Detrital zircon U-Pb chronology and geological significance of the Middle Jurassic Quesang Hot Spring Formation in Linzhou Basin, Xizang
-
摘要:
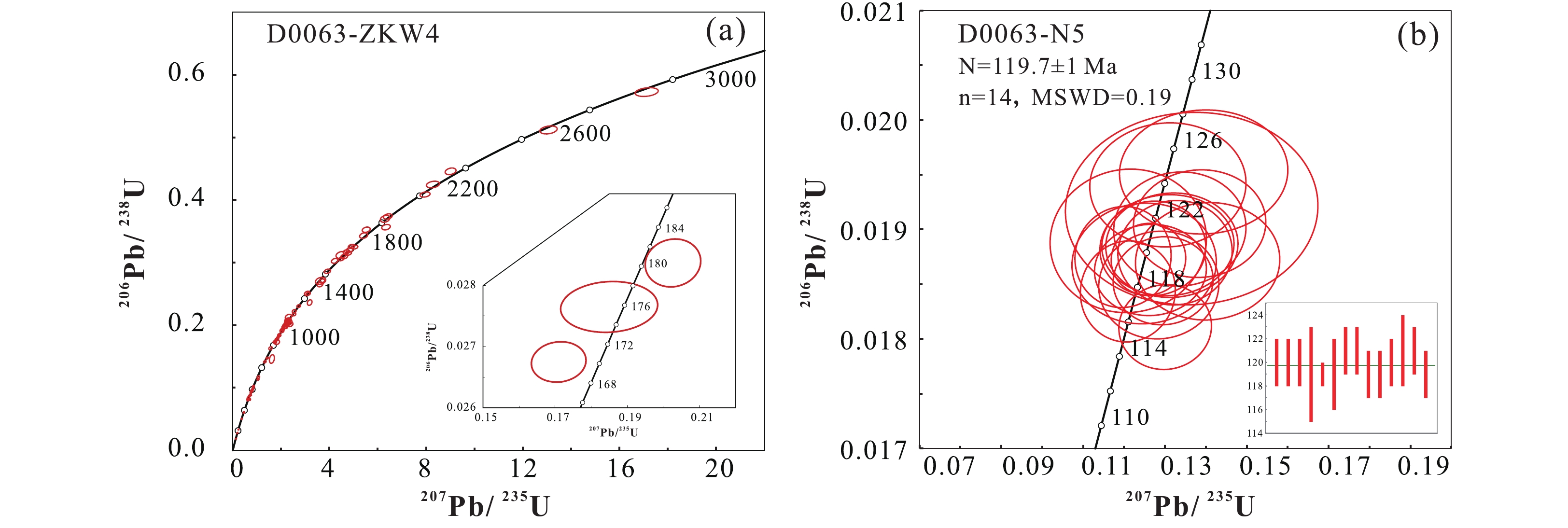
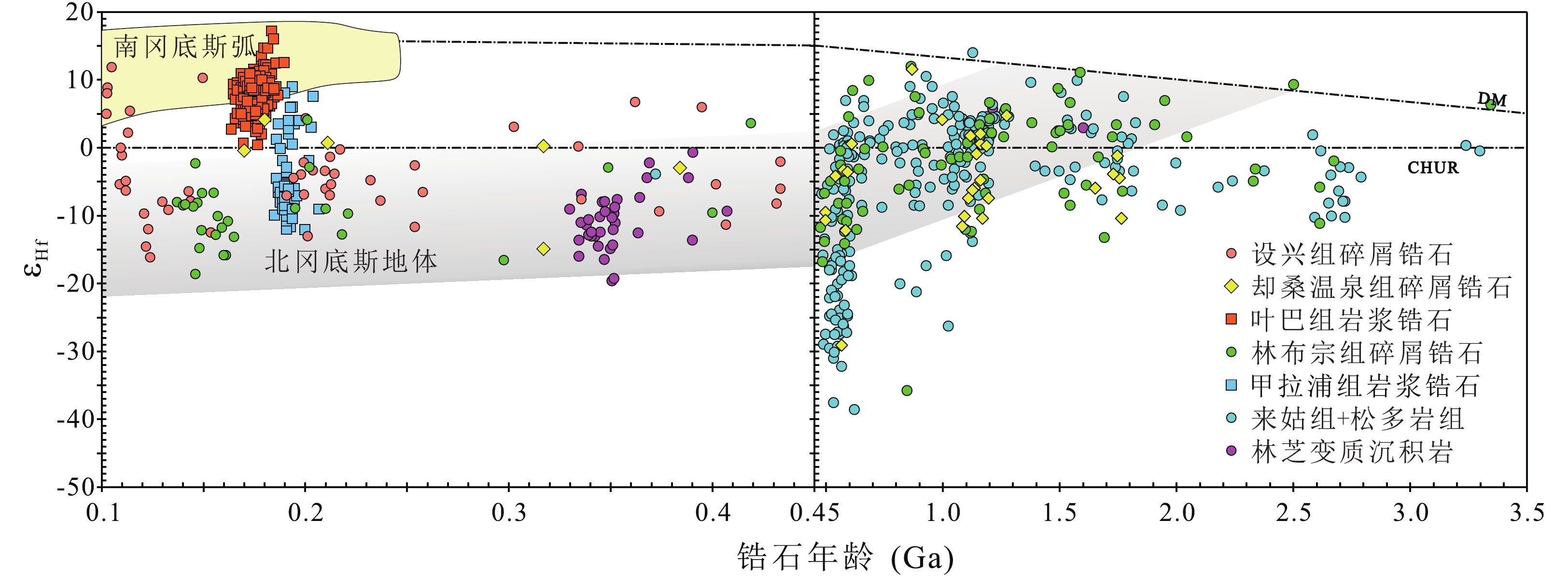
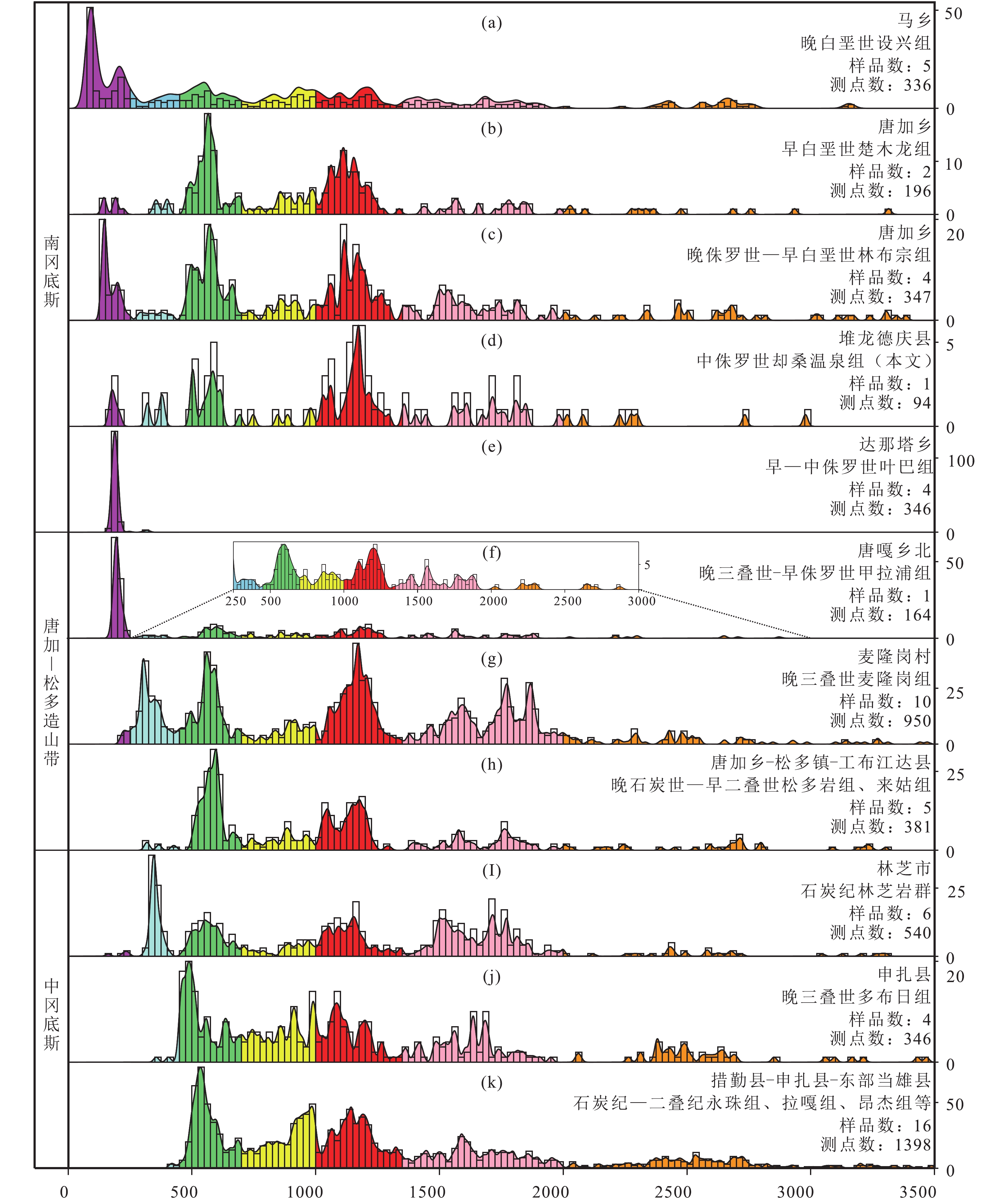
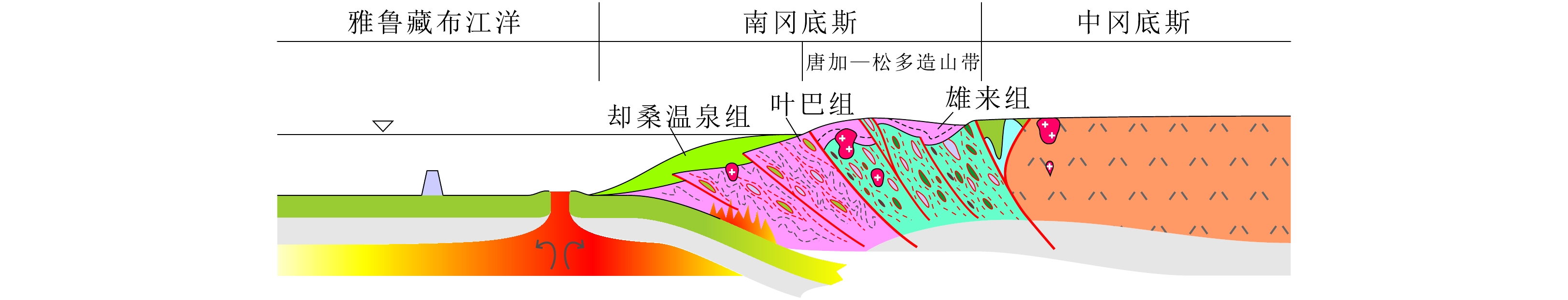
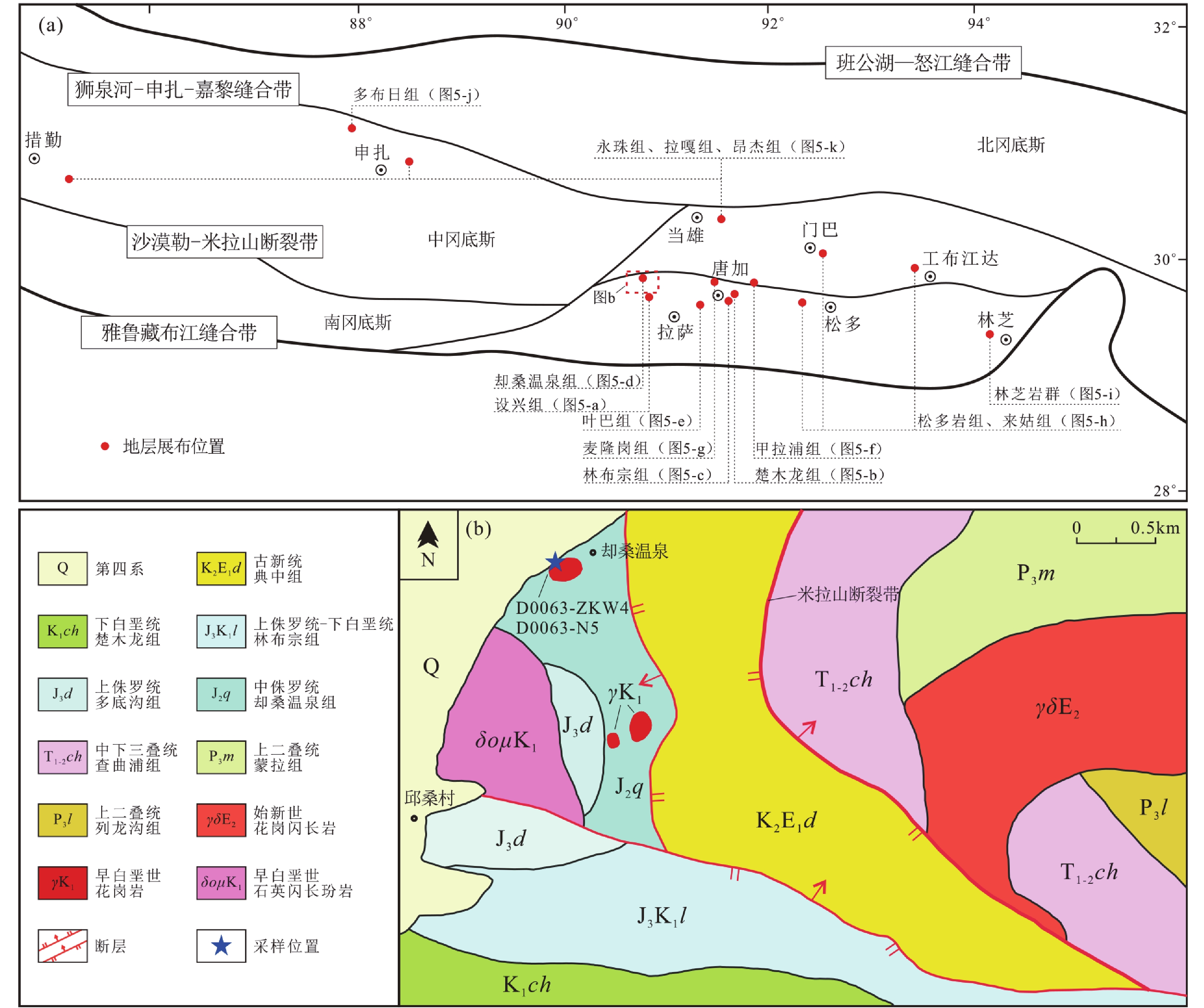
林周盆地位于冈底斯板块中部,对其进行盆地分析将为理解冈底斯板块构造演化过程提供重要的沉积学证据。本文以林周盆地中侏罗统却桑温泉组为研究对象,开展岩石学和碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学研究,结果显示却桑温泉组岩屑石英砂岩最年轻碎屑锆石年龄为169 Ma,存在620~540 Ma,
1220 ~1055 Ma等年龄峰值,其中最年轻碎屑锆石年龄是对特提斯洋壳俯冲引发的岩浆事件的响应。碎屑锆石区域对比研究表明却桑温泉组物源主要来自冈底斯中部唐加-松多造山带,为特提斯洋向北俯冲、向南增生过程的沉积记录。Abstract:The Linzhou Basin is located in the middle of the Gangdese Plate. Basin analysis of the Linzhou Basin will provide important sedimentological evidence for understanding the tectonic evolution process of the Gangdese Plate. This paper takes the Middle Jurassic Quesang Hot Spring Formation in the Linzhou Basin as the research object, and conducted petrology and detrital zircon U-Pb chronology. The results show that the youngest detrital zircon age of the lithic quartz sandstone of the Quesang Hot Spring Formation is 169 Ma, with age peaks such as 170-200 Ma, 540-620 Ma, and
1055 -1220 Ma. The youngest detrital zircon age is the response to a magmatic event triggered by the subduction of the Tethys oceanic crust. Regional comparative studies of detrital zircons show that the source of the Quesang Hot Spring Formation is mainly from the Tanga-Songduo orogenic belt in central Gangdese, which is a sedimentary record of the northward subduction and southward accretion of the Tethys Ocean.-
Key words:
- Linzhou Basin /
- Middle Jurassic /
- Quesang Hot Spring Formation /
- detrital zircons /
- provenance
-

-
[1] Cai F, Ding L, Laskowski A K, et al. , 2016. Late Triassic paleogeographic reconstruction along the Neo–Tethyan Ocean margins, southern Xizang[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 435: 105-114.
[2] Cheng H, Liu Y, Vervoort J D, et al. , 2015. Combined U-Pb, Lu-Hf, Sm-Nd and Ar-Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane, Xizang[J]. Gondwana Research. 28(4): 1482-1499.
[3] Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort J D, et al. , 2012. Zircon U–Pb and garnet Lu–Hf geochronology of eclogites from the Lhasa Block, Xizang[J]. Lithos. 155: 341-359.
[4] Corfu F, Hanchar J M, Hoskin P W O, et al. , 2003. Atlas of Zircon Textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 53(1): 469-500.
[5] Fan S, Ding L, Murphy M A, et al. , 2017. Late Paleozoic and Mesozoic evolution of the Lhasa Terrane in the Xainza area of southern Xizang[J]. Tectonophysics. 721: 415-434.
[6] Gehrels G, Kapp P, Decelles P, et al. , 2011. Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Xizang-Himalayan orogen[J]. Tectonics. 30(5): TC5016.
[7] Guo L, Zhang H, Harris N, et al. , 2016. Late Devonian-Early Carboniferous magmatism in the Lhasa terrane and its tectonic implications: Evidences from detrital zircons in the Nyingchi Complex[J]. Lithos. 245: 47-59.
[8] Hu Z, Liu Y, Gao S, et al. , 2012. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Journal of analytical atomic spectrometry. 27(9): 1391-1399.
[9] Huang Y, Ren M, Jowitt S M, et al. , 2021. Middle Triassic arc magmatism in the southern Lhasa terrane: Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos. 380-381: 105857.
[10] Kang Z, Xu J, Wilde S A, et al. , 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group Volcanic Rocks, Southern Lhasa Terrane: Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese Magmatic Arc[J]. Lithos. 200-201: 157-168.
[11] Kapp P, Decelles P G, Leier A L, et al. , 2007. The Gangdese retroarc thrust belt revealed[J]. GSA Today. 17(7): 4.
[12] Lai W, Hu X, Garzanti E, et al. , 2019. Initial growth of the Northern Lhasaplano, Xizang Plateau in the early Late Cretaceous (ca. 92 Ma)[J]. GSA Bulletin. 131(11-12): 1823-1836.
[13] Leier A L, Decelles P G, Kapp P, et al. , 2007. The Takena Formation of the Lhasa Terrane, southern Xizang; the record of a Late Cretaceous retroarc foreland basin[J]. Geological Society of America bulletin. 119(1-2): 31-48.
[14] Li G, Sandiford M, Liu X, et al. , 2014. Provenance of Late Triassic sediments in central Lhasa terrane, Xizang and its implication[J]. Gondwana Research. 25(4): 1680-1689.
[15] Li X, Mattern F, Zhang C, et al. , 2016. Multiple sources of the Upper Triassic flysch in the eastern Himalaya Orogen, Xizang, China: Implications to palaeogeography and palaeotectonic evolution[J]. Tectonophysics. 666: 12-22.
[16] Meng Y, Mooney W D, Ma Y, et al. , 2019. Back-arc basin evolution in the southern Lhasa sub-terrane, southern Xizang: Constraints from U-Pb ages and in-situ Lu-Hf isotopes of detrital zircons[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 185: 104026.
[17] Murphy M A, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. , 1997. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Xizang plateau?[J]. Geology. 25(8): 719-722.
[18] Paton C, Woodhead J D, Hellstrom J C, et al. , 2010. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 11(3): Q0AA06
[19] Pullen A, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, et al. , 2008. Triassic continental subduction in central Xizang and Mediterranean-style closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Geology. 36(5): 351-354.
[20] Wang C, Ding L, Zhang L, et al. , 2016. Petrogenesis of Middle–Late Triassic volcanic rocks from the Gangdese belt, southern Lhasa terrane: Implications for early subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic lithosphere[J]. Lithos. 262: 320-333.
[21] Wang C, Ding L, Zhang L, et al. , 2019. Early Jurassic highly fractioned rhyolites and associated sedimentary rocks in southern Xizang: constraints on the early evolution of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences. 108(1): 137-154.
[22] Wang J, Hu X, Garzanti E, et al. , 2020. From extension to tectonic inversion: Mid-Cretaceous onset of Andean-type orogeny in the Lhasa block and early topographic growth of Xizang[J]. GSA Bulletin. 132(11-12): 2432-2454.
[23] Wang J, Wu F, Garzanti E, et al. , 2016. Upper Triassic turbidites of the northern Tethyan Himalaya (Langjiexue Group): The terminal of a sediment-routing system sourced in the Gondwanide Orogen[J]. Gondwana Research. 34: 84-98.
[24] Wei Y, Zhao Z, Niu Y, et al. , 2020. Geochemistry, detrital zircon geochronology and Hf isotope of the clastic rocks in southern Xizang: Implications for the Jurassic-Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the Lhasa terrane[J]. Gondwana Research. 78: 41-57.
[25] Yu Y, Xie C, Fan J, et al. , 2018. Zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Early Jurassic granodiorites in Sumdo area, Xizang: Constraints on petrogenesis and the evolution of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean[J]. Lithos. 320-321: 134-143.
[26] Yuan H, Gao S, Liu X, et al. , 2004. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research. 28(3): 353-370.
[27] Zhu D, Zhao Z, Niu Y, et al. , 2011. Lhasa terrane in southern Xizang came from Australia[J]. Geology. 39(8): 727-730.
[28] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春, 等, 2018. 西藏措勤盆地的地层学研究进展及上二叠统—侏罗系地层序列的厘定[J]. 地球学报, 39(4): 401-407 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.071701
JI Z S, YAO J X, WU G C, et al. , 2018. Stratigraphic Progress of the Coqen Basin and Redefinition of the Upper Permian-Jurassic Stratigraphic Sequence[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(4): 401-407. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.071701
[29] 解超明, 李才, 李光明, 等, 2020. 西藏松多古特提斯洋研究进展与存在问题[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(2): 1 − 13
Xie C M, Li C, Li G M, et al., 2020. The research progress and problem of the Sumdo Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(2): 1 − 13.
[30] 解超明, 宋宇航, 王明, 等, 2019. 冈底斯中部松多岩组形成时代及物源: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地球科学, 44(7): 2224 − 2236.
Xie C M, Song Y H, Wang M, et al., 2019. Age and Provenance of Sumdo Formation in Central Gangdese, Xizang Plateau: Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronological Evidence[J].Earth Science, 44(7): 2224 − 2233.
[31] 李成志, 2020. 西藏南冈底斯白垩纪盆地林布宗组物源特征与盆地构造演化[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.
Li C Z, 2020. Provenance characteristics and structural evolution of the Linbuzong Formation in the Cretaceous Basin, south Gangdese, Xizang[D].Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology..
[32] 李光明, 张林奎, 吴建阳, 等, 2020. 青藏高原南部洋板块地质重建及科学意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(01): 1 − 14
Li G M, Zhang L K, Wu J Y, et al., 2020. Reestablishment and scientific significance of the Ocean plate geology in the Southern Xizang Plateau, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 1 − 14.
[33] 李化启, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 等, 2011. 拉萨地体内松多榴辉岩的同碰撞折返: 来自构造变形和40Ar-39Ar年代学的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 18(3): 66 − 78.
Li H Q, Xu Z Q, Yang J S, et al., 2011. Sys-collisional exhumation of Sumdo eclogite in the Lhasa Terrane, Xizang : Evidences from structural deformation and 40 Ar/39 Ar geochronology[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 66 − 78.
[34] 李楠, 朱利东, 杨文光, 等, 2020. 西藏冲尼中二叠世岛弧玄武岩的发现及意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 56(04): 722 − 731
Li N, Zhu L D, Yang W G, et al., 2020. Discovery of the Middle Permian Island Arc Basalt in the Chongni Area, Xizang and Its Tectonic Implication[J]. Geology and Exploration, 56(4): 722 − 731.
[35] 李晓雄, 江万, 梁锦海, 等, 2015. 西藏林周盆地设兴组玄武岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 31(5): 1285-1297
LI X X, JIANG W, LIANG J H, et al. , 2015. The geochemical characteristics and significance of the basalt from Shexing Formation in Linzhou basin, southern Xizang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(5): 1285-1297.
[36] 林方成, 李生, 曾琴琴, 等, 2022. 中国西南地区地质调查工作十年(2011-2020)进展综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(4): 507-528.
Lin F C, Li S, Zeng Q Q, et al., 2022. Review on the progress of geological survey works in Southwest China in the past ten years (2011-2020) [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(4): 507-528.
[37] 麦源君, 朱利东, 杨文光, 等, 2020. 西藏东南缘早二叠世长英质凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征[J]. 地球科学, 46(11): 3880 − 3891
Mai Y J, Zhu L D, Yang W G, et al., 2021. Zircon U-Pb and Hf Isotopic Composition of Permian Felsic Tuffs in Southeastern Margin of Lhasa, Xizang[J]. Earth Science, 46(11): 3880 − 3891.
[38] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等, 2006. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 521-533 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.03.001
PAN G T, MO X X, HOU Z Q, et al. , 2006. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 521-533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.03.001
[39] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 尹福光, 等, 2022. 青藏高原形成演化研究回顾、进展与展望[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(2): 151-175.
Pan G T, Wang L Q, Yin F G, et al., 2022. Researches on geological-tectonic evolution of Xizang Plateau: A review, recent advances, and directions in the future[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(2): 151-175.
[40] 苏鑫, 2020. 西藏林周盆地下白垩统楚木龙组物源分析及构造意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.
Su X, 2020. Provenance analysis and tectonic significance of Lower cretaceous ChuMulong Formation in Linzhou basin, Xizang[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology.
[41] 孙倩, 纪占胜, 廖卫华, 等, 2018. 西藏措勤盆地上侏罗统萨波直不勒组的发现及其烃源岩[J]. 地球学报, 39(4): 432-444 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.062201
SUN Q, JI Z S, LIAO W H, et al. , 2018. The Discovery of the Upper Jurassic Sabozhibule Formation in Coqen Basin, Xizang, and Its Source Rock[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(4): 432-444. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.062201
[42] 王乃文, 王思恩, 刘桂芳, 等, 1983. 西藏拉萨地区的海陆交互相侏罗系与白垩系[J]. 地质学报, 57(1): 83 − 95
Wang N W, Wang S N, Liu G F, et al., 1983. The Juro-Cretaceous marine-terrestrial alternating formations in Lhasa area, Xizang(Tebit)[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 57(1): 83 − 95.
[43] 魏友卿, 2017. 西藏拉萨地体南缘中生代火山岩与碎屑沉积岩的年代学、地球化学及构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
Wei Y Q, 2017. Mesozoic volcanic and sedimentary rocks on the southern margin of Lhasa Terrane, southern Xizang: geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing).
[44] 许志琴, 赵中宝, 彭淼, 等, 2016. 论“造山的高原”[J]. 岩石学报, 32(12): 3557-3571
XU Z Q, ZHAO Z B, PENG M, et al. , 2016. Review of “orogenic plateau”[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(12): 3557-3571.
[45] 杨洋, 2019. 西藏尼雄地区晚古生代沉积背景分析及地质意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.
Yang Y, 2019. Analysis of the sedimentary back ground and geological significance of late Paleozoic in nixiong region, Xizang[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology.
[46] 张成圆, 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 等, 2020. 冈底斯岩浆弧东段沉积岩的早新生代变质作用及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 94(5): 1413-1430 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.05.006
ZHANG C Y, ZHANG Z M, DING H X, et al. , 2020. Early Cenozoic metamorphism of the sedimentary rocks from the eastern Gangdese magmatic arc and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(5): 1413-1430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.05.006
[47] 张佳伟, 2018. 西藏中生代羌塘及马乡—林周盆地形成演化与剥露过程[D]. 中国地质大学(北京).
Zhang J W, 2018. Evolution and exhumation of the Mesozoic Qiangtang and Maqu-Linzhou basins, Xizang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing).
-



 下载:
下载: