Fire history over the past 1 500 years revealed by charcoal record from the Dongping Lake in the Lower Yellow River
-
摘要:
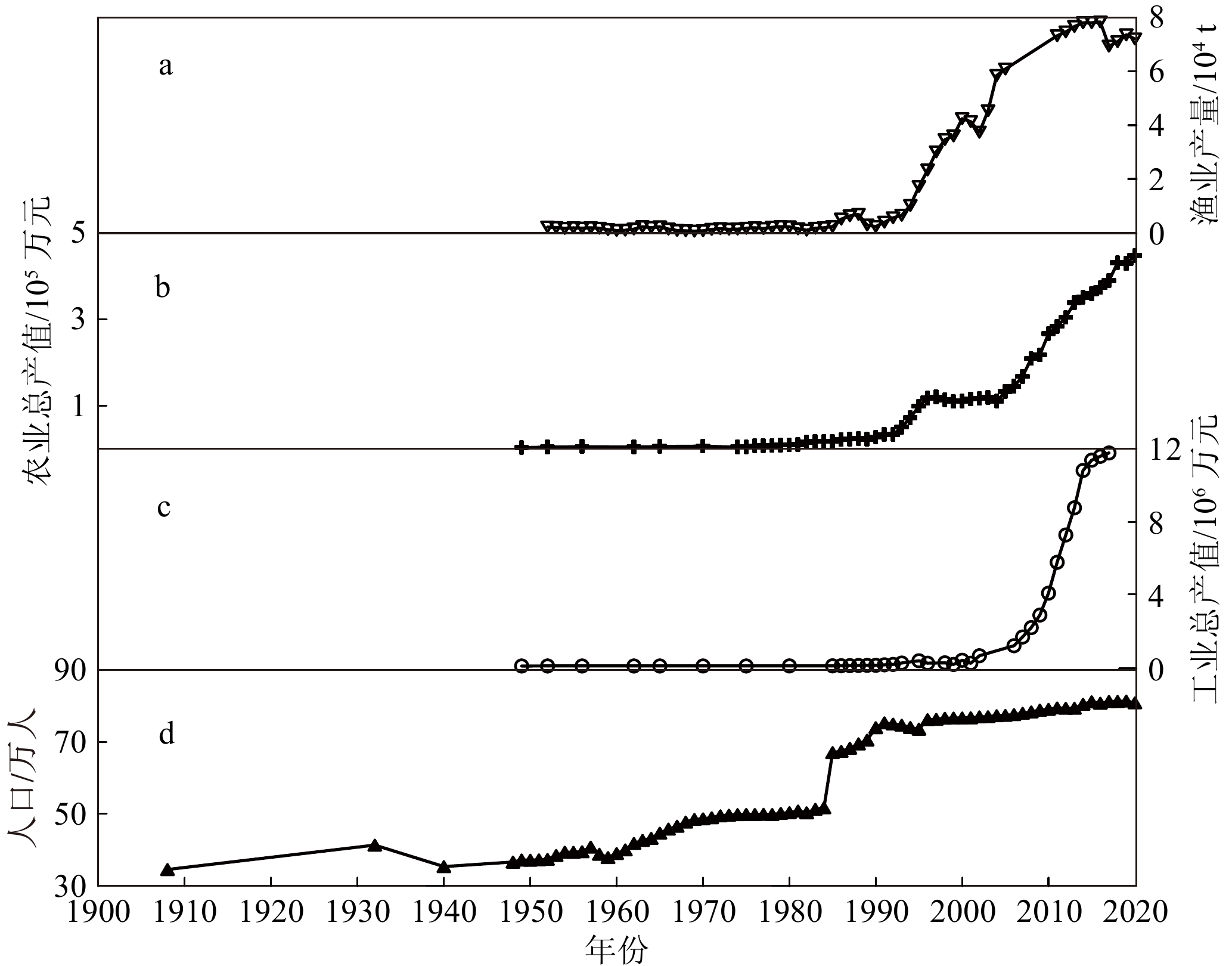
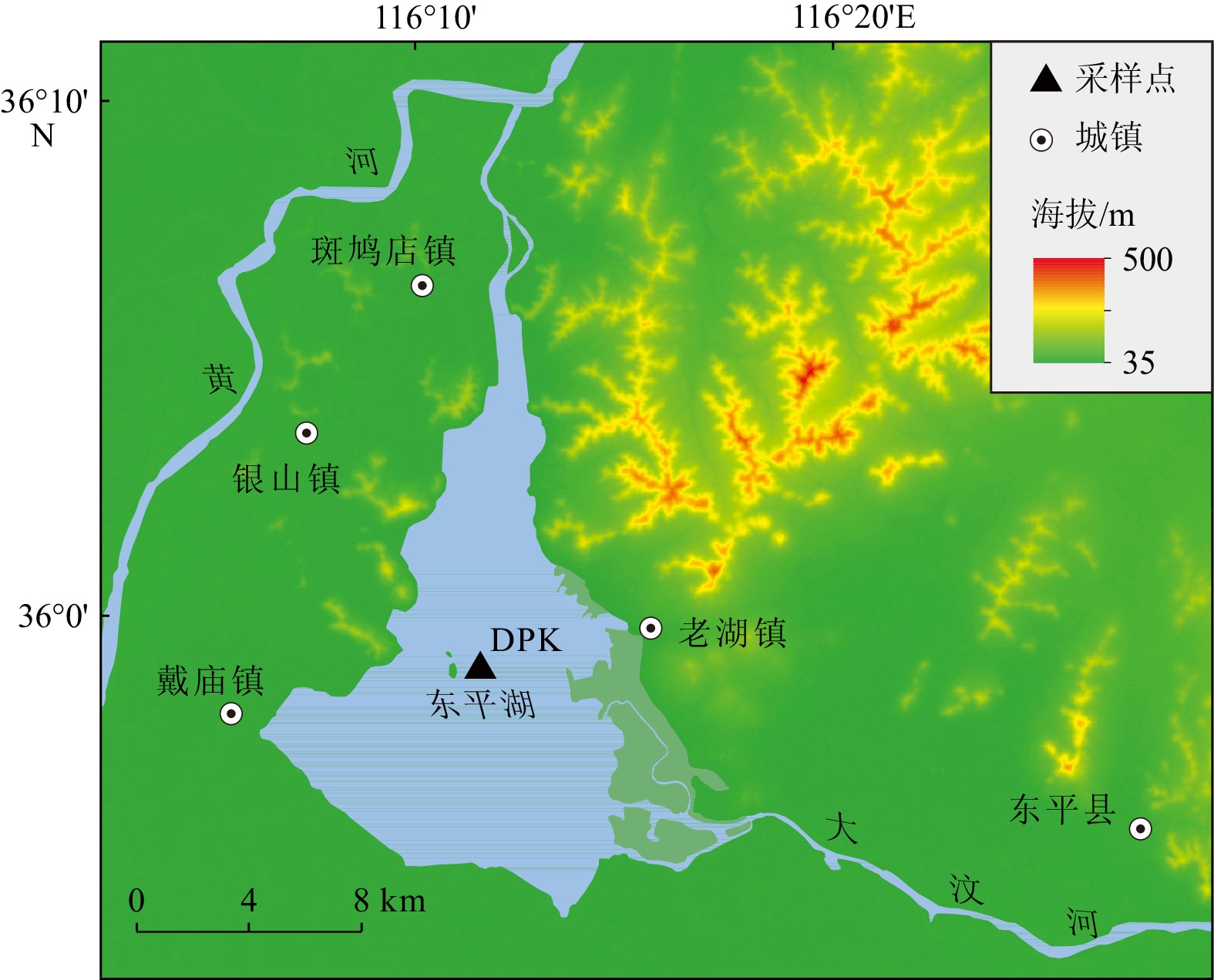
东平湖是黄河下游地区最大的蓄洪湖泊,其沉积物蕴藏着流域地质历史时期丰富的环境信息。本研究以东平湖沉积岩芯(DPK岩芯,161 cm)为研究对象,利用该岩芯的炭屑记录,并结合粒度、烧失量等古环境指标,重建了东平湖地区近1 500年以来的古火演化历史,探讨了火事件与气候变化、人类活动之间的关系。研究结果表明:(1)516—1254 AD,黄河下游东平湖地区为冷干转暖湿气候,火事件较频繁,但约1000 AD之后有降低趋势;(2)1254—1922 AD,气候寒冷,旱涝交替频繁,气候变化和人类活动共同影响下导致火事件较之前明显加频加剧;(3)1922—1962 AD,气候相对暖湿,受气候变化及黄河改道影响,火事件频率显著减少且趋于稳定;(4)1962年以来,在暖干气候条件及人类活动加剧扰动的背景下,火事件明显增加,尤其是>100 μm炭屑浓度急剧攀升至整个剖面的最高峰,粒度迅速粗化,表明人类活动干扰进一步加强。进一步分析认为,气候变化是促进该地区火活动的重要因素,而人类活动(如刀耕火种、毁林开荒、战争等)的加强可能是导致东平湖流域火事件频发的主因。研究结果对于未来全球变暖背景下区域森林火灾的防护与治理具有重要的科学意义,进而更好地服务于黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展国家战略。
Abstract:Dongping Lake is the largest flood storage lake in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, and its sediment contains rich environmental information from the geological history of the basin. This study focuses on the sediment core (Core DPK, 161 cm) from Dongping Lake, in Dongping County, Shandong, China and utilizes the charcoal records from this core. Combined with grain size and loss on ignition (LOI), we reconstructed the paleo-fire evolution history in the Dongping Lake region over the past 1500 years to explore the relationship among fire events, climate change, and human activities. Results indicate that: (1) during 516—1254 AD, the Dongping Lake region experienced a transition from cold/dry to warm/humid climate. Fire incidents were frequent, but there was a decreasing trend after around 1000 AD; (2) during 1254—1922 AD, the climate was cold, with frequent alternations between droughts and floods. The combination of climate change and human activities led to a significant increase in the frequency and intensity of fire incidents; (3) during 1922—1962 AD, climate was relatively warm and humid. Due to climate change and the diversion of the Yellow River, the frequency of fire events significantly decreased and stabilized; (4) since 1962, under the background of a warm and dry climate and increased human activities, fire incidents have increased significantly. Particularly, the concentration of charcoal fragments (>100 μm) rose sharply to the highest peak in the entire profile, accompanied by rapid coarsening of grain size, indicating intensified human interference. Further analysis suggests that climate change is a significant factor promoting fire activity in the region, while intensified human activities (such as slash-and-burn agriculture, deforestation, wars and so on) may be the primary cause of frequent fire incidents in the Dongping Lake basin. The results have important scientific significance for the prevention and management of regional forest fires under the background of global warming, and shall contribute to better serving the national strategy of ecological conservation and high-quality development of the Yellow River basin.
-
Key words:
- charcoal /
- fire history /
- climate variation /
- human activity /
- Dongping Lake
-

-
图 5 过去2000年中国东中部温度、华北地区降水(干湿)变化序列[32]
Figure 5.
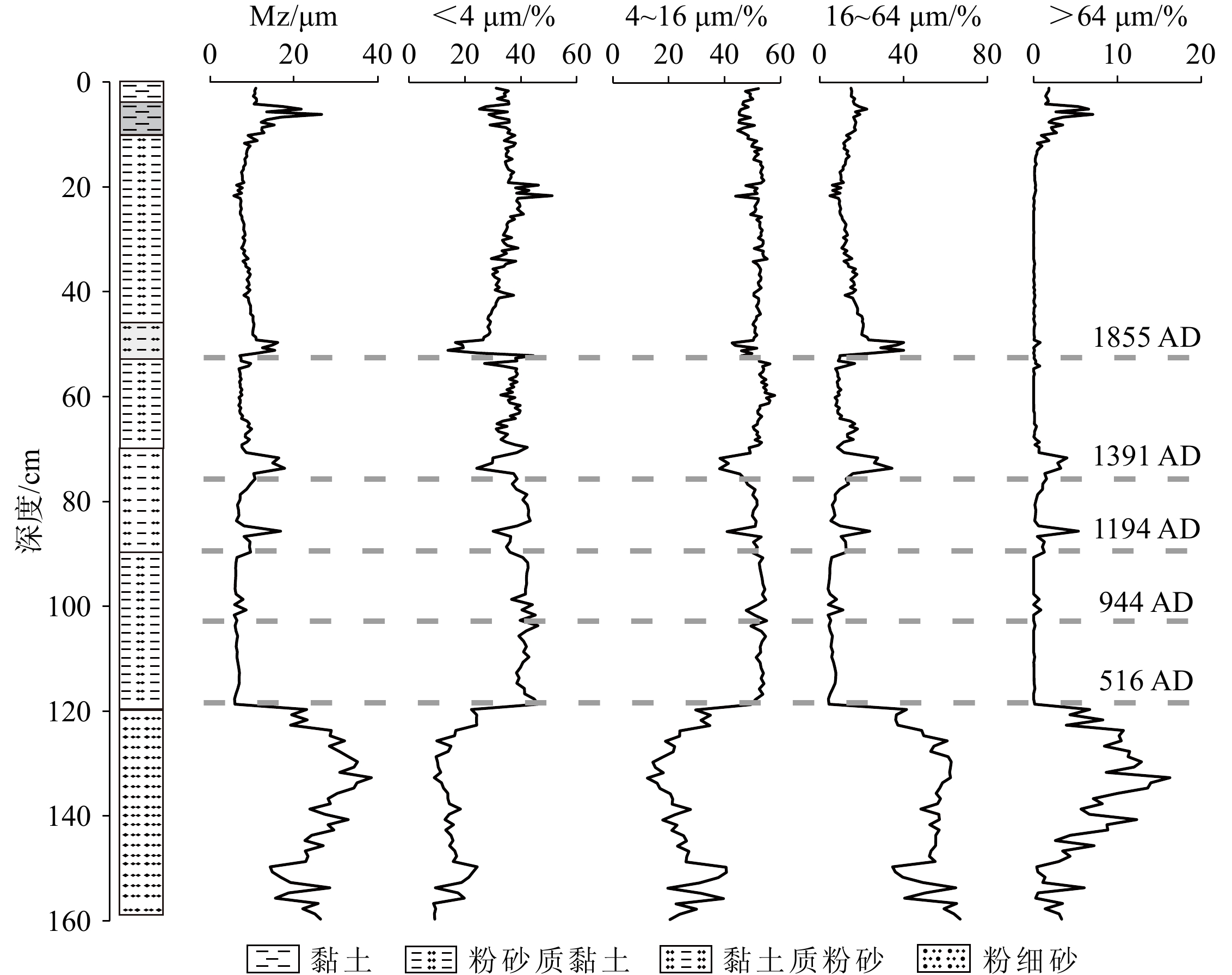
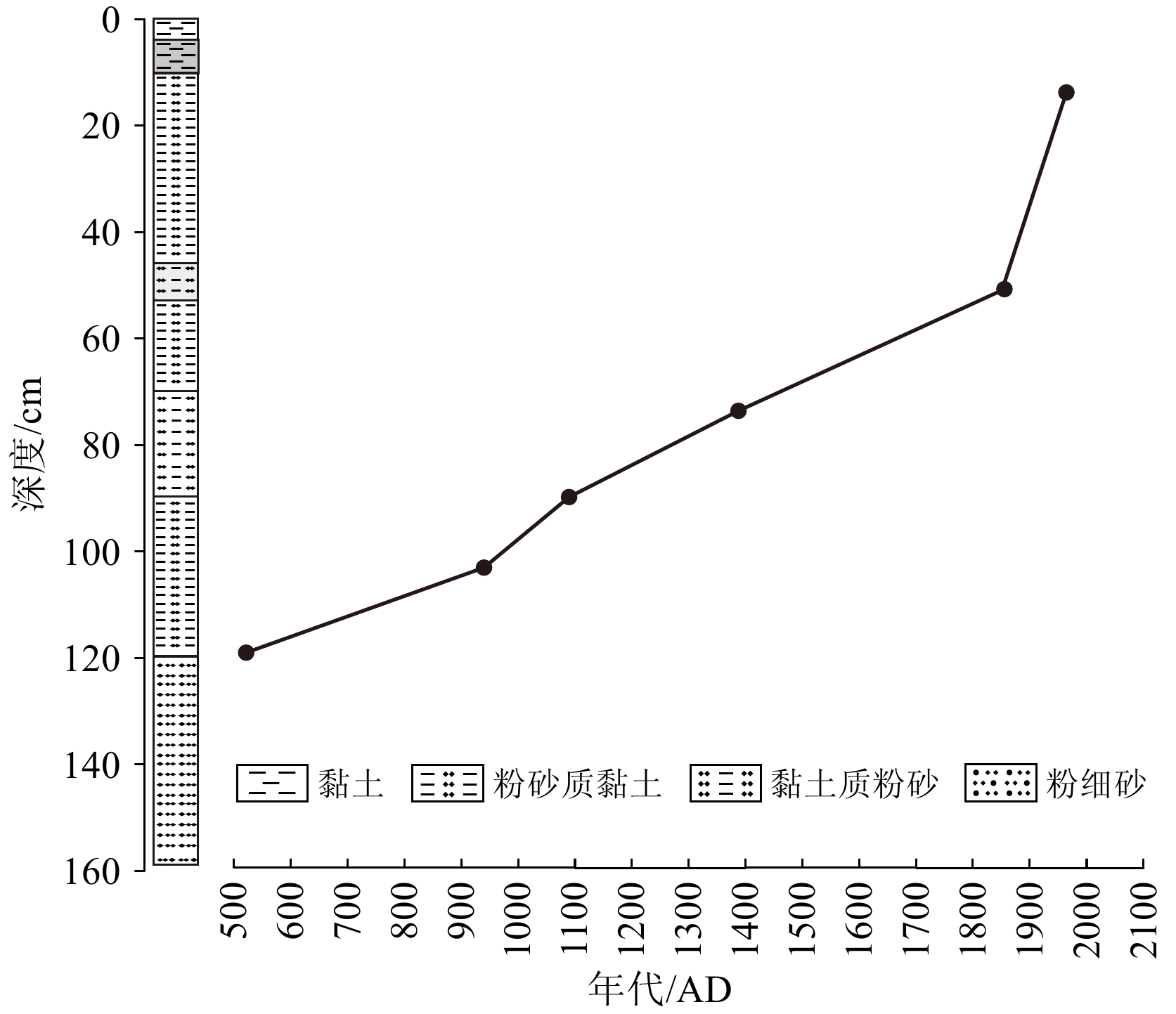
深度/cm 14C测年材料 14C/aBP 210Pb年代/AD 13 TOC 980±70 1962 28 TOC 1300±50 1935 38 TOC 1900±120 1905 52 — — 1855 72 TOC 2820±35 119 TOC 5220±40 144 TOC 5115±35 表 2 历史时期东平县战争等人类活动与地震记录[33]
Table 2. War and other human activities and seismic records in the historical period in Dongping County[33]
时期 战争等人类活动 地震记录 516—1254 AD ● 徐园朗攻陷东平(617 AD) 地震(1068 AD) ● 李祇兵讨安禄山(756 AD) ● 李正己取郓州(777 AD) ● 田宏正平郓州(819 AD) ● 黄巢起义攻克郓州(877 AD) ● 李嗣源攻克郓州,庄宗击退王彦昌(923 AD) ● 辛弃疾收复东平(1162 AD) ● 李龄领导农民起义反金(1215 AD) ● 元兵围东平(1216 AD) 1254—1922 AD ● 燕军攻陷东平(1402 AD) 地震(1830 AD) ● 农民李青山率众破东平(1641 AD) ● 赵浩然率众攻城(1848 AD) ● 张乐行部渡黄河,两次攻打州城(1861 AD、1865 AD) ● 土匪攻城,军阀哗变,在县城西、南部抢掠(1918 AD) ● 县城文庙大火灾(1920 AD) 1922—1962 AD ● 张宗昌向县城投放炸弹数枚(1925 AD) 地震(1937 AD) ● 红枪会攻城,遭“民团”镇压(1926 AD) ● 方永昌率部驻扎6个月,骚扰城乡(1926 AD) ● 济南惨案后,烧毁日货(1928 AD) ● 抗日战争、解放战争(1937—1949 AD) ● 大炼钢铁(1958—1960 AD) 1962 AD以来 ● 文化大革命,毁坏古墓、文物、古籍(1966—1976 AD) 地震(1975,1981,1982 AD) -
[1] You X Y. Surge in extreme forest fires fuels global emissions[Z]. Nature, 2023-12-20.
[2] 庞洋, 周斌, 徐向春, 等. 中国东部季风区全新世火历史及其影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(2):368-382 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2022.02.04
PANG Yang, ZHOU Bin, XU Xiangchun, et al. Holocene fire history and its influencing factors in the monsoon region of East China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2022, 42(2):368-382.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2022.02.04
[3] Miao Y F, Song Y G, Li Y, et al. Late Pleistocene Fire in the Ili Basin, Central Asia, and its potential links to paleoclimate change and human activities[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 547:109700. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109700
[4] Mu Y, Qin X G, Zhang L, et al. Link between black carbon, fires, climate change, and human activity during the Holocene period shown in the loess-paleosol sequence from Henan, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2017, 87(2):288-297. doi: 10.1017/qua.2016.18
[5] 贾宝岩, 肖霞云, 迟长婷. 云南洱海炭屑记录揭示的近千年来古火演化历史[J]. 第四纪研究, 2024, 44(1):158-173 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2024.01.12
JIA Baoyan, XIAO Xiayun, CHI Changting. Fire history over the past millennium revealed by the charcoal record from Lake Erhai, northwestern Yunnan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2024, 44(1):158-173.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2024.01.12
[6] 刘剑波, 李建勇, 韩岳婷, 等. 中国西北地区中晚全新世火历史集成重建与气候演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2024, 44(1):156-169
LIU Jianbo, LI Jianyong, HAN Yueting, et al. Integrated reconstruction of fire history and climatic changes in Northwest China since mid-late Holocene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2024, 44(1):156-169.]
[7] 裴文强, 万世明, 谭扬, 等. 过去5万年来珠江流域火历史的南海沉积记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):47-57
PEI Wenqiang, WAN Shiming, TAN Yang, et al. Fire history in Pearl River Basin since 50 kaBP: sediment records from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3):47-57.]
[8] Pei W Q, Wan S M, Clift P D, et al. Human impact overwhelms long-term climate control of fire in the Yangtze River Basin since 3.0 ka BP[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 230:106165. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106165
[9] 杜建峰, 王宁练, 李建勇, 等. 洛阳盆地全新世炭屑记录及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(2):383-396 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2022.02.05
DU Jianfeng, WANG Ninglian, LI Jianyong, et al. Charcoal records of Holocene loess-soil sequences and palaeoenvironmental significance in the Luoyang Basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2022, 42(2):383-396.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2022.02.05
[10] Xiao X Y, Yao A, Hillman A, et al. Vegetation, climate and human impact since 20 ka in central Yunnan Province based on high-resolution pollen and charcoal records from Dianchi, southwestern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 236:106297. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106297
[11] Wang X, Xiao J L, Cui L L, et al. Holocene changes in fire frequency in the Daihai Lake region (north-central China): indications and implications for an important role of human activity[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 59:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.10.033
[12] 吴立, 张梦翠, 计超, 等. 全新世巢湖沉积物炭屑记录的火环境变化[J]. 地理科学, 2016, 36(12):1920-1928
WU Li, ZHANG Mengcui, JI Chao, et al. Charcoal recorded fire environment change during the Holocene from the sediment of the Chaohu Lake, East China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2016, 36(12):1920-1928.]
[13] Chen Y Y, Li W J, Hou Z F, et al. Clay minerals and provenancial implications of surface sediments in the Dongping Lake, North China[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 673:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2023.10.009
[14] 喻宗仁, 窦素珍, 赵培才, 等. 山东东平湖的变迁与黄河改道的关系[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(4):469-479 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.04.009
YU Zongren, DOU Suzhen, ZHAO Peicai, et al. Relationship between changes of Dongping Lake and shifting of the Yellow River in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2004, 6(4):469-479.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.04.009
[15] 栗文佳, 陈影影, 于世永, 等. 近40年来东平湖水环境变迁及驱动因素[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(10):48-52
LI Wenjia, CHEN Yingying, YU Shiyong, et al. Water environment changes of Dongping Lake in nearly 40 years and its driving factors[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(10):48-52.]
[16] Zhang Z F, Yu N, Liu D Y, et al. Assessment and source analysis of heavy metal contamination in water and surface sediment in Dongping Lake, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307:136016. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136016
[17] 东平湖管理局. 东平湖志[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2014
Dongping Lake Administration Bureau. Annals of Dongping Lake[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 2014.]
[18] Heiri O, Lotter A F, Lemcke G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2001, 25(1):101-110. doi: 10.1023/A:1008119611481
[19] 陈诗越, 王苏民, 陈影影, 等. 东平湖沉积物210Pb、137Cs垂直分布及年代学意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29(5):981-987 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.05.16
CHEN Shiyue, WANG Sumin, CHEN Yingying, et al. Vertical distribution and chronological implication of 210Pb and 137Cs in sediments of Dongping Lake, Shandong Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29(5):981-987.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.05.16
[20] 杨丽伟, 陈诗越. 东平湖沉积碳库效应与形成年代探讨[J]. 地球科学前沿, 2014, 4(5):311-318 doi: 10.12677/AG.2014.45038
YANG Liwei, CHEN Shiyue. Discussion about the effects and forming times of carbon reservoir of lacustrine sediments in Lake Dongping, North of China[J]. Advances in Geosciences, 2014, 4(5):311-318.] doi: 10.12677/AG.2014.45038
[21] 沈吉, 薛彬, 吴敬禄, 等. 湖泊沉积与环境演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010
SHEN Ji, XUE Bin, WU Jinglu, et al. Lake Sedimentation and Environmental Evolution[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010.]
[22] 魏本杰, 侯战方, 陈诗越, 等. 黄河下游大野泽沉积物粒度特征及其对环境演化的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):151-161
WEI Benjie, HOU Zhanfang, CHEN Shiyue, et al. Grain-size characteristics of Dayeze lake sediments in the lower reach of Yellow River and their environmental implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3):151-161.]
[23] Schillereff D N, Chiverrell R C, Macdonald N, et al. Flood stratigraphies in lake sediments: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 135:17-37. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.011
[24] Parris A S, Bierman P R, Noren A J, et al. Holocene paleostorms identified by particle size signatures in lake sediments from the northeastern United States[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2010, 43(1):29-49. doi: 10.1007/s10933-009-9311-1
[25] 周锦清, 马春梅, 刘泽雨, 等. 宁绍平原中全新世火历史与影响因素研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2024, 44(1):84-99 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2024.01.07
ZHOU Jinqing, MA Chunmei, LIU Zeyu, et al. A study on the Middle Holocene fire history and its influencing factors in Ningshao Plain[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2024, 44(1):84-99.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2024.01.07
[26] 谭志海, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 渭河流域全新世以来野火历史与人类土地利用的炭屑记录[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(4):1297-1306
TAN Zhihai, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Wildfire history and human land use over Weihe River basin since Holocene: evidence from charcoal records[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(4):1297-1306.]
[27] 江鸿, 饶志国. 火的历史重建及其与气候变化和人类活动关系研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):185-197
JIANG Hong, RAO Zhiguo. Research progress on fire history reconstruction and its implications for climate change and human activities[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2):185-197.]
[28] Peng Y J, Xiao J, Nakamura T, et al. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(3-4):467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.02.022
[29] 茹渟淋, 陈影影, 黎心泽, 等. 历史时期黄河下游地区古湖分布与消亡原因[J]. 古地理学报, 2024, 26(1):230-240
RU Tinglin, CHEN Yingying, LI Xinze, et al. Distribution and extinction of paleolakes in the lower reaches of Yellow River during historical period[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography:Chinese Edition, 2024, 26(1):230-240.]
[30] 刘子亭, 余俊清, 张保华, 等. 烧失量分析在湖泊沉积与环境变化研究中的应用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2006, 14(2):67-72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-858X.2006.02.013
LIU Ziting, YU Junqing, ZHANG Baohua, et al. Application of loss on ignition to the study of lake sediments and environmental changes[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2006, 14(2):67-72.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-858X.2006.02.013
[31] 沈吉, 张恩楼, 夏威岚. 青海湖近千年来气候环境变化的湖泊沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(6):508-513 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.06.006
SHEN Ji, ZHANG Enlou, XIA Weilan. Records from lake sediments of the Qinghai Lake to mirror climatic and environmental changes of the past about 1000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(6):508-513.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.06.006
[32] 葛全胜, 郑景云, 郝志新, 等. 过去2000年中国气候变化的若干重要特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(6): 934-942
GE Quansheng, ZHENG Jingyun, HAO Zhixin, et al. General characteristics of climate changes during the past 2000 years in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(2): 321-329.]
[33] 山东省东平县地方史志编纂委员会. 东平县志(1986~2003)[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 2006
Compiling Team for Annals of Dongping County, Shandong Province. Annals of Dongping County[M]. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company, 2006.]
[34] 刘文耀, 刘伦辉, 荆桂芬, 等. 云南松林与常绿阔叶林中枯落叶分解研究[J]. 云南植物研究, 2000, 22(3):298-306, 316
LIU Wenyao, LIU Lunhui, JING Guifen, et al. Decomposition of leaf litter in Pinus yunnanensis forest and evergreen broad-leaved forest in central Yunnan[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2000, 22(3):298-306.]
[35] 王敏, 蒙红卫, 黄林培, 等. 云南阳宗海流域过去13000年植被演替与森林火灾[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(1):175-189 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.01.17
WANG Min, MENG Hongwei, HUANG Linpei, et al. Vegetation succession and forest fires over the past 13000 years in the catchment of Yangzonghai Lake, Yunnan[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(1):175-189.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.01.17
[36] 山东省水利厅水旱灾害编委会. 山东水旱灾害[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 1996
The Editorial Committee of Water and Drought Disasters of Shandong Provincial Department of Water Resources. Flood and Drought Disasters in Shandong[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 1996.]
[37] 泰山风景名胜区管理委员会. 中国泰山: 世界文化与自然遗产[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1993
Mount Taishan Scenic Area Management Committee. Mount Taishan in China[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relies Press, 1993.]
[38] 李采芹. 中国历朝火灾考略[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2010
LI Caiqin. A Brief Study of Fires in Various Dynasties of China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2010.]
[39] 高文学. 中国自然灾害史: 总论[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1997
GAO Wenxue. History of Natural Disasters in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1997.]
[40] Kershaw A P. Climatic change and aboriginal burning in north-east Australia during the last two glacial/interglacial cycles[J]. Nature, 1986, 322(6074):47-49. doi: 10.1038/322047a0
[41] 东平县史志办公室编. 东平年鉴[M]. 济南: 黄河出版社, 2004-2021
Compiling Team for Annals of Dongping County. Dongping Yearbook[M]. Ji’nan: Yellow River Press, 2004-2021.]
[42] 赵凤君, 舒立福. 气候异常对森林火灾发生的影响研究[J]. 森林防火, 2007(1):21-23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.009
ZHAO Fengjun, SHU Lifu. Study on the impact of climate anomaly on forest fires[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2007(1):21-23.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.009
-



 下载:
下载: