Mineralogical and geochemical features of Co-rich crust on Caiwei Guyot, Northwest Pacific Ocean
-
摘要:
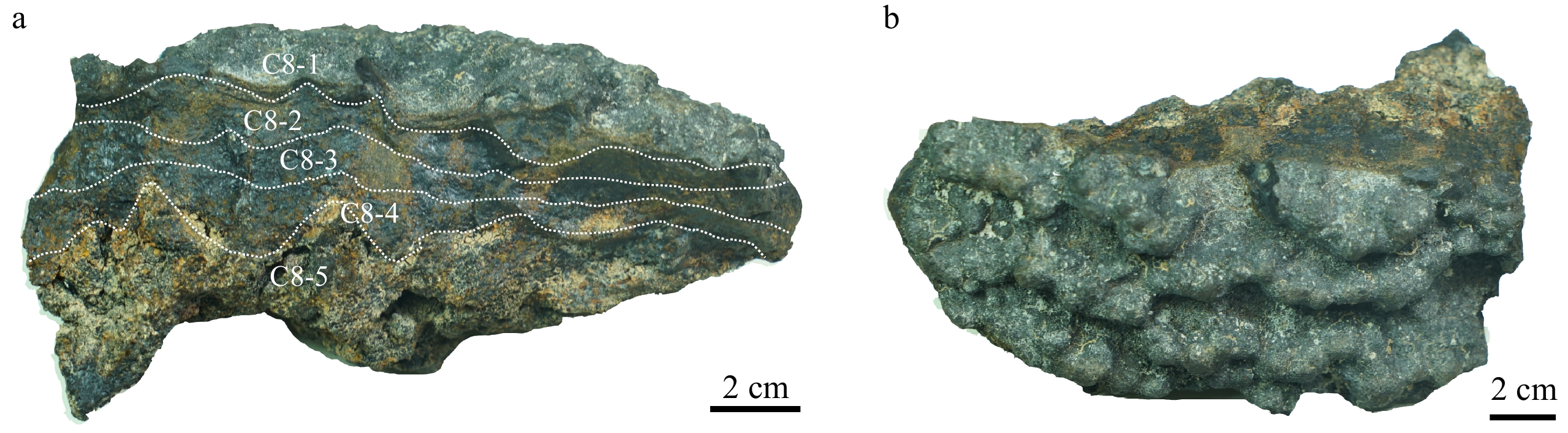
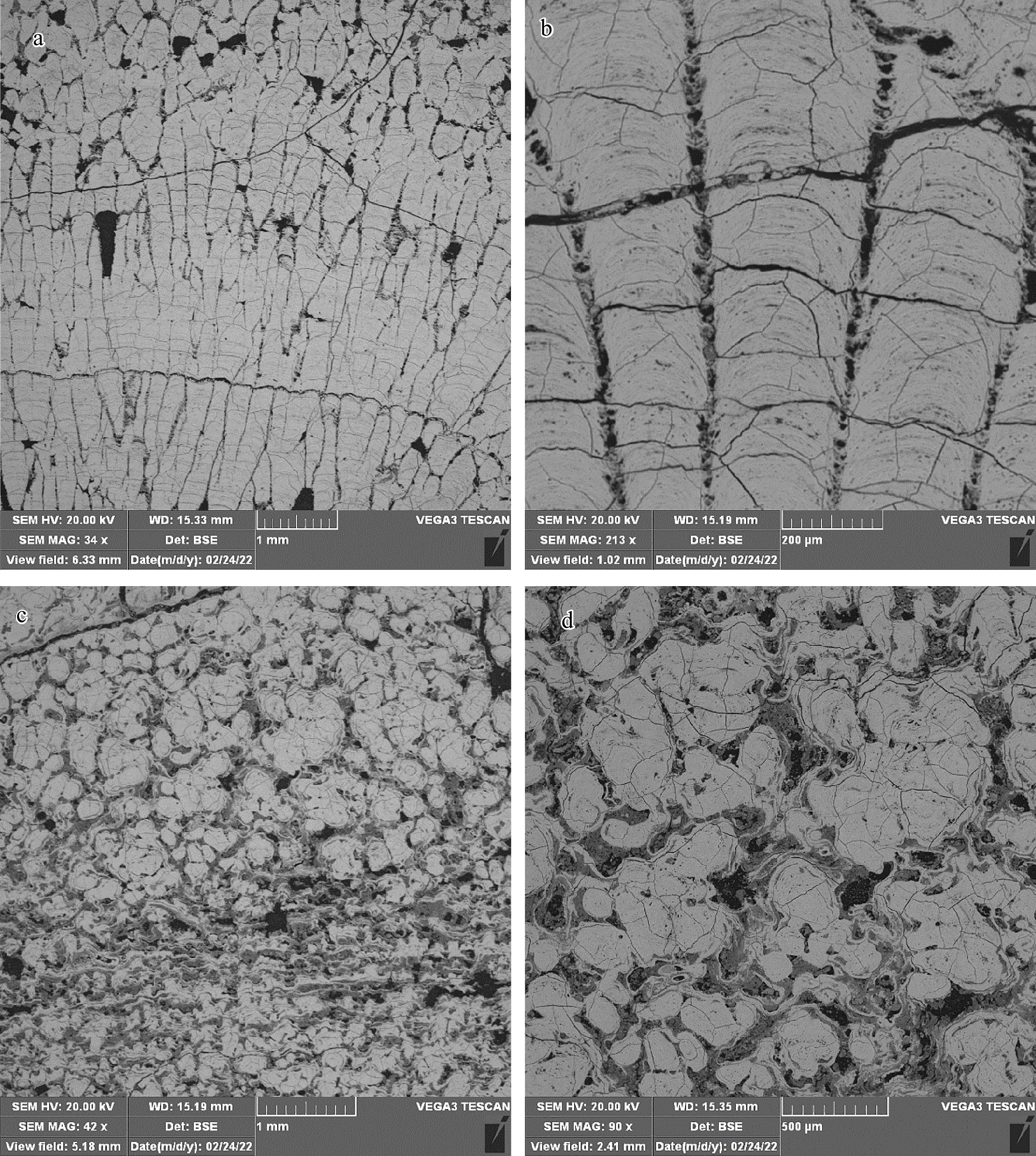
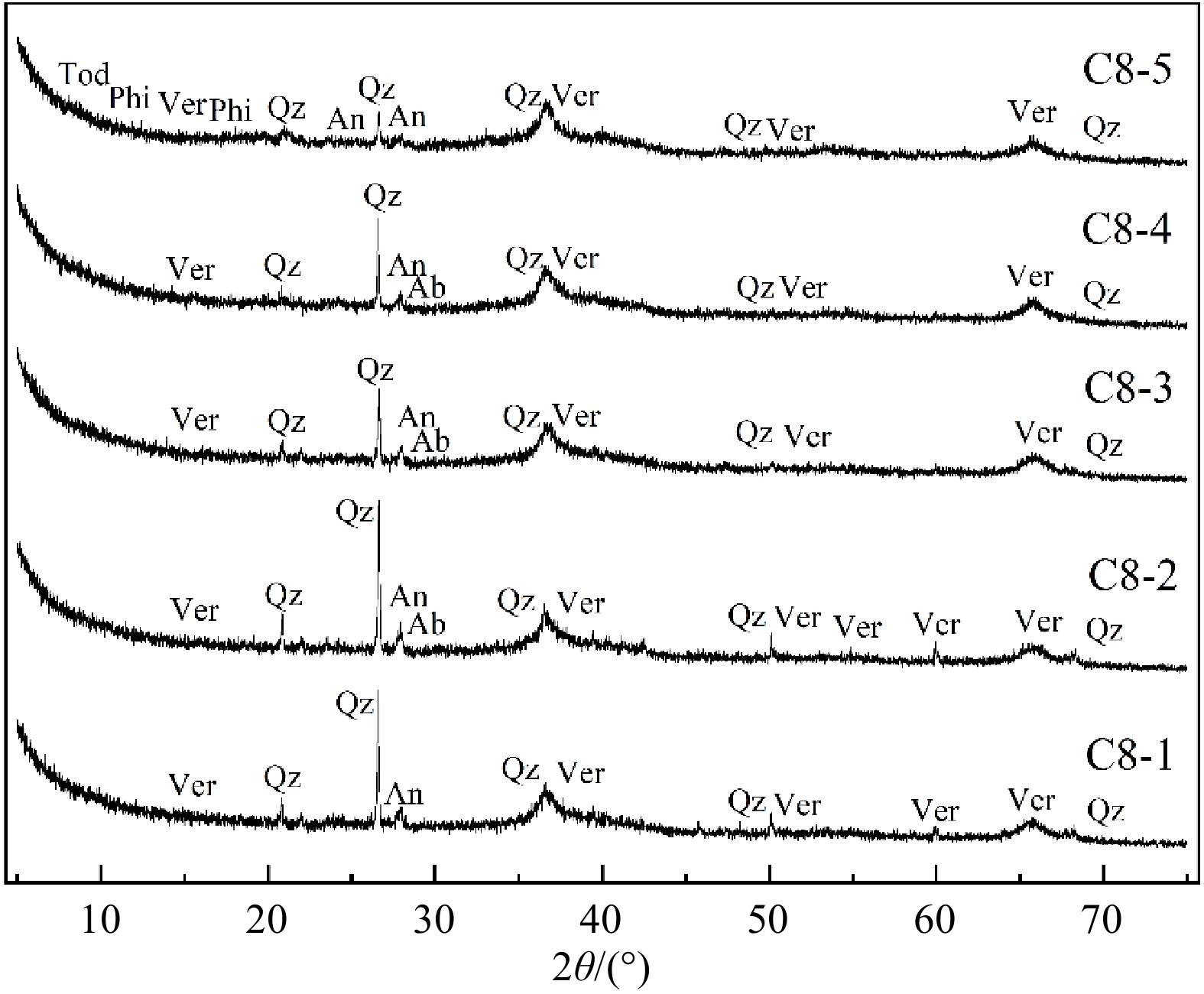
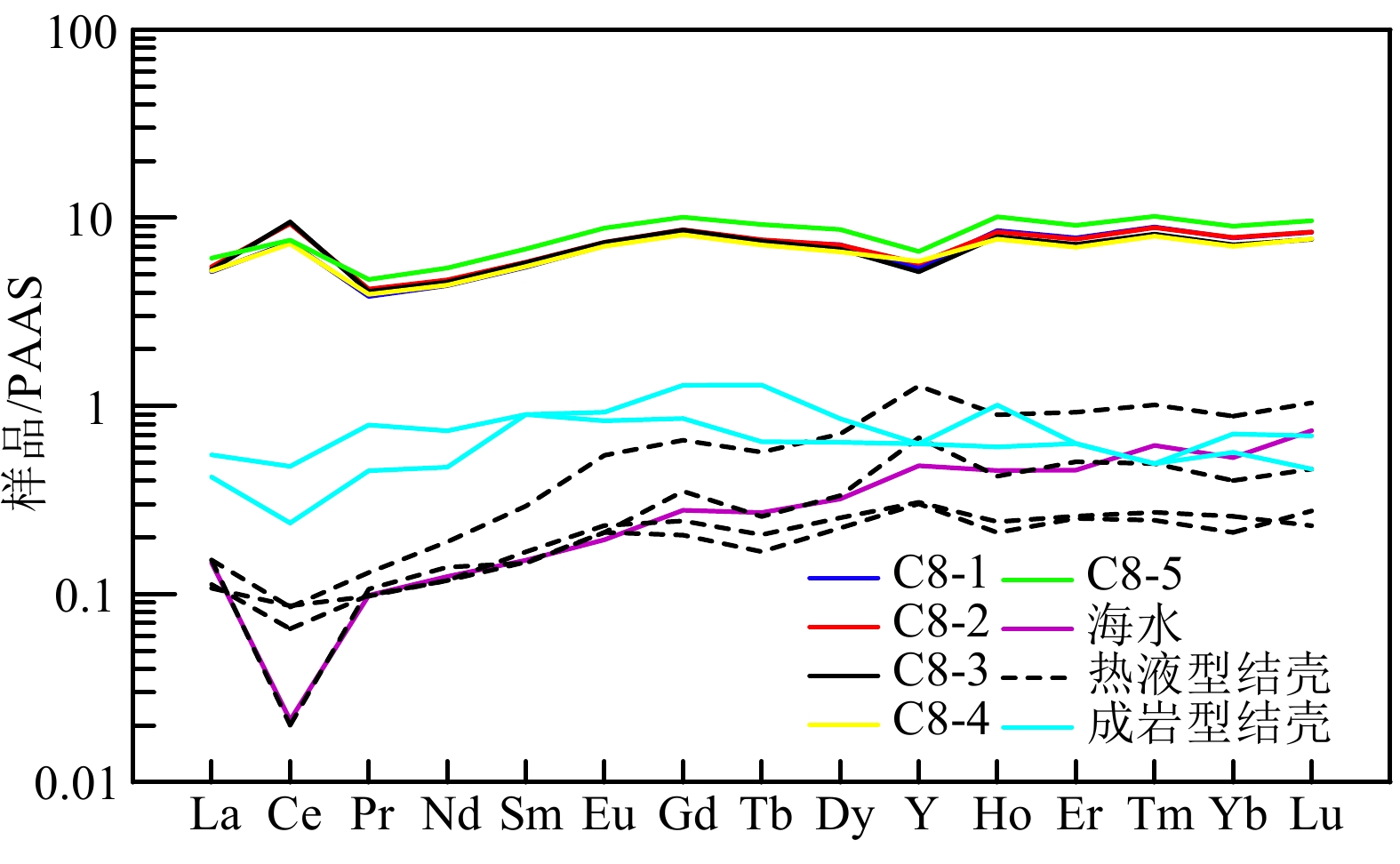
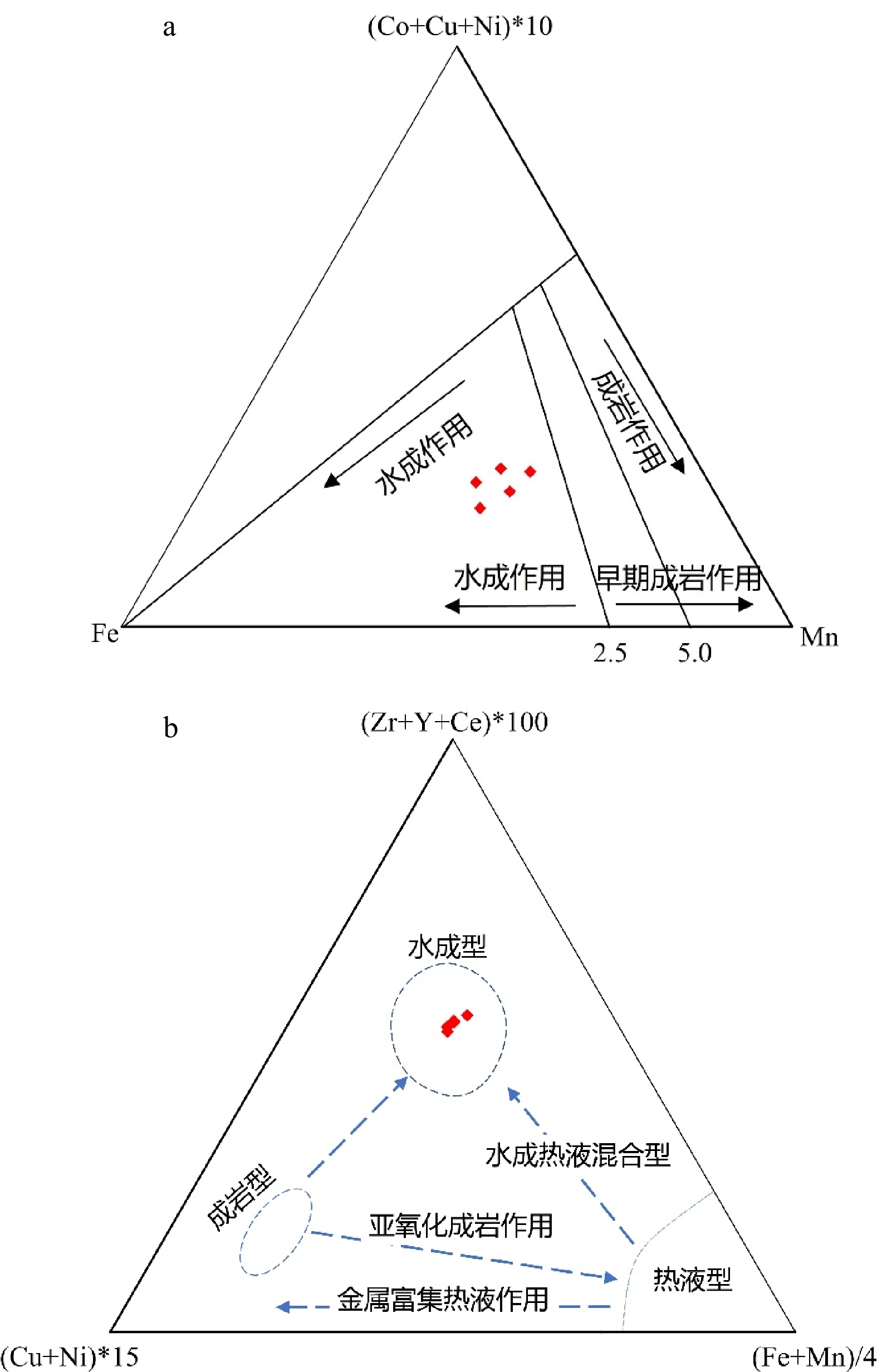
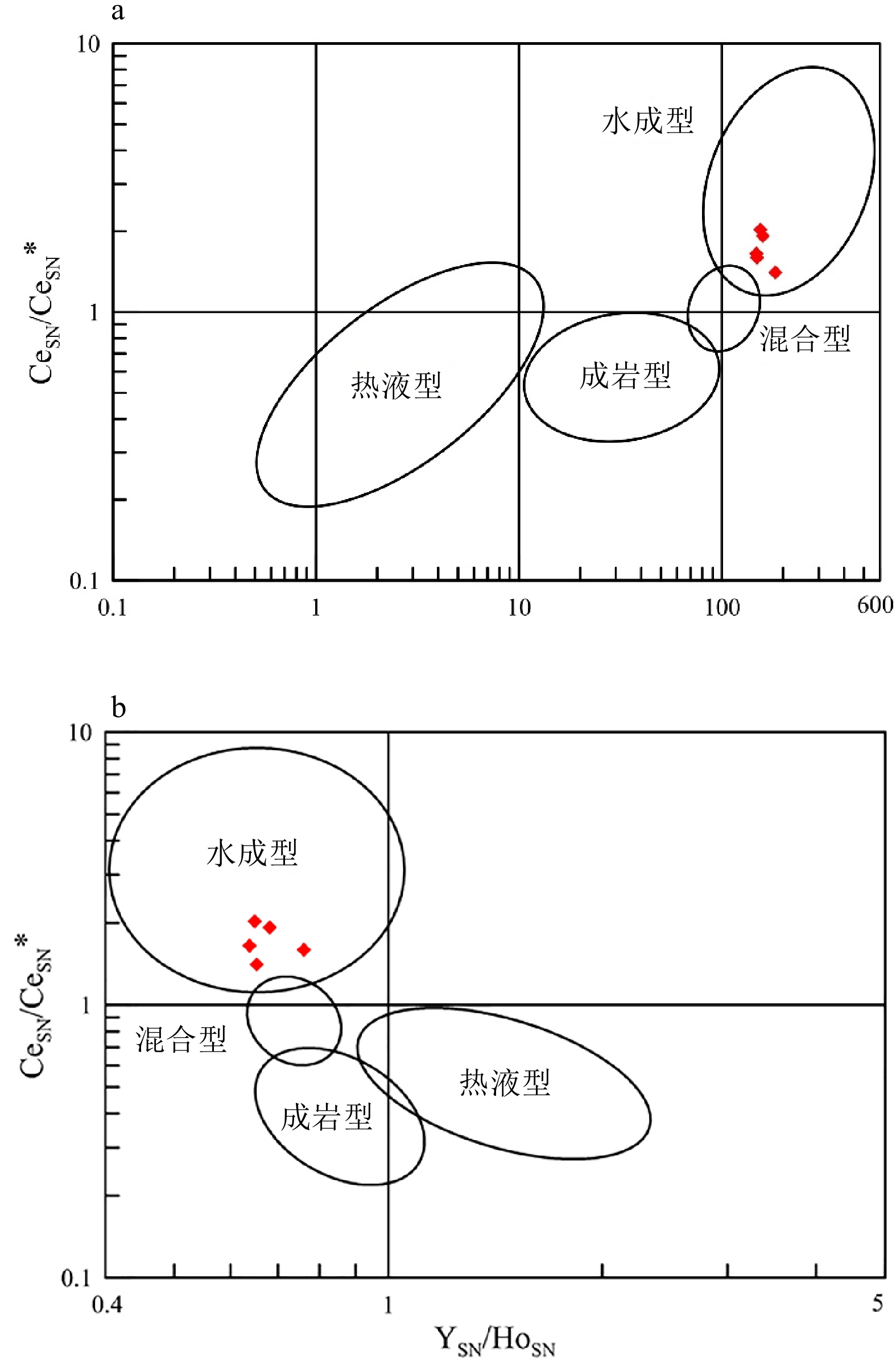
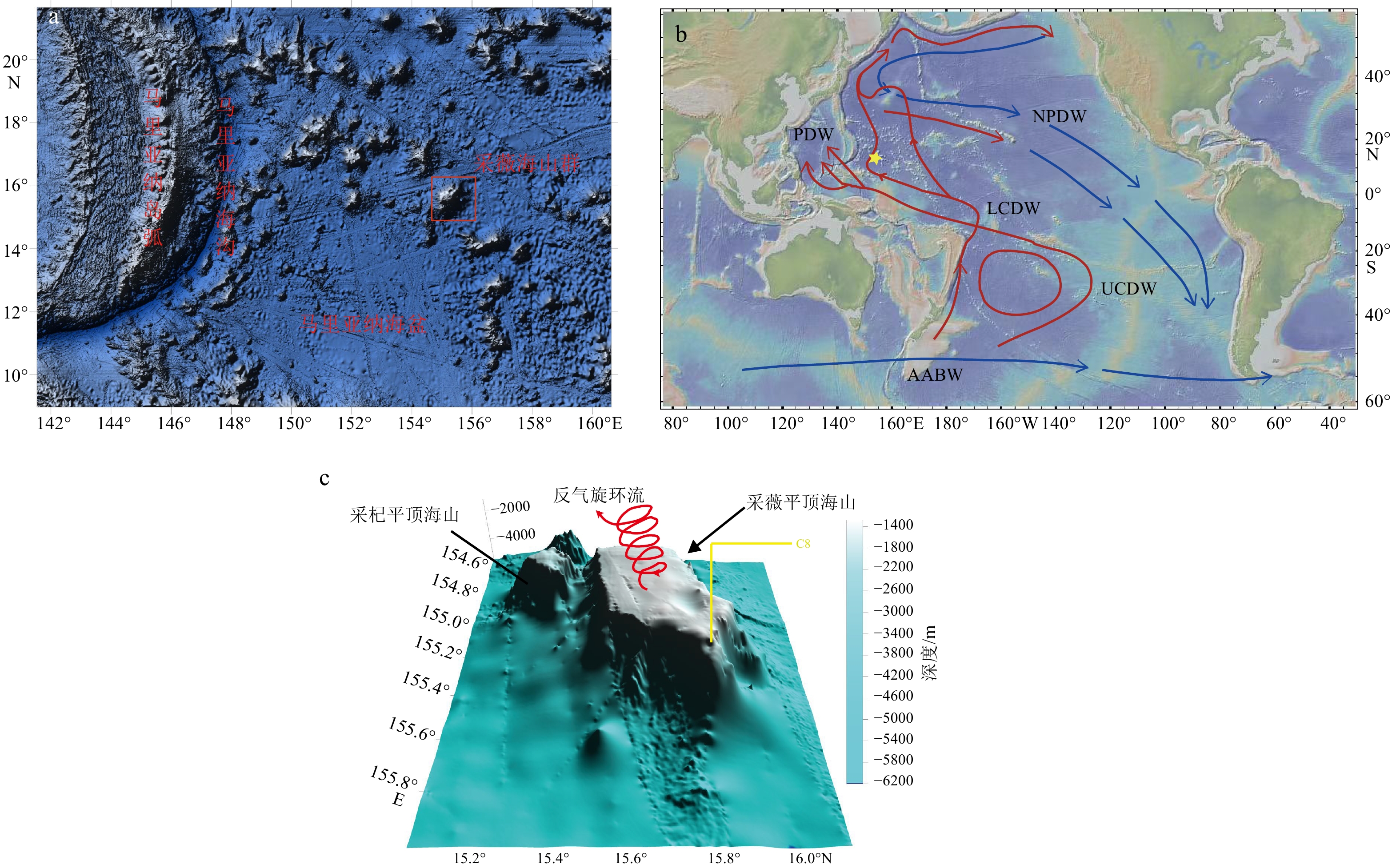
富钴结壳是一种富含Mn、Co、Ni和稀土元素(镧系元素加钇,简称REY)等元素的海底矿产资源。本文研究的富钴结壳样品是“科学”号在2018年HOBAB5航次于西北太平洋采薇海山的山顶边缘上通过电视抓斗获得的。利用扫描电镜、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)和电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)分析了富钴结壳的显微构造、矿物学特征和地球化学特征,并探讨了其成因类型和形成机制。富钴结壳的结构从内到外可分为土黄色的疏松层(C8-5)、黑色铁锰致密层(C8-2、C8-3和C8-4)和发育葡萄状球体的粗糙表面(C8-1)。土黄色疏松层孔隙度较高,主要组成矿物为水羟锰矿、石英、钙长石、钠长石、钙十字沸石和钡镁锰矿,Mn的含量较低,Al的含量较高。黑色的铁锰致密层孔隙度较低,呈柱状构造,主要组成矿物为水羟锰矿、石英、钙长石和钠长石,Al含量有所下降,Mn含量升高, 说明陆源物质的供应逐渐变少。在富钴结壳的生长后期,其主要显微构造由柱状构造向斑杂构造转变,二者的过渡区域为铁锰氧化物与富Si碎屑物质组成的层状构造。富钴结壳各层位的Mn/Fe比值为1.16~1.85,且各层位Ce呈正异常,Y呈负异常,以上特征表明富钴结壳为水成成因型,其金属元素来源于氧化性海水,未受到热液活动的影响。依据富钴结壳的年代学数据,可知从渐新世末期到上新世中期,富钴结壳的生长过程一直受控于太平洋深层水。Co/(Fe+Mn)和Co/(Ni+Cu)的不断升高表明富钴结壳一直在氧化性较高的海水环境中生长。相较于其他大洋和海区,采薇海山富钴结壳具有高含量的Co、Ni和REY,具有极高的经济价值和开采价值。
Abstract:Co-rich crusts are a kind of marine mineral resources rich in Mn, Co, Ni and rare earth elements (lanthanide and yttrium, abbreviated as REY). The Co-rich crust sample studied in this paper was collected on the mountaintop edge of Caiwei Guyot in the Northwest Pacific Ocean onboard research vessel “Kexue” (Science) with a TV grab during the HOBAB5 cruise expedition in 2018. The microstructure, mineralogy, and geochemistry of the Co-rich crust were analyzed by scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-OES), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and its genetic type and formation mechanism were discussed. The textures of the Co-rich crust could be divided into yellowish loose layer (C8-5), black dense ferromanganese layers (C8-2, C8-3 and C8-4), and rough surface in black botryoidal shape (C8-1) from inside to outside. The yellowish loose layer is composed of Fe-vernadite, quartz, albite, anorthite, todorokite, and phillipsite. It has high porosity with a high content of Al and low content of Mn. The black dense ferromanganese layers have low porosity and are mainly columnar in structure, and the main component minerals are Fe-vernadite, quartz, albite, and anorthite. Compared with C8-5, the content of Al decreases but the content of Mn increases, indicating that the supply of terrigenous materials gradually decreased. In the later growth process of the Co-rich crust, its microstructure changed mostly from columnar structure to mottled structure, and the transition area is in layered structure and composed of ferromanganese oxides and Si-rich clastic materials. The Mn/Fe ratios of layers of the Co-rich crust range from 1.16 to 1.85, and each layer shows positive Ce anomaly and negative Y anomaly. The above characteristics indicate that the Co-rich crust in the study area shows its hydrogenetic origin and is not affected by hydrothermal activities, whose metal elements are derived from oxidizing seawater. According to the chronological data, we conclude that the growth process of the Co-rich crust was controlled by Pacific Deep Water from the late Oligocene to the middle Pliocene. The continuous increases of Co/(Fe+Mn) and Co/(Ni+Cu) indicate that the Co-rich crust has been growing in a highly oxidizing marine environment. Compared with other oceans and seas, the Co-rich crust on Caiwei Guyot is enriched in Co, Ni and REY, and shall has very high economic value and mining prosperity.
-
Key words:
- mineralogy /
- geochemistry /
- Caiwei Guyot /
- Co-rich crust
-

-
表 1 采薇海山富钴结壳各层位地球化学数据
Table 1. Geochemical data of the layers of the Co-rich crust on Caiwei Guyot
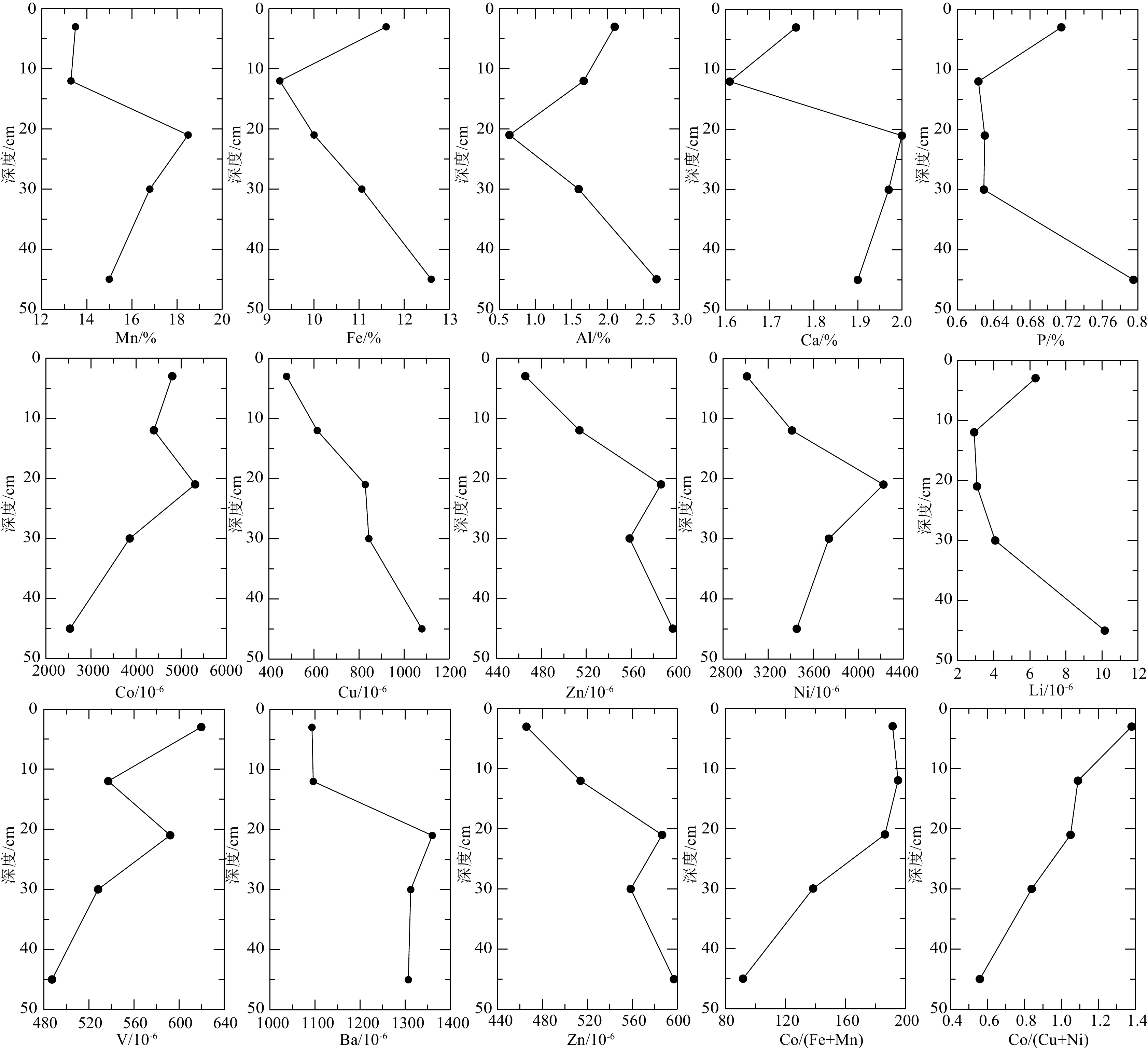
C8-1 C8-2 C8-3 C8-4 C8-5 常量元素/% Mn 13.5 13.3 18.5 16.8 15.0 Fe 11.6 9.24 10.0 11.1 12.6 Al 2.10 1.67 0.64 1.60 2.68 Mn/Fe 1.16 1.44 1.85 1.52 1.19 Na 1.62 1.46 1.88 1.71 1.73 K 0.61 0.41 0.36 0.48 0.60 Ca 1.76 1.61 2.00 1.97 1.90 Mg 1.21 0.94 1.11 1.19 1.43 Ti 1.11 0.76 0.96 1.16 1.20 P 0.72 0.62 0.63 0.63 0.80 微量元素/10−6 As 204 171 189 169 152 B 189 158 178 163 191 Ba 1093 1096 1360 1312 1307 Be 4.76 4.15 4.75 4.77 5.61 Bi 18.1 19.3 22.2 19.4 15.2 Cd 6.12 5.51 6.58 5.63 4.31 Co 4805 4396 5311 3858 2534 Cr 10.2 9.55 11.9 12.4 13.7 Cs 0.47 0.32 0.39 0.50 1.04 Cu 479 615 828 844 1080 Ga 6.03 5.51 6.71 6.49 7.35 Hf 6.74 6.89 7.82 8.93 12.5 Li 6.32 2.91 3.07 4.08 10.2 Mo 554 559 583 449 389 Nb 43.9 44.9 55.8 55.8 58.5 Ni 3012 3411 4224 3740 3454 Pb 1997 1747 1712 1560 1321 Rb 7.08 6.05 6.94 7.52 10.7 Sc 7.61 6.06 6.55 7.01 10.9 Sr 1362 1215 1411 1284 1159 Ta 0.50 0.50 0.57 0.58 0.58 Th 16.2 10.8 9.46 9.07 8.74 Tl 71.4 66.3 65.6 53.9 59.9 U 13.3 11.9 12.3 10.8 9.04 V 620 537 592 528 487 W 84.6 83.6 93.6 76 60.3 Zn 466 514 587 559 597 Zr 537 501 615 633 761 稀土元素/10−6 La 233 197 210 203 200 Ce 605 590 740 757 580 Pr 41.5 33.7 36.9 35.9 34.6 Nd 183 148 159 155 149 Sm 37.9 30.3 32.2 32.0 30.6 Eu 9.53 7.68 8.00 7.98 7.63 Gd 46.9 38.9 40.3 40.1 37.9 Tb 7.14 5.84 5.92 5.80 5.56 Dy 40.5 33.7 33.6 31.9 30.9 Y 179 147 155 139 158 Ho 10.0 8.47 8.33 7.88 7.64 Er 26.0 22.3 22.0 20.6 19.9 Tm 4.12 3.62 3.59 3.32 3.23 Yb 25.5 22.1 22.2 20.3 19.9 Lu 4.18 3.63 3.64 3.33 3.34 ΣLREE 1110 1007 1186 1191 1001 ΣHREE 164 139 139 133 128 LREE/HREE 6.76 7.27 8.51 8.94 7.80 ΣREY 1454 1293 1480 1463 1288 Co/(Fe+Mn) 191 195 186 138 91.8 Co/(Cu+Ni) 1.38 1.09 1.05 0.84 0.56 生长速率(mm/Ma) 1.46 2.10 1.76 1.37 0.65 表 2 富钴结壳元素之间相关系数矩阵
Table 2. Element Correlation matrix of the Co-rich crust
Mn Fe Al Mn/Fe K Ca Mg Ti Li Be Co Ni Zr Ba Gr Mn 1 Fe −0.093 1 Al −0.678 0.741 1 Mn/Fe 0.808 −0.659 −0.950* 1 K −0.535 0.876 0.892* −0.923* 1 Ca 0.894* 0.356 −0.310 0.460 −0.105 1 Mg 0.090 0.970** 0.637 −0.498 0.744 0.504 1 Ti 0.194 0.922* 0.493 −0.410 0.710 0.611 0.908* 1 Li −0.278 0.921* 0.849 −0.738 0.847 0.124 0.912* 0.709 1 Be 0.197 0.898* 0.547 −0.368 0.610 0.559 0.977** 0.825 0.887* 1 Co 0.219 −0.674 −0.795 0.568 −0.567 −0.086 −0.699 −0.534 −0.775 −0.699 1 Ni 0.928* −0.373 −0.774 0.925* −0.773 0.691 −0.163 −0.139 −0.444 −0.008 0.258 1 Cu 0.506 0.442 0.177 0.128 0.029 0.644 0.626 0.461 0.484 0.744 −0.694 0.487 Zn 0.709 0.172 −0.154 0.444 −0.285 0.710 0.396 0.249 0.207 0.556 −0.428 0.742 Zr 0.398 0.725 0.378 −0.120 0.344 0.672 0.862 0.717 0.720 0.931* −0.744 0.265 1 Ba 0.900* 0.226 −0.317 0.547 −0.269 0.932* 0.427 0.429 0.105 0.543 −0.220 0.813 0.749 1 Gr −0.044 −0.956* −0.696 0.528 −0.738 −0.456 −0.987** −0.884* −0.920* −0.965** 0.804 0.180 −0.886* −0.419 1 表 3 富钴结壳元素因子分析
Table 3. Element factor analysis of the Co-rich crust
因子1 因子2 因子3 Mn −0.180 −0.231 0.956 Fe 0.159 0.959 0.166 Al −0.049 0.849 −0.513 Na 0.056 0.148 0.974 K 0.345 0.868 −0.284 Ca −0.086 0.194 0.967 Mg 0.024 0.944 0.328 Ti 0.164 0.791 0.428 P 0.106 0.959 −0.091 Li 0.007 0.990 −0.050 Be −0.093 0.901 0.406 B 0.500 0.745 0.226 Sc −0.149 0.972 0.072 V 0.887 −0.440 0.103 Cr −0.411 0.643 0.646 Co 0.569 −0.798 0.142 Ni −0.393 −0.430 0.792 Cu −0.675 0.504 0.524 Zn −0.674 0.216 0.666 Ga −0.242 0.681 0.673 As 0.904 −0.422 0.060 Rb −0.293 0.922 0.222 Sr 0.697 −0.501 0.513 Zr −0.408 0.747 0.520 Nb −0.531 0.372 0.761 Mo 0.505 −0.797 −0.096 Cd 0.589 −0.744 0.316 Cs −0.296 0.940 0.113 Ba −0.405 0.151 0.901 Hf −0.529 0.799 0.275 Ta −0.492 0.321 0.806 W 0.472 −0.853 0.147 Tl 0.706 −0.216 −0.383 Pb 0.803 −0.521 −0.290 Bi 0.134 −0.898 0.417 Th 0.895 −0.003 −0.442 U 0.761 −0.635 −0.121 La 0.995 0.066 0.018 Ce −0.064 −0.458 0.787 Pr 0.980 0.085 0.104 Nd 0.989 0.056 −0.009 Sm 0.975 0.085 −0.040 Eu 0.970 0.072 −0.122 Gd 0.971 −0.016 −0.125 Tb 0.963 −0.029 −0.238 Dy 0.945 −0.114 −0.307 Y 0.844 0.387 −0.173 Ho 0.923 −0.149 −0.355 Er 0.913 −0.212 −0.347 Tm 0.902 −0.260 −0.332 Yb 0.917 −0.231 −0.302 Lu 0.921 −0.165 −0.314 方差贡献 41.1% 34.8% 20.7% -
[1] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[M]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000: 239-279.
[2] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[3] Heller C, Kuhn T, Versteegh G J M, et al. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018, 142: 16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.09.008
[4] Fitzgerald C E, Gillis K M. Hydrothermal manganese oxide deposits from Baby Bare seamount in the Northeast Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 225(1-4): 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.09.005
[5] Pelleter E, Fouquet Y, Etoubleau J, et al. Ni-Cu-Co-rich hydrothermal manganese mineralization in the Wallis and Futuna back-arc environment (SW Pacific) [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 126-146. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.014
[6] Halbach P. Processes controlling the heavy metal distribution in Pacific ferromanganese nodules and crusts [J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1986, 75(1): 235-247. doi: 10.1007/BF01770191
[7] Hein J R, Schwab W C, Davis A. Cobalt- and platinum-rich ferromanganese crusts and associated substrate rocks from the Marshall Islands [J]. Marine Geology, 1988, 78(3-4): 255-283. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(88)90113-2
[8] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: genetic implications [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[9] McMurtry G M, VonderHaar D L, Eisenhauer A, et al. Cenozoic accumulation history of a Pacific ferromanganese crust [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125(1-4): 105-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90209-7
[10] Jiang X D, Sun X M, Guan Y, et al. Biomineralisation of the ferromanganese crusts in the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 136: 58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.025
[11] Sujith P P, Gonsalves M J B D. Ferromanganese oxide deposits: geochemical and microbiological perspectives of interactions of cobalt and nickel [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139: 104458. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104458
[12] Guo B B, Wang W Q, Shu Y Q, et al. Observed deep anticyclonic cap over Caiwei Guyot [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2020, 125(10): e2020JC016254.
[13] 杨永, 何高文, 杨胜雄, 等. 采薇平顶海山群底质类型分布研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):801-802
YANG Yong, HE Gaowen, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Study on the distribution of sediment types of Caiwei Seamount Group [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(S1): 801-802.
[14] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 张辉, 等. 西太平洋采薇海山和徐福海山富钴结壳稀土元素地球化学特征及来源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(3):87-99 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021071302
GAO Jingjing, LIU Jihua, ZHANG Hui, et al. Geochemistry and sources of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Caiwei and Xufu seamounts, West Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(3): 87-99. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021071302
[15] 韦振权, 何高文, 邓希光, 等. 大洋富钴结壳资源调查与研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(3):460-472
WEI Zhenquan, HE Gaowen, DENG Xiguang, et al. The progress in the study and survey of oceanic cobalt-rich crust resources [J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(3): 460-472.
[16] 王彦美, 张伙带, 刘季花, 等. 麦哲伦海山区采薇海山富钴结壳伴生有用元素含量变化及空间分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):65-74
WANG Yanmei, ZHANG Huodai, LIU Jihua, et al. Abundances and spatial distributions of associated useful elements in Co-rich crusts from Caiwei Seamount in Magellan Seamounts [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 65-74.
[17] 中国大洋矿产资源研究开发协会办公室. 中国大洋海底地理实体名录(2016)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2016: 30-57
Chinese Ocean Mineral Resources Research and Development Association Office. Chinese Gazetteer of Undersea Features on the International Seabed (2016)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2016: 30-57.
[18] Epp D. Possible perturbations to hotspot traces and implications for the origin and structure of the Line Islands [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1984, 89(B13): 11273-11286. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB13p11273
[19] Lonsdale P. Geography and history of the Louisville Hotspot Chain in the southwest Pacific [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1988, 93(B4): 3078-3104. doi: 10.1029/JB093iB04p03078
[20] Wessel P, Kroenke L. A geometric technique for relocating hotspots and refining absolute plate motions [J]. Nature, 1997, 387(6631): 365-369. doi: 10.1038/387365a0
[21] Koppers A A P, Staudigel H, Pringle M S, et al. Short-lived and discontinuous intraplate volcanism in the South Pacific: hot spots or extensional volcanism? [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(10): 1089.
[22] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific ocean circulation based on observation [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[23] Gordon A L, Visbeck M, Huber B. Export of Weddell Sea deep and bottom water [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2001, 106(C5): 9005-9017. doi: 10.1029/2000JC000281
[24] 张亚南, 仲义, 陈艇, 等. 北太平洋大洋钻探研究进展: 古海洋与古气候[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):16-32
ZHANG Yanan, ZHONG Yi, CHEN Ting, et al. Research progress of ocean drilling in the North Pacific Ocean: paleoceanography and paleoclimate [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 16-32.
[25] 任向文. 西太平洋富钴结壳成矿系统[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2005
REN Xiangwen. The Metallogenic system of co-rich manganese crusts in western pacific[D]. Doctor Dissertation of The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[26] Yeo I A, Dobson K, Josso P, et al. Assessment of the mineral resource potential of Atlantic ferromanganese crusts based on their growth history, microstructure, and texture [J]. Minerals, 2018, 8(8): 327. doi: 10.3390/min8080327
[27] 张振国, 杜远生, 吴长航, 等. 南海西北陆缘大型多金属结核的生长过程及其对晚新生代古海洋环境变化的响应[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 56(3):453-463 doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4535-8
ZHANG Z G, DU Y S, WU C H, et al. Growth of a polymetallic nodule from the Northwestern continental margin of the South China Sea and its response to changes in the paleoceanographical environment of the late Cenozoic [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(3): 453-463. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4535-8
[28] Josso P, Rushton J, Lusty P, et al. Late cretaceous and Cenozoic paleoceanography from North-East Atlantic ferromanganese crust microstratigraphy [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 422: 106122. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106122
[29] Giovanoli R. Vernadite is random-stacked birnessite: a discussion of the paper by F. V. Chukhrov et al. : "Contributions to the mineralogy of authigenic manganese phases from marine manganese deposits" [Mineralium Deposita 14, 249–261 (1979)] [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1980, 15(2): 251-253.
[30] Villalobos M, Lanson B, Manceau A, et al. Structural model for the biogenic Mn oxide produced by Pseudomonas putida [J]. American Mineralogist, 2006, 91(4): 489-502. doi: 10.2138/am.2006.1925
[31] Grangeon S, Lanson B, Lanson M, et al. Crystal structure of Ni-sorbed synthetic vernadite: a powder X-ray diffraction study [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2008, 72(6): 1279-1291. doi: 10.1180/minmag.2008.072.6.1279
[32] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine Co-rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer, 2017: 65-141.
[33] Zhong Y, Liu Q S, Chen Z, et al. Tectonic and paleoceanographic conditions during the formation of ferromanganese nodules from the northern South China Sea based on the high-resolution geochemistry, mineralogy and isotopes [J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 410: 146-163. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.006
[34] Post J E, Heaney P J, Hanson J. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of the structure and dehydration behavior of todorokite [J]. American Mineralogist, 2003, 88(1): 142-150. doi: 10.2138/am-2003-0117
[35] Feng X H, Tan W F, Liu F, et al. Synthesis of todorokite at atmospheric pressure [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(22): 4330-4336. doi: 10.1021/cm0499545
[36] Selley R C, Cocks L R M, Plimer I R. Encyclopedia of Geology[M]. Boston: Academic Press, 2005: 591-600.
[37] Wang L Z, Zeng Z G. The geochemical features and genesis of ferromanganese deposits from Caiwei Guyot, Northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(9): 1275. doi: 10.3390/jmse10091275
[38] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust: its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 312.
[39] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[40] Addy S K. Rare earth element patterns in manganese nodules and micronodules from northwest Atlantic [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(7): 1105-1115. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90097-8
[41] Piper D Z. Rare earth elements in ferromanganese nodules and other marine phases [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1974, 38(7): 1007-1022. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(74)90002-7
[42] Amakawa H, Ingri J, Masuda A, et al. Isotopic compositions of Ce, Nd and Sr in ferromanganese nodules from the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, the Baltic and Barents Seas, and the Gulf of Bothnia [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 105(4): 554-565. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90192-K
[43] 韩吟文, 马振东. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 190-193
HAN Yinwen, MA Zhendong. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2003: 190-193.
[44] Li Y H. Distribution patterns of the elements in the ocean: a synthesis [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(11): 3223-3240. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90485-N
[45] Knaack D R, Sullivan K, Brown D J, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of ferromanganese precipitates from the southern Mariana arc: evaluation, formation, and implications [J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 568: 120132. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120132
[46] Marino E, González F J, Kuhn T, et al. Hydrogenetic, diagenetic and hydrothermal processes forming ferromanganese crusts in the Canary Island Seamounts and their influence in the metal recovery rate with hydrometallurgical methods [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(7): 439. doi: 10.3390/min9070439
[47] Halbach P, Hebisch U, Scherhag C. Geochemical variations of ferromanganese nodules and crusts from different provinces of the Pacific Ocean and their genetic control [J]. Chemical Geology, 1981, 34(1-2): 3-17. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(81)90067-X
[48] Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003
[49] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[50] Halbach P, Segl M, Puteanus D, et al. Co-fluxes and growth rates in ferromanganese deposits from central Pacific seamount areas [J]. Nature, 1983, 304(5928): 716-719. doi: 10.1038/304716a0
[51] Segl M, Mangini A, Bonani G, et al. 10Be-dating of a manganese crust from Central North Pacific and implications for ocean palaeocirculation [J]. Nature, 1984, 309(5968): 540-543. doi: 10.1038/309540a0
[52] Manheim F T, Lane-Bostwick C M. Cobalt in ferromanganese crusts as a monitor of hydrothermal discharge on the Pacific sea floor [J]. Nature, 1988, 335(6185): 59-62. doi: 10.1038/335059a0
[53] Chen S, Yin X B, Wang X Y, et al. The geochemistry and formation of ferromanganese oxides on the eastern flank of the Gagua Ridge [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 95: 118-130. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.02.026
[54] Hein J R, Konstantinova N, Mikesell M, et al. Arctic deep water ferromanganese-oxide deposits reflect the unique characteristics of the Arctic Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(11): 3771-3800. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007186
[55] Hein J R, Conrad T A, Frank M, et al. Copper-nickel-rich, amalgamated ferromanganese crust-nodule deposits from Shatsky Rise, NW Pacific [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(10): Q10022.
[56] Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present [J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517): 686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412
[57] Wu G H, Zhou H Y, Zhang H S, et al. New index of ferromanganese crusts reflecting oceanic environmental oxidation [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(3): 371-384. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-2011-7
[58] Aplin A, Michard A, Albarède F. 143Nd/144Nd in Pacific ferromanganese encrustations and nodules [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 81(1): 7-14. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90096-8
[59] Banakar V K, Borole D V. Depth profiles of 230Thexcess, transition metals and mineralogy of ferromanganese crusts of the Central Indian Basin and implications for palaeoceanographic influence on crust genesis [J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 94(1): 33-44. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(10)80015-4
[60] Liu Q, Huo Y Y, Wu Y H, et al. Bacterial community on a Guyot in the northwest Pacific Ocean influenced by physical dynamics and environmental variables [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2019, 124(9): 2883-2897. doi: 10.1029/2019JG005066
[61] Hein J R, Conrad T, Mizell K, et al. Controls on ferromanganese crust composition and reconnaissance resource potential, Ninetyeast Ridge, Indian Ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 110: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.11.006
[62] Halbach P, Puteanus D. The influence of the carbonate dissolution rate on the growth and composition of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from Central Pacific seamount areas [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 68(1): 73-87. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90141-9
[63] Yeo I A, Howarth S A, Spearman J, et al. Distribution of and hydrographic controls on ferromanganese crusts: tropic Seamount, Atlantic [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 114: 103131. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103131
[64] Takahashi Y, Manceau A, Geoffroy N, et al. Chemical and structural control of the partitioning of Co, Ce, and Pb in marine ferromanganese oxides [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(4): 984-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.11.016
[65] Schnitker D. North Atlantic oceanography as possible cause of Antarctic glaciation and eutrophication [J]. Nature, 1980, 284(5757): 615-616. doi: 10.1038/284615a0
[66] Donnelly T W. Worldwide continental denudation and climatic deterioration during the late Tertiary: evidence from deep-sea sediments [J]. Geology, 1982, 10(9): 451-454. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<451:WCDACD>2.0.CO;2
[67] Kennett J P. Paleo-oceanography: global ocean evolution [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1983, 21(5): 1258-1274. doi: 10.1029/RG021i005p01258
[68] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14.
[69] Conrad T, Hein J R, Paytan A, et al. Formation of Fe-Mn crusts within a continental margin environment [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.010
[70] Usui A, Nishi K, Sato H, et al. Continuous growth of hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts since 17 Myr ago on Takuyo-Daigo Seamount, NW Pacific, at water depths of 800-5500m [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 71-87. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.032
-



 下载:
下载: