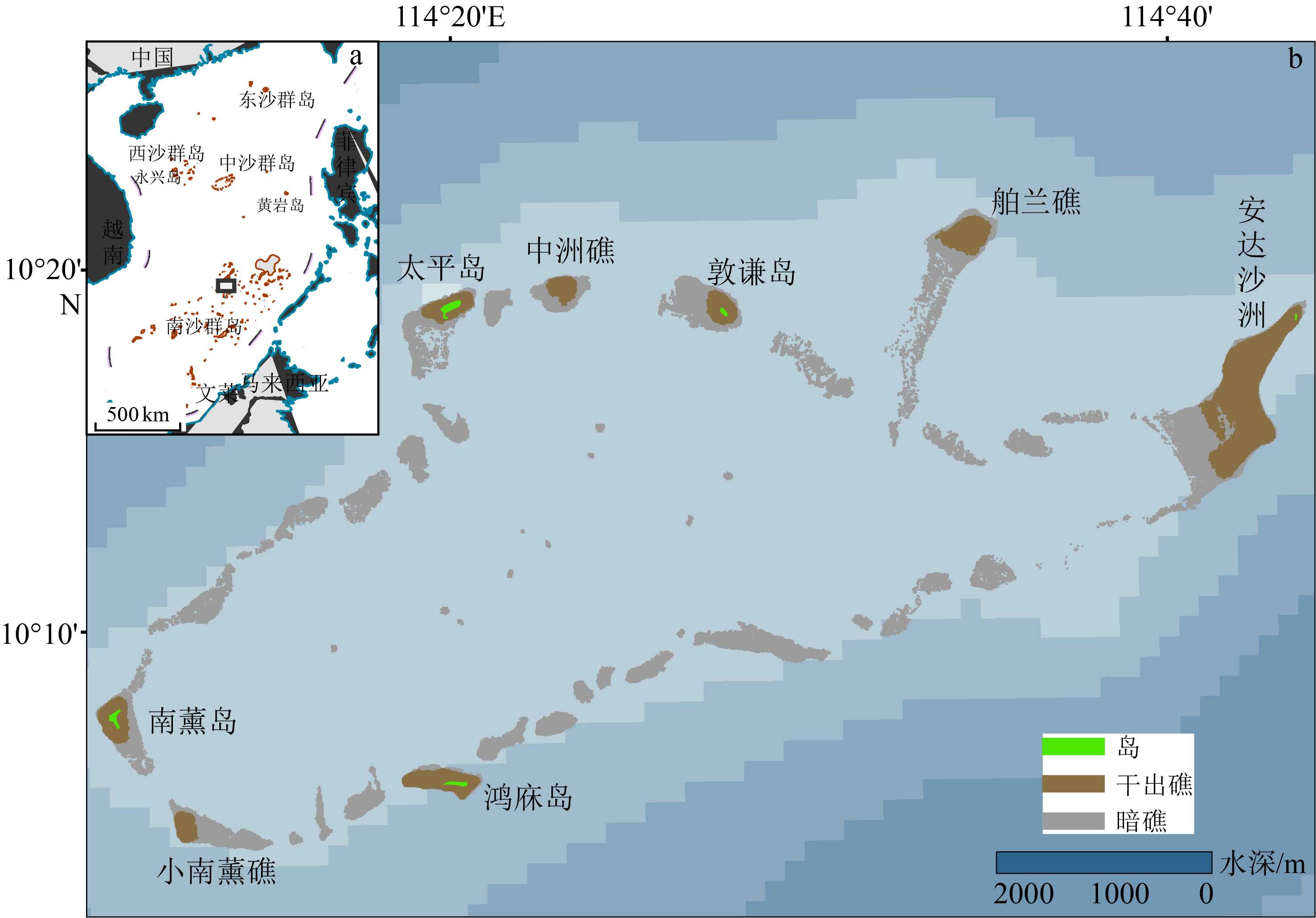
Distribution and morphological features of the patch reefs at Xiaonanxun Reef, Zhenghe Atoll of the Nansha Islands, South China Sea
-
摘要:
点礁是在空间上呈点状分布的礁体,是一种重要的珊瑚暗礁地貌类型,南海南沙群岛北部海区的一系列环礁发育有众多的珊瑚点礁。目前,对点礁地貌的形态特征、发育过程和机制的研究相对匮乏,南海地区的珊瑚点礁地貌定量研究尚为空白。以南沙群岛北部郑和环礁西南端的小南薰礁发育的点礁为研究对象,利用多波束水深实测数据结合Google Earth WorldView-2遥感影像,对所识别的123个点礁的顶底水深、高度、顶底直径等形态参数进行量测与统计分析,结果表明,其底部最大水深为35.05 m,顶部最小水深为7.89 m,平均高度2.62 m。其中,88个点礁(占71.5%)分布于水深25~35 m(深水点礁),27个(占17.9%)分布于水深10~18 m(浅水点礁)。点礁顶部和底部直径的平均值分别为8.49 和19.13 m,形状因子和顶底关系因子的平均值分别为0.15和0.42,其剖面形态呈峰丘型(21.1%)和礁坪型(占78.9%),且多呈孤立型分布,亦见少数以群落型分布。浅水点礁以礁坪型为主,其顶部和底部直径较大,而形状因子较小,反映了波浪动力的控制作用;峰丘型仅见于深水点礁,其形状因子较大(>0.23),顶底关系因子较小(<0.25),高度和直径呈正相关,反映了珊瑚生长作用对点礁地貌的影响。点礁底部直径集中呈NEE-N向延伸,显示了海域盛行风向与海水运动方向的控制作用。
Abstract:Coral reef is an efficient indicator for paleoenvironment reconstruction, as it may provide abundant information on paleoclimate changes, sea-level fluctuations and marine environmental variations. Patch reef is a kind of submerged reefs, widely distributed in isolation on reef flat in patch shape in the atolls of the northern Nansha Islands area of the South China Sea. However, the morphological features and formation mechanisms of these patch reefs remain unclear up to present. In this paper, Google Earth WorldView-2 images and multi-beam bathymetric data are processed and carefully studied for the Xiaonanxun Reef, which is located in the southwestern Zhenghe Atoll. Patch reefs are widely distributed there in secondary lagoons, tidal channels, lagoonal slopes and basin floors. Based on the data mentioned above, 123 patch reefs are recognized and measured. The maximum depth of the rim and the minimum depth of the top of the patch reefs are 35.05 m and 7.89 m, and the average height, bottom diameter and top diameter of the patch reefs are 2.62 m, 19.13 m and 8.49 m on average respectively. Most of the patch reefs is distributed in isolation in shapes of “pancake” and “knoll”, and only 3 groups are found combined as colony developed in the area in the water depth of 29 ~ 35 m. The patch reefs developed in the water depth less than 18 m are predominated by the “pancake” type, with the average height and the bottom and top diameters in 1.85 m, 21.98 m and 11.79 m, respectively. The shape index is rather small (less than 0.23), but the relational factor between top and bottom is rather large (87% between 0.30 and 0.75). Wave dynamics are believed the dominant factor to the morphological features. In contrast, “knoll” type of patch reefs is mainly developed in the area under water depth deeper than 25 m, and the average height and bottom and top diameters are 2.74 m, 17.44 m and 6.89 m respectively. The bottom diameter and height of patch reefs are positively correlated and the correlation coefficient R is up to 0.827, which indicates the biological processes of coral growth is the dominant factor to the morphological features. Furthermore, the long axis direction is mainly in NEE to N direction for 82% of the bottoms of the patch reefs, being consistent with the prevailing wind wave direction and perpendicular to the reef crest, which indicate the impacts of the wave dynamic processes as well.
-
Key words:
- submerged reef /
- patch reef /
- morphological fatures /
- wave dynamics /
- Nansha
-

-
表 1 小南薰礁地貌形态特征及其典型影像
Table 1. Morphological characteristics of Xiaonanxun Reef and representative images
地貌名称 形态特征 面积/km2 所占比例/% 典型影像 干出礁 水深较浅、破浪带激浪作用活跃,造礁石珊瑚等生长较好,部分低潮时出露[18,28] 0.89 19.4 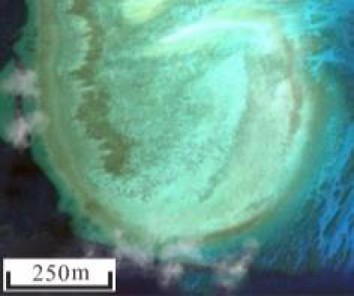
次成潟湖 礁坪上的低洼地,低潮不出露,以生物碎屑堆积为主[17,28] 0.45 9.8 
潮汐通道 相对低洼、穿过礁坪的槽道,是潟湖与外海水体交换的通道,一般较少碎屑沉积,与“口门”相比,规模更小,水深更浅[17,29,33] 0.38 8.3 
脊槽 线性的脊和槽相间组成,影像中绿色为脊部,一般为珊瑚聚集生长区;槽部为白色,一般为珊瑚贝壳碎屑堆积区[14,30,33] 0.89 19.4 
珊瑚礁垄* 带状凸起区域,与脊槽相比,规模更大,主要由活珊瑚覆盖 1.98 43.1 
注:*根据其形态特征,参照其他地貌名称进行定义。 表 2 小南薰礁的点礁地貌形态参数统计
Table 2. Statistics of morphological parameters of patch reefs of Xiaonanxun Reef
形态参数 平均值 最小值 最大值 点礁
(123个)顶部深度H1/m 24.10 7.89 33.34 底部深度H2/m 26.71 10.42 35.05 高度H/m 2.62 0.30 10.35 底部直径D/m 19.13 3.54 71.11 形状因子H/D 0.15 0.03 0.47 顶部直径d/m 8.49 1.31 50.06 顶底关系因子d/D 0.42 0.13 0.89 深水点礁(88个) 顶部深度H1 /m 27.82 19.70 33.34 底部深度H2 /m 30.56 25.17 35.05 高度H/m 2.74 0.41 10.35 底部直径D/m 17.44 3.54 71.11 形状因子H/D 0.16 0.04 0.47 顶部直径d/m 6.89 1.31 29.83 顶底关系因子d/D 0.39 0.13 0.77 浅水点礁(27个) 顶部深度H1 /m 13.88 7.89 16.89 底部深度H2 /m 15.72 10.42 17.71 高度H/m 1.85 0.30 4.06 底部直径D/m 21.98 4.95 60.12 形状因子H/D 0.11 0.03 0.21 顶部直径d/m 11.79 2.26 50.06 顶底关系因子d/D 0.49 0.24 0.89 表 3 小南薰礁的点礁形态参数相关分析结果
Table 3. Correlation of morphological parameters of patch reefs of Xiaonanxun Reef
相关系数 顶部深度 底部深度 高度 底部直径D 形状因子 顶部直径d d/D 所有点礁 顶部深度 底部深度 0.960** 高度 −0.154 0.127 底部直径D −0.361** −0.165 0.697** 形状因子 0.163 0.264** 0.358** −0.254** 顶部直径d −0.444** −0.299** 0.519** 0.878** −0.239** d/D −0.330** −0.311** 0.070 0.186* 0.041 0.558** 深水点礁 顶部深度 底部深度 0.776** 高度 −0.603** 0.036 底部直径D −0.524** −0.002 0.827** 形状因子 0.190 0.072 0.392** −0.094 顶部直径d −0.535** −0.124 0.691** 0.844** −0.068 d/D −0.144 −0.167 0.017 −0.008 0.094 0.481** 浅水点礁 顶部深度 底部深度 0.824** 高度 −0.346 0.039 底部直径D −0.125 0.137 0.666** 形状因子 0.123 0.066 0.159 −0.669** 顶部直径d −0.153 0.090 0.620** 0.936** −0.549** d/D −0.270 −0.150 0.339 0.413* 0.041 0.644** 注:**在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关,*在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。 -
[1] Fairbridge R W. Recent and Pleistocene coral reefs of Australia [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1950, 58(4): 330-401. doi: 10.1086/625751
[2] 曾昭璇. 中国环礁的类型划分[J]. 海洋通报, 1982, 1(4):43-50
ZENG Zhaoxuan. Classfication of atolls in China [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1982, 1(4): 43-50.
[3] 海洋科技名词审定委员会. 海洋科技名词[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 60
China National Marine Science and Technology Terminology Validation Committee. Chinese Terms in Marine Science and Technology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 60.
[4] Beaman R J, Webster J M, Wust R A J. New evidence for drowned shelf edge reefs in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 247(1-2): 17-34. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.08.001
[5] Harris P T, Davies P J. Submerged reefs and terraces on the shelf edge of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia [J]. Coral Reefs, 1989, 8(2): 87-98. doi: 10.1007/BF00301807
[6] Abbey E, Webster J M, Beaman R J. Geomorphology of submerged reefs on the shelf edge of the Great Barrier Reef: The influence of oscillating Pleistocene sea-levels [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 288(1-4): 61-78. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.08.006
[7] 孙宗勋, 赵焕庭. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁动力地貌特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 1996, 15(2):53-60
SUN Zongxun, ZHAO Huanting. Features of dynamic geomorphology of coral reefs in Nansha Islands [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1996, 15(2): 53-60.
[8] Brock J C, Palaseanu-Lovejoy M, Wright C W, et al. Patch-reef morphology as a proxy for Holocene sea-level variability, Northern Florida Keys, USA [J]. Coral Reefs, 2008, 27(3): 555-568. doi: 10.1007/s00338-008-0370-y
[9] Brown B E, Dunne R P. Environmental controls of patch-reef growth and development [J]. Marine Biology, 1980, 56(1): 85-96. doi: 10.1007/BF00390598
[10] Peters M, Palandro D, Hallock P, et al. Assessing the distribution of patch reef morphologies in the Lower Florida Keys, USA, using IKONOS satellite imagery[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Coral Reef Symposium. Lauderdale, 2008: 678-682.
[11] Jones J A. Morphology and development of southeastern Florida patch reefs[C]//Proceedings of the Third International Coral Reef Symposium, University of Miami. Miami, Florida, 1977: 232-235.
[12] Chu S S, Hong L, Cheng L, et al. Weighted multiscale region-level sparse representation for classification of high-spatial resolution remote sensing images [J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(4): 045005.
[13] Phinn S R, Hochberg E M, Roelfsema C M. Visible and infrared overview[M]//Goodman J A, Purkis S J, Phinn S R. Coral Reef Remote Sensing. Netherlands: Springer, 2013: 3-28.
[14] 王黎, 张永战. 九章环礁水下暗礁脊槽地貌分布与形态[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(2):485-495 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.02.18
WANG Li, ZHANG Yongzhan. Distribution and morphological characteristics of spur and groove on submerged reefs of Jiuzhang Atoll, South China Sea [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(2): 485-495. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.02.18
[15] Wang G Z. Tectonic and monsoonal controls on coral atolls in the South China Sea[M]//Camoin G F, Davies P J. Reefs and Carbonate Platforms in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Blackwells: International Association of Sedimentologists, 1998, 25: 237-248.
[16] 王国忠. 全球海平面变化与中国珊瑚礁[J]. 古地理学报, 2005, 7(4):483-492 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.04.006
WANG Guozhong. Global sea-level change and coral reefs of China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2005, 7(4): 483-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.04.006
[17] 左秀玲, 苏奋振, 赵焕庭, 等. 南海珊瑚礁高分辨率遥感地貌分类体系研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(11):1463-1472 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.11.003
ZUO Xiuling, SU Fenzhen, ZHAO Huanting, et al. Development of a geomorphic classification scheme for coral reefs in the South China Sea based on high-resolution satellite images [J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(11): 1463-1472. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.11.003
[18] 赵焕庭. 中国现代珊瑚礁研究[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 1998, 20(4):98-105
ZHAO Huanting. Researches of coral reef in modern China [J]. World SCI-TECH R& D, 1998, 20(4): 98-105.
[19] Chang J H, Hsu H H, Liu C S, et al. Seismic sequence stratigraphic analysis of the carbonate platform, north offshore Taiping Island, Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea [J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 702: 70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.010
[20] 中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 46-48.
Nansha Comprehensive Scientific Investigation Team, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Physical Geography of Nansha Islands[M]. Beijing, China: Science Press, 1996: 46-48.
[21] 胡心迪. 郑和环礁珊瑚礁地貌及其对海平面变化的响应[D]. 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2020: 19-26
HU Xindi. The geomorphology of Zhenghe Atoll and its response to sea level change[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2020: 19-26.
[22] Dong Y Z, Liu Y X, Hu C M, et al. Coral reef geomorphology of the Spratly Islands: A simple method based on time-series of Landsat-8 multi-band inundation maps [J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 157: 137-154. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.09.011
[23] 赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 孙宗勋, 等. 南海诸岛全新世珊瑚礁演化的特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 1997(4):301-309 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.04.003
ZHAO Huanting, SONG Zhaojing, SUN Zongxun, et al. The evolutionary characteristics of the Holocene coral reefs of the South China Sea Islands [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1997(4): 301-309. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.04.003
[24] 李文波, 赵军. 南沙海区波浪的季节变化特征[J]. 广东气象, 2010, 32(2):24-26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6190.2010.02.009
LI Wenbo, ZHAO Jun. Seasonal variations of wave in Nansha [J]. Guangdong Meteorology, 2010, 32(2): 24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6190.2010.02.009
[25] 王婷婷, 梁广建, 周兆黎, 等. 永暑海区波浪要素变化特征分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(3):278-282 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.03.006
WANG Tingting, LIANG Guangjian, ZHOU Zhaoli, et al. Analysis of the wave characteristics at Yongshu Reef [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(3): 278-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.03.006
[26] 余克服. 珊瑚记录之近50年南沙群岛高分辨率气候变化[D]. 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所博士学位论文, 2000: 9-16.
YU Kefu. The recent fifty years high-resolution climate of Nansha Islands recorded in reef coral[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science, 2000: 9-16.
[27] 李维锋, 梁广健, 徐刚. 南沙永暑海区潮汐特征分析[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2014, 33(5):71-77
LI Weifeng, LIANG Guangjian, XU Gang. Analysis on the tide characteristics at the Yongshu Reef of the Nansha Islands [J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2014, 33(5): 71-77.
[28] 曾昭璇. 中国珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 广东: 广东人民出版社, 1997: 142-370.
ZENG Zhaoxuan. Coral Reefs Geomorphic Research in China[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong People’s Publishing House, 1997: 142-370.
[29] Kinzie I, Robert A. The zonation of West Indian gorgonians [J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 1973, 23(1): 93-155.
[30] Xu J P, Li F, Zhao J H, et al. Geomorphic zones mapping and development status monitoring of coral reefs in Xisha, China[C]//2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Beijing: IEEE, 2016: 4588-4591.
[31] Mumby P J, Harborne A R. Development of a systematic classification scheme of marine habitats to facilitate regional management and mapping of Caribbean coral reefs [J]. Biological Conservation, 1999, 88(2): 155-163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3207(98)00108-6
[32] 赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 朱袁智. 南沙群岛“危险地带”腹地珊瑚礁的地貌与现代沉积特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 1992(4):368-377 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.04.009
ZHAO Huanting, SONG Zhaojing, ZHU Yuanzhi. Geomorphic and modern sedimentary features of coral reefs in the hinterland of "Dangerous Ground", Nansha Islands [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1992(4): 368-377. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.04.009
[33] Heap A, Harris P T. Geomorphology of the Australian margin and adjacent seafloor [J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2008, 55(4): 555-585. doi: 10.1080/08120090801888669
[34] 赵焕庭, 孙宗勋, 宋朝景, 等. 南沙群岛永暑礁90多万年以来的海平面变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1996, 27(3): 264-270 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1996.03.006
ZHAO Huanting, SONG Zhaojing, SUN Zongxun, et al. The change of sea-level of Yongshu Reef in Nansha Islands since 900000 years B. P. [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1996, 27(3): 264-270. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1996.03.006
[35] 聂宝符. 五千年来南海海平面变化的研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1996(1):80-87 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.01.009
NIE Baofu. Sea-level changes of the South China Sea in the past 5000 years [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1996(1): 80-87. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.01.009
[36] 时小军, 余克服, 陈特固, 等. 中—晚全新世高海平面的琼海珊瑚礁记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(5):1-9
SHI Xiaojun, YU Kefu, CHEN Tegu, et al. Mid-to Late-Holocene sea level highstands: Evidence from fringing coral reefs at Qionghai, Hainan Island [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(5): 1-9.
[37] 许淑梅, 吴鹏, 张威, 等. 南海关键地质历史时期的古海岸线变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1):1-10
XU Shumei, WU Peng, ZHANG Wei, et al. Paleo-coastline changes in South China Sea in some critical times [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 1-10.
[38] 曾昭璇. 南海环礁的若干地貌特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1984, 3(3):40-45
ZENG Zhaoxuan. Geomorphological features of atolls in the South China Sea [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1984, 3(3): 40-45.
[39] Marszalek D S, Babashoff G, Noel M R, et al. Reef distribution in south Florida[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Coral Reef Symposium. Miami, 1977: 223-229.
[40] 黄远静. 南沙郑和和道明环礁点礁地貌特征及其成因[D]. 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2021: 26-39.
HUANG Yuanjing. Distribution and morphological characteristics of patch reefs at Xiaonanxun Reef, Zhenghe Atoll and Kuigui Sandbank, Daoming Atoll, South China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2021: 26-39.
-



 下载:
下载:





