Tectonic evolution and drilling proposal of the subduction system of the Caroline Ridge − An oceanic plateau in the Western Pacific
-
摘要:
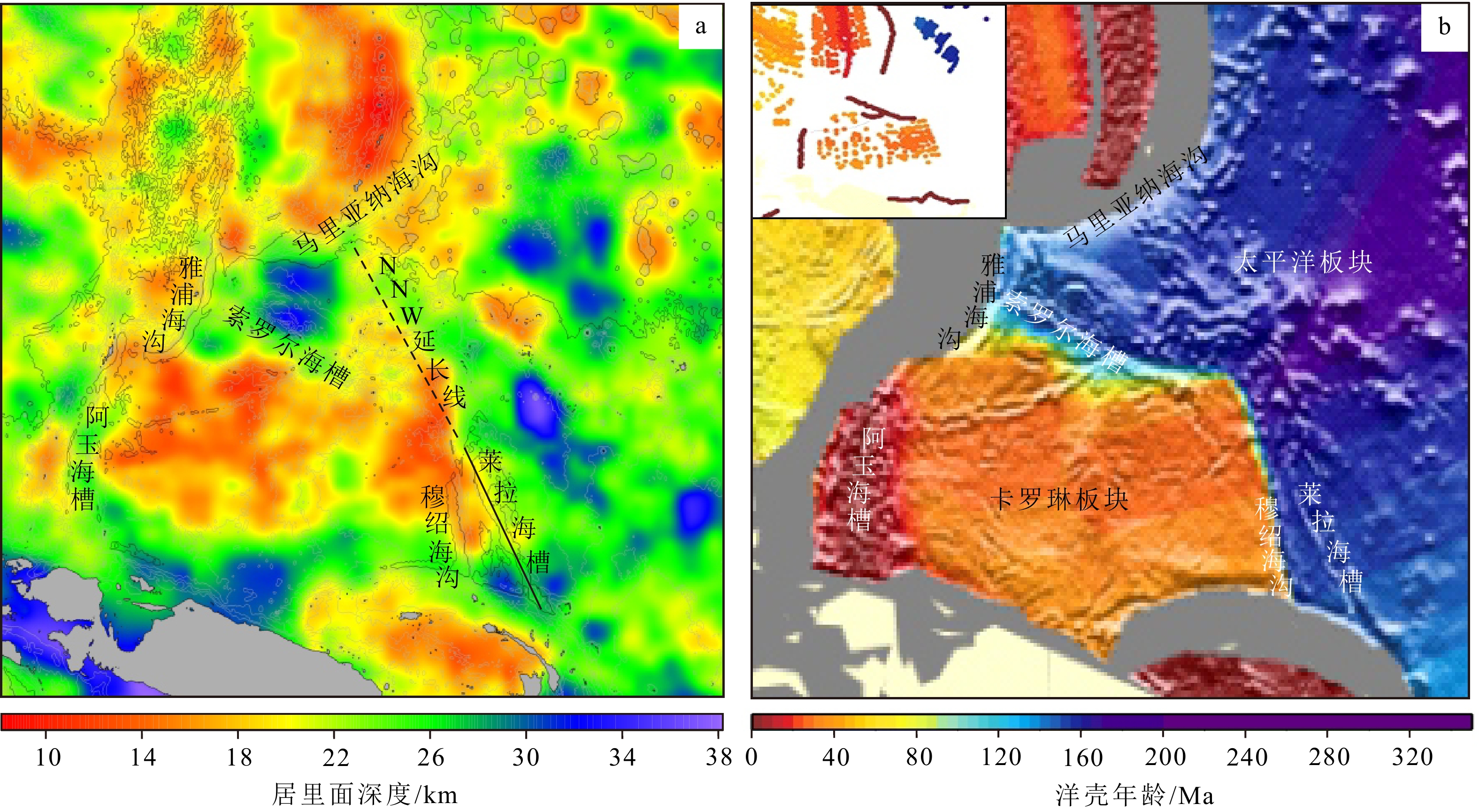
洋底高原的形成与演化过程是近年来海洋地质学关注的重点科学问题之一。卡罗琳洋底高原位于西太平洋雅浦海域,其构造演化独具特色,经历了热点火山作用、俯冲碰撞和裂解等多个地质事件,为洋底高原的研究提供了关键案例。目前对卡罗琳洋底高原演化过程的认识尚未完全明晰,未来研究可聚焦4个方面:①卡罗琳洋底高原北部正常洋壳年龄的厘定,揭示卡罗琳板块-太平洋板块边界的位置与形态;②结合钻井、地震地层学研究,建立地层年代框架,识别区域构造事件的发生时间与影响范围;③揭示索罗尔海槽岩石圈的张裂阶段及新洋壳是否形成;④阐明卡罗琳洋底高原俯冲前缘挠曲断裂带地壳的性质与年龄。近年来,我国十分重视卡罗琳海域的地质和地球物理调查研究,并有望开展大洋钻探计划。本文在前期工作的基础上提出了雅浦海域大洋钻探站位选取建议,希望可以解决以上关键科学问题,为全球洋底高原的形成演化研究贡献中国智慧。
Abstract:The formation and evolution of oceanic plateaus have been the focus of marine geology in recent years. The Caroline Plateau, also known as Caroline Ridge, near the Yap Trench in the western Pacific, is unique in tectonic evolution. It experienced from hotspot volcanism, subduction, collision, to rifting, and provided a key case for the study of oceanic plateaus. At present, the understanding of the evolutionary process of the Caroline Plateau is not completely clear. Future research shall focus on: (1) determining the age of the normal oceanic crust in the northern Caroline Plateau, and revealing the location and shape of the Caroline-Pacific plate boundary; (2) establishing stratigraphic time frame based on seismic stratigraphy in combination with drilling, and identifying the occurrence time and influence scope of regional events;(3) revealing the rifting stage and the possibility of oceanic crust formation in the Sorol Trough; (4) clarifying the nature and age of the crust in the bending-related fault zone in the incoming Caroline Plateau front. In recent years, geological and geophysical features of the Caroline plate are highly focused in China, and it is expected to carry out an ocean drilling program. On the basis of previous works, we proposed ocean drilling sites in the Caroline sea.
-
Key words:
- oceanic plateau /
- plate boundary /
- ocean drilling /
- geophysics /
- Sorol Trough /
- Yap Trench
-

-
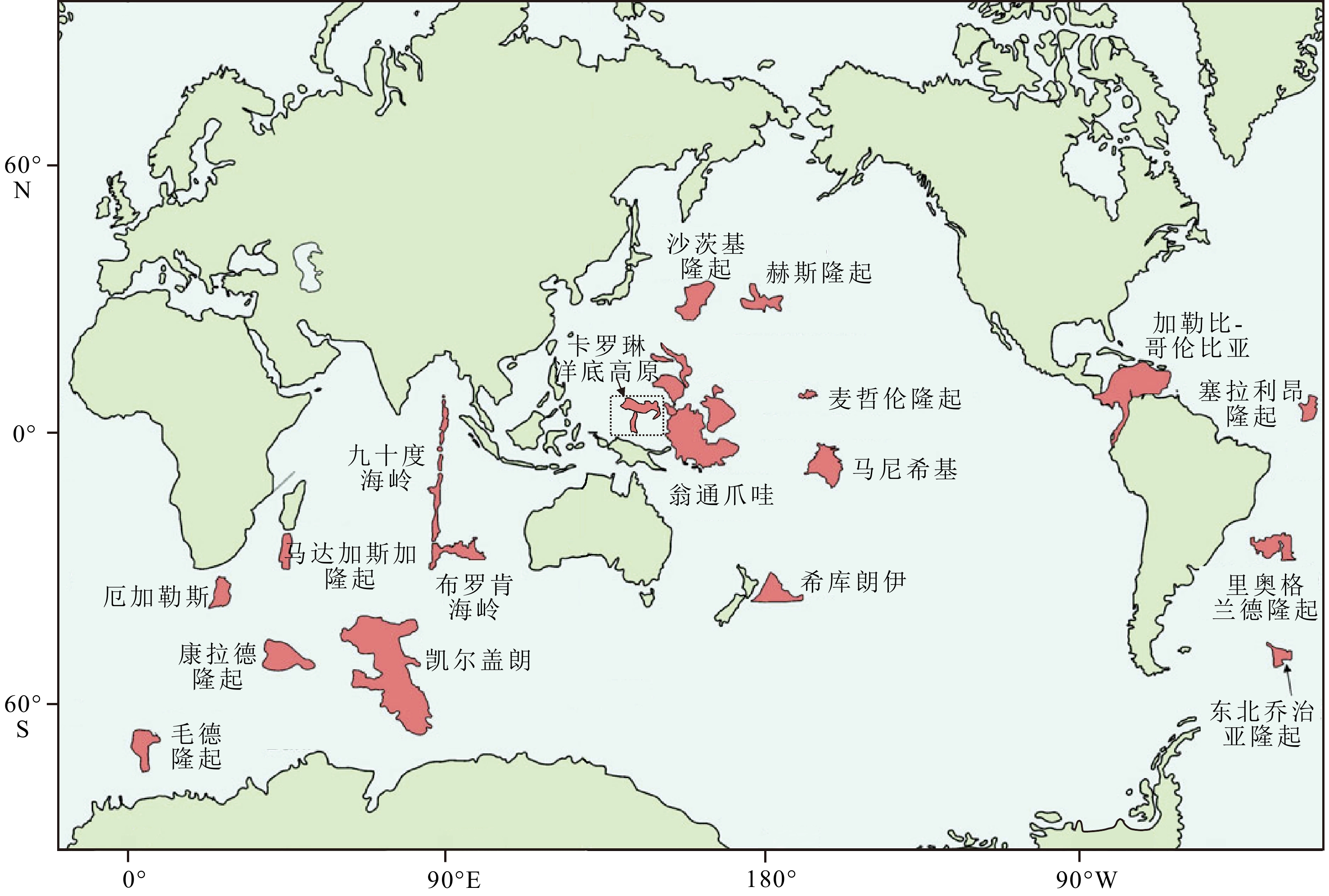
图 1 白垩纪以来主要洋底高原(红色区域)的分布[1]
Figure 1.
表 1 大洋钻探建议站位主要信息
Table 1. Specifications of the proposed drilling sites
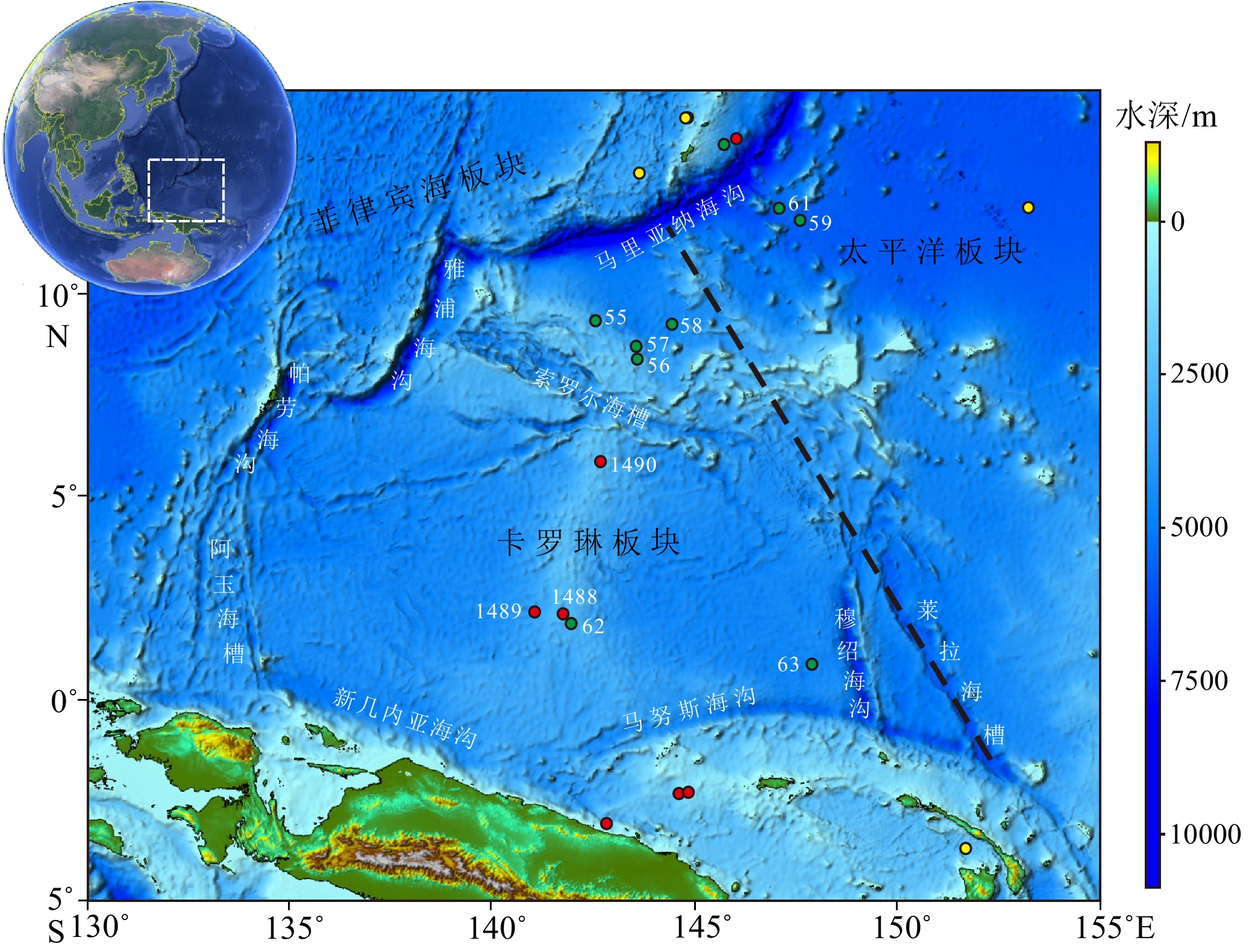
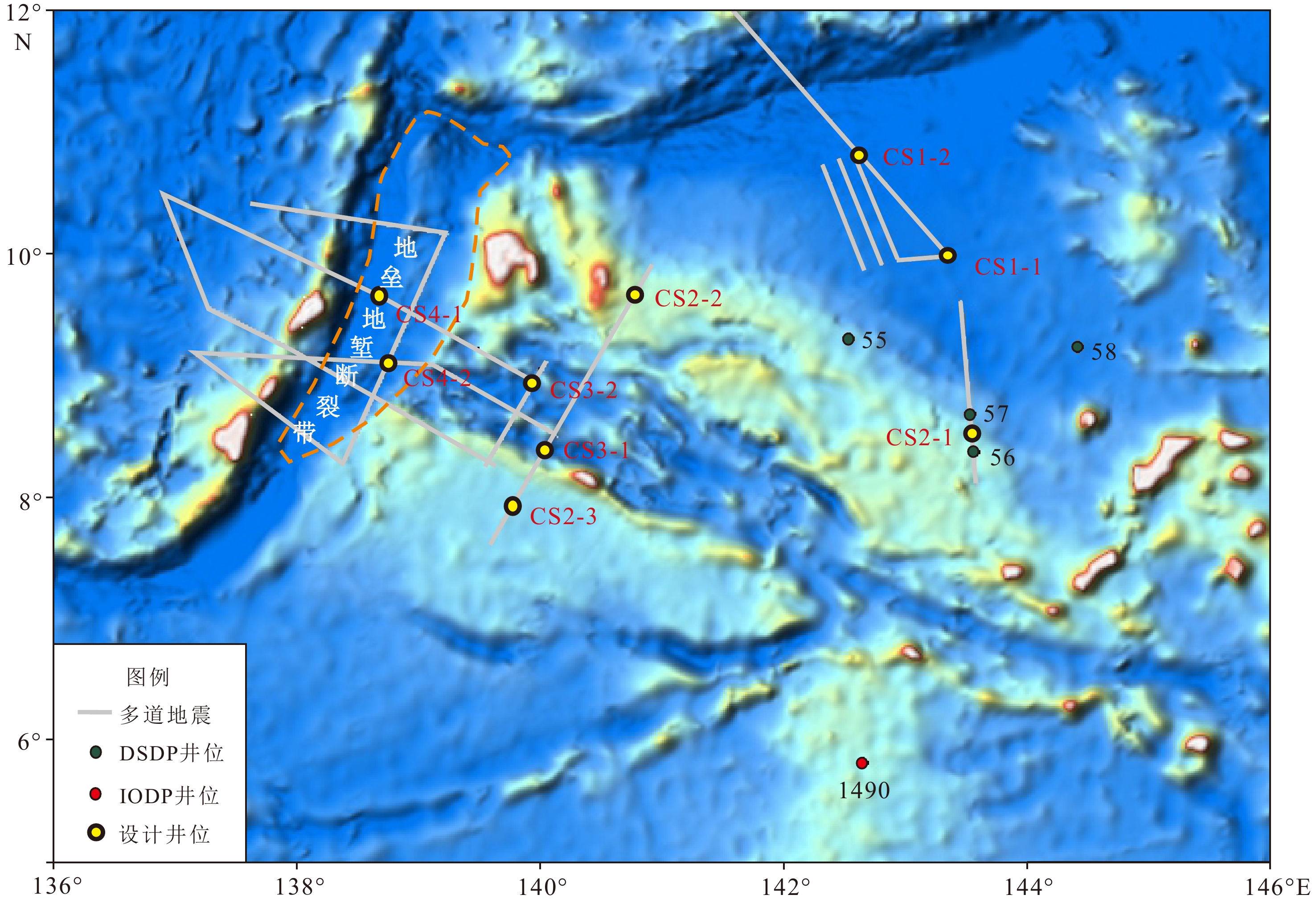
站位号 纬度 经度 水深/m 钻探深度/m CS1-1 9°59′14″N 143°20′51″E 4725 400 CS1-2 10°49′28″N 142°36′02″E 5175 200 CS2-1 8°39′45″N 143°32′00″E 3190 450 CS2-2 9°41′58″N 140°47′25″E 1970 400 CS2-3 7°50′13″N 139°42′12″E 2920 400 CS3-1 8°22′53″N 140°01′13″E 4225 100 CS3-2 8°55′37″N 139°56′22″E 4565 150 CS4-1 9°42′05″N 138°36′11″E 7060 150 CS4-2 9°04′30″N 138°46′46″E 4690 200 -
[1] Kerr A C, Mahoney J J. Oceanic plateaus: Problematic plumes, potential paradigms [J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 241(3-4): 332-353. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.01.019
[2] Kroenke L W. Origin of continents through development and coalescence of oceanic flood basalt plateaus [J]. Eos, Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, 1974, 55: 443.
[3] Arndt N, Weis D. Oceanic plateaus as windows to the earth's interior: An ODP success story [J]. JOIDES Journal, 2002, 28(1): 79-84.
[4] Saunders A D, Tarney J, Kerr A C, et al. The formation and fate of large oceanic igneous provinces [J]. Lithos, 1996, 37(2-3): 81-95. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(95)00030-5
[5] Ryberg T, Haberland C, Haberlau T, et al. Crustal structure of northwest Namibia: Evidence for plume-rift-continent interaction [J]. Geology, 2015, 43(8): 739-742. doi: 10.1130/G36768.1
[6] Barckhausen U, Ranero C R, Cande S C, et al. Birth of an intraoceanic spreading center [J]. Geology, 2008, 36(10): 767-770. doi: 10.1130/G25056A.1
[7] Taylor B. The single largest oceanic plateau: Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 372-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.11.049
[8] Campbell I H. Testing the plume theory [J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 241(3-4): 153-176. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.01.024
[9] Hegarty K A, Weissel J K. Complexities in the development of the Caroline Plate region, Western Equatorial Pacific[M]//Nairn A E M, Stehli F G, Uyeda S. The Ocean Basins and Margins. New York: Springer, 1988: 277-301.
[10] Gaina C, Müller D. Cenozoic tectonic and depth/age evolution of the Indonesian gateway and associated back-arc basins [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2007, 83(3-4): 177-203. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.04.004
[11] Seno T, Stein S, Gripp A E. A model for the motion of the Philippine Sea Plate consistent with NUVEL‐1 and geological data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1993, 98(B10): 17941-17948. doi: 10.1029/93JB00782
[12] Bracey D R, Andrews J E. Western Caroline Ridge: Relic island arc? [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 1974, 2(2): 111-125.
[13] Dong D D, Zhang Z Y, Bai Y L, et al. Topographic and sedimentary features in the Yap subduction zone and their implications for the Caroline Ridge subduction [J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 722: 410-421. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.11.030
[14] Altis S. Origin and tectonic evolution of the Caroline Ridge and the Sorol Trough, western tropical Pacific, from admittance and a tectonic modeling analysis [J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 313(3): 271-292. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00204-8
[15] Nagihara S, Kinoshita M, Fujimoto H, et al. Geophysical observations around the northern Yap Trench: seismicity, gravity and heat flow [J]. Tectonophysics, 1989, 163(1-2): 93-104. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(89)90120-0
[16] WeisselJK, Anderson R N. Is there a Caroline plate? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 41(2): 143-158. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90004-3
[17] Zhang G L, Zhang J, Wang S, et al. Geochemical and chronological constraints on the mantle plume origin of the Caroline Plateau [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 540: 119566. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119566
[18] Chen L, Tang L M, Li X H, et al. Geochemistry of peridotites from the Yap Trench, Western Pacific: implications for subduction zone mantle evolution [J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(9): 1037-1051. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1484305
[19] Yang A, Fu Y T. Estimates of effective elastic thickness at subduction zones [J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2018, 117: 75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2018.04.007
[20] Heezen B C, FischerA G, BoyceRE, et al. Initial reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project [J]. Washington, DC:US Government Printing Office, 1971, 6: 389-537.
[21] Ridley W I, Rhodes J M, Reid A M, et al. Basalts from leg 6 of the deep-sea drilling project [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1974, 15(1): 140-159. doi: 10.1093/petrology/15.1.140
[22] Keating B H, Mattey D P, Helsley C E, et al. Evidence for a hot spot origin of the Caroline Islands [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1984, 89(B12): 9937-9948. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB12p09937
[23] LarsonR L, Schlanger S O. Geological evolution of the Nauru Basin, and regionalimplications[R]. Initial Reports ofthe Deep Sea Drilling Project, Washington, D. C. : U. S. Government Printing Office, 1981, 61: 841-862.
[24] Courtillot V, Davaille A, Besse J, et al. Three distinct types of hotspots in the Earth’s mantle [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 205(3-4): 295-308. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01048-8
[25] French S W, Romanowicz B. Broad plumes rooted at the base of the Earth's mantle beneath major hotspots [J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7567): 95-99. doi: 10.1038/nature14876
[26] Zhang Z Y, Dong D D, Sun W D, et al. Subduction erosion, crustal structure, and an evolutionary model of the Northern Yap subduction zone: New observations from the latest geophysical survey [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2019, 20(1): 166-182. doi: 10.1029/2018GC007751
[27] Rehman H U, Nakaya H, Kawai K. Geological origin of the volcanic islands of the caroline group in the federated states of Micronesia, Western Pacific [J]. South Pacific Studies, 2013, 33(2): 101-118.
[28] McCabe R, Uyeda S. Hypothetical model for the bending of the Mariana Arc[M]//Hayes D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 1983, 27: 281-293.
[29] Fujiwara T, Tamura C, Nishizawa A, et al. Morphology and tectonics of the Yap Trench [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2000, 21(1-2): 69-86.
[30] Zhang J, Zhang G L. Geochemical and chronological evidence for collision of proto-Yap arc/Caroline plateau and rejuvenated plate subduction at Yap trench [J]. Lithos, 2020, 370-371: 105616. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105616
[31] Zhang Z Y, Dong D D, Sun W D, et al. The Caroline Ridge fault system and implications for the bending-related faulting of incoming oceanic plateaus [J]. Gondwana Research, 2021, 92: 133-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.11.018
[32] Fornari D J, Weissel J K, Perfit M R, et al. Petrochemistry of the Sorol and Ayu Troughs: implications for crustal accretion at the northern and western boundaries of the Caroline plate [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1979, 45(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90102-X
[33] Fan J K, Zheng H, Zhao D P, et al. Seismic structure of the caroline Plateau‐Yap trench collision zone [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(6): e2022GL098017.
[34] Xia C L, Zheng Y P, Liu B H, et al. Geological and geophysical differences between the north and south sections of the Yap trench‐arc system and their relationship with Caroline Ridge subduction [J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(12): 7775-7789. doi: 10.1002/gj.3903
[35] Lee S M. Deformation from the convergence of oceanic lithosphere into Yap trench and its implications for early-stage subduction [J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2004, 37(1): 83-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2003.10.003
[36] Zhang Z Y, Dong D D, Sun W D, et al. Investigation of an oceanic plateau formation and rifting initiation model implied by the Caroline Ridge on the Caroline Plate, western Pacific [J]. International Geology Review, 2021, 63(2): 193-207. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2019.1707126
[37] 董冬冬, 张广旭, 钱进, 等. 西太平洋雅浦俯冲带的地貌及地层结构特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):23-29 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.01.003
DONG Dongdong, ZHANG Guangxu, QIAN Jin, et al. Geomorphology and stratigraphic framework of the Yap subduction zone, western Pacific [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 23-29. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.01.003
[38] 李春峰, 李刚, 厉子龙, 等. 卡罗琳海板块实验: 初始俯冲、初始扩张与流固耦合[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(5):87-97
LI Chunfeng, LI Gang, LI Zilong, et al. Study of the Caroline plate: Initial subduction, initial spreading and fluid-solid interaction [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(5): 87-97.
[39] 栾振东, 董冬冬. 西太平洋典型海域地球物理调查图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 1-124
LUAN Zhendong, DONG Dongdong. Geophysical Atlas of the Typical Regions in Western Pacific[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 1-124.
[40] Li C F, Lu Y, Wang J. A global reference model of Curie-point depths based on EMAG2 [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 45129. doi: 10.1038/srep45129
[41] Seton M, Müller R D, Zahirovic S, et al. A global data set of present‐day oceanic crustal age and seafloor spreading parameters [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2020, 21(10): e2020GC009214.
-



 下载:
下载: