei, ZHANG Yongzhan, LIU Dezheng. Rethinking on shallow sedimentary sequence and its evolution of the Xiyang tidal channel in the Radial Sand Ridge Field, South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 13-26.
[29] 王颖. 南黄海辐射沙脊群环境与资源[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2014: 1-291.
WANG Ying. Environment and Resource of the Radial Sand Ridge Field in the South Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2014: 1-291.
[30] 王颖. 黄海陆架辐射沙脊群[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 1-368.
WANG Ying. Radiative Sandy Ridge Field on Continental Shelf of the Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002: 1-368.
[31] 张刚, 杨轮凯, 闫玉茹, 等. 江苏盐城大丰港西洋深槽冲淤变化特征[J]. 地质学刊, 2016, 40(4):683-689 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.04.683
ZHANG Gang, YANG Lunkai, YAN Yuru, et al. Variation characteristics of siltation movement at the Xiyang deep groove of Dafeng port in Yancheng, Jiangsu province [J]. Journal of Geology, 2016, 40(4): 683-689. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.04.683
[32] 国家海洋局908专项办公室. 海洋底质调查技术规程[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2006: 2−7, 33.
908 Special Office of the State Oceanic Administration. Technical Regulations for Marine Sediment Survey[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2006: 2-7, 33.
[33] Blott S J, Pye K. GRADISTAT: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2001, 26: 1237-1248. doi: 10.1002/esp.261
[34] Waelbroeck C, Labeyrie L, Michel E, et al. Sea-level and deep water temperature changes derived from benthic foraminifera isotopic records [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(1-3): 295-305. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00101-9
[35] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during the last transgression [J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00165-7
[36] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Evolution of the coastal depositional systems of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River in response to late Pleistocene-Holocene sea-level changes [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(6): 884-897. doi: 10.1306/052002720884
[37] Fan D D. Open-coast tidal flats[M]//Davis R Jr, Dalrymple R. Principles of Tidal Sedimentology. Dordrecht: Springer, 2012: 187-229.
[38] Fan D D, Tu J B, Shuai S, et al. Morphodynamics and sedimentary facies in a tidal-fluvial transition with tidal bores (the middle Qiantang Estuary, China)[M]//Tessier B, Reynaud J Y. Contributions to Modern and Ancient Tidal Sedimentology. London: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2016: 75-92.
[39] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 徐方建, 等. 东海内陆架EC2005孔沉积物磁化率与粒度组分的相关性研究[J]. 科技导报, 2009, 27(10):32-36 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2009.10.006
MENG Qingyong, LI Anchun, XU Fangjian, et al. Correlation between the grain size distribution and magnetic susceptibility of marine sediment core in the inner shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2009, 27(10): 32-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2009.10.006
[40] Yim W W S, Ivanovich M, Yu K F. Young age bias of radiocarbon dates in pre-Holocene marine deposits of Hong Kong and implications for Pleistocene stratigraphy [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1990, 10(3): 165-172. doi: 10.1007/BF02085932
[41] Nian X M, Zhang W G, Wang Z H, et al. The chronology of a sediment core from incised valley of the Yangtze River delta: Comparative OSL and AMS 14C dating [J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 395: 320-330. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.11.008
[42] 殷勇, 张宁. 南黄海辐射沙脊群西洋潮道晚更新世晚期以来沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(5):618-628 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.05.011
YIN Yong, ZHANG Ning. Sedimentary environments of Xiyang tidal channel of radial tidal sand ridge system since the late period of Late Pleistocene in South Yellow Sea [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(5): 618-628. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.05.011
[43] 顾兆峰, 张志珣. 南黄海西部浅部地层地震层序及其沉积特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):95-106
GU Zhaofeng, ZHANG Zhixun. Shallow seismic stratigraphy and sedimentary character in the western South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 95-106.
[44] 刘青松, 邓成龙. 磁化率及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(4):1041-1048 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021
LIU Qingsong, DENG Chenglong. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021
[45] 赵井东, 施雅风, 王杰. 中国第四纪冰川演化序列与MIS对比研究的新进展[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(7):867-884 doi: 10.11821/xb201107001
ZHAO Jingdong, SHI Yafeng, WANG Jie. Comparison between Quaternary glaciations in China and the Marine Oxygen Isotope Stage (MIS): An improved schema [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(7): 867-884. doi: 10.11821/xb201107001
[46] 仇建东, 刘健, 白伟明. 深海氧同位素第3阶段古气候—海平面变化研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(11):12-16
QIU Jiandong, LIU Jian, BAI Weiming. Progress of the studies of paleoclimate and sea level changes in the marine oxygen isotope stage 3 [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(11): 12-16.
[47] 柯贤坤. 潮滩沉积物的粒度特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1988, 7(4):41-48
KE Xiankun. Grain-size characteristics of tidal flat sediments [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1988, 7(4): 41-48.
[48] 陈影影, 夏非, 张振克, 等. 苏北-南黄海西部第四纪长江埋藏古河道分布研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4):40-54
CHEN Yingying, XIA Fei, ZHANG Zhenke, et al. Research progress on distribution of Quaternary buried paleo-Yangtze River channels in the North Jiangsu-western South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 40-54.
[49] 李萍, 陈刚. 长江三角洲晚更新世暗绿色硬粘土的早期成岩作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1995, 16(4):313-318+401 doi: 10.11743/ogg19950403
LI Ping, CHEN Gang. Early diagenesis of late Pleistocene dark-green stiff clay in the Yangzi River delta [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1995, 16(4): 313-318+401. doi: 10.11743/ogg19950403
[50] Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X H, et al. Delta development and channel incision during marine isotope stages 3 and 2 in the western South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 278(1-4): 54-76. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.09.003
-



 下载:
下载:


