Distribution pattern of volcanic glasses in the surficial sediments of the South China Sea and their provenance
-
摘要:
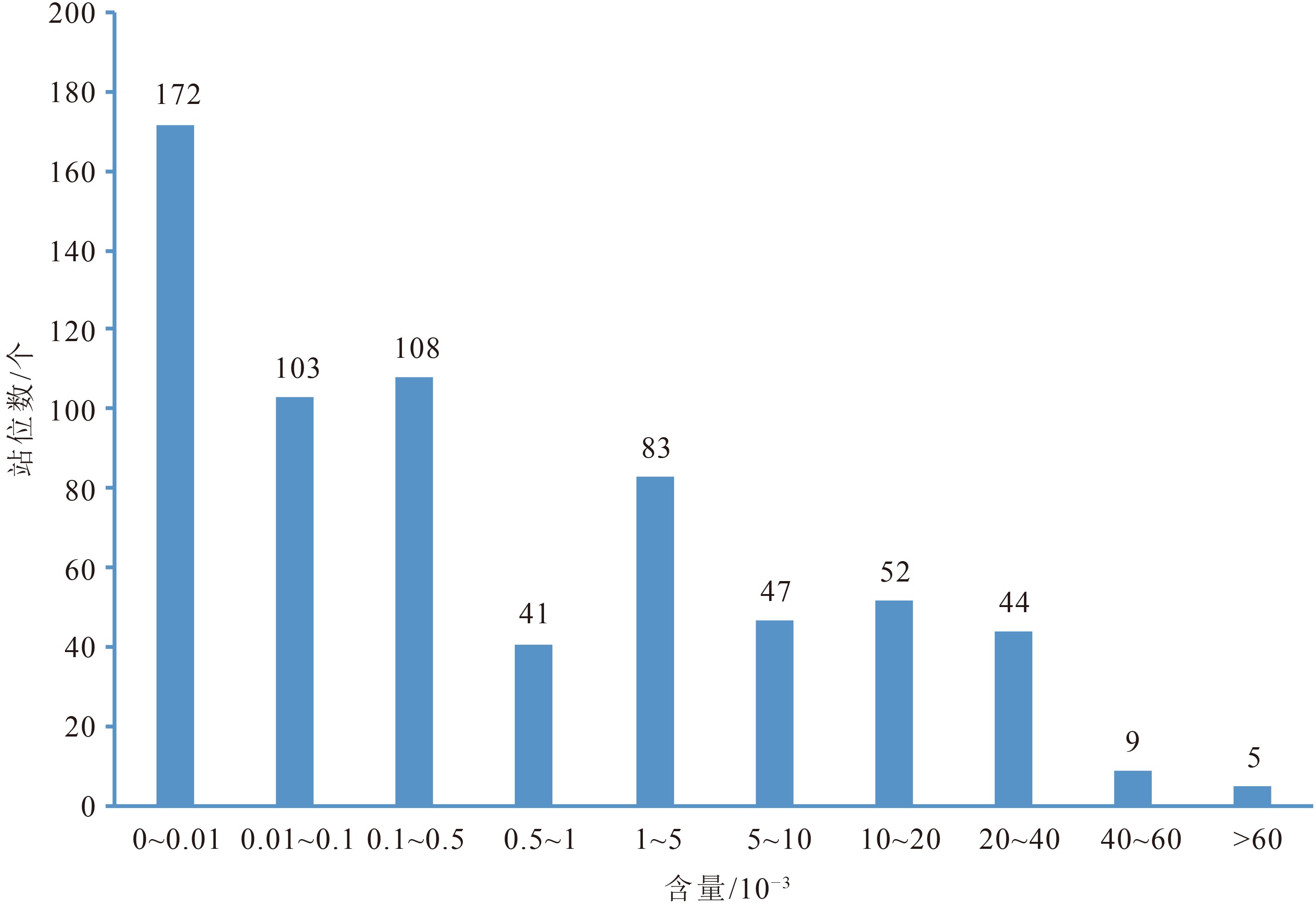
火山碎屑是边缘海沉积的重要来源,其分布特征对研究沉积作用与构造活动具有重要意义。对南海2276个表层站位碎屑矿物分析表明,664个站位含火山玻璃,占总站位数的29.17%,其中含量最高达95.8×10−3。表层沉积物火山玻璃主要出现在南海东部海域,往西呈逐渐降低趋势。南海东部主要重矿物磁铁矿和角闪石分布与火山玻璃十分相似,表明可能具有相同的来源。这些特征表明火山玻璃主要来自菲律宾群岛。这与南海东缘的琉球-台湾-菲律宾火山-地震带的吕宋岛大量活火山分布吻合。南海南缘苏门答腊-爪哇岛弧火山-地震带,虽然第四纪火山和地震活动频发,但对表层样火山玻璃贡献不大。南海海域火山可能有少量贡献,但不是主要因素,南海北缘及西缘基本没有贡献火山玻璃。
Abstract:Pyroclast is a kind of important sediment source to marginal seas and the distribution of it is of great significance to the study of sedimentation and tectonic activities. In this paper, the detrital components from 2276 surficial samples of the South China Sea are studied. Volcanic glasses are found in 664 sites, accounting for 29.17%, of which the maximum is as high as 95.8×10−3. The volcanic glasses mainly occur in the eastern part of the South China Sea and gradually decrease westward. The distribution pattern of the main heavy minerals, such as magnetite and hornblende, is similar to that of volcanic glasses, indicating that they may have the same origin. Data suggests that volcanic glasses are mainly sourced from the Philippine islands. It is consistent with the distribution pattern of active volcanoes widely distributed in the Luzon island and partial Ryukyu-Taiwan-Philippines volcanic arc and seismic zone along the eastern margin of the South China Sea. The Sumatra-Java volcanic arc and seismic zone in the southern margin of the South China Sea, although there are frequent Quaternary volcanic and seismic activities, does not contribute much volcanic glasses to the surficial sediments. Volcanoes in the South China Sea are not the main contributor and the northern and western parts of the South China Sea have almost contributed nothing.
-
Key words:
- volcanic glass /
- surficial sediment /
- provenance analysis /
- South China Sea
-

-
[1] 李志珍. 南海深海表层沉积物中的火山碎屑矿物及火山作用[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11(2):l76-l84
LI Zhizhen. Volcaniclastics minerals and volcanism in deep-sea surface sediments of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica., 1989, 11(2): l76-l84.
[2] 杨育标, 范时清. 南海深海晚第四纪火山沉积物及其起源探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 1990, 9(1):52-60
YANG Yubiao, FAN Shiqing. Research on volcanic sediments and origin of volcanic substance in South China Sea during late Quaternary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography., 1990, 9(1): 52-60.
[3] 谈丽芳. 南海火山玻璃的初步研究[J]. 南海地质研究. 1991 (3): 158-171. 广东科技出版社
TAN Lifang. Preliminary research on volcanic glass in the South China Sea[J]. Geological South China Sea. 1991 (3): 158-171. Guangdong Science and Technology Press.
[4] 陈忠, 夏斌, 颜文, 等. 南海火山玻璃的分布特征、化学成分及源区探讨[J]. 海洋学报. 2005, 27(5): 73-81
CHEN Zhong, XIA Bin, YAN Wen, et al. Distribution, chemical characteristics and source area of volcanic glass in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2005, 27(5): 73-81.
[5] 鄢全树, 石学法. 南海盆海山火山碎屑岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(12): 227-234.
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa. Characteristics of volcaniclastic rocks from seamounts in the South China Sea and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(12): 227-234.
[6] 王慧中, 周福根, 翦知缗. 中沙台缘碳酸盐软泥中的火山碎屑及其古环境意义[C]//业治铮, 汪品先. 南海晚第四纪古海洋学研究, 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社, 1992:42-55.
WANG Huizhong, ZHOU Fugen, JIAN Zhimin. Volcanic Debris in Carbonate Mud from the Margin of Zhongsha Platform and Its Paleoenvironmental Significance[C]//YE Zhizheng, WANG Pinxian. Late Quaternary paleoceanography in the South China Sea, China Ocean University Press, 1992:42- 55.
[7] Wiesner M G, Wang Y B, Zheng L F. Fallout of volcanic ash to the deep South China Sea induced by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo (Philippines) [J]. Geology, 1995, 23: 885-888.
[8] Bühring C S. Toba ash layers in the South China Sea: evidence of contrasting wind directions during ca. 74ka [J]. Geology, 2000, 28: 275-278.
[9] Song S R, Chen C H, Lee M Y, et a1. Newly discovered eastern dispersal of the youngest Toba Tuff [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 167: 303-312. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00034-7
[10] 粱细荣, 韦刚健, 邵磊, 等. Toba火山喷发在南海沉积物中的记录—ODP1143站钻孔火山玻璃的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 44(10):871-878 doi: 10.1007/BF02907078
LIANG Xirong, WEI Gangjian, SHAO Lei, et al. Records of Toba volcanic eruptions in the South China Sea [J]. Science in China, Series D, 2001, 44(10): 871-878. doi: 10.1007/BF02907078
[11] 任江波, 王嘹亮, 鄢全树, 等. 南海玳瑁海山玄武质火山角砾岩的地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报. 2013, 38(增刊1): 10-20
REN Jiangbo, WANG Liaoliang, YAN Quanshu, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its geological implications for Basalts in volcaniclastic rock from Daimao Seamount[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences. 2013, 38(supplement 1): 10-20.
[12] 冯英辞, 詹文欢, 孙杰, 等. 西沙海域上新世以来火山特征及其形成机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3):73-79
FENG Yingci, ZHAN Wenhuan, SUN Jie, et al. The formation mechanism and characteristics of volcanoes in the Xisha waters since Pliocene [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography., 2017, 36(3): 73-79.
[13] 鄢全树, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 中沙群岛近海表层沉积物中的火山灰及其对构造环境的响应[J], 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4): 9-16
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Characteristics of volcanic ash in surface sediments around Zhongsha Islands: response to tectonic setting in the north margin of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 9-16
[14] 杨群慧, 林振宏, 张富元, 等. 南海东部重矿物分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报., 2002, 32(6):956-964
YANG Qunhui, LIN Zhenhong, ZHANG Fuyuan, et al. The distribution characteristics of heavy minerals in the East of South China Sea and their controlling factors [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao., 2002, 32(6): 956-964.
[15] 时振波, 林晓彤, 杨群慧, 等. 南海东部晚更新世以来的火山沉积特征[J], 中国海洋大学学报, 2004, 34(6): 1063-1068.
SHI Zhenbo, LIN Xiaotong, YANG Qunhui, et al. Volcanic sediments in the eastern South China Sea during the Late Pleistocene [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(6): 1063-1068
[16] 马东东, 刘芳, 祝红丽, 等. 菲律宾马尼拉新生代火山岩的 Sr-Nd-Pb-Ca 同位素特征: 对南海俯冲过程中深部碳循环的制约[J]. 地球化学, 2018, 47(6):593-603
MA Dongdong, LIU Fang, ZHU Hongli, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb-Ca isotopic compositions of the Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Manila, Philippines: Implication to deep carbon cycle during the subduction of South China Sea [J]. Geochimica, 2018, 47(6): 593-603.
[17] 冯文科, 薛万俊, 杨达源. 南海北部晚第四纪地质环境[M]. 广州: 广东科学技术出版社, 1988
FENG Wenke, XUE Wanjun, YANG Dayuan. Late Quaternary Geological environment in northern South China Sea[M]. Guangdong Science and Technology Press. 1988.
[18] 李学杰, 王哲, 姚永坚, 等. 西太平洋边缘构造特征及其演化[J]. 中国地质. 2017, 44(6): 1102-1114
LI Xuejie, WANG Zhe, YAO Yongjian, et al. The tectonic features and evolution of the west Pacific margin[J]. 2017, Geology in China, 44(6): 1102-1114.
[19] Torres R C, Self S, Punongbayan R S, Attention focuses on Taal: Decade volcano of the Philippines[J]. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union. 1995, 76(24): 241-247.
[20] Listanco E, Space-time patterns in the geologic and magmatic evolution of calderas: a case study at Taal Volcano, Philippines, PhD. Thesis. Tokyo University, Tokyo, Japan, 1994.
[21] Robin C, Eissen J P, Monzier M. Ignimbrites of basaltic andesite and andesite compositions from Tanna, New Hebrides Arc [J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 1994, 56(1): 10-22. doi: 10.1007/BF00279725
[22] Knittel U, Dietmar O. Basaltic volcanism associated with extensional tectonics in the Taiwan-Luzon island arc: evidence for non-depleted sources and subduction zone enrichment [J]. Geological Society London Special Publications., 1994, 81(1): 77-93. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1994.081.01.05
[23] Lagmay A, Valdivia W. Regional stress influence on the opening direction of crater amphitheaters in Southeast Asian volcanoes [J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2006, 158(1/2): 139-150.
[24] Miklius A, Flower, M, Huijsmans J, et al. Geochemistry of Lavas from Taal volcano, southwestern Luzon, Philippines: evidence for multiple magma supply systems and mantle source Heterogeneity[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1991, 32(3): 593-627.
[25] Haeckel M, Beusekom J V, Wiesner M G, et a1. The impact of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo tephra fallout on the geochemical environment of the deep-sea sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters., 2001, 193: 151-166. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00496-4
[26] Pallister J S, Hoblitt R P, Reyes A G. A basalt trigger for the 1991 eruptions of Pinatubo volcano? [J]. Nature, 1992, 356: 426-428. doi: 10.1038/356426a0
[27] Jentzsch G, Haase O, Kroner C, et al. Mayon volcano, Philippines: some insights into stress balance [J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2001, 109(1-3): 205-217.
[28] Castillo P R, Newhall C G. Geochemical Constraints on possible subduction components in Lavas of Mayon and Taal Volcanoes, Southern Luzon, Philippines [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 6: 1089-1108.
[29] Aldiss D T, Ghazali S A. The regional geology and evolution of the Toba volcano-tectonic depression, Indonesia [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1984, 141(3): 487-500. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.141.3.0487
[30] Lorius C, Barkov N I, Jouzel J, et al. Antarctic ice core: CO2 and climatic change over the last climatic cycle[J]. EOS, 1988, 69: 681-684.
[31] Rose W I, Chesner C A. Worldwide dispersal of ash and gases from earth’s largest known eruption: Toba, Sumatra, 75ka [J]. Palaeageography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology (Global and Planetary Change Section), 1990, 89: 269-275. doi: 10.1016/0921-8181(90)90023-6
[32] 孙嘉诗. 南海北部及广东沿海新生代火山活动[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 11(3):45-67
SUN Jiashi. Cenozoic volcanic activity in the Northern South China Sea and guangdong coastal area [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary geology., 1991, 11(3): 45-67.
[33] 张斌, 王璞琚, 张功成, 等. 珠一琼盆地新生界火山岩特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发., 2013, 40(6):657-665
ZHANG Bin, WANG Pujun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Pearl River Mouth and Southeast Hainan Basins of South China Sea and their implications for petroleum geology [J]. Petroleum exploration and development., 2013, 40(6): 657-665.
[34] 杨金玉, 张训华, 王修田. 南海中部海山性质研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2001, 25(7):31-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2001.07.010
YANG Jinyu, ZHANG Xunhua, WANG Xiutian. Some discussion about the character of the seamounts in South China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences., 2001, 25(7): 31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2001.07.010
[35] Yan Quanshu, Shi Xuefa, Wang Kunshan, et al. Major element, trace element, and Sr, Nd and Pb isotope studies of Cenozoic basalts from the South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(4): 550-566. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0026-3
[36] 石学法, 鄢全树. 南海新生代岩浆活动的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 31(2):59-72
SHI Xuefa, YAN Quanshu. Geochemistry of cenozoic magmatism in the South China Sea and its tectonic implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 31(2): 59-72.
[37] 李诗颖, 余克服, 张瑜, 等. 西沙群岛基底火山碎屑岩中单斜辉石的矿物化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋学报., 2019, 41(7):66-76
LI Shiying, YU Kefu, ZHANG Yu, et al. Mineral chemistry of clinopyroxene in pyroclastic rocks of the Xisha Islands and their geological significance [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica., 2019, 41(7): 66-76.
[38] 张富元, 张霄宇, 等. 南海东部海域的沉积作用和物质来源研究[J]. 海洋学报., 2005, 27(2):79-90
ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Xiao Yu, YANG Qunhui, et al. Research on sedimentations and material sources in the eastern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica., 2005, 27(2): 79-90.
[39] 李学杰, 汪品先, 廖志良, 等. 南海西部表层沉积物碎屑矿物分布特征及其物源[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(1):123-130 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.013
LI Xuejie, WANG Pinxian, LIAO Zhiliang, et al. Distribution of clastic minerals of surface sediments in the western China and their provenance [J]. Geology in China., 2008, 35(1): 123-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.013
[40] 王汝建. 南沙海区更新世以来的火山灰及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1):5l-56
WANG Rujian. Pleistocene volcanic shards and their geological significance in the Nansha area of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(1): 5l-56.
-




 下载:
下载: