Reconstructing the climate and environmental characteristics of Chengdu in the Middle Tang Dynasty from Du Fu's "Thousand Autumns of Snows"
-
摘要:
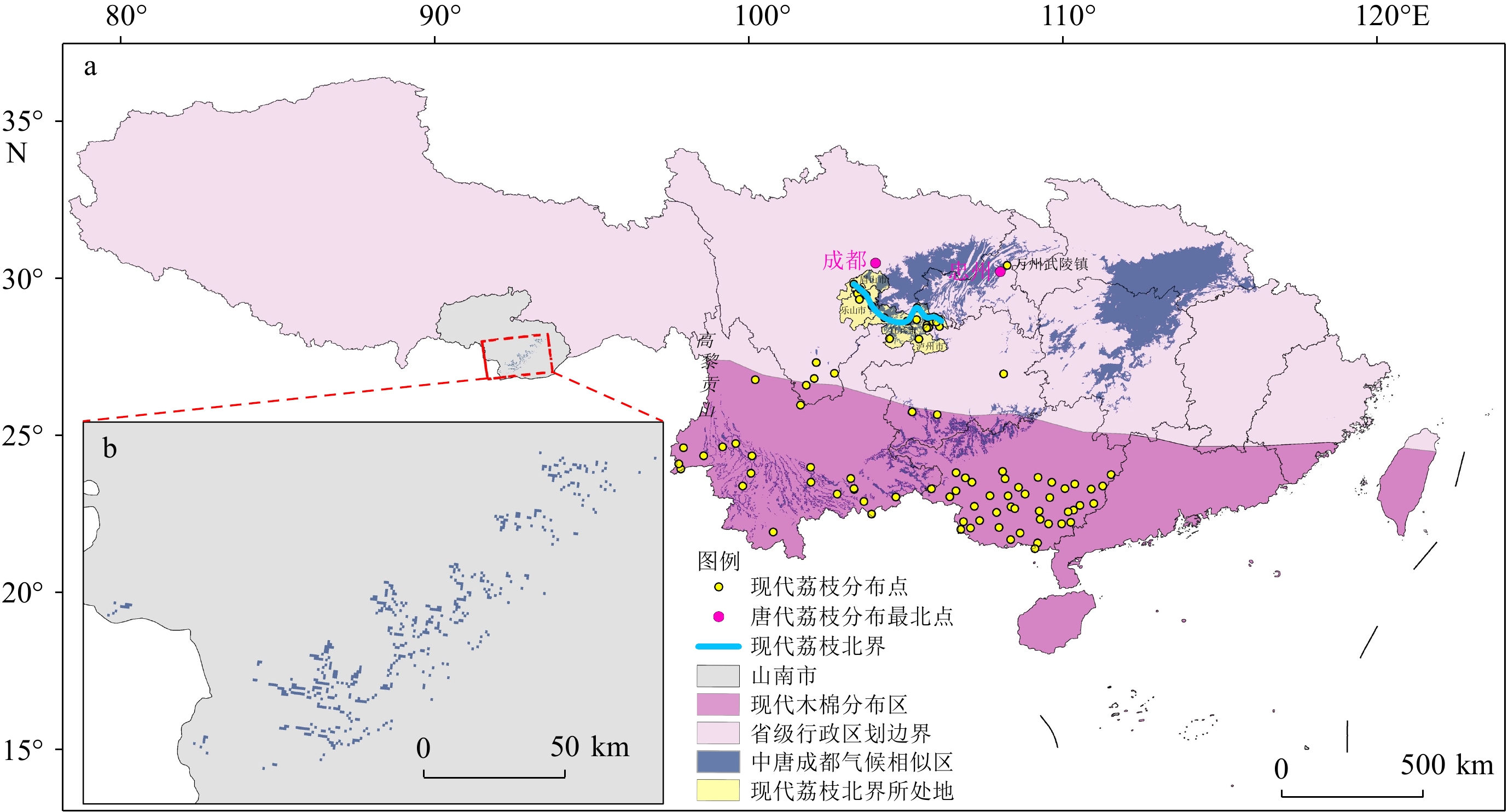
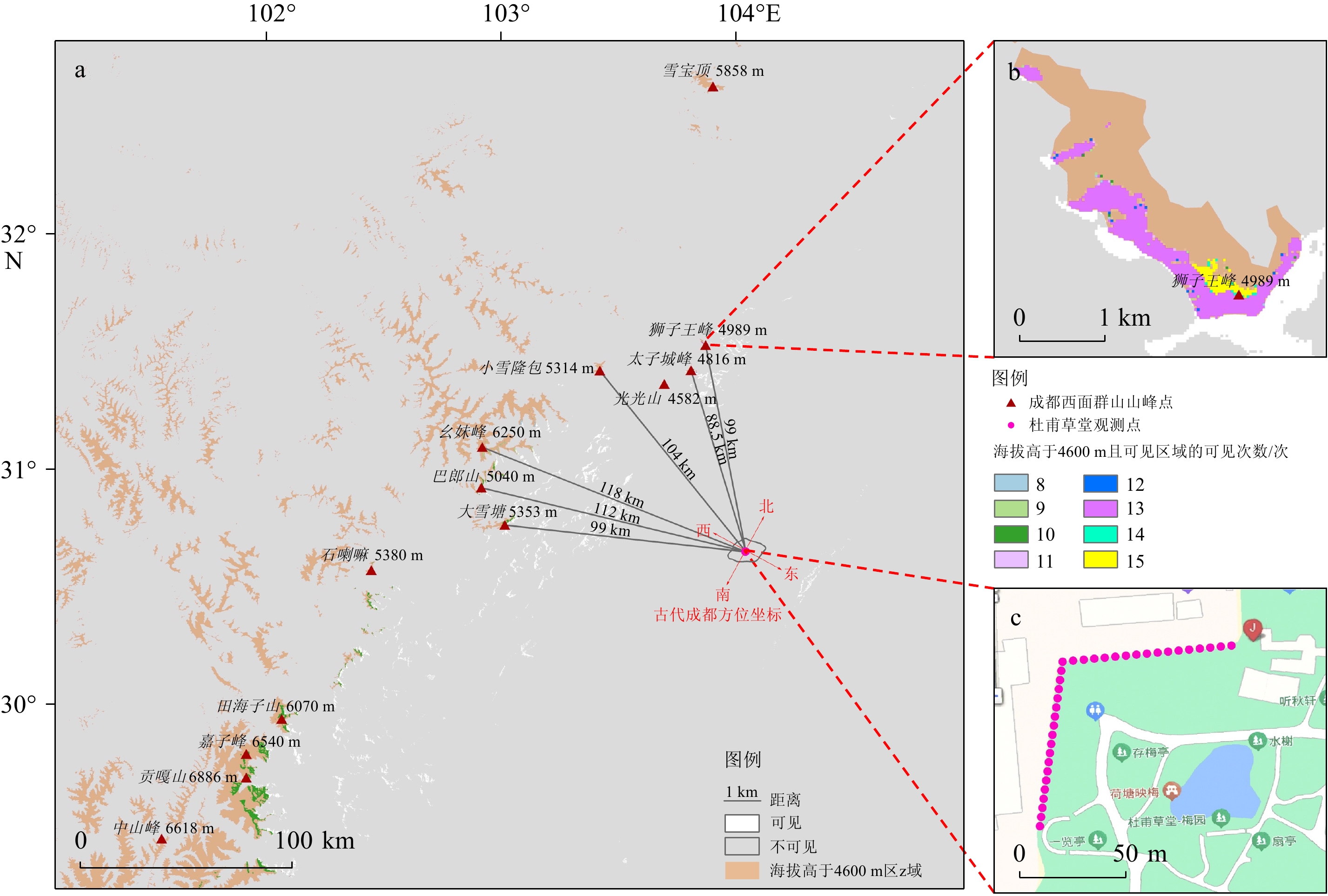
解析唐诗记载的地理景观和物候信息可重建诗人所处时代的气候环境特征。本文以唐代诗人杜甫 (公元712—770年)的《绝句四首·其三》和张籍(公元767—830年)的《成都曲》为例,选取诗中“千秋雪”和“荔枝熟”作为分析要素,结合物候学及地理信息系统 (GIS)等手段定量重建中唐时期成都地区的温度、降水和雪线。基于成都处于唐朝荔枝北界这一前提,通过GIS对现代荔枝分布点进行空间分析,初步限定中唐时期成都地区的最低年均温和年降水量分别为 (18 ± 0.4) ℃和 (
1230 ± 260) mm,较现代分别高约2 ℃和250 mm;进一步依据现代雪线、温度和降水的关系,通过GIS空间分析和理论计算推知中唐时期成都地区的雪线高度为 (4600 ± 200) m,较现代低约700 m。最后,通过重建的雪线高度及GIS的可见性分析,推测杜甫诗中“千秋雪”最有可能是九顶山的主峰狮子王峰。Abstract:Through the analysis of the geographical landscapes and climatic information recorded in Tang poems, it is possible to reconstruct the characteristics of the climate and environments of the times in which the poets lived. In this paper, we take the "Four Quatrains (No. 3)" by Du Fu (712—770 AD) and "Ode to Chengdu" by Zhang Ji (767—830 AD) of the Tang Dynasty to gain insight into the climatic conditions of their time, and select "Thousand Autumns of Snows" and "Lychee Ripening" as analyzing elements, then combine them with phenology and GIS to quantitatively reconstruct the temperature, precipitation, and snowline of the Chengdu during the Middle Tang Dynasty. Based on the premise that Chengdu was located at the northern boundary of lychee cultivation during the Tang Dynasty, a spatial analysis of modern lychee distribution points was conducted through GIS. The analysis initially identified the minimum annual mean temperature and annual precipitation of Chengdu during the Middle Tang Dynasty to be (18 ± 0.4) ℃ and (
1230 ± 260) mm, which were about 2 ℃ and 250 mm higher than those in modern times. Furthermore, based on the relationship between the modern snowline, temperature and precipitation, the snowline height in Chengdu during the Middle Tang Dynasty is estimated to be (4600 ± 200) m, which is about 700 meters lower than that in modern times. Based on the reconstructed snowline height and GIS visibility analysis, it is hypothesized that the 'Thousand Autumns of Snows' in Du Fu's poem refers to the main peak of Jiu Ding Mountains, Lion King Peak.-
Key words:
- northern boundary of Lychee /
- snowline /
- Tang poetry /
- Middle Tang Dynasty /
- Chengdu
-

-
表 1 研究数据及其来源汇总
Table 1. Data for this research and their sources
数据名称 数据来源 荔枝分布点数据 《中国果树志 荔枝卷》[15],四川省植物资源信息网(http://www.scpri.ac.cn),《四川荔枝种植公布的历史考证》[30] 现代荔枝北界所处地2016—2020年年均温、年降水量数据 四川统计年鉴,来源于四川省统计局 (http://tjj.sc.gov.cn)[31-35] 中国2022年地市行政区划边界数据 中国多年度地市行政区划边界数据,数据来源于资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统 (https://www.resdc.cn)[36] 中国2022年省级行政区划边界数据 中国多年度省级行政区划边界数据,数据来源于资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统 (https://www.resdc.cn)[37] 2016—2020年中国1km分辨率年降水量数据 中国1km分辨率年降水量数据 (1982—2022年),数据来源于国家科技资源共享服务平台—国家地球系统科学数据中心 (http://www.geodata.cn) 2016—2020年中国1km分辨率年平均气温数据 中国1km分辨率年平均气温数据 (1982—2022年),数据来源于国家科技资源共享服务平台—国家地球系统科学数据中心 (http://www.geodata.cn) 现代雪线高程数据 《中国山河全书》[38],《青藏高原地区雪线时空变化动态研究》[39] GDEMV3 30M分辨率数字高程数据 中国科学院计算机网络信息中心地理空间数据云平台(https://www.gscloud.cn) 成都西面群山山峰点数据 基于谷歌地球卫星影像对山峰拾取坐标点 注:本研究所有数据采用统一的GCS_WGS_1984坐标系。 表 2 《全唐诗》中四川荔枝诗
Table 2. Lychee of Sichuan mentioned in the poems of Tang Dynasty
地点 时间 作者 诗名 提及“荔枝”的诗句 文献来源 成都 中唐 张籍 成都曲 “锦江近西烟水绿,新雨山头荔枝熟” 中唐 李端 送何兆下第还蜀 “袅猿枫子落,过雨荔枝香。劝尔成都住,文翁有草堂” [52] 779年 卢纶 送从舅成都县丞广归蜀 “晚程椒瘴热,野饭荔枝阴” 乐山 中唐 卢纶 送张郎中还蜀歌 “邛竹笋长椒瘴起,荔枝花发杜鹃鸣” 807年 薛涛 忆荔枝 “近有青衣连楚水,素浆还得类琼浆” [52] 866年 薛能 荔枝诗 “颗如松子色如樱,未识蹉跎欲半生” 宜宾 765年 杜甫 宴戎州杨使君东楼 “重碧拈春酒,轻红擘荔枝” [52] 泸州 767年 杜甫 解闷十二首·其十 “忆过泸戎摘荔枝,青峰隐映石逶迤” 891年 郑谷 荔枝树 “肠断渝泸霜霰薄,不教叶似灞陵红” [52] 891年 郑谷 将之泸郡旅次遂州遇裴晤员外谪居于此话旧凄凉因寄二首·其二 “我拜师门更南去,荔枝春熟向渝泸” 万县
(唐朝忠州)819年 白居易 重寄荔枝与杨使君,时闻杨使君欲种植故有落句之戏 “香连翠叶真堪画,红透青笼实可怜” 819年 白居易 种荔枝 “十年结子知谁在,自向庭中种荔枝” [52] 820年 白居易 荔枝楼对酒 “荔枝新熟鸡冠色,烧酒初开琥珀香” 表 3 现代荔枝分布点信息
Table 3. Information of modern lychee distribution sites
序号 地名 地区 位置 年均温/℃ 年降水量/mm 1 洪雅县 四川省眉山市 29.90°N、103.37°E 16.6 1435.5 2 峨眉山市 四川省乐山市 29.60°N、103.48°E 17.2 1555.3 3 犍为县 四川省乐山市 29.21°N、103.94°E 17.5 1141.3 4 市中区 四川省乐山市 29.55°N、103.76°E / 1082.0 5 沙湾区 四川省乐山市 29.41°N、103.54°E / 1530.3 6 夹江县 四川省乐山市 29.74°N、103.57°E 17.1 1428.4 7 屏山县 四川省宜宾市 28.83°N、104.34°E 18.2 1209.8 8 江安县 四川省宜宾市 28.72°N、105.06°E 18.1 1132.0 9 筠连县 四川省宜宾市 28.16°N、104.50°E 17.6 / 10 泸县 四川省泸州市 29.15°N、105.37°E 18.1 1179.4 11 纳溪区 四川省泸州市 28.77°N、105.36°E 17.4 1150.8 12 叙永县 四川省泸州市 28.15°N、105.44°E 17.9 1172.6 13 凤鸣镇 四川省泸州市合江县 28.71°N、105.88°E 18.2
(合江县年均温)1134.9
(合江县年降水量)14 榕山镇 四川省泸州市合江县 28.86°N、105.91°E 18.2
(合江县年均温)1134.9
(合江县年降水量)15 大桥镇 四川省泸州市合江县 28.83°N、105.71°E 18.2
(合江县年均温)1134.9
(合江县年降水量)16 福宝镇 四川省泸州市合江县 28.78°N、106.08°E 18.2
(合江县年均温)1134.9
(合江县年降水量)17 盐边县 四川省攀枝花市 26.68°N、101.85°E 19.2 1065.6 18 米易县 四川省攀枝花市 26.90°N、102.10°E 19.7 1112.6 19 德昌县 四川省凉山彝族自治州 27.40°N、102.17°E 17.7 1049.0 20 宁南县 四川省凉山彝族自治州 27.06°N、102.75°E 19.3 960.0 21 武陵镇 重庆市万州区 30.50°N、108.25°E 18.2 1155.8 注:表中位置来源于百度地图拾取坐标系统https://api.map.baidu.com/lbsapi/getpoint/,并已经将百度地图的BD09坐标系转换为WGS84坐标系;表中的年均温、年降水量数据来源于各地政府网及四川省公共气象服务网https://www.scggqx.com。 表 4 现代荔枝北界所处地2016—2020年年均温和年降水量
Table 4. Averages of annual temperature and annual precipitation of the sites where the modern northern boundary of lychee are located during 2016—2020
年份 年均温/℃ 年降水量/mm 泸州市 乐山市 宜宾市 眉山市 泸州市 乐山市 宜宾市 眉山市 2020 18.0 18.3 17.7 18.2 1396.8 1555.3 1746.0 1292.6 2019 18.1 18.2 17.5 17.7 1036.3 1483.1 1130.5 1167.9 2018 18.2 18.5 17.7 18.1 1388.4 1511.9 1190.0 924.6 2017 18.2 18.6 19.1 18.2 975.2 849.5 823.5 1083.1 2016 18.3 18.6 19.0 18.4 1443.7 1187.8 1482.5 990.2 平均值 18.2 1232.9 标准差 (σ) 0.4 260 表 5 三种“木棉”区别
Table 5. Differences among the three types of "Mumian" (cotton-like plants)
科属名 种名 古称或别名 生长条件 分布地区 锦葵科 棉属
(Gossypium)草棉 (herbaceum) 棉花、吉贝、木棉 年均温18~24 ℃为宜* 现主要分布于广东、云南、四川、
甘肃和新疆等省区**树棉 (arboreum) 橦树、梧桐木、娑罗木、木棉、吉贝树 年均温约17.8 ℃[46] 云南禄丰等县低海拔温暖地区尚有栽培[46] 木棉科 木棉属 (Gossampinus) 木棉 (malabarica) 攀枝花、英雄树 生长最适温度为23~
31 ℃,喜高温湿润气候,不耐寒[57]主要分布于广西、广东、贵州、
云南和四川南部等省区[57-58]注:参考郭声波[46]。*来源于https://www.cma.gov.cn/kppd/kppdqxyr/kppdnyqx/201212/t20121215_197016.html;**来源于https://baike.baidu.com/item/草棉/1914485。 表 6 学者对“西岭”的认识
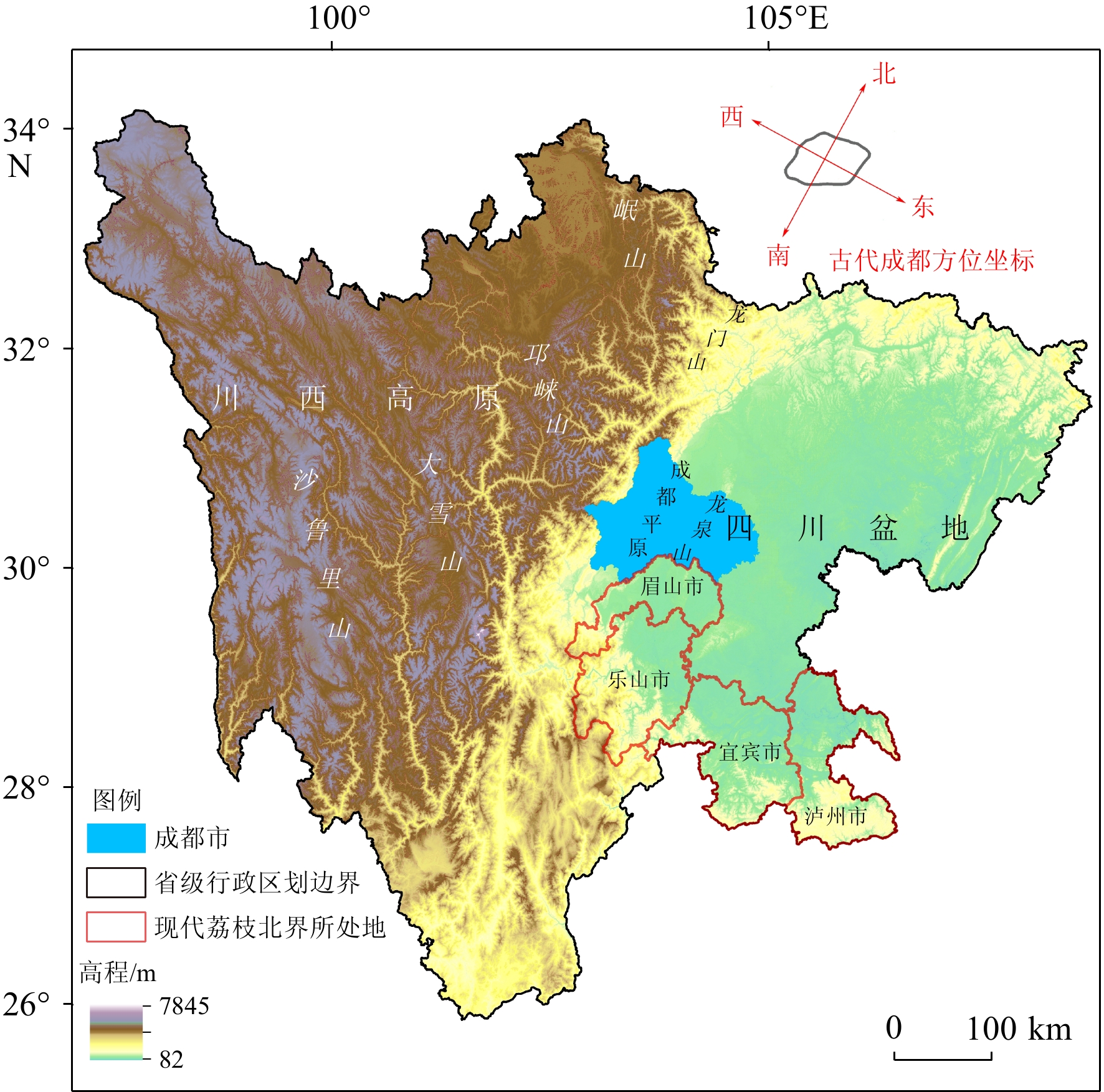
Table 6. Different explanations to the “Western Mountains” by modern researchers
学者/官修 学者/著作
年代泛指/
确指山脉/山峰 出处 胡三省 宋末元初 泛指 西山在成都西 《资治通鉴音注》疏陈子昂上书云:“西山在成都西,松、茂二州都督府所统诸羌州,皆西山羌也。”[62] 仇兆鳌 明末清初 确指 岷山 《杜诗详注》引《元和郡县志》注《西山三首》云:“岷山,即汶山,南去青城山百里,天色晴朗,望见成都。山顶停雪,常深百丈,夏月融泮,江川为之洪溢,即陇之南首也。”仇注又引李宗谔《图经》云:“维州,南界,江城,岷山连岭而西,不知其极,北望高山,积雪如玉,东望成都若井底,一面孤峰,三面临江,是西蜀控吐蕃之要冲。”[60] 浦起龙 清 泛指 松、维等州诸山 《读杜心解》注云:“西山,即松、维等州诸山”[63] 杨伦 清 确指 岷山 《杜诗镜诠》引注与仇注同[18] 中国清朝官修地理总志 清 确指 九顶山 《嘉庆重修一统志》:在茂州列鹅村,去州四十里,实威茂彭灌之中。其高六十里,山有九峰,四时积雪,经暑不消,晨光射之,烂若红玉,去成都五百里。“西望之若在户牖,居人呼为九顶山,杜子美所咏西山即此也。”[61] 李绍明 1980年 泛指 唐代西山为成都平原以西岷江上游诸山之泛称 《唐代西山诸羌考略》引胡三省注[64] 高文德 1995年 泛指 西山为唐代对成都平原以西,岷江上游诸山的泛称 《中国少数民族史大辞典》[65] 张天健 1996年 确指 大雪塘 (又名庙基岭) 《杜甫“窗含西岭千秋”“西岭”考实》[66] 山东大学古典
文学教研室1998年 确指 松潘县南之雪栏山 《杜甫诗选》“西岭”即“雪岭”,在松潘县南之雪栏山,积雪终年不消,故名。[67] 郭声波 2002年 泛指 唐宋剑南道之“西山”,通常认为是对成都平原以西岷江上游的岷山、龙门山、甘松岭、羊拱山、鹧鸪山、大白山、邛崃山、夹金山等山脉的统称 《川西北羌族探源---唐宋岷江西山羁縻州部族研究》[20] 王军 2013年 确指 西岭,即西山,为岷山主峰 (雪宝顶) 《诗心:从<诗经>到<红楼梦>》西岭,即西山,因在成都西得名,为岷山主峰(雪宝顶)。因山顶终年积雪,故又称雪岭、雪山。“千秋雪”,岭上终年不化的积雪,言时间之久。[68] 赵华 2013年 泛指 西岭是泛指,千秋雪是四姑娘山幺妹峰 《由两幅照片看杜甫“窗含西岭千秋雪”的指向——成都的自然人文之旅[缩略版]》① 田峰 2016年 泛指 西山包含了松、茂、维等州的诸多山脉,即今之川西北的岷山 《杜甫从秦州到巴蜀荆湘到地理感知和文化体验》[69] 马玮 2017年 泛指 西岭指岷山,岷山在成都西 《杜甫诗歌赏析》[70] 吴石玉 2020年 确指 雪岭、西山,也称西岭、雪山,今名雪宝顶,为岷山主峰,在今四川松潘县东 嘉庆《四川通志》中的成都杜甫草堂历史资料综述[71] -
[1] 侯甬坚, 祝一志. 历史记录提取的近5~2.7ka黄河中下游平原重要气候事件及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(4):23-29
HOU Yongjian, ZHU Yizhi. Important climatic events showed by historical records from middle and lower reach plain of the Yellow River during 5~2.7 Ka and their environmental significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(4):23-29.]
[2] 费杰, 侯甬坚, 刘晓东, 等. 基于黄土高原南部地区历史文献记录的唐代气候冷暖波动特征研究[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2001, 16(4):74-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5205.2001.04.013
FEI Jie, HOU Yongjian, LIU Xiaodong, et al. Fluctuation characteristics of climatic change in temperature of Tang Dynasty based on historical document records in South Loess Plateau[J]. Collections of Essays on Chinese Historical Geography, 2001, 16(4):74-81.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5205.2001.04.013
[3] 刘炳涛, 满志敏. 古代诗歌中的气候信息及其运用[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2010, 25(4):5-14
LIU Bingtao, MAN Zhimin. Climate information of ancient poetry and its application[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography, 2010, 25(4):5-14.]
[4] 刘亚辰, 方修琦, 陶泽兴, 等. 诗歌中物候记录的基本特征及用于历史气候重建的处理方法[J]. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(4):483-490 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.04.009
LIU Yachen, FANG Xiuqi, TAO Zexing, et al. Basic features of phenological records in poetry and their usage for reconstructing past climate change[J]. Progress in Geography, 2017, 36(4):483-490.] doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.04.009
[5] 满志敏. 关于唐代气候冷暖问题的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 18(1):20-30 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.01.003
MAN Zhimin. Climate in Tang Dynasty of China: Discussion for its evidence[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 18(1):20-30.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.01.003
[6] 马亚玲, 崔玉娟, 方修琦, 等. 杜诗记载的唐代荆湘地区寒冬及其古气候意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(1):137-142 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.01.012
MA Yaling, CUI Yujuan, FANG Xiuqi, et al. Cold winters of Jing-Xiang region in Tang Dynasty recorded in Du Fu's poems and their palaeoclimatic significance[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(1):137-142.] doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.01.012
[7] 蓝勇. 中国西南历史气候初步研究[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 1993, 8(2):13-39
LAN Yong. A preliminary study of the historical climate in South-West of China[J]. Collections of Essays on Chinese Historical Geography, 1993, 8(2):13-39.]
[8] 费杰, 周杰, 安芷生. 历史文献记录的唐五代时期(618-959AD)气候冷暖变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(2):109-118
FEI Jie, ZHOU Jie, AN Zhisheng. Temperature change in China over 618-959 AD: Based on historical records[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(2):109-118.]
[9] 葛全胜, 刘浩龙, 郑景云, 等. 隋唐时期东中部地区温度变化的重建(601~920年)[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(31): 3048-3055
GE Quansheng, LIU Haolong, ZHENG Jingyun, et al. Reconstructing temperature change in Central East China during 601-920 AD[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(34): 3944-3949.]
[10] 郭忠明, 顾祝军, 吴红波, 等. 冰川雪线高度研究进展[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2016, 31(4):645-652
GUO Zhongming, GU Zhujun, WU Hongbo, et al. Research progress of glacier snowline altitude[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2016, 31(4):645-652.]
[11] 于希贤. 苍山雪与历史气候冷期变迁研究[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 1996, 11(2):25-39
YU Xixian. Snow in Cangshan Mountain and the cold period variation of historical climate[J]. Collections of Essays on Chinese Historical Geography, 1996, 11(2):25-39.]
[12] 璩向宁, 汪一鸣. 近一千年来贺兰山积雪和气候变化[J]. 地理研究, 2006, 25(1):35-42 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.01.005
QU Xiangning, WANG Yiming. Investigation on changes of snow cover and climate in Helanshan mountains for the past approximate millennium[J]. Geographical Research, 2006, 25(1):35-42.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.01.005
[13] 杨景春, 李有利. 地貌学原理(4版)[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2017: 78-79
YANG Jingchun, LI Youli. Principles of Geomorphology(4th ed.)[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2017: 78-79.]
[14] 张籍. 张籍诗集[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 1959: 80, 67
ZHANG Ji. The Collected Poems of Zhang Ji[M]. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company, 1959: 80, 67.]
[15] 吴淑娴. 中国果树志 荔枝卷[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1998: 20-39
WU Shuxian. Chinese Fruit Trees: Litchi Volume[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1998: 20-39.]
[16] 白慧卿, 吴建国, 潘学标. 影响我国荔枝分布的关键气候要素分析[J]. 果树学报, 2016, 33(4):436-443
BAI Huiqing, WU Jianguo, PAN Xuebiao. Key climatic factors affecting the distribution of litchi in China[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2016, 33(4):436-443.]
[17] 吴怀东. 杜甫的美学——《绝句四首》之三“两个黄鹂鸣翠柳”解读[J]. 杜甫研究学刊, 2018, 38(3):37-44
WU Huaidong. On Du Fu's Aesthetics——Interpretation of "Two Golden Orioles Sing amid the Willows Green 'in' Four Quatrains"[J]. Journal of Dufu Studies, 2018, 38(3):37-44.]
[18] 杜甫. 杜诗镜铨[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 1998: 559-560, 317, 334, 575, 472
DU Fu. Du Fu's Poems[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Classics Publishing House, 1998: 559-560, 317, 334, 575, 472.]
[19] 严钦尚, 曾昭璇. 地貌学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1985: 124-125
YAN Qingshang, ZENG Zhaoxuan. Geomorphology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1985: 124-125.]
[20] 郭声波. 川西北羌族探源——唐宋岷江西山羁縻州部族研究[J]. 中南民族大学学报: 人文社会科学版, 2002, 22(4):74-79
GUO Shengbo. The origin of the Ch'iang People in the Northwest Sichuan——A research into Xishan Jimi prefectures[J]. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities: Humanities and Social Science, 2002, 22(4):74-79.]
[21] 刘亚辰, 陶泽兴, 呼雪梅. 唐宋诗歌中物候记录的规律总结及其对环境的指示意义[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2022, 37(4):12-21
LIU Yachen, TAO Zexing, HU Xuemei. Phenological records’ regularity in poems of the Tang and Song Dynasties and its indications of the environment[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography, 2022, 37(4):12-21.]
[22] 卡列斯尼克 C B. 普通冰川学[M]. 兰州: 中国科学院地理研究所冰川冻土研究室, 1965: 32-33
Kalesnik C B. General Glaciology[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Institute of Glaciology and Cryopedology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1965: 32-33.]
[23] 姚永慧, 张百平. 青藏高原气温空间分布规律及其生态意义[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34(11):2084-2094
YAO Yonghui, ZHANG Baiping. The spatial pattern of monthly air temperature of the Tibetan Plateau and its implications for the geo-ecology pattern of the Plateau[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34(11):2084-2094.]
[24] 曾寒梅. 成渝两地城市形态特征形成与演变研究[D]. 重庆大学硕士学位论文, 2015
ZENG Hanmei. A study of the formation and evolution of urban morphology features in Chengdu and Chongqing[D]. Master Dissertation of Chongqing University, 2015.]
[25] 周斌, 邹强, 蒋虎, 等. 川西高原气候变化特征及泥石流动态危险性响应研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2022, 31(4):241-255
ZHOU Bin, ZOU Qiang, JIANG Hu, et al. Research on climate change characteristics and change of debris flow hazard in the Chuanxi plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2022, 31(4):241-255.]
[26] 星球研究所, 中国青藏高原研究会. 这里是中国[M]. 北京: 中信出版集团股份有限公司, 2019: 90
Institute for Planets, The China Society on Tibet Plateau. HI I'M China[M]. Beijing: CITIC Press Corporation, 2019: 90.]
[27] 雷传扬, 王波, 刘兆鑫, 等. 成都平原河流阶地的发育及其对古气候和新构造运动的指示[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2024, 44(1):20-33
LEI Chuanyang, WANG Bo, LIU Zhaoxin, et al. Development of fluvial terraces in Chengdu Plain: Implications for the paleoclimate and neotectonic movement[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2024, 44(1):20-33.]
[28] 王羽珂, 陈浩, 冯兴雷, 等. 成都平原东郊台地中更新统合江组沉积特征及工程地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2019, 39(3):33-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.03.004
WANG Yuke, CHEN Hao, FENG Xinglei, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and engineering geological significance of the middle Pleistocene Hejiang Formation in the eastern suburb platform on the Chengdu Plain, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2019, 39(3):33-39.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.03.004
[29] 马志刚. 成都平原卵砾石层地震响应研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2009
MA Zhigang. The study on the seismic response of gravel formation on Chengdu Plain[D]. Master Dissertation of Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.]
[30] 蓝勇. 四川荔枝种植公布的历史考证[J]. 西南师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 1985, 10(4):86-99
LAN Yong. An investigation of the history and distribution of litchi planting in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 1985, 10(4):86-99.]
[31] 四川省统计局, 国家统计局四川调查总队. 四川统计年鉴2017[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2017: 187-188
Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Sichuan. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2017[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2017: 187-188.]
[32] 四川省统计局, 国家统计局四川调查总队. 四川统计年鉴2018[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018: 187-188
Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Sichuan. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2018[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018: 187-188.]
[33] 四川省统计局, 国家统计局四川调查总队. 四川统计年鉴2019[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2019: 179-180
Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Sichuan. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2019[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019: 179-180.]
[34] 四川省统计局, 国家统计局四川调查总队. 四川统计年鉴2020[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020: 143-144
Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Sichuan. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2020[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020: 143-144.]
[35] 四川省统计局, 国家统计局四川调查总队. 四川统计年鉴2021[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021: 137-138
Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Sichuan. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2021[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021: 137-138.]
[36] 徐新良. 中国多年度地市行政区划边界数据[DB/OL]. 资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统, 2023.
2024-03-21]. http: //www. resdc. cn/. [XU Xinliang. Multi-year administrative boundary data for municipalities in China[DB/OL]. Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publication System, 2023. [2024-03-21]. http://www.resdc.cn/.
[37] 徐新良. 中国多年度省级行政区划边界数据[DB/OL]. 资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统, 2023. [2024-03-21]. http://www.resdc.cn/.
XU Xinliang. Multi-year administrative boundary data for provinces in China[DB/OL]. Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publication System, 2023. [2024-03-21]. http://www.resdc.cn/.
[38] 张立汉. 中国山河全书(上)[M]. 青岛: 青岛出版社, 2005: 1249
ZHANG Lihan. Mountains and Rivers of China( Volume One) [M]. Qingdao: Qingdao Publishing House, 2005: 1249.]
[39] 陈梦蝶. 青藏高原地区雪线时空变化动态研究[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2014
CHEN Mengdie. Spatio-temporal change dynamic of snowline on Tibetan Plateau[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2014.]
[40] 吴锡浩, 赵文龙. 固态降水率及其与气候雪线的关系[C]//第四纪冰川与第四纪地质文集 第五集. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 174-182
WU Xihao, ZHAO Wenlong. Solid precipitation rate and its relation to climatic snow line[C]//Quaternary Glaciation and Quaternary Geology 5th Collection. Beijing: Geology Press, 1988: 174-182.]
[41] 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 王书兵, 等. 中国气候雪线空间分布特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 2002, 8(4):289-296 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.04.001
JIANG Fuchu, WU Xihao, WANG Shubing, et al. Characteristics of space distribution of the climatic snowline in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2002, 8(4):289-296.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.04.001
[42] 周维扬, 丁浩. 杜甫草堂史话[M]. 成都: 天地出版社, 2009: 42-45
ZHOU Weiyang, DING Hao. The history of Du Fu thatched[M]. Chengdu: Tiandi Press, 2009: 42-45.]
[43] 竺可桢. 中国近五千年来气候变迁的初步研究[J]. 考古学报, 1972, 17(1):15-38
ZHU Kezhen. A preliminary study on the climatic fluctuations during the last 5000 years in China[J]. Acta Archaeologica Sinica, 1972, 17(1):15-38.]
[44] 蓝勇. 近2000年来长江上游荔枝分布北界的推移与气温波动[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 14(1):39-45 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.01.005
LAN Yong. The movements of the northern boundary of Litchi distribution and fluctuations of temperature in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River in the past 2000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 14(1):39-45.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.01.005
[45] 郭声波. 成都荔枝与十二世纪的寒冷气候[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 1989, 4(3):38
GUO Shengbo. Chengdu Lychee and the cold climate of the twelfth century[J]. Collections of Essays on Chinese Historical Geography, 1989, 4(3):38.]
[46] 郭声波. 历史时期四川手工业原料作物的分布[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 1990, 5(1):67-88
GUO Shengbo. Distribution of raw material crops for handicrafts in Sichuan during the historical period[J]. Collections of Essays on Chinese Historical Geography, 1990, 5(1):67-88.]
[47] 葛全胜. 中国历朝气候变化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 308
GE Quansheng. Climate Change in Chinese Dynasties[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 308.]
[48] 娄雨亭. 薛涛与唐代成都的荔枝及气候冷暖问题[J]. 中国史研究, 2001, 23(3):38
LOU Yuting. Xue Tao and Lychee in Chengdu in the Tang Dynasty and the Problem of Warm and Cold Climate[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Studies, 2001, 23(3):38.]
[49] 聂顺新. 再论唐代长江上游地区的荔枝分布北界及其与气温波动的关系[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2011, 26(1):139-144,158
NIE Shunxin. Northern boundary of litchi's distribution in the upper Yangtze of Tang Dynasty and it's relationship with the temperature fluctuations[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography, 2011, 26(1):139-144,158.]
[50] 满志敏. 唐代气候冷暖分期及各期气候冷暖特征的研究[J]. 历史地理, 1990, 7(2):1-15
MAN Zhimin. The division of cold and warm climatic periods of the Tang Dynasty Time and the clmracteristies of the respective term[J]. Historical Geography, 1990, 7(2):1-15.]
[51] 蓝勇. 采用物候学研究历史气候方法问题的讨论——答《再论唐代长江上游地区的荔枝分布北界及其与气温波动的关系》一文[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2011, 26(2):14-20
LAN Yong. A discussion on research's method of historical climate with the Phenology: answers on the northern boundary of Litchi's distribution in the upper Yangtze River in Tang Dynasty and the relationship with the temperature fluctuations[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography, 2011, 26(2):14-20.]
[52] 唐圭璋. 全唐诗[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 2018
TANG Guizhang. Tang Poems[M]. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company, 2018.]
[53] 张晓婷, 庄赟, 董嘉辉, 等. 荔枝种质资源抗寒性综合评价[J]. 果树学报, 2024, 41(3):403-425
ZHANG Xiaoting, ZHUANG Yun, DONG Jiahui, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of cold tolerance in Litchi Germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2024, 41(3):403-425.]
[54] 邓乐群. 杜甫诗歌所叙唐代陇蜀荆湘气候特征[J]. 南通大学学报: 社会科学版, 2009, 25(6):58-64
DENG Lequn. Climatic features of Long, Shu, Jin and Xiang in the Tang Dynasty revealed in DU Fu’s Poems[J]. Journal of Nantong University: Social Sciences Edition, 2009, 25(6):58-64.]
[55] 史学通. 我国历史上的木棉问题[J]. 中国史研究, 1981, 3(2):85-91
SHI Xutong. The problem of "Mumian" in China's history[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Studies, 1981, 3(2):85-91.]
[56] 辛如如. 木棉栽培技术综述[J]. 防护林科技, 2014, 32(11):120-121
XIN Ruru. An overview of Bombax malabaricum cultivation technology[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2014, 32(11):120-121.]
[57] 高平, 谌振, 林忠, 等. 木棉名称考据与应用研究[J]. 南方农业, 2016, 10(22):24-27
GAO Ping, CHEN Zhen, LIN Zhong, et al. Research on the name evidence and application of Bombax malabaricum[J]. South China Agriculture, 2016, 10(22):24-27.]
[58] 韩茂莉. 中国历史农业地理[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2012: 626-627
HAN Maoli. Historical Agricultural Geography of China[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2012: 626-627.]
[59] 吴锡浩. 青藏高原东南部现代雪线和林线及其关系的初步研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 1989, 11(2):113-124
WU Xihao. A preliminary study on existing snowline tember line and their relations in southeastern part of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1989, 11(2):113-124.]
[60] 杜甫. 杜诗详注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 1992: 412
DU Fu. The Detailed Annotations on Du Fu's Poems[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Classics Publishing House, 1992: 412.]
[61] 清)仁宗敕撰. 四部丛刊续编 史部 嘉庆重修一统志 23 卷三百八十四[M]. 上海: 上海书店出版社, 1984
Qing dynasty) by Emperor Renzong. Si Bu Cong Kan Sequels, sequel to the history part, Yi Tong Zhi revision by Jiaqing 23 vol. 384[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Bookstore Publishing House, 1984.]
[62] 胡三省. 资治通鉴音注 卷二百四[M]. 胡克家, 清嘉庆21
HU Sanxing. Zizhi Tongjian Yinzhu, Volume 244[M]. Hu Kejia, Qing Jiaqing 21.]
[63] 浦起龙. 读杜心解[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 1981: 462
PU Qilong. Explanation of Dufu's Poems[M]. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company, 1981: 462.]
[64] 李绍明. 唐代西山诸羌考略[J]. 四川大学学报: 哲学社会科学版, 1980, 13(1):83-95
LI Shaoming. A study of the Qiang in the Western Mountains during the Tang Dynasty[J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Philosophy and Social Science Edition, 1980, 13(1):83-95.]
[65] 高文德. 中国少数民族史大辞典[M]. 长春: 吉林教育出版社, 1995: 700
GAO Wende. Dictionary of Chinese Minority History[M]. Changchun: Jilin Education Publishing House, 1995: 700.]
[66] 张天健. 杜甫“窗含西岭千秋雪”“西岭”考实[J]. 中国地名, 1996, 1(4):23
ZHANG Tianjian. The textual research of the "Western Mountain" in Du Fu's "The Window Contains Thousands of Autumn Snow in the Western Mountain"[J]. China Place Name, 1996, 1(4):23.]
[67] 山东大学中文系古典文学教研室选注, 袁世硕修订. 杜甫诗选[M]. 北京: 人民文学出版社, 1998: 258
Selected and annotated by the Department of Classical Literature, Shandong University, revised by YUAN Shishuo. Selected Poems of Du Fu[M]. Beijing: People's Literature Publishing House, 1998: 258.]
[68] 王军. 诗心: 从《诗经》到《红楼梦》[M]. 北京: 东方出版社, 2013: 76
WANG Jun. Poetic Heart: From the Book of Songs to The Story of the Stone[M]. Beijing: Oriental Publishing House, 2013: 76.]
[69] 田峰. 杜甫从秦州到巴蜀荆湘的地理感知与文化体验[J]. 中国韵文学刊, 2016, 30(1):11-17 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2491.2016.01.003
TIAN Feng. Du Fu's Geographical Perception and Cultural Experience from Qinzhou to Bashu Jingxiang[J]. Journal of Chinese Verse Studies, 2016, 30(1):11-17.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2491.2016.01.003
[70] 马玮. 杜甫诗歌赏析[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆国际有限公司, 2017: 214
MA Wei. An Appreciation of Du Fu's Poetry[M]. Beijing: Business Book Printing Place International Co. , Ltd. , 2017: 214.]
[71] 吴石玉. 嘉庆《四川通志》中的成都杜甫草堂历史资料综述[J]. 杜甫研究学刊, 2020, 40(4):63-81
WU Shiyu. A textual research on historical documents of Du Fu Thatched Cottage in Chengdu in general history of Sichuan in Jiaqing Period of the Qing Dynasty[J]. Journal of Dufu Studies, 2020, 40(4):63-81.]
[72] 汤国安, 杨昕, 张海平. ArcGIS地理信息系统空间分析实验教程[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021: 381-382, 385
TANG Guoan, YANG Xin, ZHANG Haiping. ArcGIS Geographic Information System Spatial Analysis Experimental Tutorial[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2021: 381-382, 385.]
[73] 肖时珍, 肖华, 吴宇辉. 基于GIS视域分析的项目建设对世界遗产景观美学价值的影响评价——以武陵源世界自然遗产地为例[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2020, 40(3):516-522 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2020.03.008
XIAO Shizhen, XIAO Hua, WU Yuhui. Assessment of construction project on the aesthetic values of world heritage landscape based on GIS viewshed analysis: a case study of Wulingyuan World Natural Heritage Site[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2020, 40(3):516-522.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2020.03.008
[74] 四川省阿坝藏族羌族自治州茂汶羌族自治县地方志编纂委员会. 茂汶羌族自治县志[M]. 成都: 四川辞书出版社, 1997: 80
Committee of Chorography Mao-wen Qiang Nationality Autonomous County, Aba Zang and Qiang Nationality Autonomous District, Sichuan Province. Chorography of Mao-wen Qiang Nationality Autonomous County[M]. Chengdu: Dictionary Press of Sichuan, 1997: 80.]
[75] 张宗福, 张晓英. 略论杜甫《西山三首》[J]. 杜甫研究学刊, 2012, 32(1):9-15
ZHANG Zongfu, ZHANG Xiaoying. A brief discussion of Du Fu's Three Songs from the Western Mountains[J]. Journal of Dufu Studies, 2012, 32(1):9-15.]
-



 下载:
下载: