Assessment of water level threshold for groundwater restoration and over-exploitation remediation the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain
-
Abstract:
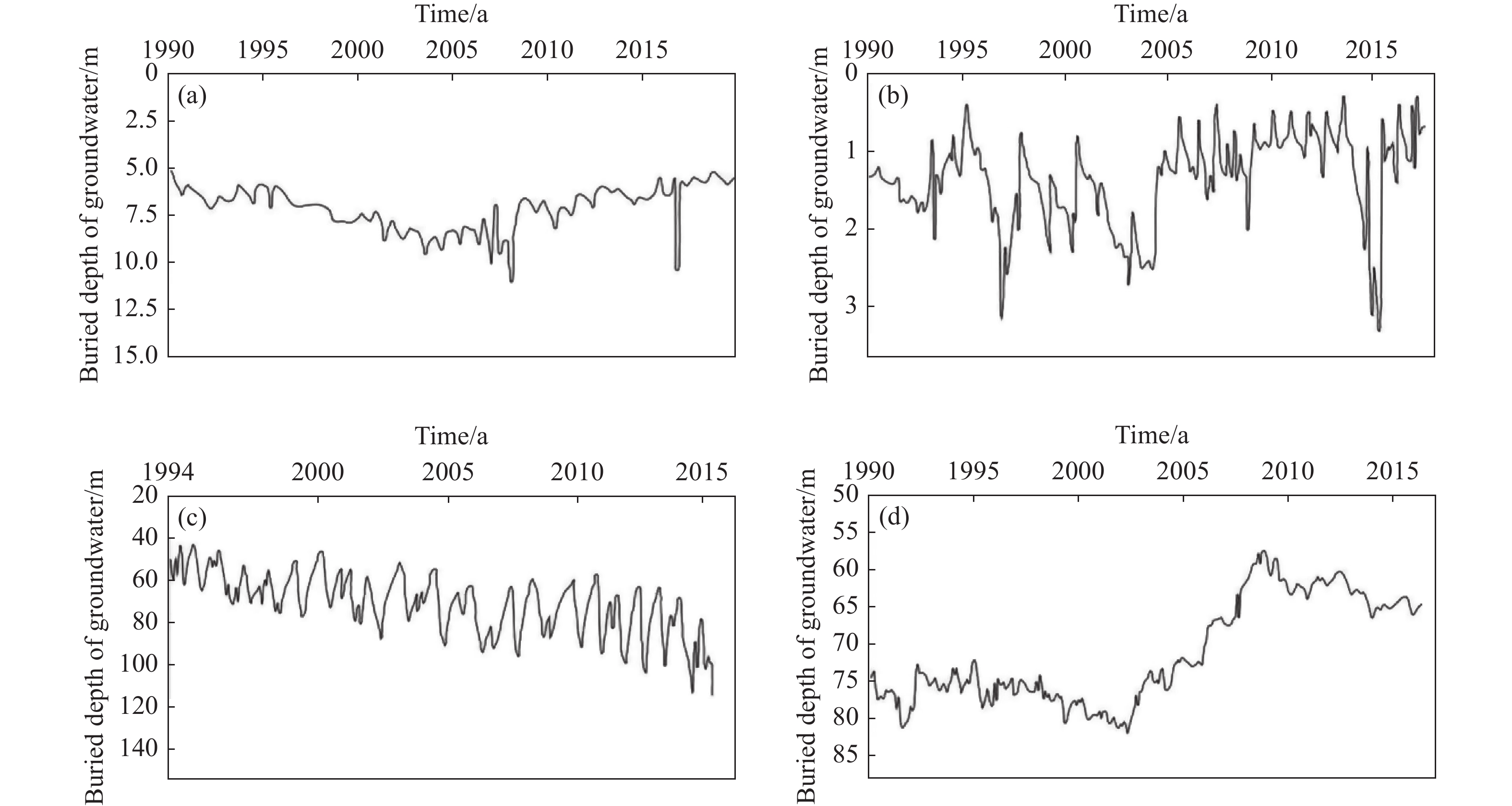
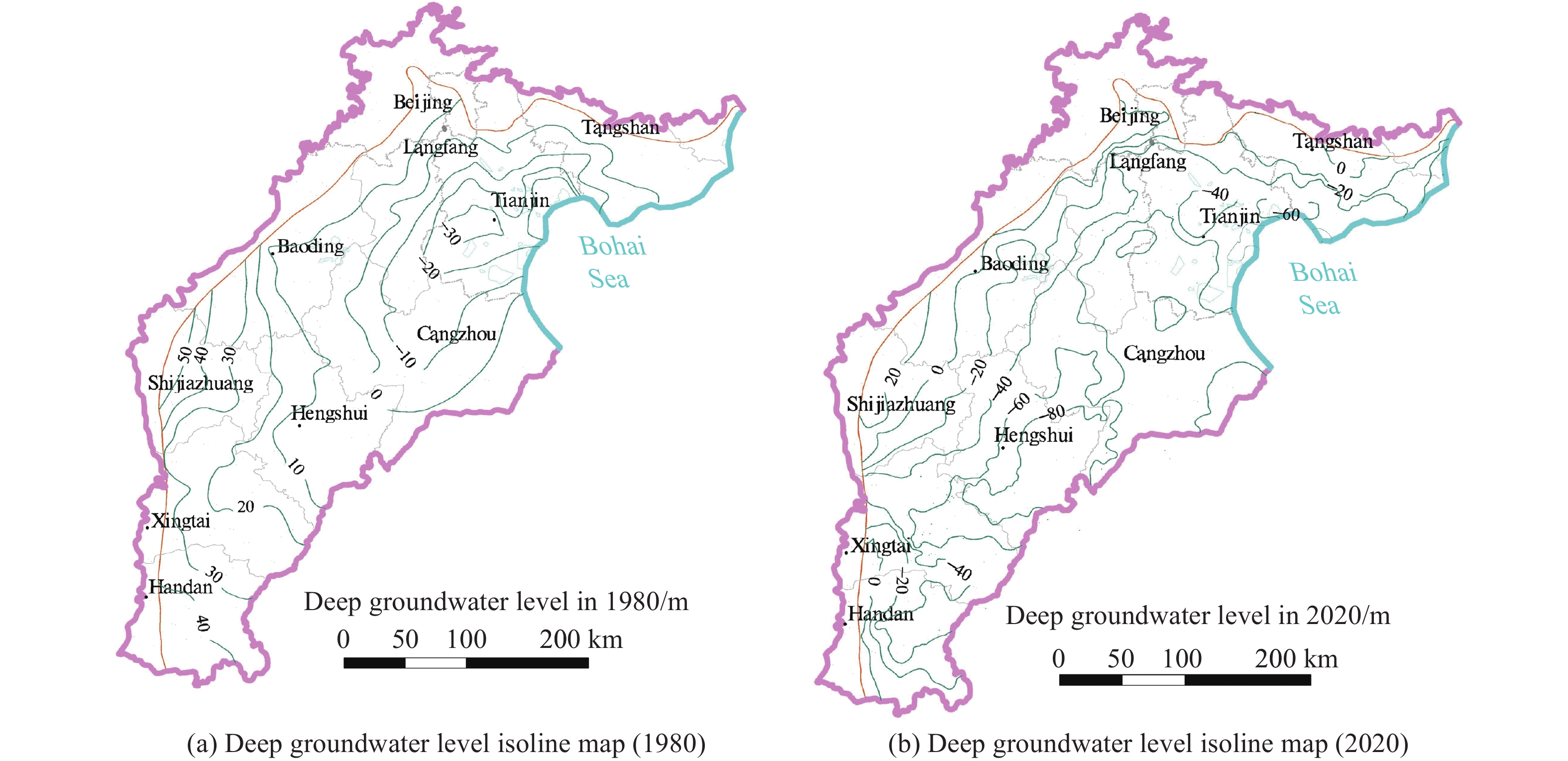
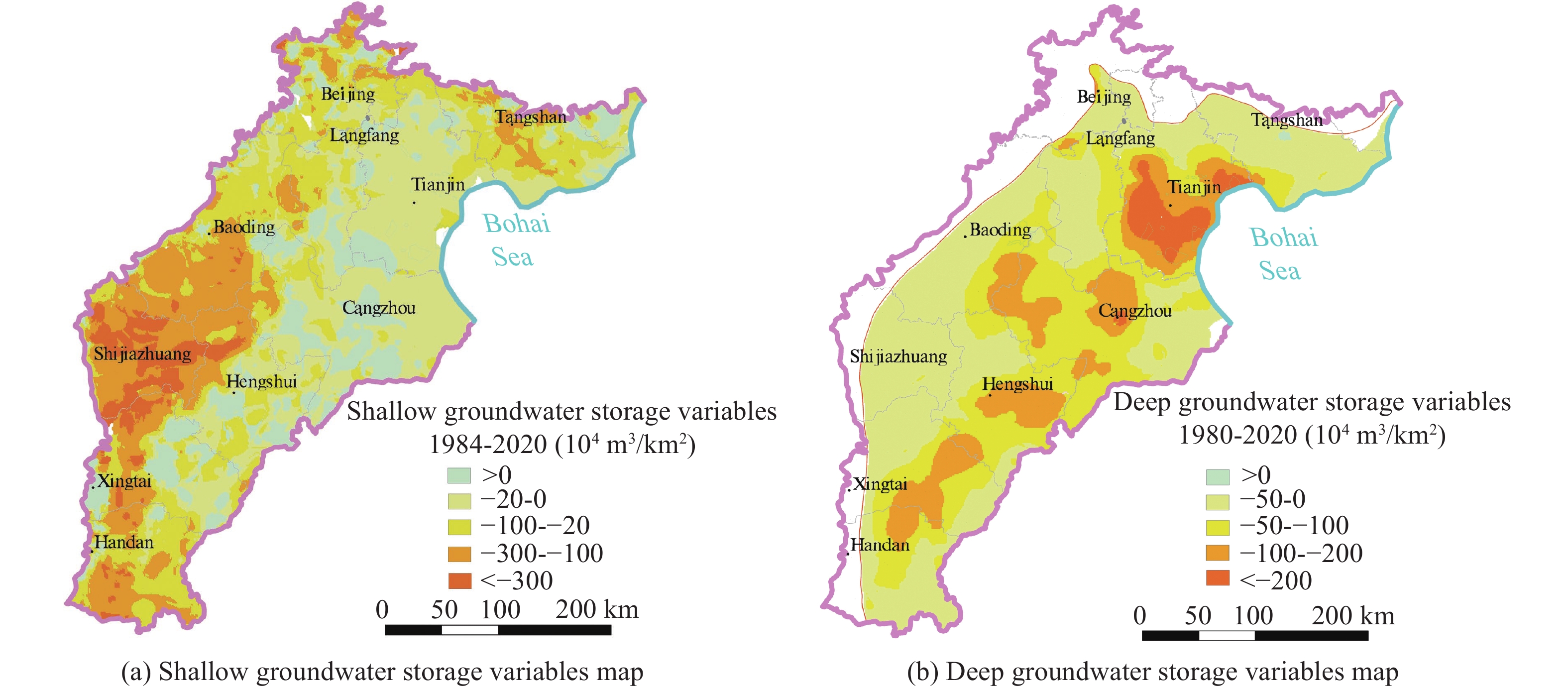
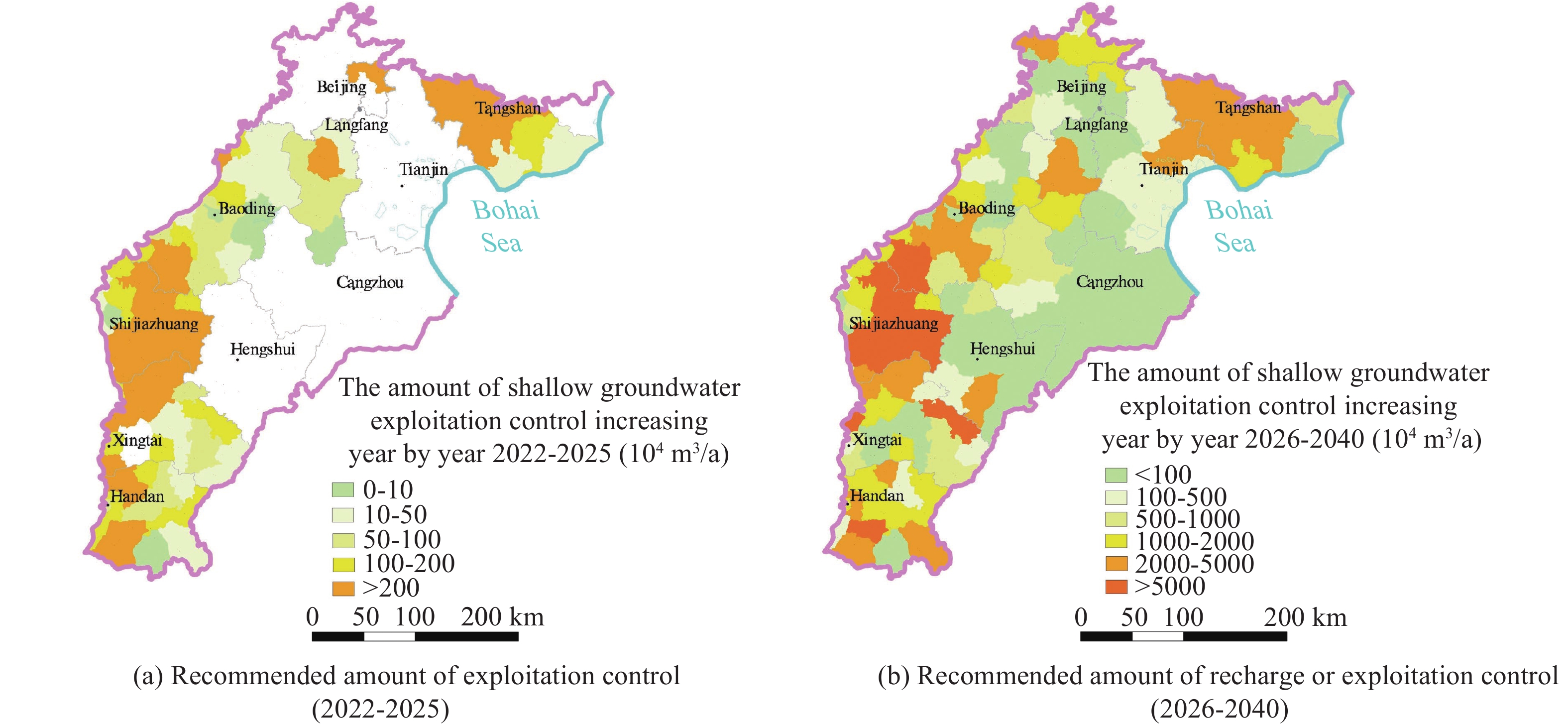
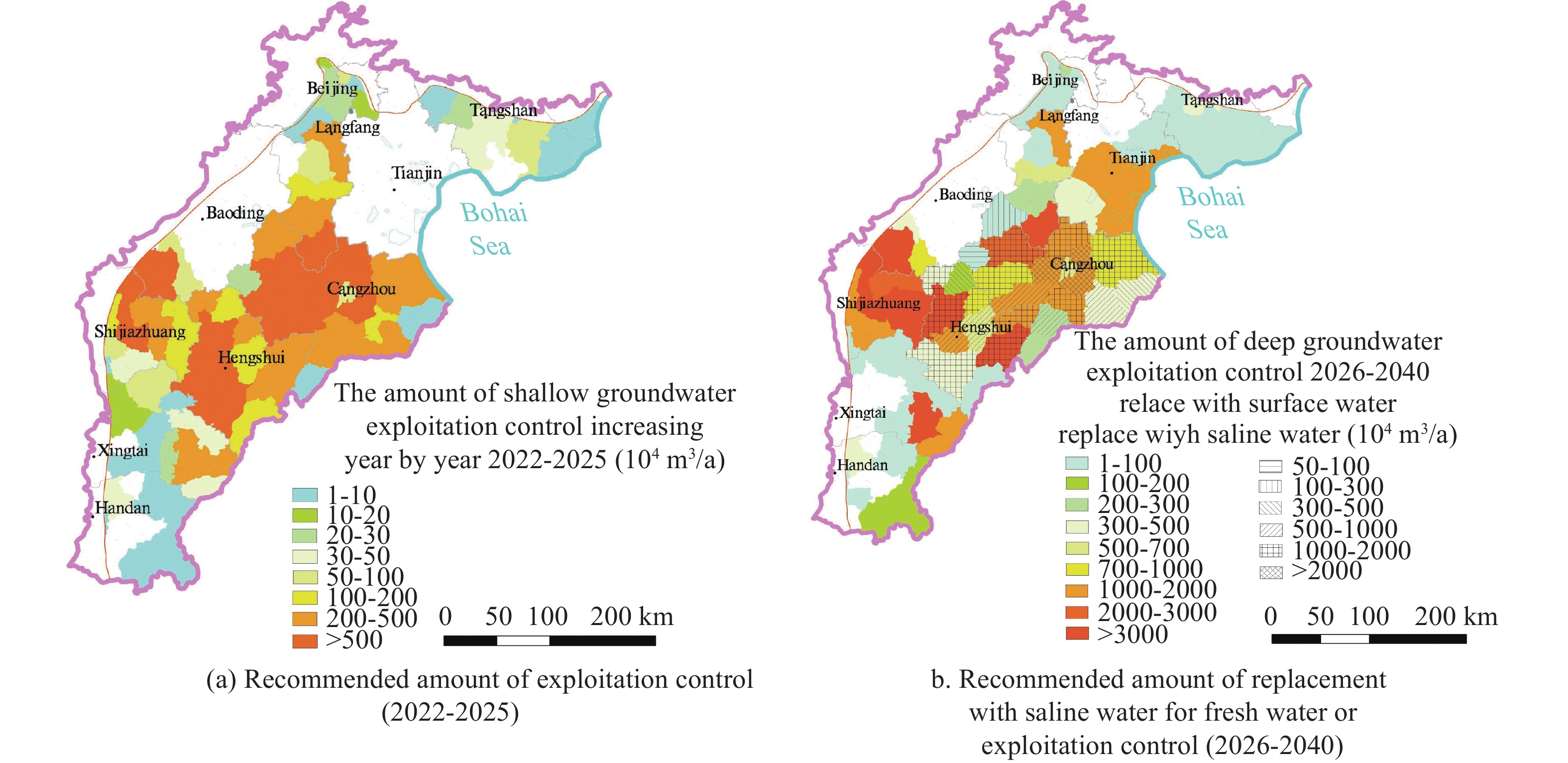
The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain (BTHP) is the political, economic and cultural center of China, where groundwater is the main source of water supply to support social and economic development. Continuous overdraft of the resources has caused a persistent decline of groundwater level and formed a huge cone of depression at a regional scale. This paper addresses current groundwater situation over the BTHP area. The paper also delineates the groundwater flow field, using groundwater level data, in order to provide an effective method for the restoration of groundwater level and associated water resources management. Based on the analysis of multiple factors, such as groundwater level, soil salinization, ground subsidence, groundwater recharge and storage, urban underground space security, formation of fractures, and seawater intrusion, the threshold for groundwater level restoration is defined, and some measures for groundwater over-exploitation management are accordingly proposed. The study shows that: (i) Since the 1980s to 2020, shallow groundwater level in the western part of the BTHP area has dropped by 25 m to 60 m, while the cumulative decline of deep groundwater in the central and eastern regions is in the range of 40–80 m; (ii) The water table of the shallow groundwater within the depression zone over the Western Piedmont Plain should be controlled in the range of 15–30 m below ground level (mbgl), while the depth of groundwater level in large and medium-sized urban areas should be controlled within 20–30 mbgl. The groundwater level in the resource preservation area should be controlled within 10–15 mbgl, and the groundwater level in the area with identified soil salinization in the central and eastern plain should be controlled within 3–10 mbgl. However, for the deep groundwater in the central and eastern plainwater, the main focus of the resources management is to control the land subsidence. The water level in the severe land subsidence area should be controlled within 45–60 mbgl, and in the general subsidence area should be controlled within 30–45 mbgl; (iii) Based on the water level recovery threshold and proposed groundwater overdraft management program, if the balance of abstraction and recharge is reached in 2025, the shallow groundwater abstraction needs to be gradually reduced by about 2×108 m3. Meanwhile, the ecological water replenishment of rivers through the South-to-North Water Transfer Project should be increased to 28.58×108 m3/a, and the deep groundwater abstraction needs to be gradually reduced by 2.24×108 m3. To reach the target of shallow groundwater level in 2040, surface water replacement is recommended with a rate of 25.77×108 m3/a and the ecological water replenishment of rivers in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project should reach 33.51×108 m3/a. For deep groundwater recovery, it is recommended to replace the deep freshwater extraction with the utilization of shallow salt water by 2.82×108 m3 , in addition to the amount of 7.86×108 m3 by water diversion. The results are of great significance to the remediation of groundwater over-exploitation, the regulation of water resources development and utilization, and ecological protection in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei plain.
-

-
Table 1. Groundwater level recovery threshold index system
Groundwater level Geomorphological unit Element Target water level depth (mbgl) Shallow layer Mountain front plain Impact of large-scale exploitation on groundwater Water level buried depth in the 1980s Groundwater level recovery in the drop funnel area Water level buried depth in the 1980s Safety of underground space utilization in large and medium-sized cities 20–30 Beneficial to infiltration and recharge of precipitation and groundwater regulation and storage 10–15 Ground fissure prevention and control 7-10 Central East
PlainSoil salinization prevention and control 3–4 Ground fissure prevention and control 4-7 Ecological water level of major wetlands 3–4 Seawater intrusion prevention and control 0–1 Deep layer / Impact of large-scale exploitation on groundwater Water level buried depth in the 1980s Land subsidence prevention and control Severe subsidence area, water level buried depth 45–60 m General subsidence area, water level buried depth 30–45 m Funnel area where land subsidence has not yet occurred Water level buried depth in the 1980s -
Chen F, Ding YY, Li YY, et al. 2020. Practice and consideration of groundwater over-exploitation in North China. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology, 18(02): 191-198. (in Chinese)
Chen SM, Liu FT, Zhang Z, et al. 2021. Changes of groundwater flow field of Luanhe River Delta under the human activities and its impact on the ecological environment in the past 30 years. China Geology, 4: 455-462. doi: 10.31035/cg2021060
Dong KG, Xu M, Yu Q, et al. 2010. Threshold of groundwater over-exploitation and conservation-restoration in Tianjin Land Subsidence Area. Groundwater, 32(01): 30-33. (in Chinese)
Fei YH, Zhang ZJ, Li YS, et al. 2015. Quality evaluation of groundwater in the North China Plain. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 3(04): 306-315.
Feng HM, Zhang GH, Wang DL, et al. 2014. Analysis on driving force for groundwater flow field evolution in Shijiazhuang Area in recent 50 years. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 45(02): 180-186. (in Chinese)
Guo HP, Bai JB, Zhang YQ, et al. 2017. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain. Geology in China, 44(6): 1115-1127. (in Chinese)
Hu LT, Guo JL, Zhang SQ, et al. 2020. Response of groundwater regime to ecological water replenishment of the Yongding River. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(5): 5-11. (in Chinese)
Jiang Y, Tian F, Luo Y, et al. 2015. Groundwater control target under different threshold of land subsidence in Beijing. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 26(01): 37-42. (in Chinese)
Li W, Zhong HP, Bian JY. 2010. Study on the delimitation of water level protection targets in the deep water table drop area of North China. Zhejiang Ningbo: China. (in Chinese)
Li WP, Wang LF, Yang HF, et al. 2020. Over-extraction of groundwater in the North China Plain and suggestions for treatment. China Water Resources, (13): 26-30. (in Chinese)
Li X, Ye SY, Song F, et al. 2018. Quantitative identification of major factors affecting groundwater change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Journal of China Hydrology, 38(01): 21-27. (in Chinese)
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhou PP, et al. 2017. Dynamics and evolution of the groundwater in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain in a long time scale. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 31(03): 164-170. (in Chinese)
Li YS, Zhang FW, Han ZT, et al. 2014. Evolution characteristics and influence factors of deep groundwater depression cone in North China Plain, China — A case study in Cangzhou Region. Journal of Earth Science (Wuhan, China), 25(6): 1051-1058.
Liu CM, Yu JJ, Kendy E. 2001. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China Plain. Water International, 26(2): 265-272. doi: 10.1080/02508060108686913
Liu JX, Wang D, Sun HL, et al. 2016. On the construction of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region groundwater pollution prevention and control system. Environmental Protection, 44(09): 47-50. (in Chinese)
Liu M, Nie ZL, Wang JZ, et al. 2016. An assessment of the carrying capacity of groundwater resources in North China Plain region — Analysis of potential for development. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 4(3): 174-187.
Ma XL, Meng JS, Fu DP. 2020. Comparison study on the method of groundwater control water level division in the typical area of central North China Plain. Groundwater, 42(01): 59-62. (in Chinese)
Shi JS, Wang Z, Zhang ZJ, et al. 2010. Assessment of over-exploitation of deep groundwater in the North China Plain. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(06): 215-220. (in Chinese)
Shi JS, Wang Z, Zhang ZJ, et al. 2011. Assessment of deep groundwater over-exploitation in the North China Plain, Earth Science Frontiers, 2(4): 593-598. (in Chinese)
Wang GL, Wang WL, Zhang W, et al. 2020. The status quo and prospect of geothermal resources exploration and development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. China Geology, 3: 173-181. doi: 10.31035/cg2020013
Wang SQ, Song XF, Wang QX, et al. 2012. Shallow groundwater dynamics and origin of salinity at two sites in salinated and water-deficient region of North China Plain, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66(03): 729-739.
Wang XY, Fei YH. 2014. Environmental effect caused by over-exploitation of deep groundwater in North China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, (01): 12-20.
Wei L, Yang GL, Lu CP, et al. 2019. Analysis of buried depth variation and controlling factors of shallow groundwater over-exploited areas in North China Plain. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 30(06): 39-44. (in Chinese)
Xie XM, Chai FX, Yan Y, et al. 2007. Preliminary study on critical depth of ground water table. Groundwater(06): 47-50. (in Chinese)
Xu GM, Liu LJ, Fei YH, et al. 2009. Research on the adjustment of groundwater storage in North China Plain. Resources Science, 31(03): 375-381. (in Chinese)
Xu GM, Qi JF, Bi P, et al. 2015. Distribution and evolution features of salinized soil in Hebei Plain. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 3(01): 21-29.
Yang HF, Cao WG, Zhi CS, et al. 2021a. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on its overexploitation treatment. Geology in China, 48(4): 1142-1155. (in Chinese)
Yang HF, Meng RF, Li WP, et al. 2021b. Groundwater resources of the Haihe River Basin and its development potential. Geology in China, 48(4): 1032-1051. (in Chinese)
Yu LL, Ling MH, Chen F, et al. 2020. Practices of groundwater over-exploitation control in Hebei Province. Water Policy, 22(04): 591-601. doi: 10.2166/wp.2020.183
Zhao H, Chen WF, Cui YL. 2010. Control function of groundwater table on the environment of typical areas in China and the study of thresholds. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(06): 159-165. (in Chinese)
Zhao K, Qi JX, Chen Y, et al. 2021. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater and pore-water and the paleo-environmental evolution in the past 3.10 Ma in the Xiong’an New Area, North China. China Geology, 4: 476-486. doi: 10.31035/cg2021058
Zhao Y, Wang LZ, Li HH. 2020. Evaluation of groundwater overdraft governance measures in Hengshui City, China. Sustainability, 12(09): 3564. doi: 10.3390/su12093564
Zhang ZJ. 2009. Investigation and evaluation of sustainable utilization of groundwater in North China Plain. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
Zhu JS, Wang Z, Li ZP. 2020. Research on early warning of groundwater level in the over-exploitation control area in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Water Resources Planning and Design, (09): 13-15. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: