Regional characteristics and mechanisms of lake water level decline in the Tibetan Plateau since 2 000 years ago
-
摘要:
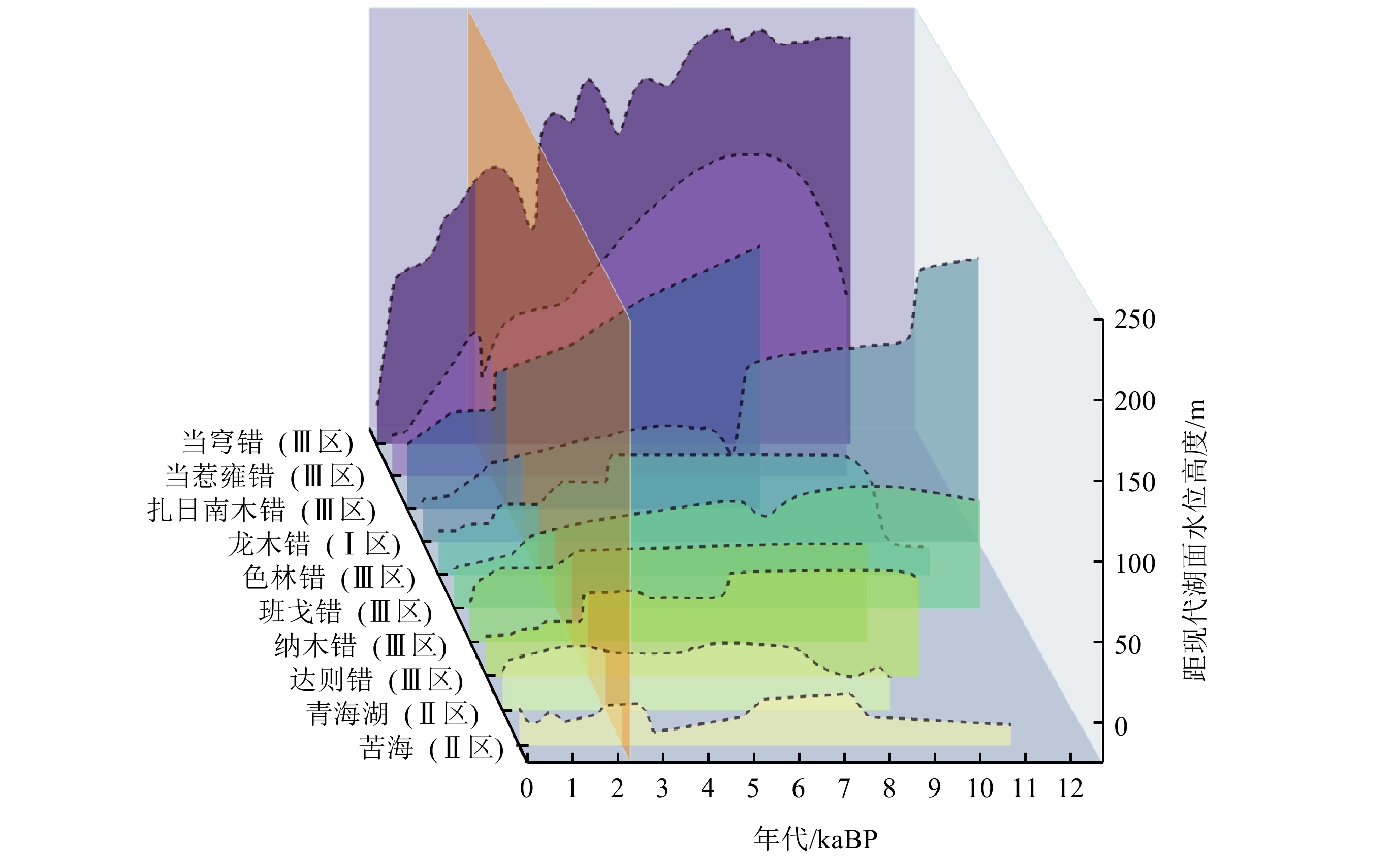
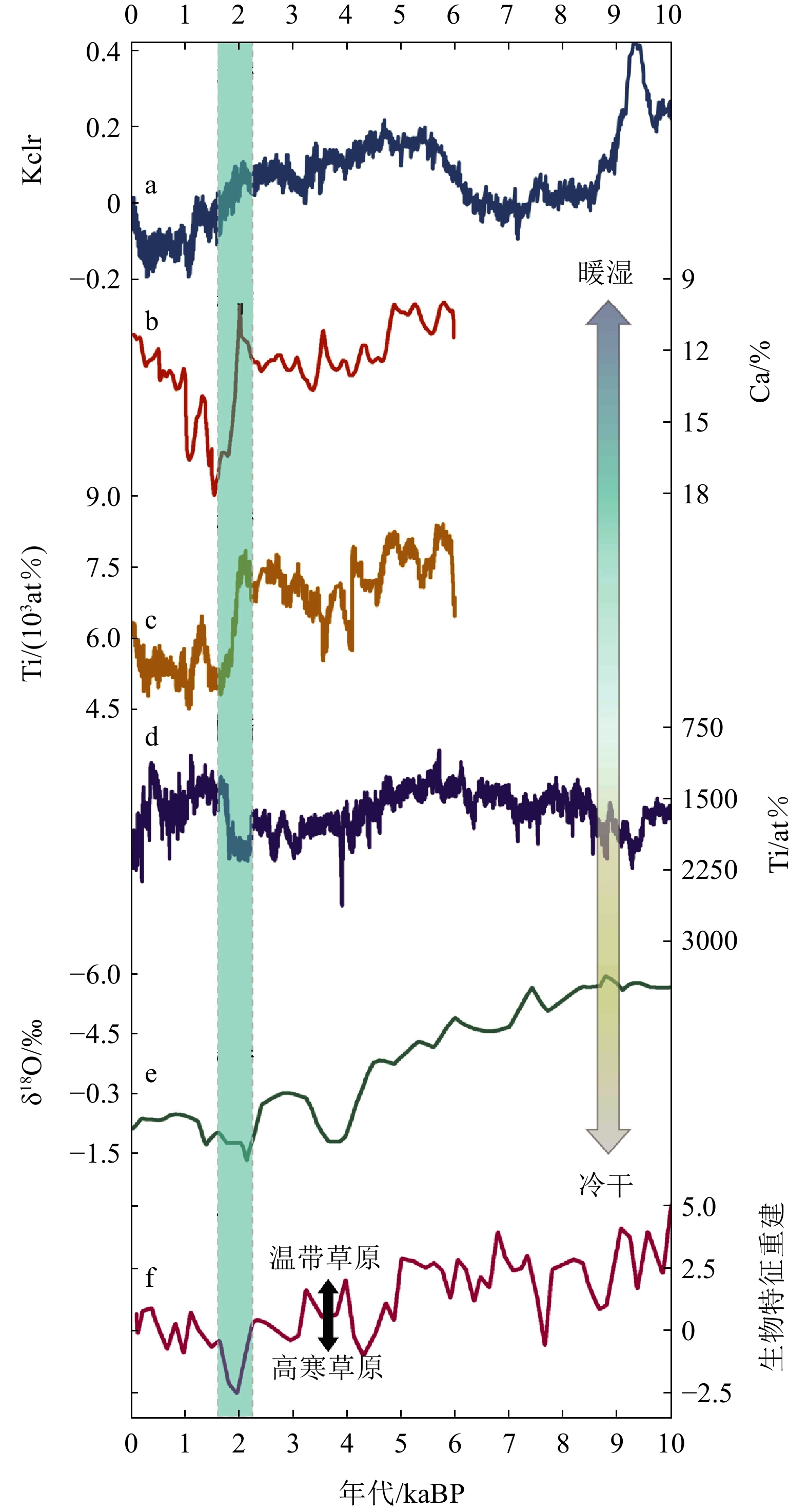
基于亚洲夏季风与西风的影响范围将青藏高原划分为3个研究区,通过对比湖泊沉积物中多代用指标与晚全新世火山活动、北半球温度和亚洲季风指数,探讨了2 kaBP前后高原湖泊水位下降的原因,并分析了不同区域湖泊对气候波动响应的空间差异。结果表明,青藏高原西南部湖面水位下降幅度大于西北部,更甚于高原东北部。这可能是因印度夏季风(Indian Summer Monsoon,简称ISM)强度减弱,高原西南部的湖泊更依赖于ISM降水的补给,因此对该季风所带来的水汽通量的减少更加敏感。而且,该时期的北大西洋涛动(North Atlantic Oscillation,简称NAO)的位相由负转正,使得青藏高原北部水汽辐合增强、降水偏多而南部降水偏少,进而导致高原南部湖面水位下降幅度普遍大于北部湖泊。导致青藏高原气候趋于冷干的主要原因,本文归因于该阶段厄尔尼诺(EI Niño)的加强。除此之外,该时期南半球环状模(Southern Annular Mode,简称SAM)冬夏季的不同位相也通过复杂的海气耦合过程,跨越赤道对青藏高原气候起到了降温减湿的作用。
Abstract:The Tibetan Plateau (TP) was divided into three zones based on the influence of the Asian summer monsoon and the westerlies. By comparing multiple proxy indicators in sediments with late Holocene volcanic activity, the Northern Hemisphere temperatures, and the Asian monsoon index, the reasons for the decline in plateau lake levels ~2 kaBP were explored and the spatial differences in lake responses to climate fluctuations in the different zones were analyzed. Results show that the decline in lake water level in the southwestern part of the TP is greater than in the northwestern part, and even greater in the northeastern TP. This may be due to the weakening in the intensity of the Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM), which made lakes in the southwestern TP more dependent on the ISM precipitation replenishment and thus more sensitive to the reduction in water vapor flux brought by the ISM. Moreover, during this period, the phase of the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) shifted from negative to positive, leading to the increase in water vapor convergence in the northern part of the TP with more precipitation there, while the southern part of the TP received less rainfall, resulting in a generally greater decline in water levels in the southern lakes compared to those in the north. The main cause of the climate turning to colder and drier in the TP ~2 kaBP is attributed to the intensification of El Niño. In addition, the different phases of the Southern Annular Mode in winter and summer through complex ocean-atmosphere coupling processes crossing the equator, also played a role in cooling and dehumidifying the climate of the TP.
-
Key words:
- climate change /
- Tibetan Plateau lakes /
- Indian Summer Monsoon /
- ENSO /
- NAO
-

-
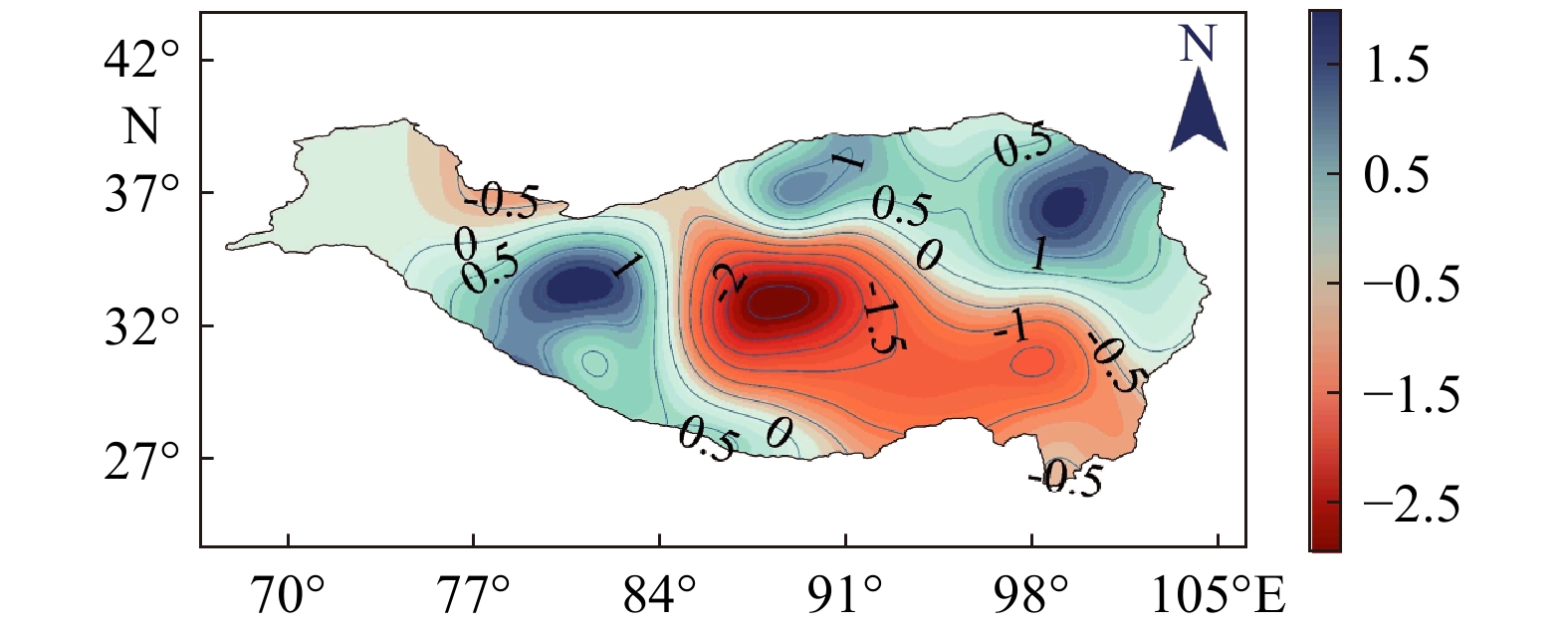
图 9 NAO和ENSO处于正位相而PDO处于负位相时高原的干湿空间分布[107]
Figure 9.
-
[1] Qiu J. China: the third pole[J]. Nature, 2008, 454(7203):393-396. doi: 10.1038/454393a
[2] Chen F H, Yu Z C, Yang M L, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3-4):351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.10.017
[3] Liu X J, Madsen D B, Liu R Y, et al. Holocene lake level variations of Longmu Co, western Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(4):301. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5188-7
[4] Liu X J, Lai Z P, Madsen D, et al. Last deglacial and Holocene lake level variations of Qinghai lake, north-eastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2015, 30(3):245-257. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2777
[5] Shi X H, Kirby E, Furlong K P, et al. Rapid and punctuated late Holocene recession of Siling Co, central Tibet[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 172:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.07.017
[6] Huang C, Yu L P, Lai Z P. Holocene millennial lake-level fluctuations of Lake Nam Co in Tibet using OSL dating of shorelines[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 618:128643. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128643
[7] Huang L, Chen Y W, Wu Y, et al. Lake level changes of Nam Co since 25 ka as revealed by OSL dating of paleo-shorelines[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2022, 70:101274. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2022.101274
[8] Ahlborn M, Haberzettl T, Wang J B, et al. Holocene lake level history of the Tangra Yumco lake system, southern-central Tibetan Plateau[J]. The Holocene, 2016, 26(2):176-187. doi: 10.1177/0959683615596840
[9] Cong L, Wang Y X, Zhang X Y, et al. Radiocarbon and luminescence dating of lacustrine sediments in Zhari Namco, southern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9:640172. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.640172
[10] Chen Y W, Zong Y Q, Li B, et al. Shrinking lakes in Tibet linked to the weakening Asian monsoon in the past 8.2 ka[J]. Quaternary Research, 2013, 80(2):189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.06.008
[11] Liu X J, Madsen D, Zhang X J. The driving forces underlying spatiotemporal lake extent changes in the inner Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9:685928. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.685928
[12] 丛禄, 王懿萱, 孙爱军, 等. 青藏高原中部当穹错末次冰消期以来湖面变化研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(6):1619-1631 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.06.10
CONG Lu, WANG Yixuan, SUN Aijun, et al. Lake level variations of Tanqung Co since last deglaciation, central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(6):1619-1631.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.06.10
[13] 丛禄. 青藏高原全新世湖泊演化与其湖岸风成沉积物相关性研究[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院青海盐湖研究所)博士学位论文, 2021
CONG Lu. The research of correlation relationship between evolution of typical lakes and lakeside's aeolian sediments within Tibetan Plateau[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021.]
[14] Herzschuh U. Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50, 000 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1-2):163-178. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.02.006
[15] Herzschuh U, Mischke S, Meyer H, et al. Using variations in the stable carbon isotope composition of macrophyte remains to quantify nutrient dynamics in lakes[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2010, 43(4):739-750. doi: 10.1007/s10933-009-9365-0
[16] Cane M A. The evolution of El Niño, past and future[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 230(3-4):227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.12.003
[17] Clement A C, Seager R, Cane M A. Suppression of El Niño during the mid-Holocene by changes in the Earth's orbit[J]. Paleoceanography, 2000, 15(6):731-737. doi: 10.1029/1999PA000466
[18] Li C G, Wang M D, Liu W G, et al. Quantitative estimates of Holocene glacier meltwater variations on the Western Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 559:116766. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2021.116766
[19] Gasse F, Fontes J C, Van Campo E, et al. Holocene environmental changes in Bangong Co basin (Western Tibet). Part 4: discussion and conclusions[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1996, 120(1-2):79-92. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(95)00035-6
[20] Zhang Y Z, Zhang J W, McGowan S, et al. Climatic and environmental change in the western Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene, recorded by lake sediments from Aweng Co[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 259:106889. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.106889
[21] Mishra P K, Prasad S, Anoop A, et al. Carbonate isotopes from high altitude Tso Moriri Lake (NW Himalayas) provide clues to late glacial and Holocene moisture source and atmospheric circulation changes[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 425:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.02.031
[22] Yan D D, Wünnemann B. Late Quaternary water depth changes in Hala Lake, northeastern Tibetan Plateau, derived from ostracod assemblages and sediment properties in multiple sediment records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 95:95-114. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.04.030
[23] Zhang W Y, Mischke S, Hosner D, et al. Late glacial and Holocene climate in the Kunlun Pass region (northern Tibetan Plateau) inferred from a multi-proxy lake record[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 643:46-60. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2022.10.013
[24] Wünnemann B, Yan D D, Andersen N, et al. A 14 ka high-resolution δ18O lake record reveals a paradigm shift for the process-based reconstruction of hydroclimate on the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 200:65-84. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.09.040
[25] 李友谟, 吴铎, 袁子杰, 等. 青藏高原腹地班德湖记录的全新世夏季风变化与流域环境响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(5):1328-1348
LI Youmo, WU Duo, YUAN Zijie, et al. Holocene summer monsoon variation and environmental response in the drainage basin of Lake Bande in the inner Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2022, 42(5):1328-1348.]
[26] Bird B W, Lei Y B, Perello M, et al. Late-Holocene Indian summer monsoon variability revealed from a 3300-year-long lake sediment record from Nir’pa Co, southeastern Tibet[J]. The Holocene, 2017, 27(4):541-552. doi: 10.1177/0959683616670220
[27] Feng X P, Zhao C, D'Andrea W J, et al. Evidence for a relatively warm mid-to late holocene on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(15):e2022GL098740. doi: 10.1029/2022GL098740
[28] 赵光通, 都永生, 魏海成, 等. 班戈错盐湖古湖岸堤石英光释光年代学及其古环境指示意义研究[J]. 盐湖研究, 2018, 26(3):26-34
ZHAO Guangtong, DU Yongsheng, WEI Haicheng, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of paleo-shorelines of bange Co, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its implications for palaeo-environment[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2018, 26(3):26-34.]
[29] Herzschuh U, Winter K, Wünnemann B, et al. A general cooling trend on the central Tibetan Plateau throughout the Holocene recorded by the Lake Zigetang pollen spectra[J]. Quaternary International, 2006, 154-155:113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2006.02.005
[30] 黄凌昕, 陈婕, 阳坤, 等. 现代青藏高原亚洲夏季风气候北界及其西风区和季风区划分[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2023, 53(4): 866-678
HUANG Lingxin, CHEN Jie, YANG Kun, et al. The northern boundary of the Asian summer monsoon and division of westerlies and monsoon regimes over the Tibetan Plateau in present-day[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2023, 66(4): 882-893.]
[31] 张镱锂, 李炳元, 刘林山, 等. 再论青藏高原范围[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(6):1543-1553
ZHANG Yili, LI Bingyuan, LIU Linshan, et al. Redetermine the region and boundaries of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(6):1543-1553.]
[32] Gomez B, Carter L, Orpin A R, et al. ENSO/SAM interactions during the middle and late Holocene[J]. The Holocene, 2012, 22(1):23-30. doi: 10.1177/0959683611405241
[33] Qiao B J, Zhu L P, Yang R M. Temporal-spatial differences in lake water storage changes and their links to climate change throughout the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 222:232-243. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.12.037
[34] Yu W S, Ma Y M, Sun W Z, et al. Climatic significance of δ18O records from precipitation on the western Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(16):2732-2741. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0495-6
[35] Gasse F, Arnold M, Fontes J C, et al. A 13, 000-year climate record from western Tibet[J]. Nature, 1991, 353(6346):742-745. doi: 10.1038/353742a0
[36] Thompson L G, Severinghaus J P, Yao T D, et al. Use of δ18Oatm in dating a Tibetan ice core record of Holocene/Late Glacial climate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(45):e2205545119.
[37] Wu D, Ma X Y, Yuan Z J, et al. Holocene hydroclimatic variations on the Tibetan Plateau: an isotopic perspective[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 233:104169. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104169
[38] Quade J, Broecker W S. Dryland hydrology in a warmer world: lessons from the Last Glacial period[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2009, 176(1):21-36. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2009-01146-y
[39] Rades E F, Tsukamoto S, Frechen M, et al. A lake-level chronology based on feldspar luminescence dating of beach ridges at Tangra Yum Co (southern Tibet)[J]. Quaternary Research, 2015, 83(3):469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2015.03.002
[40] Rades E F, Hetzel R, Xu Q, et al. Constraining Holocene lake-level highstands on the Tibetan Plateau by 10Be exposure dating: a case study at Tangra Yumco, southern Tibet[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 82:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.09.016
[41] 郑度, 李炳元. 青藏高原自然地理研究的进展[J]. 地理学报, 1990, 45(2):235-244
ZHENG Du, LI Bingyuan. Recent progress of geographical studies on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1990, 45(2):235-244.]
[42] Hou S G, Zhang W B, Pang H X, et al. Apparent discrepancy of Tibetan ice core δ18O records may be attributed to misinterpretation of chronology[J]. The Cryosphere, 2019, 13(6):1743-1752. doi: 10.5194/tc-13-1743-2019
[43] 俞鸣同, 林振山, 杜建丽, 等. 格陵兰冰芯氧同位素显示近千年气候变化的多尺度分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2009, 31(6):1037-1042
YU Mingtong, LIN Zhenshan, DU Jianli, et al. Multi-scale analysis of the last millennium climate variations in Greenland derived from ice core oxygen isotope[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2009, 31(6):1037-1042.]
[44] 威廉斯, Dunkerley D L, De Deckker P, 等. 第四纪环境[M]. 刘东生, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997
Williams M A J, Dunkerley D L, De Deckker P, et al. Quaternary Environments[M]. LIU Dongsheng, trans. Beijing: Science Press, 1997.]
[45] Yang B, Qin C, Bräuning A, et al. Long-term decrease in Asian monsoon rainfall and abrupt climate change events over the past 6, 700 years[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(30):e2102007118.
[46] Shen J, Liu X Q, Wang S M, et al. Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18, 000 years[J]. Quaternary International, 2005, 136(1):131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2004.11.014
[47] Hou J Z, Huang Y S, Zhao J T, et al. Large Holocene summer temperature oscillations and impact on the peopling of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(3):1323-1330. doi: 10.1002/2015GL067317
[48] Kasper T, Wang J B, Schwalb A, et al. Precipitation dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau during the Late Quaternary – Hydroclimatic sedimentary proxies versus lake level variability[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2021, 205:103594. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2021.103594
[49] Doberschütz S, Frenzel P, Haberzettl T, et al. Monsoonal forcing of Holocene paleoenvironmental change on the central Tibetan Plateau inferred using a sediment record from Lake Nam Co (Xizang, China)[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2014, 51(2):253-266. doi: 10.1007/s10933-013-9702-1
[50] Kylander M E, Ampel L, Wohlfarth B, et al. High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning analysis of Les Echets (France) sedimentary sequence: new insights from chemical proxies[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2011, 26(1):109-117. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1438
[51] Gyawali A R, Wang J B, Ma Q F, et al. Paleo-environmental change since the Late Glacial inferred from lacustrine sediment in Selin Co, central Tibet[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 516:101-112. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.11.033
[52] Gu Z Y, Liu J Q, Yuan B Y, et al. Monsoon variations of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau during the last 12, 000 years: geochemical evidence from the sediments in the Siling Lake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1993, 38(7):577-581. doi: 10.1360/csb1993-38-7-577
[53] Yao T D, Masson-Delmotte V, Gao J, et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: observations and simulations[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2013, 51(4):525-548. doi: 10.1002/rog.20023
[54] Chen F H, Zhang J F, Liu J B, et al. Climate change, vegetation history, and landscape responses on the Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene: a comprehensive review[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 243:106444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106444
[55] Pang H X, Hou S G, Zhang W B, et al. Temperature trends in the northwestern Tibetan Plateau constrained by ice core water isotopes over the past 7, 000 years[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2020, 125(19):e2020JD032560. doi: 10.1029/2020JD032560
[56] Lang T J, Barros A P. Winter storms in the central Himalayas[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. II, 2004, 82(3):829-844. doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2004.829
[57] Pang H, Hou S, Kaspari S, et al. Influence of regional precipitation patterns on stable isotopes in ice cores from the central Himalayas[J]. The Cryosphere, 2014, 8(1):289-301. doi: 10.5194/tc-8-289-2014
[58] Feng L, Zhou T J. Water vapor transport for summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: multidata set analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2012, 117(D20):D20114.
[59] Zhang X J, Jin L Y, Jia W N. Centennial-scale teleconnection between North Atlantic sea surface temperatures and the Indian summer monsoon during the Holocene[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 46(9):3323-3336.
[60] Grossmann I, Klotzbach P J. A review of North Atlantic modes of natural variability and their driving mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2009, 114(D24):D24107.
[61] Knight J R, Folland C K, Scaife A A. Climate impacts of the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(17):L17706.
[62] Li S L, Bates G T. Influence of the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation on the winter climate of East China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 24(1):126-135. doi: 10.1007/s00376-007-0126-6
[63] 刘焕才, 段克勤. 北大西洋涛动对青藏高原夏季降水的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2012, 34(2):311-318
LIU Huancai, DUAN Keqin. Effects of North Atlantic Oscillation on summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2012, 34(2):311-318.]
[64] Overpeck J, Anderson D, Trumbore S, et al. The southwest Indian Monsoon over the last 18 000 years[J]. Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12(3):213-225. doi: 10.1007/BF00211619
[65] Wang C Z, Deser C, Yu J Y, et al. El Niño and southern oscillation (ENSO): a review[M]//Glynn P W, Manzello D P, Enochs I C. Coral Reefs of the Eastern Tropical Pacific: Persistence and Loss in a Dynamic Environment. Dordrecht: Springer, 2017: 85-106.
[66] Srivastava G, Chakraborty A, Nanjundiah R S. Multidecadal variations in ENSO-Indian summer monsoon relationship at sub-seasonal timescales[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2020, 140(3):1299-1314.
[67] Lin S H, Yang S, He S, et al. Atmospheric–oceanic processes over the Pacific involved in the effects of the Indian summer monsoon on ENSO[J]. Journal of Climate, 2023, 36(17):6021-6043. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-22-0822.1
[68] Brown J R, Hope P, Gergis J, et al. ENSO teleconnections with Australian rainfall in coupled model simulations of the last millennium[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 47(1):79-93.
[69] Conroy J L, Overpeck J T, Cole J E, et al. Holocene changes in eastern tropical Pacific climate inferred from a Galápagos lake sediment record[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(11-12):1166-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.02.015
[70] Moy C M, Seltzer G O, Rodbell D T, et al. Variability of El Niño/Southern Oscillation activity at millennial timescales during the Holocene epoch[J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6912):162-165. doi: 10.1038/nature01194
[71] Saji N H, Goswami B N, Vinayachandran P N, et al. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean[J]. Nature, 1999, 401(6751):360-363.
[72] Zinke J, Pfeiffer M, Park W, et al. Seychelles coral record of changes in sea surface temperature bimodality in the western Indian Ocean from the Mid-Holocene to the present[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2014, 43(3-4):689-708. doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2082-z
[73] Zinke J, Rountrey A, Feng M, et al. Corals record long-term Leeuwin current variability including Ningaloo Niño/Niña since 1795[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1):3607. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4607
[74] Stuecker M F, Timmermann A, Jin F F, et al. Revisiting ENSO/Indian Ocean dipole phase relationships[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(5):2481-2492. doi: 10.1002/2016GL072308
[75] Hong C C, Li T, LinHo, et al. Asymmetry of the Indian Ocean Dipole. Part I: observational analysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 2008, 21(18):4834-4848. doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2222.1
[76] Cai W J, Zheng X T, Weller E, et al. Projected response of the Indian Ocean Dipole to greenhouse warming[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(12):999-1007. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2009
[77] 黄怡陶, 张文君, 薛奥运. ENSO对印度洋偶极子非对称性的影响及机制研究[J]. 气象科学, 2023, 43(1):1-14
HUANG Yitao, ZHANG Wenjun, XUE Aoyun. Influence of ENSO on Indian Ocean Dipole skewness and its physical mechanism[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2023, 43(1):1-14.]
[78] Haug G H, Hughen K A, Sigman D M, et al. Southward migration of the intertropical convergence zone through the Holocene[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5533):1304-1308. doi: 10.1126/science.1059725
[79] Schneider T, Bischoff T, Haug G H. Migrations and dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516):45-53. doi: 10.1038/nature13636
[80] Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1-2):71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.01.036
[81] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723):854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296
[82] Mamalakis A, Randerson J T, Yu J Y, et al. Zonally contrasting shifts of the tropical rain belt in response to climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11(2):143-151. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00963-x
[83] Marcott S A, Shakun J D, Clark P U, et al. A reconstruction of regional and global temperature for the past 11, 300 years[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6124):1198-1201. doi: 10.1126/science.1228026
[84] Moreno P I, Vilanova I, Villa-Martínez R, et al. Onset and evolution of southern annular mode-like changes at centennial timescale[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):3458. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21836-6
[85] Kobashi T, Menviel L, Jeltsch-Thömmes A, et al. Volcanic influence on centennial to millennial Holocene Greenland temperature change[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):1441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01451-7
[86] Thompson D W J, Wallace J M. Annular modes in the extratropical circulation. Part I: month-to-month variability[J]. Journal of Climate, 2000, 13(5):1000-1016. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1000:AMITEC>2.0.CO;2
[87] 郑菲, 李建平, 刘婷. 南半球环状模气候影响的若干研究进展[J]. 气象学报, 2014, 72(5):926-939
ZHENG Fei, LI Jianping, LIU Ting. Some advances in studies of the climatic impacts of the Southern Hemisphere annular mode[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2014, 72(5):926-939.]
[88] 豆娟. 南半球环状模对青藏高原及周边气候的可能影响[D]. 南京信息工程大学博士学位论文, 2019
DOU Juan. Possible influence of the Southern Hemiphere annular mode on the climate over the Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2019.]
[89] Zheng F, Li J P, Ding R Q. Influence of the preceding austral summer Southern Hemisphere annular mode on the amplitude of ENSO decay[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 34(11):1358-1379. doi: 10.1007/s00376-017-6339-4
[90] Silvestri G, Berman A L, Braconnot P, et al. Long-term trends in the Southern Annular Mode from transient Mid- to Late Holocene simulation with the IPSL-CM5A2 climate model[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2022, 59(3-4):903-914. doi: 10.1007/s00382-022-06160-0
[91] Barnett T P, Dümenil L, Schlese U, et al. The effect of Eurasian snow cover on global climate[J]. Science, 1988, 239(4839):504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.239.4839.504
[92] Yasunari T, Kitoh A, Tokioka T. Local and remote responses to excessive snow mass over Eurasia appearing in the northern spring and summer climate[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. II, 1991, 69(4):473-487. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.69.4_473
[93] Hall A, Visbeck M. Synchronous variability in the Southern Hemisphere atmosphere, sea ice, and ocean resulting from the annular mode[J]. Journal of Climate, 2002, 15(21):3043-3057. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<3043:SVITSH>2.0.CO;2
[94] Lefebvre W, Goosse H, Timmermann R, et al. Influence of the Southern Annular Mode on the sea ice–ocean system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2004, 109(C9):C09005.
[95] Zhang Y Z, Li J P, Zhao S, et al. Indian Ocean tripole mode and its associated atmospheric and oceanic processes[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55(5-6):1367-1383. doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05331-1
[96] Gill A E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1980, 106(449):447-462.
[97] Hoskins B J, Simmons A J, Andrews D G. Energy dispersion in a barotropic atmosphere[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1977, 103(438):553-567. doi: 10.1002/qj.49710343802
[98] Hoskins B J, Karoly D J. The steady linear response of a spherical atmosphere to thermal and orographic forcing[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1981, 38(6):1179-1196. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1981)038<1179:TSLROA>2.0.CO;2
[99] Karoly D J. Southern hemisphere circulation features associated with El Niño-Southern Oscillation events[J]. Journal of Climate, 1989, 2(11):1239-1252. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1989)002<1239:SHCFAW>2.0.CO;2
[100] Li L, Nathan T R. Effects of low-frequency tropical forcing on intraseasonal tropical–extratropical interactions[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1997, 54(2):332-346. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1997)054<0332:EOLFTF>2.0.CO;2
[101] Dou J, Wu Z W. Southern Hemisphere origins for interannual variations of snow cover over the western Tibetan Plateau in boreal summer[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31(19):7701-7718. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0327.1
[102] Xiao M Z, Zhang Q, Singh V P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35(12):3556-3567. doi: 10.1002/joc.4228
[103] Wang L, Chen W, Huang R H. Interdecadal modulation of PDO on the impact of ENSO on the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(20):L20702.
[104] Sung M K, Kwon W T, Baek H J, et al. A possible impact of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the east Asian summer monsoon precipitation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(21):L21713.
[105] Olsen J, Anderson N J, Knudsen M F. Variability of the North Atlantic Oscillation over the past 5, 200 years[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(11):808-812. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1589
[106] Chen C Z, Zhao W W, Zhang X J. Pacific Decadal Oscillation-like variability at a millennial timescale during the Holocene[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2021, 199:103448. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2021.103448
[107] Wang J L, Yang B, Qin C, et al. Spatial patterns of moisture variations across the Tibetan Plateau during the past 700 years and their relationship with Atmospheric Oscillation modes[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2014, 34(3):728-741. doi: 10.1002/joc.3715
-




 下载:
下载: