Cd accumulation and human health risk assessment of rice in high background areas of heavy metals: A case study of Nagu Town, Huize County, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
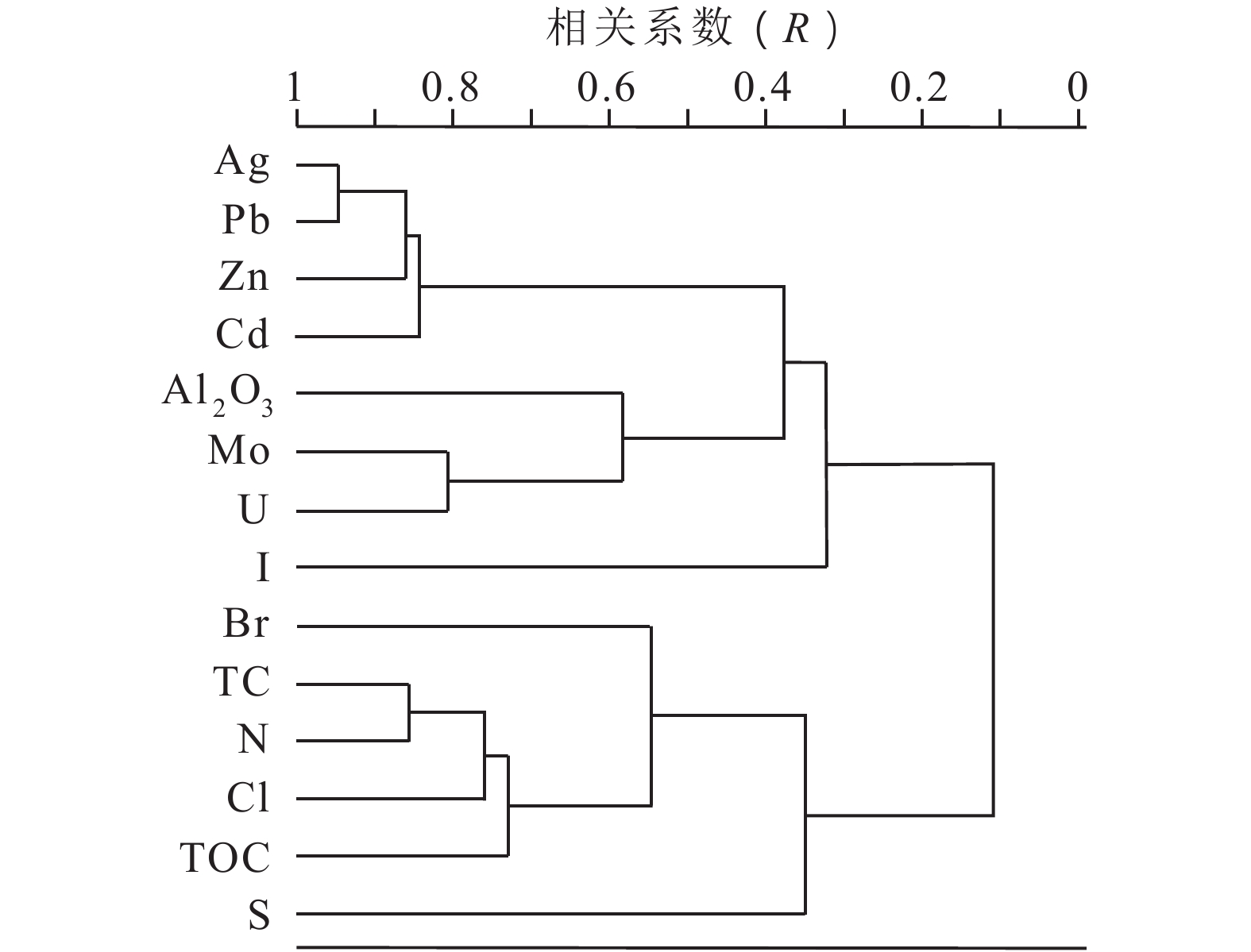
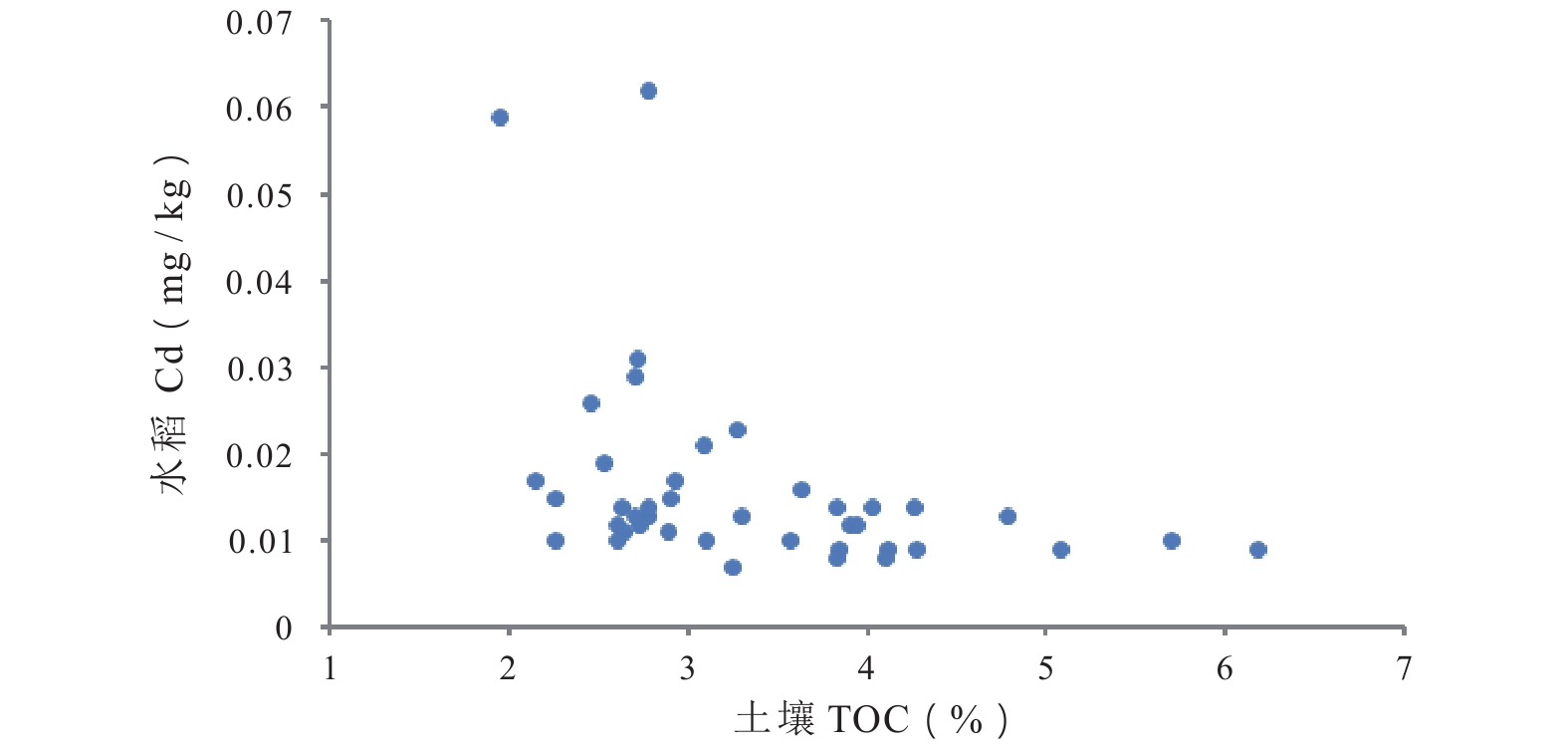
调查发现,重金属高背景区存在土壤中的镉含量超标,而农作物中的镉含量并未超标的现象,但对其原因知之甚少。开展区内农作物镉积累研究并探寻制约农作物镉吸收的因素,对土壤环境质量评价和污染土地生态修复都具有重要意义。以云南省会泽县娜姑镇娜姑坝子为研究区,采集了水稻籽实和配套土壤样品各41件,采用ICP-MS方法检测了Cd含量。通过偏相关、R型聚类、逐步线性回归等分析了水稻镉与土壤元素(指标)之间的相关关系。结果显示,水田土壤镉(Cd)含量为 0.467~1.87 mg/kg,平均为 0.78 mg/kg,是全国土壤背景值的 5.69 倍,58.5% 的样品超过农用地土壤污染风险筛选值。水稻(糙米)镉含量为 0.007~0.062 mg/kg,平均 0.016 mg/kg,均低于食品安全国家标准限值。水稻镉与土壤铀(U)、钼(Mo)等呈显著正相关,与土壤有机碳(TOC)、硫(S)等呈显著负相关,与土壤 Cd 总量和酸碱度(pH)无显著相关性。土壤镉超标而水稻镉不超标的现象可能与土壤富含有机碳有关,该地区土壤有机碳(TOC)含量达全国背景值的5.57倍。当 TOC > 3% 时,水稻镉含量迅速下降。据此提出土壤镉环境等级的有机碳修正方法,将研究区3.42 km2(
5129 亩)Ⅱ等水田修正为Ⅰ等。此外,还提出了一些土壤养护和修复的建议。Abstract:A study comparing cadmium (Cd) accumulation in soil and rice in an area of high background heavy metal concentrations in Huize County, Yunnan, showed that, occasionally, the cadmium content in soil exceeds the standard, whereas the cadmium content in crops remains within the standard. However, our understanding of the reasons for this phenomenon is limited. It is of great significance for soil environmental quality evaluation and ecological restoration to study cadmium accumulation in crops and its control factors in these areas. In this study, 41 rice seed samples and 41 corresponding soil samples were collected from the Nagubazi, Nagu Town, Huize County, Yunnan Province, and their cadmium content was determined by ICP-MS. The correlation between rice cadmium and soil elements (indices) was analyzed by partial correlation, R-type clustering, and stepwise linear regression. The results showed that the soil cadmium content ranged from 0.467 to 1.87 mg/kg, with an average of 0.78 mg/kg, which is 5.69 times that of the national soil background value. Moreover, 58.5% of the soil samples exceeded the soil pollution risk threshold for agricultural land. In contrast, the cadmium content of rice (brown rice) ranged from 0.007 to 0.062 mg/kg, with an average of 0.016 mg/kg, which is lower than the national threshold for food safety.The content of cadmium in rice was significantly positively correlated with the content of U and Mo , and significantly negatively correlated with soil organic carbon (TOC) and the content of S in soil, but not significantly correlated with soil cadmium content and pH value. The phenomenon that soil cadmium exceeds the standard but rice cadmium does not exceed the standard may be related to the enrichment of organic matter in the soil. The content of soil TOC is 5.57 times that of the national background value. When TOC is greater than 3%, cadmium content in rice decreases rapidly. Therefore, the organic matter correction method for soil cadmium environmental grade evaluation was proposed, and the 3.42 km2 (5129 Mu) of paddy field originally classified as Class Ⅱ in the study area was revised to Class Ⅰ. In addition, some suggestions on soil protection and remediation were put forward.
-
Key words:
- cadmium /
- soil-rice system /
- soil organic carbon /
- high background of heavy metals /
- Huize, Yunnan
-

-
表 1 水稻和土壤分析测试指标、方法及检出限
Table 1. Analysis items, methods and detection limits of the rice and soil
样品类型 分析指标 指标代号 分析方法 单位 检出限 水稻 镉 Cd 等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) mg/kg 0.002 土壤 镉 Cd 等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) mg/kg 0.02 银 Ag 发射光谱法(ES) mg/kg 0.02 铅 Pb X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) mg/kg 2 铀 U 等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) mg/kg 0.05 钼 Mo 等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) mg/kg 0.1 有机碳 TOC 重铬酸钾容量法 % 0.05 全碳 TC 高频红外碳硫仪法 % 0.1 氮 N 酸碱滴定容量法 mg/kg 15 硫 S 容量法 mg/kg 20 氯 Cl X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) mg/kg 15 溴 Br X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) mg/kg 0.8 碘 I 催化比色法(COL) mg/kg 0.3 三氧化二铝 Al2O3 X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) % 0.01 酸碱度 pH pH计电极法(ISE) 1 表 2 研究区土壤地球化学特征统计参数
Table 2. Statistical parameters of soil geochemistry in the study area
指标名称 指标代号 单位 含量值范围 平均值(  )
)中位值 标准差 变异系数 全国土壤背景值 (X0A) 与全国土壤
背景值之比( /X0A)
/X0A)镉 Cd mg/kg 0.467~1.87 0.78 0.71 0.30 0.42 0.137 5.69 银 Ag mg/kg 0.057~0.457 0.12 0.10 0.08 0.80 0.077 1.56 铅 Pb mg/kg 18.9~298 57.5 37.6 54.9 1.46 22 2.62 锌 Zn mg/kg 72.7~441 166 146 72.49 0.50 66 2.52 铀 U mg/kg 1.59~4.53 2.88 2.69 0.62 0.23 2.5 1.15 钼 Mo mg/kg 0.434~2.13 1.10 1.05 0.34 0.32 0.7 1.57 三氧化二铝 Al2O3 % 8.04~17.75 13.9 13.9 1.72 0.12 11.9 1.17 碘 I mg/kg 0.79~2.83 1.48 1.39 0.45 0.33 1.1 1.35 有机碳 TOC % 1.95~6.18 3.34 3.08 0.95 0.31 0.6 5.57 全碳 TC % 2.66~11.33 4.53 4.07 1.76 0.43 1.3 3.48 氮 N mg/kg 1902~ 6567 3393 3219 960 0.30 707 4.80 硫 S mg/kg 317~ 2464 669 653 336 0.51 245 2.73 氯 Cl mg/kg 62~154 90.5 82.9 25.2 0.30 78 1.16 溴 Br mg/kg 1.86~5.27 3.61 3.47 0.95 0.27 2.2 1.64 酸碱度 pH 5.84~8.13 7.26 7.44 0.68 0.09 8 0.91 注:全国土壤背景值数据来源于王学求等(2016)。 表 3 研究区水稻镉含量特征统计表(含量单位:mg/kg)
Table 3. Statistical parameters of rice cadmium in the study area (content unit: mg/kg)
样品数 水稻 Cd 土壤 Cd
平均值水稻 Cd /土壤 Cd 含量值范围 平均值 中位值 标准差 变异系数 41 0.007~0.062 0.016 0.013 0.012 0.75 0.78 0.21 表 4 研究区水稻镉含量与土壤元素(指标)相关、偏相关系数
Table 4. Correlation and partial correlation coefficients between rice cadmium and soil elements (indices) in the study area
控制
变量U Mo Ag Pb Zn Al2O3 Cd pH I N S TC Cl Br TOC 无 0.52** 0.48** 0.44** 0.42* 0.35* 0.14 0.29 -0.04 -0.22 -0.23 -0.29 -0.29 -0.30 -0.37* -0.39* U 0.24 0.18 0.20 0.22 -0.21 -0.11 -0.12 -0.43** -0.05 -0.41** -0.11 -0.21 -0.21 -0.18 TOC 0.35* 0.42** 0.35* 0.37* 0.37* -0.09 0.30 -0.04 -0.20 0.10 -0.26 -0.03 -0.11 -0.23 注:“**”表示显著水平(< 0.01);“*”表示显著水平(< 0.05);当无控制变量时,为Pearson相关系数。 表 5 逐步线性回归过程及参数
Table 5. Stepwise linear regression process and parameters
步骤 变量/常量 非标准化系数 标准化系数 τ 值 显著性* 系数 标准误差 1 常量 -2.362 0.138 -17.132 <0.001 Usoil 0.176 0.047 0.515 3.754 0.001 2 常量 -0.796 0.468 -1.700 0.097 Usoil 0.164 0.041 0.480 3.946 <0.001 lgSsoil -0.549 0.158 -0.422 -3.466 0.001 3 常量 0.472 0.578 0.817 0.419 Usoil 0.256 0.047 0.751 5.432 <0.001 lgSsoil -0.800 0.162 -0.615 -4.927 <0.001 Al2O3soil -0.060 0.019 -0.490 -3.193 0.003 4 常量 0.048 0.560 0.085 0.932 Usoil 0.272 0.044 0.799 6.173 <0.001 lgSsoil -0.682 0.157 -0.524 -4.336 <0.001 Al2O3soil -0.051 0.018 -0.421 -2.909 0.006 lgIsoil -0.472 0.178 -0.290 -2.644 0.012 注:“*”表示显著水平 < 0.05 时,变量入选模型。 表 6 土壤镉环境等级修正方法
Table 6. Correction method of soil cadmium environmental grade
修正条件 修正前等级 修正后等级 土壤污染风险 土壤养护及修复建议 土壤有机碳(TOC)含量
> 3%Ⅲ Ⅱ 污染风险可控 通过施用农家肥、秸秆还田等方法,确保土壤有机碳含量不降低。 Ⅱ Ⅰ 污染风险低 Ⅰ Ⅰ 污染风险低 土壤有机碳(TOC)含量
≤ 3%维持原有评级 污染风险等级
不变增加农家肥、有机肥等施用量,以提高土壤有机碳含量,同时监测农作物镉含量。 -
[1] Alloway B J, 2013. Bioavailability of elements in soil [C] // Selinus O, Essentials of Medical Geology (2nd ed. ), Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 351 − 373.
[2] Eriksson, J E, 1988. The effects of clay, organic matter and time on adsorption and plant uptake of cadmium added to the soil[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 40 : 359-373. . doi: 10.1007/BF00163740
[3] Fergusson J E, 1990. The Heavy Elements: Chemistry, Environmental Impact and Health Effects [M]. Oxford, UK.
[4] Gu Q, Yang Z, Yu T, et al. , 2018. From soil to rice – a typical study of transfer and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 68 (7) : 631-642.
[5] 和淑娟, 李丽娜, 杨牧青, 等, 2020. 云南某冰川侵蚀区域土壤高背景值成因及农作物重金属累积规律探究[J]. 环境科学导刊, 40 (2): 68-74
He S J, Li L N, Yang M Q, et al. , 2020. Research on the causes of high soil background value and the accumulation of heavy metals in crops in a glacier eroded area in Yunnan[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 40 (2): 68-74 .
[6] Johnson A H M, Lalor G C, Preston J, et al. , 1996. Heavy metals in Jamaican surface soils[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 18 (3) : 113-121. doi: 10.1007/BF01771287
[7] Kabata-pendias A, Pendias H, 1984. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants [M]. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
[8] 李汇文, 王世杰, 白晓永, 等, 2019. 中国石灰岩化学风化碳汇时空演变特征分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49 (6) : 986 − 1003.
Li H W, Wang S J, Bai X Y, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal evolution of carbon sequestration of limestone weathering in China[J]. Science China-Earth Sciences, 62 : 974 − 991(in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] 李佳桐, 李雪, 葛成军, 等, 2018. 琼北土壤重金属高背景值区人群健康风险评价[J]. 热带作物学报, 39 (1): 189-196
Li J T, Li X, Ge C J, et al. , 2018. Health risk assessment of heavy metal in soils in the north of Hainan province with high background value[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 39 (1): 189-196 .
[10] 李杰, 战明国, 钟晓宇, 等, 2021. 广西典型岩溶地区重金属在土壤⁃农作物系统中累积特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 41 (2): 597-606
Li J, Zhan M G, Zhong X Y, et al. , 2021. Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in soil⁃crop systems from a typical carbonate rocks area in Guangxi[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41 (2): 597-606 .
[11] 李兴振, 许效松, 潘桂棠, 1995. 泛华夏大陆群与东特提斯构造域演化[J]. 岩相古地理, 15 (4): 1-13
Li X Z, Xu X S, Pan G T, 1995. Evolution of the Pan-Cathaysian Landmass group and eastern Tethyan tectonic domain[J]. Lithofacies Paleogeography, 15 (4): 1-13 .
[12] 廖启林, 刘聪, 王轶, 等, 2015. 水稻吸收Cd的地球化学控制因素研究--以苏锡常典型区为例[J]. 中国地质, 42 (5): 1621 − 1632
Liao Q L, Liu C, Wang Y, et a1., Geochemical characteristics of rice uptake of cadmium and its main controlling factors: A case study of the Suxichang (Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou) typical area[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42 (5): 1621 − 1632(in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] 刘才泽, 王永华, 赵禁, 等, 2022. 川东北地区水稻镉积累与生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49 (3): 695-705 doi: 10.12029/gc20220302
Liu C Z, Wang Y H, Zhao J, et al. , 2022. Assessment of cadmium accumulation in rice and risk on human health in the northeast SichuanProvince[J]. Geology in China, 49 (3): 695-705 . doi: 10.12029/gc20220302
[14] 刘鸿雁, 蒋子涵, 戴景钰, 等, 2019. 岩石裂隙决定喀斯特关键带地表木本与草本植物覆盖[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49 (12) : 1974 − 1981.
Liu H Y, Jiang Z H, Dai J Y, et al., 2019. Rock crevices determine woody and herbaceous plant cover in the karst critical zone[J]. Science China-Earth Sciences, 62 : 1756 − 1763(in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] 刘巍, 陈效民, 景峰, 等, 2019. 生物质炭对土壤-水稻系统中Cd迁移累积的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 33 (1): 323-327
Liu W, Chen X M, Jing F, et al. , 2019. Effects of biochar amendment on translocation and accumulation of Cd in soil-rice system[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33 (1): 323-327 .
[16] 骆永明, 滕应, 2018. 我国土壤污染的区域差异与分区治理修复策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33 (2): 145-152
Luo Y M, Teng Y, 2018. Regional difference in soil pollution and strategy of soil zonal governance and remediation in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33 (2): 145-152 .
[17] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 郭飞, 等, 2021. 广西典型岩溶区农田土壤-作物系统Cd迁移富集影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 42 (3): 1514-1522
Ma H H, Peng M, Ge F, et al. , 2021. Factors affecting the translocation and accumulation of cadmium in a soil-crop system in a typical karst area of Guangxi province, China[J]. Environmental Science, 42 (3): 1514-1522 .
[18] 唐豆豆, 袁旭音, 汪宜敏, 等, 2018. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37 (1): 18-26
Tang D D, Yuan X Y, Wang Y M, et al. , 2018. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37 (1): 18-26 .
[19] 唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 等, 2020. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 34 (5): 917 − 927
Tang R L, Wang H Y, Lü X P, et al., Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland system from an area with high background of heavy metals, Southwestern China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34 (5): 917 − 927(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] 田发祥, 纪雄辉, 郭勇军, 等, 2015. 有机水溶肥在镉污染稻田中的应用效果研究[J]. 湖南农业科学, (8): 53-56
Tian F X, Ji X H, Guo Y J, et al. , 2015. Application efects of organic water soluble fertilizer in cadmium-polluted paddy fields[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, (8): 53-56 .
[21] 王学求, 周建, 徐善法, 等, 2016. 全国地球化学基准网建立与土壤地球化学基准值特征[J]. 中国地质, 43 (5): 1469-1480
Wang X Q, Zhou J, Xu S F, et al. , 2016. China soil geochemical baselines networks: Data characteristics[J]. Geology in China, 43 (5): 1469-1480 .
[22] 王永华, 周雪梅, 谢岿锐, 等, 2019. 中国西南地区地球化学图集[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
Wang Y H, Zhou X M, Xie K R, 2019. Geochemical atlas of South China[M]. Wuhan : China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese)(in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Wen Y B, Li W, Yang Z F, et al. , 2020. Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Polluttion, 258 : 113645. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113645
[24] 温琰茂, 曾水泉, 潘树荣, 等, 1994. 中国东部石灰岩土壤元素含量分异规律研究[J]. 地理科学, 14 (1): 16-21
Wen Y M, Zeng S Q, Pan S R, et al. , 1994. Distributive tendency 0f elem ent c0ncentrations in soils derived from limestone in eastern china[J]. Sclentia Geographica Sinica, 14 (1): 16-21 .
[25] 吴见珣, 杨赵, 杨涛明, 等, 2020. 云南某典型喀斯特区域农田土壤镉、砷污染特征及来源[J]. 环境科学导刊, 40 (3): 28-33
Wu J X, Yang Z, Yang T M, et al. , 2020. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of cadmium and arsenic in farmland soils of a typical karst region in Yunnan[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 40 (3): 28-33 .
[26] 夏学齐, 季峻峰, 杨忠芳, 等, 2022. 母岩类型对土壤和沉积物镉背景的控制: 以贵州为例[J]. 地学前缘, 29 (4): 438-447
Xia X Q, Ji J F, Yang Z F, et al. , 2022. Parent rock type control on cadmium background in soil and sediment: an example from Guizhou province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29 (4): 438-447 .
[27] 熊婕, 朱奇宏, 黄道友, 等, 2019. 南方典型稻区稻米镉累积量的预测模型研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38 (01) : 28 − 34.
Xiong J, Zhu Q H, Huang D Y, et al., 2019. Prediction model for the accumulation of cadmium in rice in typical paddy fields of south China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38 (1) : 22 − 28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] 徐克全, 金立新, 张华, 等, 2021. 高硒、高镉地质背景下水稻种植实验研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41 (4): 649-656
Xu K Q, Jin L X, Zhang H, et al. , 2021. Rice planting experiment under Se-rich and Cd-high geological background[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41 (4): 649-656 .
[29] 杨琼, 杨忠芳, 张起钻, 等, 2021. 中国广西岩溶地质高背景区土壤-水稻系统 Cd 等重金属生态风险评价[J]. 51 (8) : 1317 − 1331.
Yang Q, Yang Z F, Zhang Q Z, et al., 2021. Ecological risk assessment of Cd and other heavy metals in soil-rice system in the karst areas with high geochemical background of Guangxi, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 64 (7) : 1126 − 1139(in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Yang Q, Yang Z F, Filippelli G M, et al. , 2021. Distribution and secondary enrichment of heavy metal elements in karstic soils with high geochemical background in Guangxi, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 567: 120081 doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120081
[31] 易甜, 彭立军, 崔文文, 等, 2020. 湖北省地质高背景地区水稻-镉的耕地安全生产阈值研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 59 (24): 164-168
Yi T, Peng L J, Cui W W, et al. , 2020. Study on rice-Cadmium of safety production threshold of cultivated land in high geological background area of Hubei province[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 59 (24): 164-168 .
[32] 尹福光, 孙洁, 任飞, 等, 2016. 中国西南区域地质[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
Yin F G, Sun J, Ren F, et al., 2016. Regional geology of Southwest China[M]. Wuhan : China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese)(in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 殷鸿福, 吴顺宝, 杜远生, 等, 1999. 华南是特提斯多岛洋体系的一部分[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 24 (1): 1-12
Yin H F, Wu S B, Du Y S, et al. , 1999. South China defined as part of Tethyan archipelagic ocean system[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24 (1): 1-12 .
[34] 袁吉文, 万青青, 2004. 云南城乡居民膳食结构的20年变迁[J]. 昆明医学院学报, 25 (专辑): 4-9
Yuan J W, Wan Q Q, 2004. The transition of dietary pattern of residents in rural and urban of Yunnan between 1982 and 2002[J]. Academic Journal of Kunming Medical College, 25: 4-9 .
[35] 曾琴琴, 王永华, 刘才泽, 等, 2021. 四川省南部县土壤地球化学元素分布特征研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41 (4): 657-663
Zeng Q Q, Wang Y H, Liu C Z, et al. , 2021. A study on distribution of elements of soil in Nanbu county, Sichuan province[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41 (4): 657-663 .
[36] 张风雷, 郑循艺, 陈琦伟, 等, 2017. 重金属地质高背景区及工业区农作物重金属健康风险评价——以重庆市梁平区现代农业示范区为例[J]. 地球与环境, 45 (5): 567-575
Zhang F H, Zheng X Y, Chen Q W, et al. , 2017. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in crops from geological background of high heavy metals and industrial suburb—taking a modern agricultural demonstration zone of Liangping county as an example[J]. Earth and Environment, 45 (5): 567-575 .
[37] 张富贵, 成晓梦, 马宏宏, 等, 2022. 科学构建土壤重金属高背景区生态风险评价方法的探讨[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 48 (1): 57-67
Zhang F G, Cheng X M, Ma H H, et al. , 2022. Discuss on scientific construction of ecological risk assessment methods in the high background areas of soil heavy metals[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 48 (1): 57-67 .
[38] 张强, 万青青, 刘志涛, 等, 2016. 云南城乡居民营养素摄入状况及膳食结构分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 32 (5): 661-663 doi: 10.11847/zgggws2016-32-05-26
Zhang Q, Wan Q Q, Liu Z T, et al. , 2016. Nutrients intake and dietary structure among residents in Yunnan province[J]. China Journal Public Health, 32(5): 661-663 . doi: 10.11847/zgggws2016-32-05-26
[39] 张艳, 王丹, 李黎, 2013. 豌豆对U和Cd复合胁迫反应及其积累特征[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 31 (1): 010401
Zhang Y, Wang D, Li L, 2013. Response of peas to U and Cd combined stress and their accumulation characteristic[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Proces, 31 (1): 010401 .
[40] 张振明, 肖艳辉, 何金明, 等, 2015. 钼对低镉水平下小白菜的生长及镉含量的影响[J]. 韶关学院学报·自然科学, 36 (4): 36-40
Zhang Z M, Xiao Y H, He J M, et al. , 2015. Effect of molybdenum on growth and cadmium content in Chinese white cabbage under low cadmium concentration medium[J]. Journal of Shaoguan University-Natural Science, 36 (4): 36-40 .
[41] Zhao K, Zhang W, Zhou L, et al. , 2009. Modeling transfer of heavy metals in soil–rice system and their risk assessment in paddy fields[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59 (3) : 519-527. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0049-x
[42] 赵中秋, 后立胜, 蔡运龙, 2006. 西南喀斯特地区土壤退化过程与机理探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 13 (3): 185-189 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.03.025
Zhao Z Q, Hou L S, Cai Y L, 2006. The process and mechanism of soil degradation in karst area in Southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13 (3): 185-189 . doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.03.025
-




 下载:
下载: