Evaluation on of geological suitability for CO2 storage in salty aquifers in the East China Sea Shelf Basin
-
摘要:
系统分析了东海陆架盆地咸水层CO2封存的关键地质要素,认为在构造和沉积演化的控制下盆地表现出“整体封存有利、东西封存差异”的特征,东部坳陷裂陷充分,构造单元面积大、沉积厚并且地层发育全,潜在封存层系为中新统和渐新统;西部坳陷裂陷早,构造单元面积相对小、地层薄并且地层时代老,CO2封存的有利储盖组合为古新统—始新统。对各二级构造单元咸水层CO2的封存量进行了计算,结果表明,东海陆架盆地D级咸水层CO2封存量为636.2亿t,其中东部坳陷的西湖凹陷和基隆凹陷封存量最大,均超过100亿t,其次为西部坳陷的瓯江凹陷,达到64亿t。结合关键封存要素建立了东海陆架盆地D级CO2地质储存适宜性评价指标体系,并对各评价单元进行了适宜性评价,结果表明西湖凹陷和瓯江凹陷CO2封存适宜性最好,为东海陆架盆地CO2封存的有利远景区。
Abstract:Abstracts: Based on the systematic analysis of key geological elements of CO2 storage in salty aquifers in the East China Sea Shelf Basin, it is believed that under the control of tectonic and sedimentary evolution, the basin shows the characteristics of "Favorable for overall storage, but having differences in the eastern and western depression". The eastern depression is fully rifted, with a large tectonic unit area, thick sediment, and full stratigraphic development; and the potential sequestration systems are the Miocene and Oligocene. The western depression was rifted early, the tectonic unit area is relatively small, with thin and old strata, and the favorable reservoir-cap assemblages for CO2 storage are the Paleocene and Eocene. The CO2 storage capacity of the salty aquifers in each secondary tectonic unit was calculated. Results show that the CO2 storage in the D-level salty aquifers of the East China Sea shelf basin is 63.62 billion tons, among which the storage capacity in the Xihu Sag and the Jilong Sag in the eastern depression is the largest, both exceeding 10 billion tons, followed by the Oujiang Sag in the western depression, reaching 6.4 billion tons. Combined with the key storage factors, an index system for evaluating the suitability of D-class CO2 geological storage in the East China Sea shelf basin was established. An index system for evaluating the suitability of D-level CO2 geological storage in the East China Sea shelf basin was established. The suitability of each evaluation unit was also evaluated. Overall, Xihu Sag and Oujiang Sag have the best suitability for CO2 storage and are favorable prospective areas for CO2 storage in the East China Sea shelf basin.
-
Key words:
- CO2 storage /
- storage capacity /
- storage suitability /
- East China Sea shelf basin
-

-
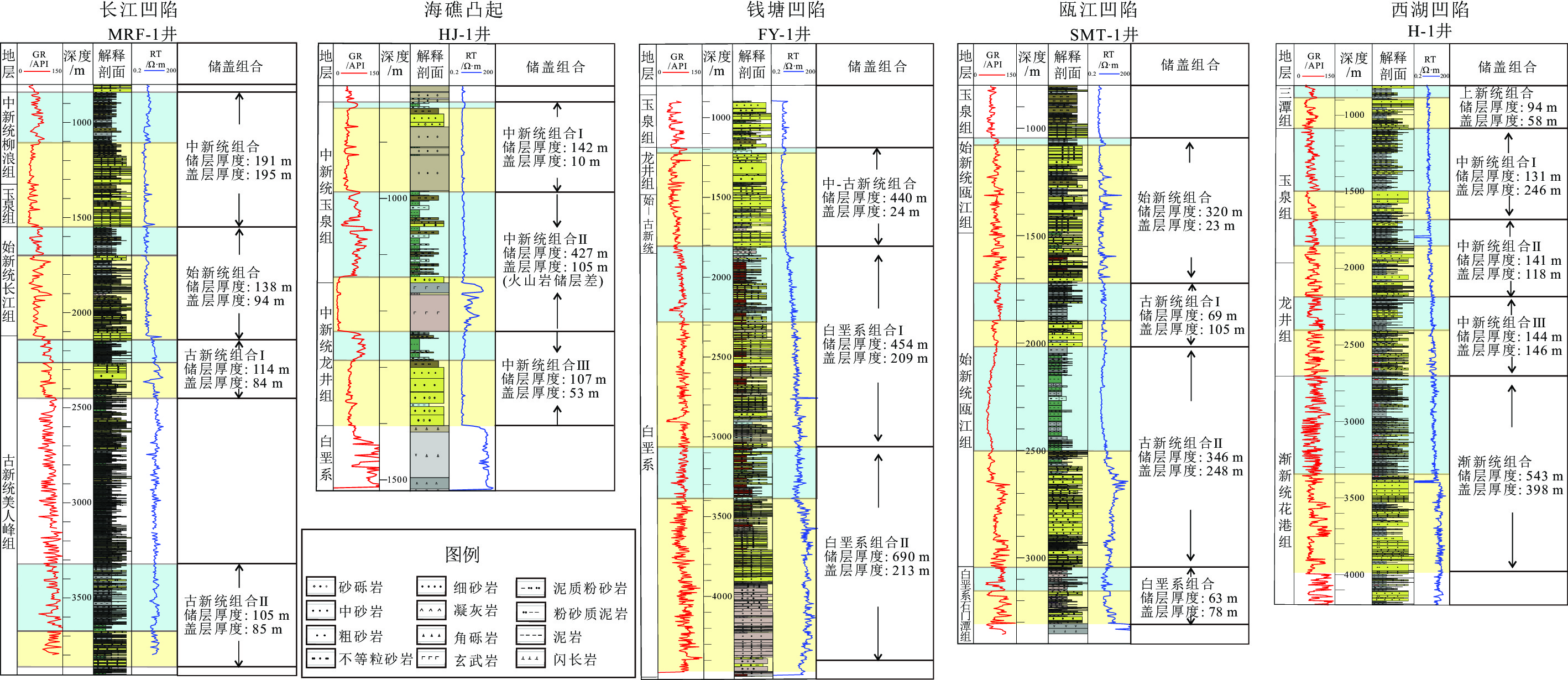
表 1 东海陆架盆地二级构造单元咸水层封存潜力计算表
Table 1. Calculation of salty aquifers’ storage capacity of the secondary structural unit in East China Sea Shelf Basin
评价单元 单元面积/
(104 km2)束缚封存量/
(106 t)溶解封存量/
(106 t)有效封存量/
(108 t)主要封存层系 长江凹陷 1.6 3 064.7 1 482.7 45.5 中新统、始新统 钱塘凹陷 1.5 3 414.9 1 585.3 50.0 中新统、白垩系 瓯江凹陷 1.9 4 975.9 1 456.5 64.3 中新统、始新统—古新统 虎皮礁凸起 1.6 603.8 402.2 10.1 中新统为主 海礁凸起 1.8 679.3 452.5 11.3 中新统为主 鱼山凸起 0.8 301.9 201.1 5.0 中新统为主 雁荡构造带 0.4 770.6 35.6 8.1 中新统为主 台北构造带 0.5 1 582.1 517.8 21.0 中新统、白垩系 闽江凹陷 2.8 3 864.4 1 245.6 51.1 中新统、白垩系 西湖凹陷 5.9 21 580.1 4 633.8 262.1 渐新统、中新统 基隆凹陷 2.9 8 843.8 1 928.5 107.7 渐新统、中新统 总计 21.7 49 681.5 13 941.6 636.2 表 2 东海陆架盆地D级CO2地质封存适宜性指标标准分级表
Table 2. Classification of suitability index criteria for D-level CO2 geological storage in the East China Sea Shelf Basin
评价指标层 评价指标(权重) 适宜 较适宜 一般适宜 较不适宜 不适宜 地质安全性 地壳稳定性 活动断裂 远离活动断裂带,无活动断裂通过 距活动断裂较近,无活动断裂通过 有新近纪断裂通过,但断裂在全新世活动不明显 有活动断裂通过,但活动断裂规模较小、活动较弱 位于大活动断裂带上,断裂活动强烈 区域性盖层 盖层的岩性 泥岩、钙质泥岩 含砂泥岩、含粉砂泥岩 粉砂质泥岩、砂岩泥岩 泥质粉砂岩、泥质砂岩 裂缝发育的灰岩、粗碎屑砂岩 盖层厚度/m >100 100~50 50~30 10~30 <10 盖层分布的连续性 连续,稳定 较连续,较稳定 连续性中等,较稳定 连续性较差,较不稳定 连续性差,不稳定 渗透率(K)/
10−3 μm2K<0.0001 0.0001≤K<0.001 0.001≤K<0.01 0.01≤K<0.1 K>0.1 盖层二次截留能力 多套,质量好 多套,质量一般 一套,质量好 一套,质量一般 无 储存规模 构造单元
规模评价单元的面积(S)/km2 S≥30000 20000≤S<30000 10000≤S<20000 5000≤S<10000 S<5000 沉积地层厚度(H)/m H≥10000 6000≤H<10000 3000≤H<6000 800≤H<3000 H<800 区域性储层 储集岩的岩性 碎屑岩 碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩混合 碳酸盐岩 岩浆岩、变质岩等特殊储层 无 储层厚度/m >100 50~80 20~50 10~20 <10 储层砂厚比/% >60 60~40 40~20 20~10 <10 沉积相带 河流-三角洲 扇三角洲 滨海 浅海 深湖-半深湖 孔隙度(Φ)/% Φ≥25 15≤Φ<25 11≤Φ<15 7≤Φ<11 Φ<7 渗透率(K)/
10−3 μm2K≥100 10≤K<100 1≤K<10 0.2≤K<1 K<0.2 储存潜力 D级推定潜力(M)/
108 tM>100 50<M≤100 20<M≤50 10<M≤20 M<10 单位面积D级推定潜力(m)/(104 t·km−2) m>30 20<m≤30 10<m≤20 5<m≤10 m<5 经济适宜性 勘探开发程度 三维覆盖、钻井丰富、开发程度高 较多三维覆盖和钻井,开发程度低 二维数据覆盖,
少量钻井少量二维地震和
钻井无地震和钻井 离岸距离/km 0~100 100~200 200~300 300~400 >400 表 3 评价指标层权重计算结果
Table 3. Results of weight calculation on the evaluation index layer
地质安全性 储存规模 经济适宜性 权重Wi 地质安全性 1 1 2 0.387 储存规模 1 1 3 0.444 经济适宜性 1/2 1/3 1 0.169 λmax(最大特征根)=3.018,CI(一致性指标)=0.009,CR(平均随机一致性)=0.018<0.1 注:表格中数值代表横行指标相对纵列指标进行重要性两两比较的值。 表 4 评价指标权重计算结果
Table 4. Results of weight calculation on the evaluation index
活动断裂 盖层岩性 盖层厚度 盖层连续性 盖层渗透率 二次截留能力 权重 0.125 0.047 0.068 0.054 0.063 0.029 单元面积 地层厚度 储层岩性 储层厚度 储层砂地比 沉积相 权重 0.056 0.056 0.038 0.044 0.024 0.024 储层孔隙度 储层渗透率 D级推定潜力 单位面积D级推定潜力 勘探程度 离岸距离 权重 0.039 0.028 0.068 0.068 0.0845 0.0845 表 5 东海陆架盆地二级评价单元打分及综合评价
Table 5. Scoring and comprehensive evaluation of the secondary evaluation unit of East China Sea Shelf Basin
虎皮礁
凸起长江凹陷 鱼山凸起 钱塘凹陷 海礁凸起 瓯江凹陷 雁荡
低凸起闽江凹陷 台北
低凸起基隆凹陷 西湖凹陷 活动断裂 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 5 7 盖层的岩性 5 7 5 7 7 7 5 7 7 7 7 盖层厚度/m 5 9 5 7 5 9 5 7 7 9 9 盖层分布的连续性 3 7 3 5 3 7 3 7 3 9 9 渗透率(K)/10−3 μm2 7 9 7 9 7 9 9 9 7 9 9 盖层二次截留能力 7 9 7 9 7 9 9 9 7 9 9 评价单元的面积(S)/km2 5 5 3 5 5 5 3 5 3 9 9 沉积地层厚度(H)/m 3 5 3 5 3 7 3 7 5 9 9 储集岩的岩性 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 9 9 9 9 储层厚度/m 9 7 7 7 7 9 9 7 7 7 9 储层砂厚比/% 9 9 9 9 9 7 5 5 5 7 9 沉积相带 9 9 9 9 9 7 5 5 5 7 9 孔隙度(Φ)/% 9 9 9 7 9 9 9 7 7 7 9 渗透率(K)/10−3 μm2 9 9 9 7 9 9 9 7 7 7 9 D级推定潜力(M)/108 t 3 5 1 7 3 7 1 7 5 9 9 单位面积D级推定潜力(m)/(104 t·km−2) 3 7 3 9 3 9 5 9 7 9 9 勘探程度 3 5 3 5 5 7 5 5 3 3 9 离岸距离/km 3 5 5 7 7 9 7 5 5 3 3 综合得分 5.78 7.32 5.62 7.33 6.30 8.20 6.17 7.27 6.20 7.24 8.37 -
[1] Bachu S. Sequestration of CO2 in geological media: criteria and approach for site selection in response to climate change [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2000, 41(9): 953-970. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(99)00149-1
[2] 路萍, 白勇, 刘伟刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地马家沟组二氧化碳地质封存有利区优选[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(3):816-827 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.03.031
LU Ping, BAI Yong, LIU Weigang, et al. Optimization of favorable areas for carbon dioxide geological storage in Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin [J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(3): 816-827. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.03.031
[3] 李小春, 方志明. 中国CO2地质埋存关联技术的现状[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(10):2229-2233,2239 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.10.043
LI Xiaochun, FANG Zhiming. Status quo of connection technologies of CO2 geological storage in China [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(10): 2229-2233,2239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.10.043
[4] 刘廷, 马鑫, 刁玉杰, 等. 国内外CO2地质封存潜力评价方法研究现状[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4):101-108
LIU Ting, MA Xin, DIAO Yujie, et al. Research status of CO2 geological storage potential evaluation methods at home and abroad [J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(4): 101-108.
[5] 白云云, 丁鑫, 梁颖, 等. 碳中和背景下鄂尔多斯盆地地质封存CO2封堵层特征研究[J]. 河南科学, 2021, 39(8):1373-1376 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2021.08.025
BAI Yunyun, DING Xin, LIANG Ying, et al. The characteristics of CO2 sealing layer in the Ordos Basin under the background of carbon neutrality [J]. Henan Science, 2021, 39(8): 1373-1376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2021.08.025
[6] 蔡博峰, 李琦, 张贤, 等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)年度报告(2021): 中国CCUS路径研究[R]. 生态环境部环境规划院, 中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所, 中国21世纪议程管理中心, 2021
CAI Bofeng, LI Qi, ZHANG Xian, et al. Annual report of China carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) (2021): China CCUS pathway research[R]. Environmental Planning Institute of Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Wuhan Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China 21st Century Agenda Management Center, 2021.
[7] 曹龙, 边利恒. CO2地质封存技术与封存潜力评价方法研究进展[J]. 地下水, 2013, 35(6):211-213 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2013.06.082
CAO Long, BIAN Liheng. Advances in CO2 geological storage technology and evaluation methods of storage potential [J]. Ground Water, 2013, 35(6): 211-213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2013.06.082
[8] 李光, 刘建军, 刘强, 等. 二氧化碳地质封存研究进展综述[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2016, 3(4):41-48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6361.2016.04.008
LI Guang, LIU Jianjun, LIU Qiang, et al. Review on geological storage of carbon dioxide [J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science, 2016, 3(4): 41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6361.2016.04.008
[9] Bachu S. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers [J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2015, 40: 188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.01.007
[10] Shan Y L, Guan D B, Zheng H R, et al. China CO2 emission accounts 1997-2015 [J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5: 170201. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017.201
[11] Shan Y L, Huang Q, Guan D B, et al. China CO2 emission accounts 2016-2017 [J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(1): 54. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0393-y
[12] Guan Y R, Shan Y L, Huang Q, et al. Assessment to China's recent emission pattern shifts [J]. Earth's Future, 2021, 9(11): e2021EF002241.
[13] Shan Y L, Liu J H, Liu Z, et al. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 184: 742-750. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.073
[14] 郭建强, 文冬光, 张森琦, 等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存适宜性评价与示范工程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014: 1-348
GUO Jianqiang, WEN Dongguang, ZHANG Senqi, et al. Evaluation and Demonstration Project of Carbon Dioxide Geological Storage Suitability in China [M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2014: 1-348.
[15] 臧雅琼. 我国含油气盆地CO2地质封存潜力分析[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2013: 1-55
ZANG Yaqiong. Analysis of CO2 geological sequestration potential of Chinese Petroliferous Basins[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013: 1-55.
[16] 霍传林. 我国近海二氧化碳海底封存潜力评估和封存区域研究[D]. 大连海事大学博士学位论文, 2014: 1-197
HUO Chuanlin. Study on the potential evaluation and the storage areas of the carbon dioxide seabed storage in offshore China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Dalian Maritime University, 2014: 1-197.
[17] 曹珂, 许瑞军. 中国东部海域CO2地质储存潜力与适宜性评价[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(S1):3
CAO Ke, XU Ruijun. Evaluation of CO2 geological storage potential and suitability in the East China Sea [J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1): 3.
[18] 李小春, 刘延锋, 白冰, 等. 中国深部咸水含水层CO2储存优先区域选择[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(5):963-968 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.015
LI Xiaochun, LIU Yanfeng, BAI Bing, et al. Ranking and screening of CO2 saline aquifer storage zones in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(5): 963-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.015
[19] 白莹. 中国东部中、新生代盆地演化特征及构造迁移规律[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2014: 1-67
BAI Ying. Evolution features and tectonic migration trends of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Basins in eastern China[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014: 1-67.
[20] 刘金水, 许怀智, 蒋一鸣, 等. 东海盆地中、新生代盆架结构与构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3):675-691 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.001
LIU Jinshui, XU Huaizhi, JIANG Yiming, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic Basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China Sea Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 675-691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.001
[21] 赵磊. 东海陆架盆地古近系沉积体系研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2013: 1-73
ZHAO Lei. Study on Paleogene Sedimentary System of East China Sea shelf Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013: 1-73.
[22] 李小军, 陈苏, 任治坤, 等. 海域地震区划关键技术研究项目及研究进展[J]. 地震科学进展, 2020, 50(1):2-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-7780.2020.01.001
LI Xiaojun, CHEN Su, REN Zhikun, et al. Project plan and research progress on key technologies of seismic zoning in sea areas [J]. Progress in Earthquake Sciences, 2020, 50(1): 2-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-7780.2020.01.001
[23] 孙和清, 黄福林. 东海晚新生代断裂活动的初步研究[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1992(1):6-8
SUN Heqing, HUANG Fulin. A preliminary study of Late Cenozoic fault activity in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geological Dynamics, 1992(1): 6-8.
[24] 杨传胜, 李刚, 杨长清, 等. 东海陆架盆地及其邻域岩浆岩时空分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):125-133
YANG Chuansheng, LI Gang, YANG Changqing, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of the igneous rocks in the East China Sea Shelf Basin and its adjacent regions [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 125-133.
[25] 许薇龄, 焦荣昌, 乐俊英, 等. 东海陆架区地热研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1995, 10(2):32-38
XU Weiling, JIAO Rongchang, YUE Junying, et al. Geothermal study on the continent shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1995, 10(2): 32-38.
[26] 汪蕴璞, 林锦璇, 汪林. 论含油气盆地含水系统和水文地质期的划分: 以东海西湖凹陷为例[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 1995, 20(4):393-398
WANG Yunpu, LIN Jinxuan, WANG Lin. Division of water-bearing systems and hydrogeological periods of oil (gas): bearing Basin-with Xihu Depression in East China Sea as an example [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1995, 20(4): 393-398.
[27] 胡必规, 张韫. 东海盆地油田水文地球化学特征与油气聚集关系探讨[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1988(5):16-19
HU Bigui, ZHANG Yun. Relationship between hydrologic geochemistry and hydrocarbon accumulation in the East China Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geological Dynamics, 1988(5): 16-19.
[28] Bachu S, Bonijoly D, Bradshaw J, et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation: methodology and gaps [J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2007, 1(4): 430-443. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00086-2
[29] Bradshaw J, Bachu S, Bonijoly D, et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation: issues and development of standards [J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2007, 1(1): 62-68. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00027-8
[30] Bachu S. Estimation of CO2 storage capacity in geological media-phase II[R]. Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF), 2007.
[31] 杨红, 赵习森, 康宇龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地CO2地质封存适宜性与潜力评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(1):95-102
YANG Hong, ZHAO Xisen, KANG Yulong, et al. Evaluation on geological sequestration suitability and potential of CO2 in Ordos Basin [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(1): 95-102.
[32] IEA GHG (International Energy Agency Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme). Development of Storage Coefficients for CO2 storage in deep saline formations[EB/OL]. (2009-11-13)[2021-06-25]. http://www.Ieaghg.org/.
[33] 李海兵. 塔里木盆地二氧化碳地质储存潜力与适宜性评价[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2012: 1-96
LI Haibing. Carbon dioxide geological storage potential and of Tarim Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012: 1-96.
[34] 杨霄翼, 刘延锋, 徐连三. 深部盐水层CO2地质埋存适宜性评价指标体系及其应用[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2014, 21(5):71-77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2014.05.012
YANG Xiaoyi, LIU Yanfeng, XU Liansan. Construction and application of comprehensive evaluation index system for the suitability of CO2 geological storage in deep saline aquifer [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2014, 21(5): 71-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2014.05.012
[35] Bachu S. Screening and ranking of sedimentary basins for sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change [J]. Environmental Geology, 2003, 44(3): 277-289. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0762-9
[36] 曹茂林. 层次分析法确定评价指标权重及Excel计算[J]. 江苏科技信息, 2012, 29(2):39-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7530.2012.02.019
CAO Maolin. Analytic hierarchy process to determine the weight of evaluation index and Excel calculation [J]. Jiangsu Science and Technology Information, 2012, 29(2): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7530.2012.02.019
-




 下载:
下载: