Study on the impact of cross-river engineering on sedimentary dynamic environment in Yulong Island, Shandong
-
摘要:
根据裕龙岛附近海域水文和地形等实测资料,采用数值模拟的方法,模拟了研究区跨河道工程建设前后的水动力、冲淤和水交换等沉积动力特征,探讨了跨河道工程建设对裕龙岛内部沉积动力环境的影响。结果表明,跨河道工程建设使裕龙岛内部水道潮流流速整体减小,最大减小量超过20 cm/s,减弱了水道内水动力环境;工程建设对水道内冲淤环境产生一定影响,改变了水道的微侵蚀环境,部分地区发生淤积,最大年淤积量超过2 cm;工程建设明显影响水道内水交换,造成水交换率下降,部分区域水交换率低于60%。整体而言,经一河、经二河建设桥梁,纬一河建设管涵对水道内沉积动力环境影响相对较小,符合工程建设的实际要求。海岸工程建设应优先考虑海洋环境保护,实现工程和环境的协调发展。
Abstract:With the hydrological and topographic data from sea area near Yulong Island, Shandong, the sedimentary dynamic patterns of current, erosion and deposition, water exchange rate before and after the cross-river engineering (bridges or tunnels) were simulated numerically, and the impact of the engineering on the internal sedimentary dynamic environment of the Yulong Island was discussed. Results show that the engineering would decrease the tidal current velocity in overall, and the maximum reduction is over 20 cm/s. This situation would weaken the hydrodynamic environment such as the erosion and deposition in waterways, and change the micro erosion environment. In some regions, siltation would occur and the maximum annual siltation is over 2cm. In addition, the project will influence the water exchange within waterway. The rate of water exchange would be reduced by less than 60% locally. As a whole, it is suggested to build bridges across Jingyi River and Jinger River, while to use pipe and culvert in Weiyi River would be the best option with a minimal impact, which accords with the actual requirements of engineering construction. Coastal engineering construction should prioritize marine environmental protection and achieve coordinated development between engineering and the environment.
-
Key words:
- cross-river project /
- water exchange /
- tidal current field /
- Yulong Island
-

-
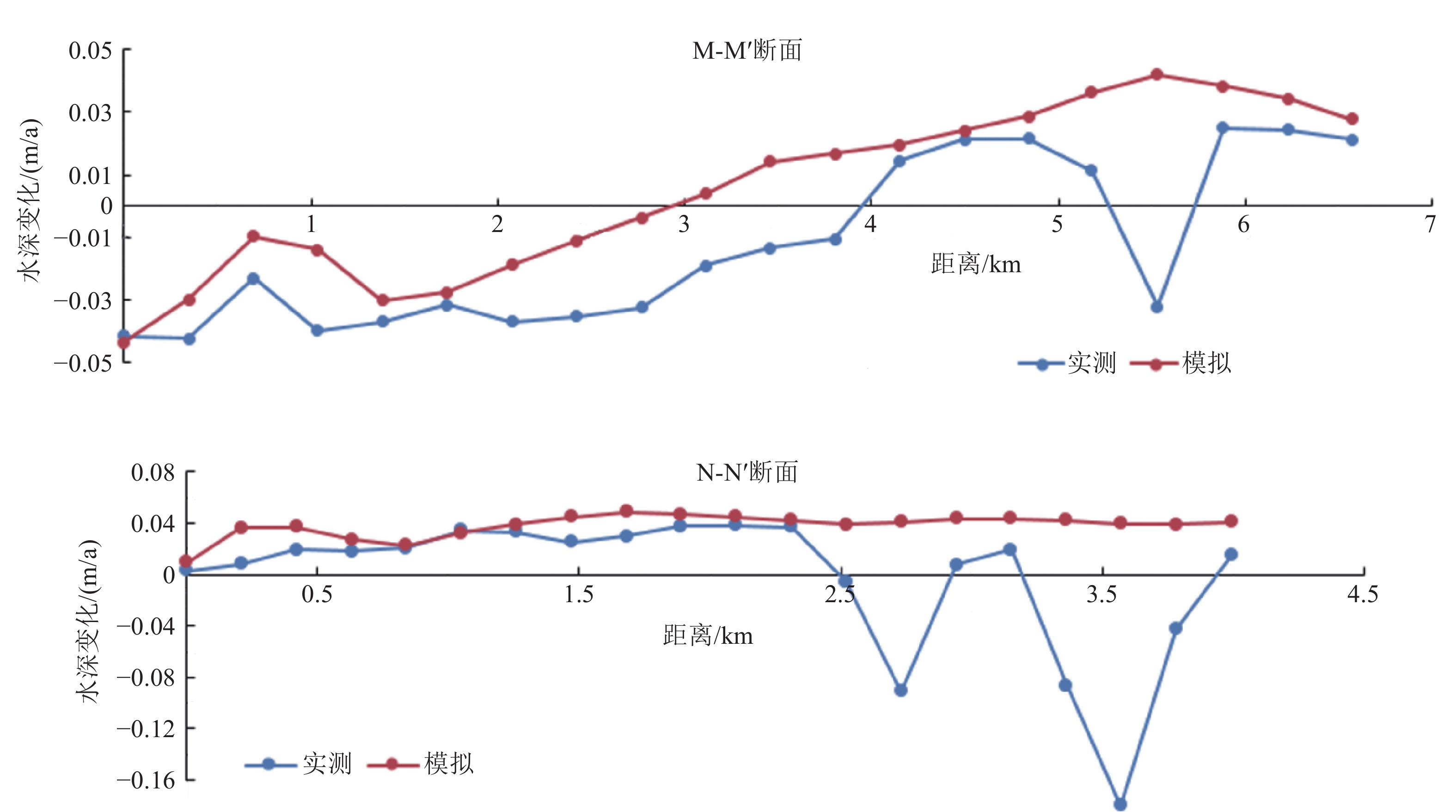
表 1 不同方案各特征站位平均流速表
Table 1. The average velocity at feature points of each plan
cm/s 方案 W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 J1 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 J8 J9 J10 建设前 23.7 26.1 27.1 11.6 9.7 29.4 30.1 49.9 21.9 23.8 2.1 8.1 28.2 9.7 6.1 方案1 6.1 3.6 3.6 1.9 1.8 5.2 5.3 4.7 1.9 3.1 2.2 8.7 5.6 3.4 0.7 方案2 2.8 1.3 0.8 4.0 2.4 33.6 26.5 36.8 21.9 24.3 1.9 3.6 4.1 1.1 0.4 方案3 2.1 1.1 0.7 2.7 2.4 7.4 2.6 4.1 7.2 7.9 1.3 5.2 4.5 1.4 1.9 方案4 2.9 1.3 0.9 9.1 7.8 37.8 23.1 33.0 18.6 20.5 2.1 7.8 23.0 7.8 5.3 表 2 不同方案综合对比表
Table 2. Comprehensive comparison of each lan
方案 水动力 地形地貌冲淤 水交换 建设前 较强 微侵蚀为主 100%,较好 方案1 较弱 微淤积为主 大部分区域小于60%,较差 方案2 纬一河、经二河影响较大 纬一河微淤积,其他河道微侵蚀为主 纬一河、经二河大部分区域小于60%,整体较差 方案3 较弱 微淤积为主 大部分区域小于50%,较差 方案4 较强 微侵蚀为主,年侵蚀量2~8 cm 大部分区域超过90%,整体较好 -
[1] Kassas M. Coastal processes with engineering applications, by R. G. Dean and R. A. Dalrymple, 2002[J]. Environmentalist, 2004, 24(1):60-61. doi: 10.1023/B:ENVR.0000046451.85342.a9
[2] Byun D S, Wang X H, Holloway P E. Tidal characteristic adjustment due to dyke and seawall construction in the Mokpo Coastal Zone, Korea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 59(2):185-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.007
[3] Rtimi R, Sottolichio A, Tassi P. Hydrodynamics of a hyper-tidal estuary influenced by the world's second largest tidal power station (Rance estuary, France)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2021, 250:107143. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107143
[4] Torres-Freyermuth A, Medellín G, Salles P. Human impact on the spatiotemporal evolution of beach resilience on the Northwestern Yucatan Coast[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021, 8:637205. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.637205
[5] Ranasinghe R, Larson M, Savioli J. Shoreline response to a single shore-parallel submerged breakwater[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57(11-12):1006-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.06.002
[6] Neumann B, Vafeidis A T, Zimmermann J, et al. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding-a global assessment[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3):e0131375.
[7] Hendriyono W, Wibowo M, Subarkah A, et al. Wave model for the design of sustainable coastal infrastructures at an industrial site in Tuban, East Java[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2020, 1625(1):012049. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1625/1/012049
[8] Gou H, Luo F, Li R J, et al. Modeling study on the hydrodynamic environmental impact caused by the sea for regional construction near the Yanwo Island in Zhoushan, China[J]. Water, 2019, 11(8):1674. doi: 10.3390/w11081674
[9] 陈静, 王永学. 岸线变迁对大连湾内湾海域纳潮量的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 2016, 35(4):390-395 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.04.005
CHEN Jing, WANG Yongxue. Effect of the coastline changes on the tidal prism water quality of Dalian inner bays[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2016, 35(4):390-395.] doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.04.005
[10] 孙永根, 高俊国, 朱晓明. 钦州保税港区填海造地工程对海洋环境的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(12):84-89
SUN Yonggen, GAO Junguo, ZHU Xiaoming. Effect of reclamation engineering in Qinzhou Bond Harbor on marine environment of Qinzhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(12):84-89.]
[11] Wang C, Zhang X Q, Sun Y L. Numerical simulation of water exchange characteristics of the Jiaozhou bay based on a three-dimensional Lagrangian model[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2009, 23(2):277-290.
[12] Rusdiansyah A, Tang Y L, He Z G, et al. The impacts of the large-scale hydraulic structures on tidal dynamics in open-type bay: numerical study in Jakarta Bay[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2018, 68(9):1141-1154. doi: 10.1007/s10236-018-1183-3
[13] Barnes B B, Hu C M. Island building in the South China Sea: detection of turbidity plumes and artificial islands using Landsat and MODIS data[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1):33194. doi: 10.1038/srep33194
[14] Yuan Y, Jalón-Rojas I, Wang X H. Response of water-exchange capacity to human interventions in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2021, 249:107088. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107088
[15] 中国海湾志编委会. 中国海湾志(第三分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993
China Bay Record Committee. The Bay Chorography in China: Bays in the South Shandong Peninsula and Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993.]
[16] 刘金鹏, 拾兵, 吴殿春. 龙口市人工岛周边海域波浪场和水动力场的数值模拟[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2021(1):1-10 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.01.001
LIU Jinpeng, SHI Bing, WU Dianchun. Numerical simulation of wave field and hydrodynamic field around the artificial island in Longkou[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2021(1):1-10.] doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.01.001
[17] 费成鹏, 胡日军, 雒敏义, 等. 龙口湾水动力特征及其对人工岛群建设的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):81-95 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021021301
FEI Chengpeng, HU Rijun, LUO Minyi, et al. Hydrodynamic characteristics of Longkou Bay and its response to artificial island groups[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1):81-95.] doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021021301
[18] 刘星池, 王永学, 陈静. 人工岛群分阶段建设对附近水沙环境影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(3):302-310 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.008
LIU Xingchi, WANG Yongxue, CHEN Jing. Study on the water-sediment environment of artificial islands constructed in stages by numerical simulation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(3):302-310.] doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.008
[19] Hu R J, Ma F, Wu J Z, et al. Sediment transport in the nearshore area of Phoenix Island[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2016, 15(5):767-782. doi: 10.1007/s11802-016-2967-z
[20] Jiang S H, Hu R J, Feng X L, et al. Influence of the construction of the Yantai West Port on the dynamic sedimentary environment[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2018, 36(1):43-51.
[21] 曲绵旭, 王文海, 丰鉴章, 等. 龙口湾自然环境[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1995
QU Mianxu, WANG Wenhai, FENG Jianzhang, et al. Natural Environment of Longkou Bay[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1995.]
[22] 王文海. 龙口湾的开发利用与保护[J]. 海岸工程, 1994, 13(1):10-19
WANG Wenhai. The development, utilization and protection of Longkou Bay[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1994, 13(1):10-19.]
[23] 刘波, 胡日军, 袁晓东, 等. 龙口近岸海域潮流作用下悬浮泥沙时空分布特征及输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4):55-66 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019072301
LIU Bo, HU Rijun, YUAN Xiaodong, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution pattern and transport mechanism of suspended sediments in Longkou offshore under the action of tidal current[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4):55-66.] doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019072301
[24] 任鹏, 孙志高, 王传远, 等. 人工岛建设对龙口湾表层沉积物粒度及黏土矿物组成特征的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(4):578-587 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
REN Peng, SUN Zhigao, WANG Chuanyuan, et al. Impacts of construction of artificial islands on the flow-sediment regulation scheme on grain and clay compositions in the Longkou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(4):578-587.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
[25] 冯兴如, 杨德周, 尹宝树. FVCOM在龙口海域潮汐潮流模拟中的应用研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(6):94-99
FENG Xingru, YANG Dezhou, YIN Baoshu. Application of FVCOM in tidal modeling of the seas adjacent to Longkou City[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(6):94-99.]
[26] Li T H, Han P, Zhao Z J. Impact analysis of coastal engineering projects on mangrove wetland area change with remote sensing[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2008, 22(2):347-358.
[27] Chen J Y, Chen S L. Estuarine and coastal challenges in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2002, 20(2):174-181. doi: 10.1007/BF02849656
[28] 许婷. 丹麦MIKE21模型概述及应用实例[J]. 水利科技与经济, 2010, 16(8):867-869 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2010.08.013
XU Ting. Calculation principle and application example of a two-dimensional flow model-MIKE21 HD[J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 2010, 16(8):867-869.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2010.08.013
[29] 王阳, 杨红, 张午. 基于MIKE21的江苏如东海上风电场泥沙冲淤数值模拟[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2021, 43(2):48-57 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.02.007
WANG Yang, YANG Hong, ZHANG Wu. Simulation of Sediment erosion and silting on Rudong Offshore Wind Farm Project in Jiangsu province by MIKE21[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2021, 43(2):48-57.] doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.02.007
[30] Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI) MIKE21 Flow Model: Hydrodynamic Module Scientific Documentatic[M]. Horsholm: DHI, 2007.
[31] Müller M, De Cesare G, Schleiss A J. Experiments on turbulence and settling down of fine sediments induced by pumped storage operations in a cuboidal reservoir[C]//Proceedings of 34th IAHR World Congress-Balance and Uncertainty. Brisbane, Australia: Engineers Australia, 2011: 1795-1802.
[32] DHI Water & Environment. MIKE21 User Guide[M]. Denmark: DHI Water & Environment, 2002.
[33] 罗锋, 廖光洪, 杨成浩, 等. 乐清湾水交换特征研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2011, 29(2):79-88 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.02.009
LUO Feng, LIAO Guanghong, YANG Chenghao, et al. Study on the features of water exchange in Yueqingwan Bay[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2011, 29(2):79-88.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.02.009
[34] 姜胜辉, 朱龙海, 胡日军, 等. 围填海工程对莱州湾水动力条件的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2015, 45(10):74-80
JIANG Shenghui, ZHU Longhai, HU Rijun, et al. The hydrodynamic response to reclamation in Laizhou Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(10):74-80.]
[35] Shen J, Kuo A Y. Numerical investigation of an estuarine front and its associated eddy[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1999, 125(3):127-135. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1999)125:3(127)
[36] Ji Z G, Hamrick J H, Pagenkopf J. Sediment and metals modeling in shallow river[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2002, 128(2):105-119. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2002)128:2(105)
[37] 黄祖珂, 黄磊. 潮汐原理与计算[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2005
HUANG Zuke, HUANG Lei. Tidal Theory and Calculation[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2005.]
[38] 李孟国, 曹祖德. 海岸河口潮流数值模拟的研究与发展[J]. 海洋学报, 1999, 21(1):111-125
LI Mengguo, CAO Zude. Research and progress in the numerical simulation of tidal current in coastal estuarie estuaries[J]. Beijing. Journal of Oceanography, 1999, 21(1):111-125.]
-



 下载:
下载: