High-resolution sequence stratigraphic characteristics and organic matter enrichment mechanism of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the Tiesiao-Datangpo Formations in northeastern Guizhou
-
摘要:
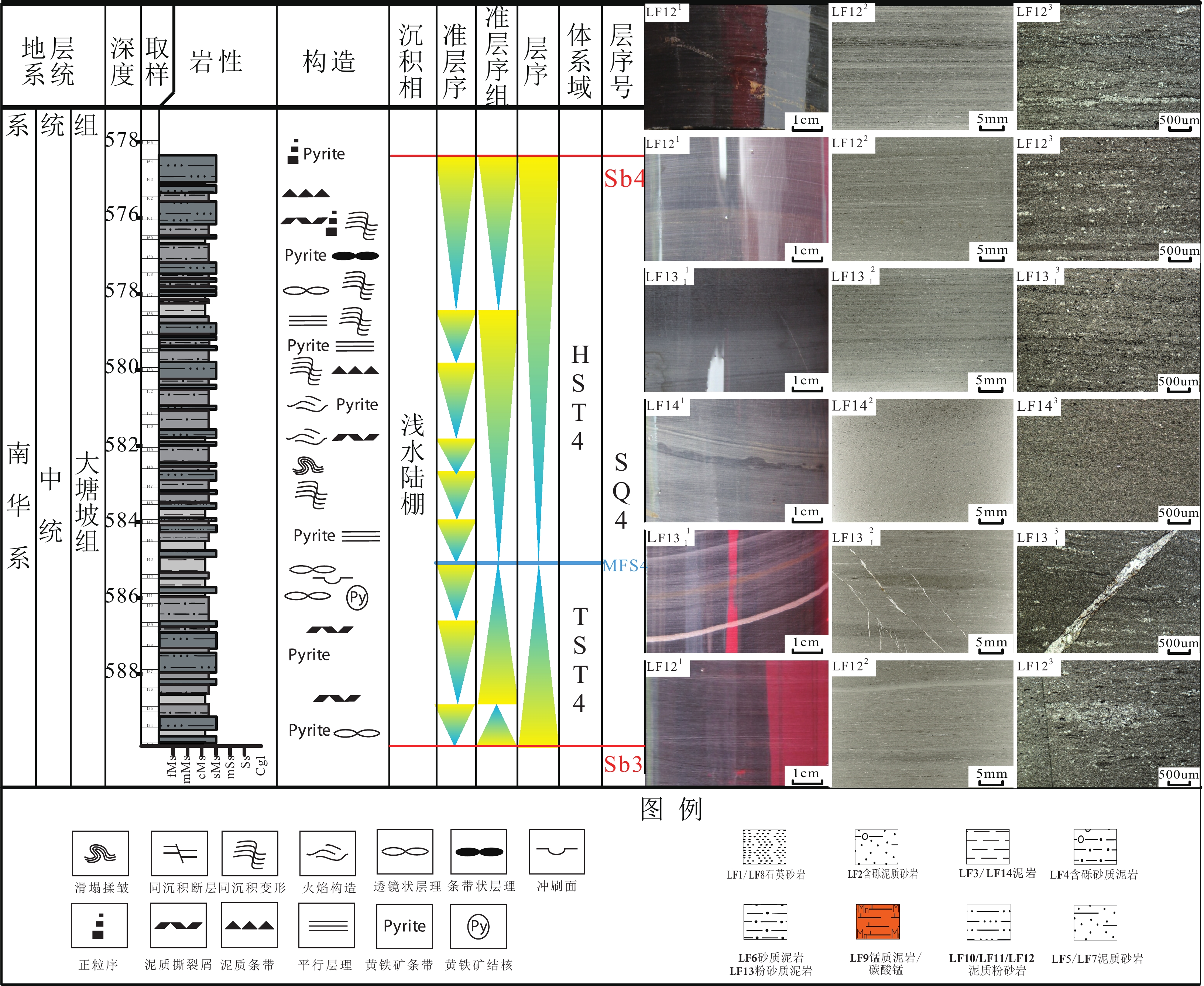
南华系大塘坡组是一套优质烃源岩和潜在非常规油气储层,具有重要的地史研究和油气勘探意义,然而关于其沉积过程及高精度层序地层方面的研究还较为薄弱。作者以黔东北ZK513井岩心描述及薄片观察为主要研究手段,运用了新的细粒沉积物的分类标准,精细划分识别了以石英砂岩、含砾泥质砂岩、灰色泥岩、灰色含砾砂质泥岩、灰色泥质砂岩、黑色炭质–硅质砂质泥岩、黑色含砾炭质–硅质泥质砂岩、灰色石英砂岩、黑色锰质泥岩、黑色泥质粉砂岩、黑灰色泥质粉砂岩、灰黑色泥质粉砂岩、灰色粉砂质泥岩、灰白色泥岩为代表的14种岩相。并根据岩相组合特征识别了陆棚内盆地、深水陆棚、浅水陆棚3种沉积相,以及前滨、冰海浅水陆棚、陆棚内富锰盆地、陆棚内深水盆地、陆棚内盆地边缘、深水陆棚、浅水陆棚7种沉积亚相。据岩相、沉积相分析,认为陆棚内盆地相内LF9黑色锰质泥岩、LF10黑色泥质粉砂岩为烃源岩的有利相区和层段。通过对岩相、沉积相的研究,识别出5个三级层序SQ1—SQ5,以及4个三级层序界面SB1—SB4;在三级层序内部,根据岩相叠加样式并结合沉积构造定量化统计,总结出4种典型的准层序类型,根据准层序的叠加形式识别了三级层序内部若干准层序组,进而识别出5个海侵(TST)—高位(HST)体系域旋回及内部的5次最大海泛面MFS1—MFS5,进而建立单井层序地层格架。综合ZK513井和研究区其他井岩相、沉积相、层序等资料,通过连井对比,建立了黔东北大塘坡组一段沉积期充填演化模式,预测了研究区内有利相区陆棚内盆地的分布,以及相区内富有机质层段LF9—LF10的展布模式。
Abstract:The Datangpo Formation of the Nanhua System is a set of high-quality source rocks and potential unconventional oil and gas reservoirs, which has important geological historical research and oil and gas exploration significance. However, research on its sedimentary process and high-precision sequence stratigraphy remains relatively limited. The current study, using the core description and thin section observation from Well ZK513 in northeast Guizhou as the primary research methods, employed updated classification criteria for fine-grained sediments to meticulously classify and identify 14 distinct lithofacies, including quartz sandstone, pebbly argillaceous sandstone, grey mudstone, grey pebbly sandy mudstone, grey argillaceous sandstone, black carbonaceous-siliceous sandy mudstone, black pebbly carbonaceous-siliceous argillaceous sandstone, grey quartz sandstone, black manganese mudstone, black argillaceous siltstone, black grey argillaceous siltstone, grey-black argillaceous siltstone, grey silty mudstone and grey-white mudstone. Based on the characteristics of lithofacies combination, three sedimentary facies—intra-shelf basin, deep-water shelf and shallow-water shelf—were identified. These three facies were subsequently subdivided into seven sedimentary subfacies: foreshore, ice sea shallow continental shelf, manganese-rich basin in continental shelf, deep-water basin in continental shelf, margin of basin in continental shelf, deep-water continental shelf and shallow-water continental shelf. Based on the analysis of lithofacies and sedimentary facies, it is considered that LF9 black manganese mudstone and LF10 black argillaceous siltstone in the continental intra-shelf basin facies are favorable facies and intervals for hydrocarbon source rocks. Through the study of lithofacies and sedimentary facies, five third-order sequences SQ1-SQ5 and four third-order sequence boundaries SB1-SB4 were identified. According to the lithofacies superposition pattern and quantitative statistics of sedimentary structure, four typical parasequence types were summarized in the third-order sequence. Based on the superposition form of parasequence, several parasequence sets in the third-order sequence were identified, and then five transgressive (TST)-highstand system tract (HST) cycles and five internal maximum flooding surfaces MFS1-MFS5 were identified, and then the single well sequence stratigraphic framework was established. Based on the data of lithofacies, sedimentary facies and sequence of Well ZK513 and other wells in the study area, the filling evolution model of the sedimentary period of Datangpo 1 member in northeast Guizhou was established by well comparison. The distribution of the basin in the continental shelf of the favorable facies area in the study area and the distribution pattern of the organic-rich interval LF9-LF10 in the facies area were predicted.
-
Key words:
- northeast Guizhou /
- Tiesiao-Datangpo Formations /
- lithofacies /
- sedimentary facies /
- strata sequence /
- evolution model
-

-
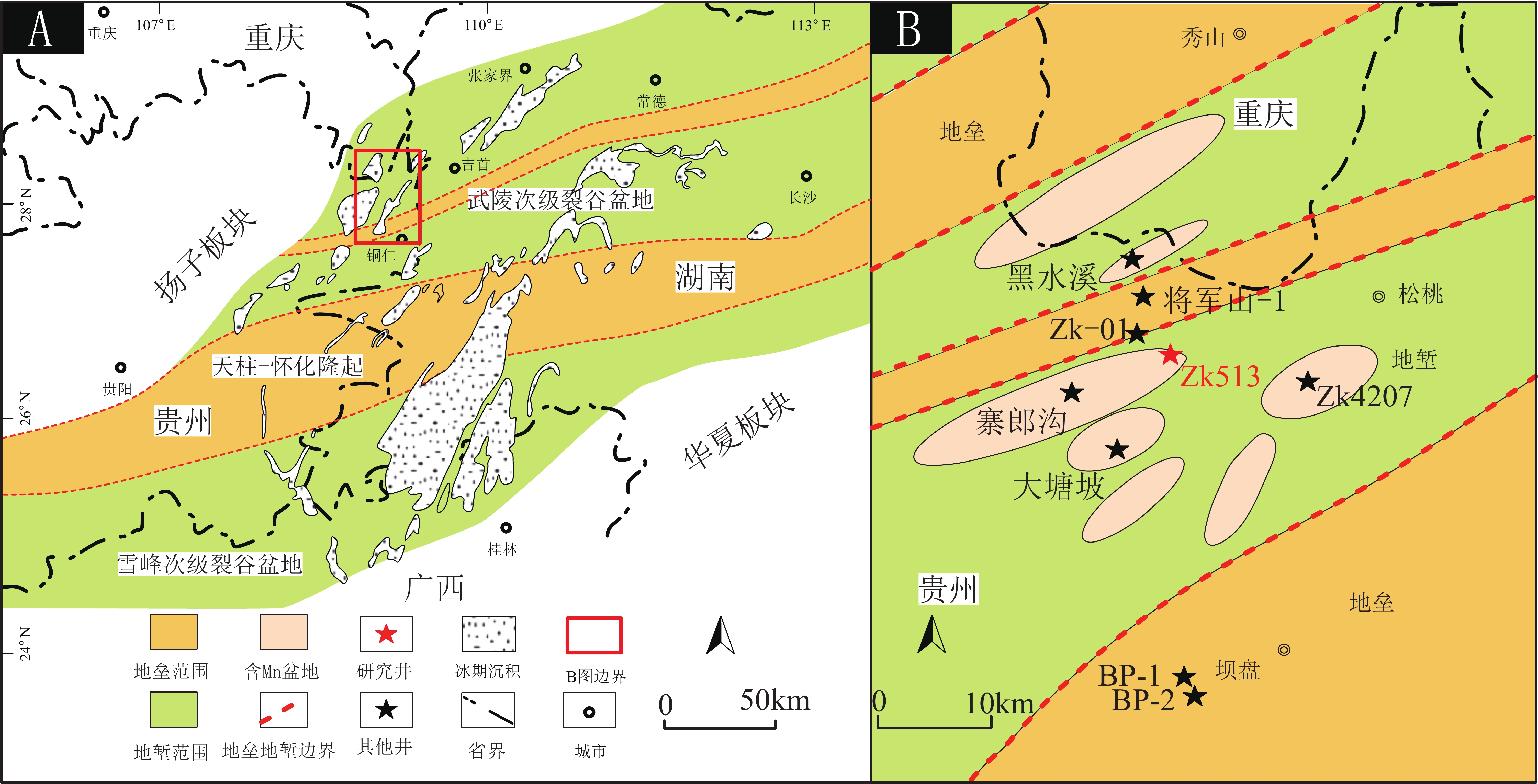
图 1 中上扬子地区南华裂谷盆地及研究区构造简图(A, 据Li et al., 2022修改;B, 据Yu et al., 2017修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 中上扬子地区南华系地层划分对比图(据张予杰等, 2020修改)
Figure 2.
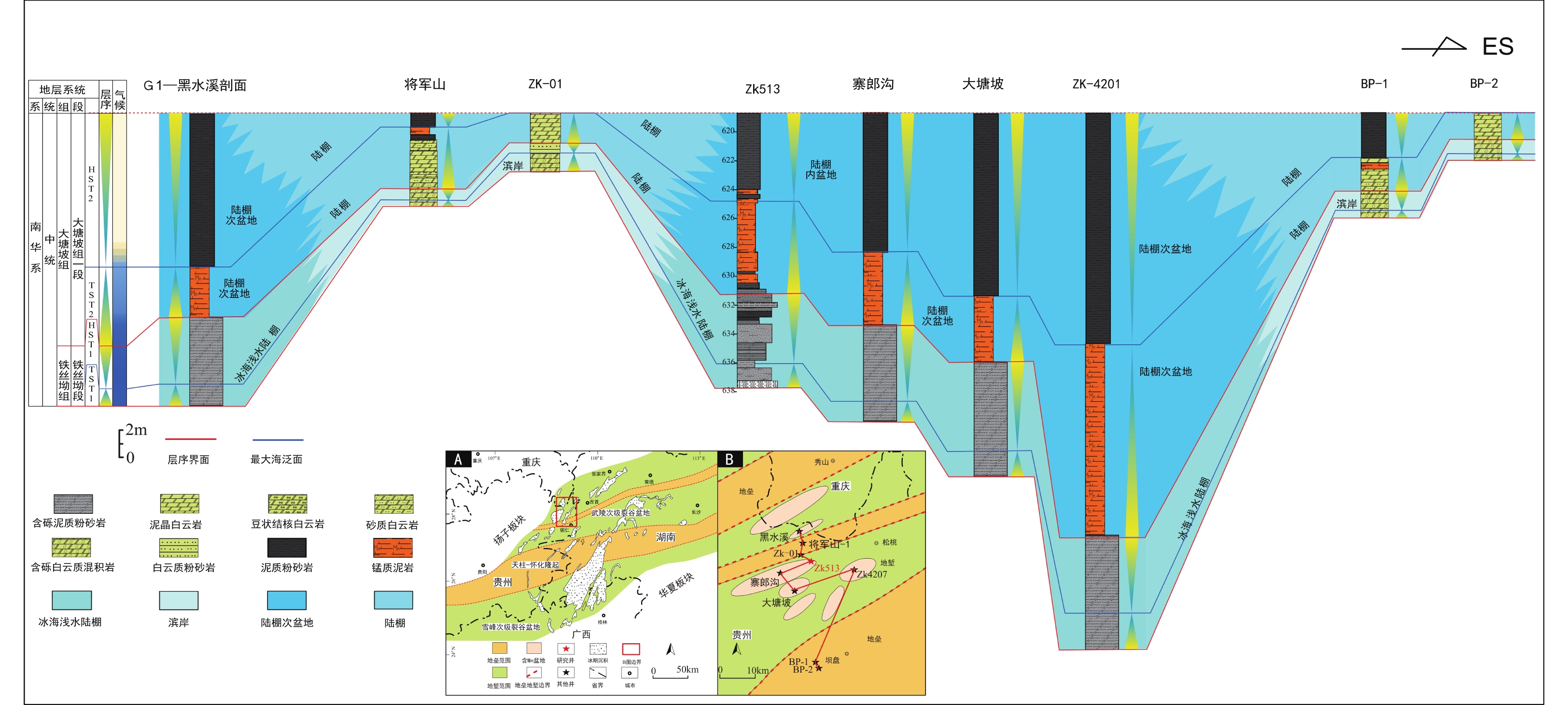
图 15 研究区铁丝坳组—大塘坡组一段连井对比(其他井资料据Yu et al., 2017修改)
Figure 15.
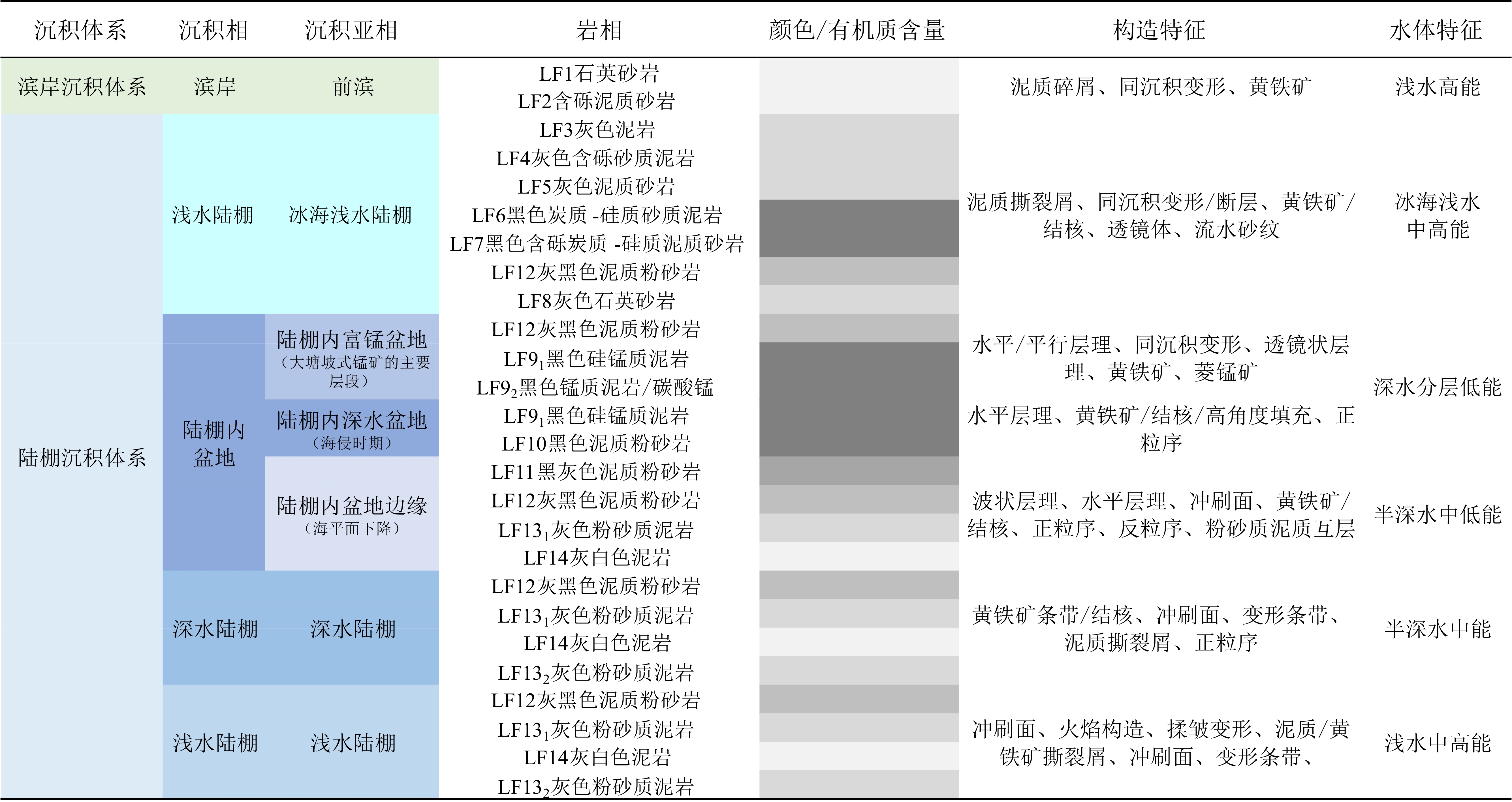
表 1 黔东北南华系中统研究区沉积体系划分表
Table 1. Division table of sedimentary system in the study area of Nanhua system in northeastern Guizhou
-
[1] Cheng M, Li C, Chen X, et al. , 2018. Delayed neoproterozoic oceanic oxygenation: evidence from Mo isotopes of the Cryogenian Datangpo Formation[J]. Precambrian Research, 319: 187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.12.007
[2] Cheng M, Zhang Z, Algeo T J, et al. , 2021. Hydrological controls on marine chemistry in the Cryogenian Nanhua basin (South China)[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 218: 103678. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103678
[3] Li C, Love G D, Lyons T W, et al. , 2012. Evidence for a redox stratified Cryogenian marine basin, Datangpo Formation, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 331-332: 246-256. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.03.018
[4] Li T, Zhu G, Zhao K, et al. , 2022. Geochemical characteristics of organic-rich intervals within the Cryogenian non-glacial Datangpo Formation in southeastern Yangtze Block-implications for paleoenvironment and its control on organic matter accumulation[J]. Precambrian Research, 378: 106777. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2022.106777
[5] Shen W, Zhu X, Li J, et al. , 2022. Mechanism of organic matter accumulation in black shale of the Datangpo Formation: insights from paleo-environmental variation during the Cryogenian non-glaciation[J]. Precambrian Research, 383: 106889. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2022.106889
[6] Tan Z, Jia W, Li J, et al. , 2021. Geochemistry and molybdenum isotopes of the basal Datangpo Formation: implications for ocean-redox conditions and organic matter accumulation during the Cryogenian interglaciation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 563: 110169.
[7] Wei G, Wei W, Wang D, et al. , 2020. Enhanced chemical weathering triggered an expansion of euxinic seawater in the aftermath of the Sturtian glaciation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 539: 116244. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2020.116244
[8] Yu W, Algeo T J, Du Y, et al. , 2017. Newly discovered sturtian cap carbonate in the Nanhua basin, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 293: 112-130. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.011
[9] 陈小妍, 2020. 中-新元古代期间海洋化学条件的变化[D]: 中国科学技术大学.
Chen X Y, 2020. The ocean chemistry changes during Meso-to Neoproterozoic[D]: University of Science and Technology of China.
[10] 黄文魁, 2016. 贵州松桃大塘坡锰矿中固体沥青的地球化学特征及其成因研究[D]: 长江大学.
Huang W K, 2016. The geochemical characteristics and genesis study of solid bitumen from Datangpo manganese ore in Songtao, Guizhou[D]: Yangtze University.
[11] 李明龙, 田景春, 方喜林, 等, 2019. 鄂西走马地区大塘坡组顶部泥岩碎屑锆石la-icp-ms u-pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(01): 22-31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.01.003
Li M L, Tian J C, Fang X L, et al. , 2019. Mudstones from the topmost part of the Datangpo Formation in the Zouma area, western Hubei: LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and its geological implications[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(01): 22-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.01.003
[12] 李一凡, 2016. 黔西北地区上奥陶统至下志留统细粒沉积岩形成环境与孔隙表征[D]: 中国地质大学(北京).
Li Y F, 2016. Depositional environment and pore characteristics of the Odorvician-Silurian fine-grained sedimentary rocks, northwestern Guizhou, South China[D]: China University of Geosciences( Beijing ).
[13] 罗亮, 孙志明, 马志鑫, 等, 2015. 黔东渝东南地区南华纪沉积序列与沉积环境演变[J]. 地质科技情报, 34(02): 27-35
Luo L, Sun Z M, Ma Z X, et al. , 2015. Sedimentary sequence and evolution of depositional environment of Nanhua System, east of Guizhou and southeast of Chongqing[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(02): 27-35.
[14] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等, 2016. 黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪武陵裂谷盆地结构及其对锰矿的控制作用[J]. 地球科学(2): 177 − 188
Zhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al., 2016. The structure of the Wuling rift basin and its control on the manganese deposit during the Nanhua period in Guizhou-Hunan-Chongqing border area, South China[J]. Earth Science(2): 177 − 188.
[15] 郭昱宏, 2015. 重庆酉阳秀山大塘坡组层序地层及与成锰关系研究[D]: 成都理工大学.
Guo Y H, 2015. Research and relationship with a manganese in Chongqing Xiushan Youyang Datangpo Formation sequence stratigraphy[D]: Chengdu University of Technology.
[16] 李一凡, 魏小洁, 樊太亮, 2021. 海相泥页岩沉积过程研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 39(1): 73-87
Li Y F, Wei X J, Fan T L, 2021. A review on sedimentary processes of marine mudstones and shales[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 39(1): 73-87.
[17] 刘振, 马志鑫, 刘伟, 等, 2021. 重庆秀山小茶园地区南华纪大塘坡组沉积环境与锰矿产出规律[J]. 沉积学报, 39(3): 513-524
Liu Z, Ma Z X, Wei L, et al. , 2021. Sedimentary environment and manganese ore deposits in the Nanhua period Datangpo Formation in Xiaochayuan area, Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 39(3): 513-524.
[18] 马志鑫, 罗亮, 刘喜停, 等, 2016. 重庆秀山小茶园锰矿南华系大塘坡组古环境[J]. 古地理学报, 18(3): 473-486
Ma Z X, Luo L, Liu X T, et al. , 2016. Palaeoenvironment of the Datangpo Formation of Nanhua System in Xiaochayuan manganese deposit in Xiushan area of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 18(3): 473-486.
[19] 饶莉, 2017. 松桃地区大塘坡组地球化学特征与古海洋化学状态研究[D]: 中国矿业大学.
Rao L, 2017. Study on the sedimentary geochemical of Datangpo Formation and chemical state of ocean in Songtao area[D]: China University of Mining & Technology.
[20] 郑杰, 2019. 黔东北地区大塘坡式锰矿床沉积相分析[D]: 成都理工大学.
Zheng J, 2019. Sedimentary facies analysis of Datangpo type manganese deposit in northeast Guizhou[D]: Chengdu University of Technology.
[21] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等, 2016. 贵州铜仁松桃锰矿国家整装勘查区地质找矿主要进展及潜力预测[J]. 贵州地质, 33(4): 237-244
Zhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al. , 2016. Prediction of geologic exploration in Songtao manganese national fully equipped exploration district in Tongren, Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 33(4): 237-244.
[22] 曹默雷, 陈建平, 2022. 由层序地层学角度分析大塘坡式锰矿沉积过程——以湘西北民乐锰矿为例[J]. 沉积学报, 40(04): 1083-1094
Cao M L, Chen J P, 2022. The analysis of the sedimentary process for Datangpo-type manganese ores from the point of sequence stratigraphy: a case of the minle manganese deposits in northwestern Hunan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 40(04): 1083-1094.
[23] 陈建书, 戴传固, 彭成龙, 等, 2016. 湘黔桂相邻区新元古代820~635Ma时期裂谷盆地充填序列与地层格架[J]. 中国地质, 43(03): 899-920
Chen J S, Dai C G, Peng C L, et al. , 2016. The filling sequence and stratigraphic framework of rift basin during the Neoproterozoic 820-635 Ma in Hunan, Guizhou and Guangxi[J]. Geology in China, 43(03): 899-920.
[24] 杜远生, 周琦, 余文超, 等, 2015. Rodinia超大陆裂解、sturtian冰期事件和扬子地块东南缘大规模锰成矿作用[J]. 地质科技情报: 1 − 7
Du Y S, Zhou Q, Yu W C, et al., 2015. Linking the cryogenian manganese metallogenic process in the southeast margin of Yangtze Block to break-up of Rodinia supercontinent and Sturtian glaciation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information: 1 − 7.
[25] 何明华, 2021. 南华系大塘坡组菱锰矿矿床地质特征及成因新见解[J]. 科技创新与应用, 11(21): 65-67
He M H, 2021. New insights on geological characteristics and genesis of the Nanhua Datangpo Formation rhodochrosite deposit[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 11(21): 65-67.
[26] 李婷婷, 朱光有, 赵坤, 等, 2021. 华南地区南华系大塘坡组黑色岩系地质地球化学特征与有机质富集机制[J]. 石油学报, 42(09): 1142-1162
Li T T, Zhu G Y, Zhao K, et al. , 2021. Geological, geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment of the black rock series in Datangpo Formation in Nanhua System, South China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 42(09): 1142-1162.
[27] 瞿永泽, 徐林刚, 毛景文, 等, 2018. 贵州铜仁地区南华系大塘坡组黑色页岩型菱锰矿碳、氧同位素特征及锰矿成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 37(01): 50-66 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2018.01.004
Qu Y Z, Xu L G, Mao J W, et al. , 2018. Carbon and oxygen isotope characteristics and mineralization of black shalehosted manganese carbonate of Datangpo Formation in Tongren, Guizhou province[J]. Deposit Geology, 37(01): 50-66. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2018.01.004
[28] 宋腾, 林拓, 李飞, 等, 2022. 中上扬子地区南华系大塘坡组沉积期岩相古地理及对油气成藏的指示[J]. 中国地质: 1 − 23
Song T, Lin T, Li F, et al., 2022. Lithofacies paleogeography in the depositional period of the Datangpo Formation of Nanhua System in the Middle and Upper Yangtze region, SW China and its indication of hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Geology in China: 1 − 23.
[29] 唐婷婷, 牟军, 王安华, 等, 2019. 贵州铜仁地区南华系铁丝坳组—南沱组沉积环境及古气候演变[J]. 贵州科学, 37(06): 67-73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2019.06.015
Tang T T, Mou J, Wang A H, et al. , 2019. Sedimentary environment and paleoclimate research of Tiesi′ao Formation-Nantuo Formation in Tongren, Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Science, 37(06): 67-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2019.06.015
[30] 王萍, 周琦, 余文超, 等, 2019. 湘黔渝邻接区南华纪“大塘坡式”锰矿的高δ34S成因与成矿意义//第九届全国成矿理论与找矿方法学术讨论会论文摘要集[C].
Wang P, Zhou Q, Yu W C, et al., 2019. The high δ34S genesis and metallogenic significance of the Nanhua 'Datangpo' manganese deposit in the adjacent area of Hunan, Guizhou and Chongqing// Abstracts of the 9 th National Symposium on Metallogenic Theory and Prospecting Methods[C].
[31] 余文超, 杜远生, 周琦, 等, 2020. 华南成冰纪“大塘坡式”锰矿沉积成矿作用与重大地质事件的耦合关系[J]. 古地理学报, 22(05): 855-871
Yu W C, Du Y S, Zhou Q, et al. , 2020. Coupling between metallogenesis of the cryogenian Datangpo-type manganese deposit in South China and major geological events[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 22(05): 855-871.
[32] 张予杰, 安显银, 刘石磊, 等, 2020. 黔东北地区大塘坡组早期含锰沉积充填、岩相古地理与锰矿的关系[J]. 中国地质, 47(03): 607-626
Zhang Y J, An X Y, Liu S L, et al. , 2020. The lithofaces, Mn-bearing sedimentary filling and palaeogeographic pattern of early Datangpo stage and implied for manganese in the Northeastern Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 47(03): 607-626.
[33] 赵文智, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等, 2018. 中国元古界—寒武系油气地质条件与勘探地位[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 45(01): 1-13 doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30001-6
Zhao W Z, Hu S Y, Wang Z C, et al. , 2018. Petroleum geological conditions and exploration importance of Proterozoic to Cambrian in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(01): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30001-6
-



 下载:
下载: