The C-H-O Isotopic Composition and Significance of Spodumene for Redamen Pegmatite Type Rare Metal Deposit in Western Sichuan
-
摘要:
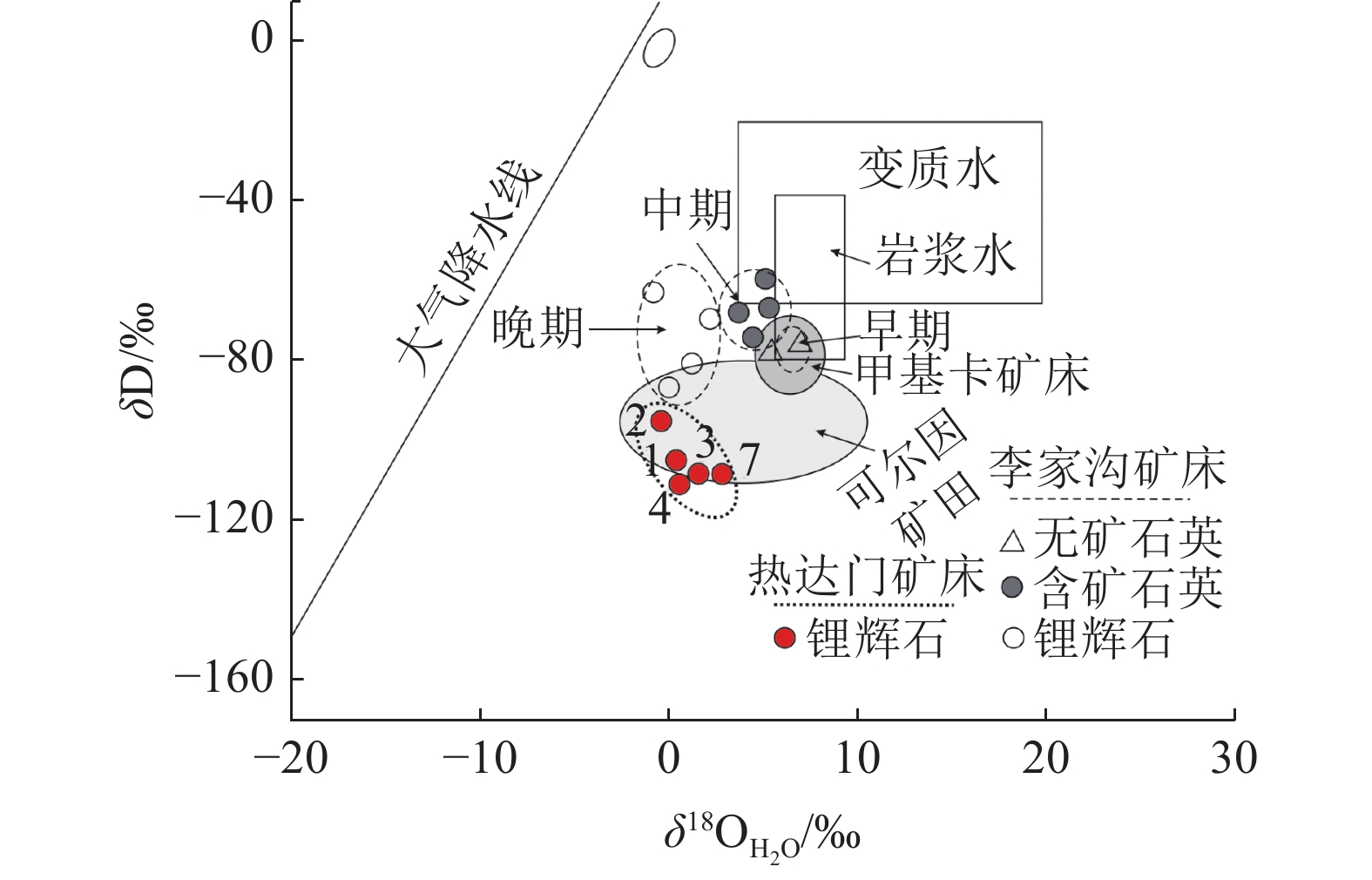
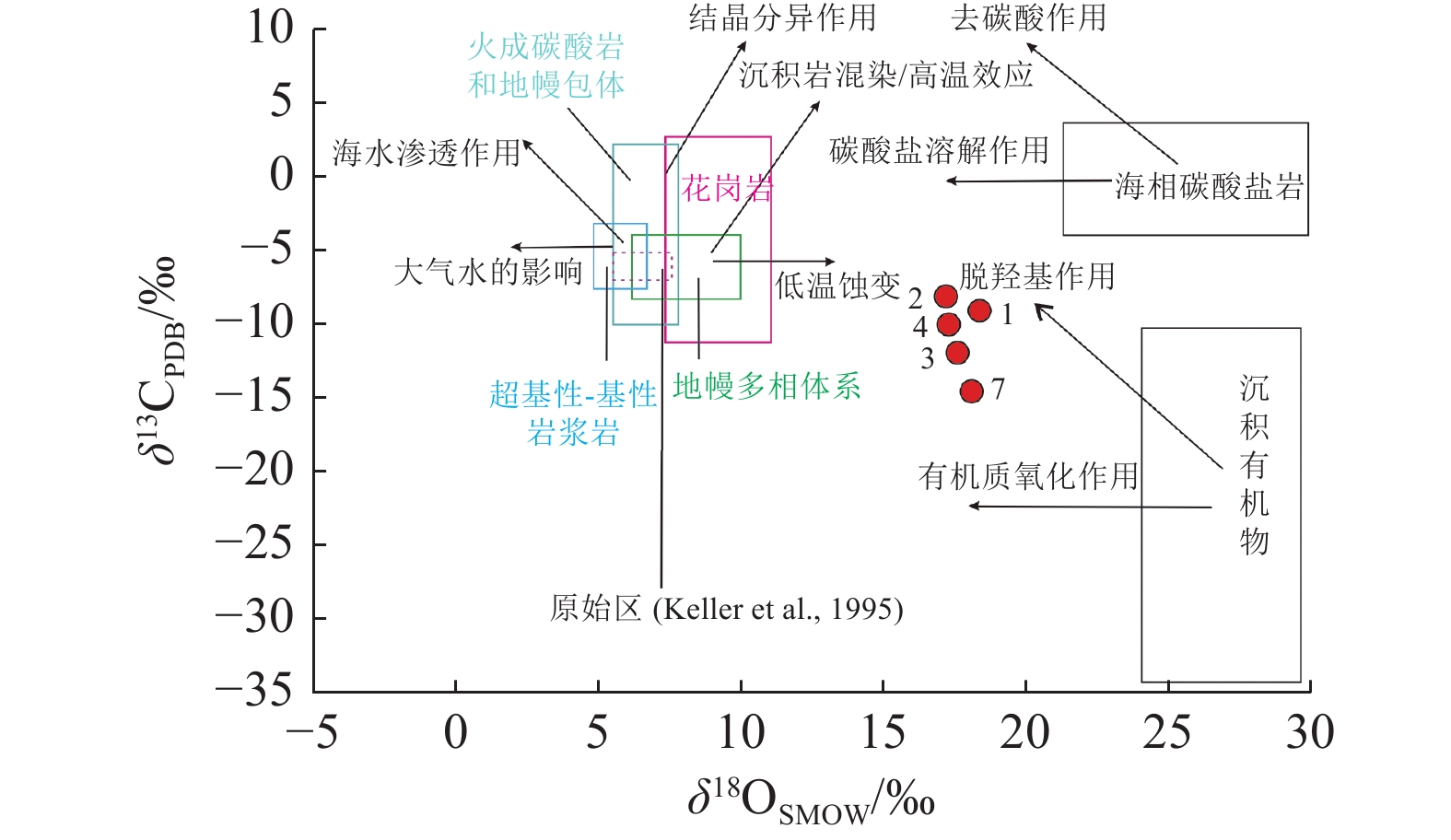
热达门稀有金属矿床位于川西可尔因伟晶岩型矿田的南西部,文章在详细的矿床地质特征研究基础上,系统采集同一矿脉同一矿体不同标高(3540~3830 m)的矿石,分析测试了锂辉石单矿物中的C-H-O同位素组成以及不同矿物中的包裹体特征。矿物中包裹体主要以富液相包裹体为主,锂辉石中包裹体盐度集中于8%~20%,均一温度180~330℃,属于中-低盐度、中-高温成矿流体;石英中包裹体盐度集中于0%~8%,均一温度150~240℃,属于低盐度、低温流体。C-H-O同位素测试结果显示热达门稀有金属矿床中的锂辉石δD值为-97.5‰~-104.7‰(平均-102.8‰),相对于可尔因地区其他锂矿床,δD值明显偏小,δ18OH2O值为-0.34‰~2.88‰(平均1.032‰),表明成矿流体可能有大气降水的混入,并受到了围岩黑云母而长花岗岩体的影响。矿床中锂辉石的δ13CV-PDB值为-10‰~-16.6‰,平均-12.7‰,反映主成矿期碳的来源具有岩浆系统和大气降水系统的混合性质,与岩浆-地幔源(花岗岩、地幔多相体系)的低温蚀变有关,并可能混入部分由沉积有机物质经脱羧基作用(decarboxylation)生成CO2。通过对矿物C-H-O同位素及流体包裹体进行研究,进一步明确了成矿流体来源及演化过程。
Abstract:The Redamen rare metal deposit is located in the south western part of Keeryin pegmetite typed ore field in western Sichuan. It is a special deposit in the aspects of surrounding rock, element mineralization zoning and distance. The ore with different elevation (3540~3830 m) of the same vein and the same orebody is systematically collected, spodumene single mineral is selected to analyze the C-H-O isotope composition and features of inclusions in different minerals.The inclusions in minerals are mainly liquid-rich inclusions. The salinity of the inclusions in spodumene is 8%~20%, and the homogenization temperature is 180~330℃. The inclusions belong to the ore-forming fluid with medium-low salinity and medium-high temperature. The inclusions in quartz have salinity of 0%~8%, homogenization temperature of 150~240℃, and belong to low salinity and low temperature fluid. The results of C-H-O isotope test show that the δD/‰ of spotamene in the Redamen rare metal deposit ranges from -97.5 to -104.7 (average of -102.8). Compared with the Lijiagou deposit in the southeast of the ore field, the δD/‰ of spodumene is obviously smaller, with the δ18OH2O/‰ ranging from -0.34 to 2.88 (average of 1.032). However, it is basically consistent with the main metallogenic period of spodumene in Lijiagou deposit, indicating that the ore-forming fluid of late mineralization (that is, the main metallogenic period of spodumene) is mixed with meteoric water. The δ13CV-PDB/‰ of spodumene in the Redamen rare metal deposit ranges from -10 to -16.6, with an average of -12.7, indicating that the carbon source in the main mineralization period (spodumene formation period) has a mixed nature of magmatic system and meteoric precipitation system, which is related to the low temperature alteration of magmatic mantle source (granite, mantle multi-phase system) and may be mixed with CO2 generated by the decarboxylation of deposited organic materials. Through the study of mineral C-H-O isotopes and fluid inclusions, the source and evolution process of ore-forming fluids were further clarified.
-
Key words:
- Pegmatite type /
- Rare metal /
- Spodumene /
- C-H-O isotopee /
- Redamen
-

-
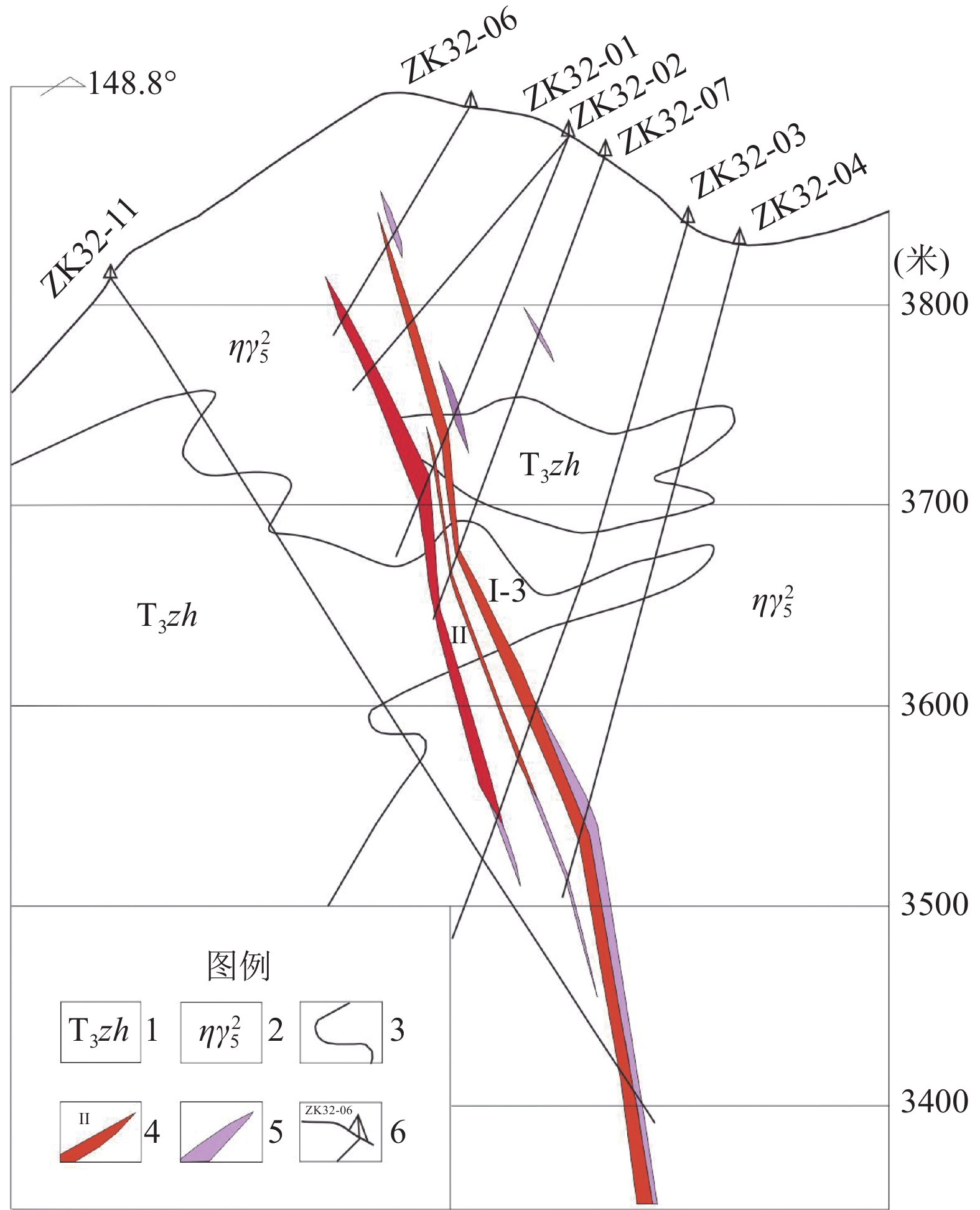
表 1 热达门稀有金属矿床P32剖面采样情况
Table 1. P32 profile sampling situation of Redamen rare metal deposit
序号 工程名称 矿体名称 样号 高程/m 品位(Li2O/%) 1 ZK32-01 I-3 H2、H3 3793 (2.38, 1.77)
(平均2.08)2 ZK32-02 H8、H10 3735 (1.85, 1.62)
(平均1.74)3 ZK32-07 H8、H7 3678 (1.28, 1.25)
(平均1.27)4 ZK32-03 H3、H2 3615 (1.51, 1.28)
(平均1.40)5 ZK32-04 H10、H9 3540 (2.12, 2.21)
(平均2.17)表 2 流体包裹体测试结果
Table 2. Fluid inclusion test results
样品编号 赋存矿物 个数 气液比/% 均一温度/℃ Th,CO2/℃ 盐度/% ZK32-01-H3 石英 13 10~85 169~303 24.9~28.2 3.01~8.82 锂辉石 11 10~35 166~271 29.1~29.3 8.00~12.32 ZK32-02-H10 石英 9 10~40 149~307 26.4 1.91~7.92 锂辉石 13 10~80 179~331 29.2 2.57~19.29 ZK32-07-H7 石英 7 10~35 146~297 29.0~29.2 1.64~13.57 锂辉石 18 20~25 269~317 \ 5.51~6.03 ZK32-03-H3 石英 9 10~35 189~332 22.9~27.4 4.33~14.46 锂辉石 24 10~15 178~259 \ 10.73~16.15 ZK32-04-H10 石英 6 15~60 197~332 29.6~29.7 5.05~7.05 锂辉石 29 10~60 158~338 25.9~30.4 7.59~17.87 表 3 可尔因矿田稀有金属矿床锂辉石C、H、O同位素组成
Table 3. Spodumene C, H, O isotopic composition of rare metal deposit in Keeryin ore field
序号 样号 岩性 矿床 δ18OV-SMOW
/‰δ18OV-PDB
/‰δDV-SMOW
/‰δ13CV-PDB
/‰δ18OH2O
/‰T
/℃来源 1 KEYK-1 白云母钠长石锂辉
石伟晶岩可尔因 16 -14.5 -89 -7 5.64 242 据文献[17] 2 KEYK-10 10.9 -19.4 -83 -9.8 0.54 242 3 KEYK-2 14.4 -16.0 -97 -10.3 4.04 242 4 KEYK-6 16.9 -13.6 -100 -7.2 6.54 242 5 LPD1H2 钠长石锂辉
石伟晶岩李家沟矿床晚期
成矿阶段11.1 -19.2 -61.6 -11.8 -0.21 220 据文献[9] 6 LPD2H2 14 -16.4 -68.7 -16.2 2.69 220 7 LPD3H2 13 -17.4 -79.4 -17.2 1.69 220 8 LPD4H2 11.7 -18.6 -85.5 -18.7 0.39 220 9 ZK32-01 钠长石锂辉
石伟晶岩热达门床 12.4 -17.9 -104.1 -11 1.58 231 本文 10 ZK32-02 11.2 -19.1 -97.5 -10 -0.34 215 11 ZK32-07 12.1 -18.2 -104.3 -16.6 2.88 273 12 ZK32-03 11.6 -18.8 -102.5 -14 0.43 223 13 ZK32-04 11.3 -19.1 -105.6 -12 0.61 234 注:①锂辉石的δ18OH2O值通过平衡分馏公式方程1000 lnα=2.75×106/T2 [32]计算得出;②δ18OPDB=0.97002×δ18OSMOW-21.98 [33];③ δ18OV-SMOW/‰=1.03092×δ18OV-PDB/‰+30.92 [33] -
[1] 费光春, 杨峥, 杨继忆, 等. 四川马尔康党坝花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床成矿时代的限定: 来自LA-MC-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb定年的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3):836-849. FEI G C, YANG Z, YANG J Y, et al. Definition of metallogenic epoch of Dangba granite pegmatite type rare metal deposit in Marcand, Sichuan: evidence from LA-MC-ICP-MS cassiterite U-Pb dating[J]. Journal of Geology, 2020, 94(3):836-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.012
[2] 张伟, 邹林, 范映武, 等. 四川金川县热达门锂辉石矿地质特征及矿床成矿模型浅析[J]. 四川地质学报, 2019, 39(增刊.):55-59. ZHANG W, ZOU L, FAN Y W, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic model of spodumene deposit in Jedaias, Jinchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Sichuan Geology, 2019, 39(Suppl.):55-59.
[3] 廖芝华, 周中国, 张洪平. 可尔因稀有金属矿床液态不混溶作用的地球化学特征证据[J]. 四川地质学报, 2019, 39(增刊.):60-69. LIAO Z H, ZHOU Z G, ZHANG H P. Evidence of geochemical characteristics of liquid immiscibility of Kerin rare metal deposit[J]. Journal of Sichuan Geology, 2019, 39(Suppl.):60-69.
[4] G Fei, JF Menuge, C Chen, et al. Petrogenesis of the Lijiagou spodumene pegmatites in Songpan-Garze Fold Belt, West Sichuan, China: Evidence from geochemistry, zircon, cassiterite and coltan U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Lithos, 2020:364.
[5] 李建康, 王登红, 张德会, 等. 川西伟晶岩型矿床的形成机制及大陆动力学背景[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007, 1-20.
LI J K, WANG D H, ZHANG D H, et al. Formation mechanism and continental dynamic background of pegmatite deposits in western Sichuan [M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007, 1-20.
[6] 李金. 四川金川马场沟锂辉石矿床地质特征及成因分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018, 1-66.
LI J. Geological characteristics and genesis analysis of Machanggou spodumene deposit in Jinchuan, Sichuan [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018, 1-66.
[7] 古城会. 四川省可尔因伟晶岩田东南密集区锂辉石矿床成矿规律[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2014, 29(1):59-65. GU C H. Mineralization law of spodumene deposit in the southeast dense area of Kelin pegmatite field in Sichuan province[J]. Geological Prospecting Thesis, 2014, 29(1):59-65. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2014.01.007
[8] 王子平, 刘善宝, 马圣钞, 等. 四川阿坝州党坝超大型锂辉石矿床成矿规律及深部和外围找矿方向[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(6):2029-2041. WANG Z P, LIU S B, MA S C, et al. Metallogenic regularity of Dangba super-large spodumene deposit in Aba Prefecture, Sichuan Province and prospecting direction in deep and peripheral areas[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(6):2029-2041.
[9] 邓运, 费光春, 李剑, 等. 四川李家沟伟晶岩型锂辉石矿床碳氢氧同位素及成矿时代研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018, 38(3):40-47. DENG Y, FEI G C, LI J, et al. Study on hydrocarbon oxygen isotope and metallogenic epoch of pegmatite type spodumene deposit in Lijiagou, Sichuan[J]. Minerals and Rocks, 2018, 38(3):40-47.
[10] 许志琴, 王汝成, 赵中宝, 等. 试论中国大陆“硬岩型”大型锂矿带的构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(6):1091-1106. XU Z Q, WANG R C, ZHAO Z B, et al. On the tectonic setting of “hard rock type” large lithium ore belt in Chinese mainland[J]. Acta geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(6):1091-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001
[11] 唐文春, 段威, 邹林, 等. 川西可尔因地区伟晶岩型锂矿地球化学指标定位矿体的方法[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(5): 765-792.
TANG W C, DUAN W, ZOU L, et al. A method for locating ore bodies by geochemical indexes of pegmatite-type lithium deposits in the Ke'eryin area, western Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 765−792.
[12] 岳相元, 张贻, 周雄, 等. 川西可尔因矿集区稀有金属矿床成矿规律与找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4):867-876. YUE X Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU X, et al. Mineralization law and prospecting direction of rare metal deposits in Kelin ore concentration area, western Sichuan[J]. Deposit Geology, 2019, 38(4):867-876. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.04.012
[13] Deschamps, Fabien, Benoit, et al. Coeval mantle-derived and crust-derived magmas forming two neighbouring plutons in the Songpan Ganze accretionary orogenic wedge (SW China)(Article)[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2017, 58(11):2221-2256. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egy007
[14] 许家斌, 费光春, 覃立业, 等. 四川可尔因矿田李家沟伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床锡石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(2):346-358. XU J B, FEI G C, QIN L Y, et al. Cassiterite LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and geological significance of Lijiagou Pegmatite-type rare metal deposit in Keelin ore field, Sichuan[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(2):346-358.
[15] 马圣钞, 王登红, 刘善宝, 等. 综合勘查方法在硬岩型锂矿找矿中的应用—以马尔康稀有金属矿田加达锂矿为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8):2341-2353. MA S C, WANG D H, LIU S B, et al. Application of comprehensive exploration method in hard rock lithium ore prospecting-taking Jiada lithium ore field in Marcand as an example[J]. Acta geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8):2341-2353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.012
[16] 许志琴, 侯立玮, 王宗秀, 等. 中国松潘—甘孜造山带的造山过程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992, 20-70.
XU Z Q, HOU L W, WANG Z X, et al. The orogenic process of Songpan-Ganzi orogenic belt in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992, 20-70.
[17] 李建康, 王登红, 付小方. 川西可尔因伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的40Ar/39Ar年代及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(6):843-848. LI J K, WANG D H, FU X F. The 40Ar/39Ar age and tectonic significance of the rare metal deposit of Koeryin pegmatite type in western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geology, 2006, 80(6):843-848. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.06.006
[18] 马圣钞, 王登红, 刘善宝, 等. 川西可尔因锂矿田云母矿物化学及稀有金属成矿和找矿指示[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4):877-897. MA S C, WANG D H, LIU S B, et al. Mica mineral chemistry and rare metal mineralization and prospecting indicators in the Kelin lithium ore field, western Sichuan[J]. Deposit Geology, 2019, 38(4):877-897.
[19] 赵永久. 松潘-甘孜东部中生代中酸性侵入体的地球化学特征、岩石成因及构造意义[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2007, 1-101.
ZHAO Y J. Geochemical characteristics, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusive bodies in the east of Songpan-Ganzi [D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, China Academy of Sciences, 2007, 1-101.
[20] 岳相元, 杨波, 周雄, 等. 川西地区热达门石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征: 岩石成因与构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5):1015-1024. YUE X Y, YANG B, ZHOU X, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and rock geochemical characteristics of Jedaias quartz diorite in western Sichuan: petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Modern Geology, 2019, 33(5):1015-1024.
[21] 岳相元, 郭佳, 毛树林, 等. 川西太阳河黑云母二长花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(6):142-1151. YUE X Y, GUO J, MAO S L, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, rock geochemical characteristics and geological significance of biotite monzonite granite in Taiyanghe, western Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Mineral Rock Geochemistry, 2018, 37(6):142-1151. doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2018.37.084
[22] Nie S Y, Yin A, Rowley D B, et al. Exhumation of the Dabie Shan ultra-high- pressure rocks and accumulation of the Songpan-Ganzi flysch sequence, central China[J]. Geology, 1994, 22:999-1002.
[23] Sengor A M C and Natalin B A. Paleotectonics of Asia: Fragments of a synthesis [A]. In: Yin A, Harrison T M. , eds. , The Tectonics of Asia [C]. Cambridge University Press, New York, 1996, 486-640.
[24] Bruguier O, Lancelot J R, Malavieille J. U-Pb dating on single detrital zircon grains from the Triassic Songpan-Ganze flysch (Central China): Provenance and tectonic correlations[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 152(1-4):217-231.
[25] 时章亮, 张宏飞, 蔡宏明. 松潘造山带马尔康强过铝质花岗岩的成因及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 34(4):569-584. SHI Z L, ZHANG H F, CAI H M. Genesis and tectonic significance of Marcand peraluminous granite in Songpan orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science, 2009, 34(4):569-584. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.04.002
[26] 罗伟, 岳相元, 周雄, 等. 四川金川县列门地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿意义[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1):1-7. LUO W, YUE X Y, ZHOU X, et al. Soil geochemical characteristics and prospecting significance in Liemen area, Jinchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Mineral Comprehensive Utilization, 2022(1):1-7.
[27] 廖远安, 姚学良. 金川—过铝多阶段花岗岩体演化特征及其与成矿关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 1992, 12(1):12-22. LIAO Y A, YAO X L. Evolution characteristics of Jinchuan-peraluminous granite body and its relationship with mineralization[J]. Minerals and Rocks, 1992, 12(1):12-22. doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.1992.01.003
[28] 王全伟, 梁斌, 朱兵, 等. 川西北壤塘地区西康群深海浊积砂岩沉积地球化学特征[J]. 地质地球化学, 2001, 29(4):82-85. WANG Q W, LIANG B, ZHU B, et al. Sedimentary geochemical characteristics of deep-sea turbidite sandstone of Xikang Group in Zamtang area, northwest Sichuan[J]. Geology and Geochemistry, 2001, 29(4):82-85.
[29] Fei G C, Li B H, Yang J Y, et al. Geology, Fluid inclusion characteristics and H-O-C isotopes of large Lijiegou pegmatite spodumene deposit in Songpan-Garze fold belt, eastern Tiber: implications for ore genesis[J]. Resour Geol, 2018, 68(1):37-50. doi: 10.1111/rge.12145
[30] Clayton R N, Mayeda T K. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1963, 27:43-52. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(63)90071-1
[31] Coleman M L, Shepherd T J, Durham J J, et al. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis[J]. Anal Chem, 1982, 54:993-995. doi: 10.1021/ac00243a035
[32] Javoy M. Stable isotopes and geothermometry[J]. J Geol Soc London, 1977, 133:609-639. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.133.6.0609
[33] Coplen T B, Kendall C, Hopple J. Comparison of stable isotope reference samples[J]. Nature, 1983, 302:236-238. doi: 10.1038/302236a0
[34] Taylor S R, Mclennan S H. The continental crust: its composition and envolution[J]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1985:117-140.
[35] 杨学明, 杨晓勇, 陈双喜. 译. 岩石地球化学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2000, 206-227.
YANG X M, YANG X Y, CHEN S X. Rock geochemistry[M]. Hefei: China University of Science and Technology Press, 2000, 206-227.
[36] 李培忠, 虞福基, 刘德平, 等. 黑龙江碾子山晶洞碱性花岗岩氢同位素组成与岩浆去气作用[J]. 地球化学, 1992(1):70-76. LI P Z, YU F J, LIU D P, et al. Hydrogen isotope composition and magma degassing of alkaline granite in Nianzishan, Heilongjiang[J]. Geochemistry, 1992(1):70-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1992.01.009
[37] 李培忠, 申佑林, 李春岭, 等. 黑龙江碾子山晶洞碱性花岗岩δ18O等值线图与古化石热水体系研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1990(8):862-869. LI P Z, SHEN Y L, LI C L, et al. δ18O contour map of alkaline granite in Nianzishan, Heilongjiang Province and study on fossil hot water system[J]. China Science (Series B), 1990(8):862-869.
[38] 李培忠, 于津生. 山海关晶洞碱性花岗岩H、O同位素地球化学研究[J]. 科学通报, 1989(1):51-52. LI P Z, YU J S. H and O isotopic geochemistry of alkaline granite in Shanhaiguan geode[J]. Science Bulletin, 1989(1):51-52.
[39] 李培忠. 就“关于碱性花岗岩H同位素组成及其有关问题的讨论”有关问题的回答[J]. 地球化学, 1995, 24(2): 196-197.
LI P Z. Answers to some questions about “Discussion on H isotope composition of alkaline granite and related problems”[J]. Geochemistry, 1995, 24(2): 196-197.
[40] 郑永飞, 傅斌, 龚冰. 大别造山带超高压变质岩稳定同位素地球化学[J]. 安徽地质, 2000(3):161-165. ZHENG Y F, FU B, GONG B. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Anhui Geology, 2000(3):161-165.
[41] 温春齐, 多吉. 矿床学研究方法[M]. 成都: 四川科技出版社, 2009, 123-136.
WEN C Q, DUO J. Research methods of mineralogy [M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 2009, 123-136.
[42] Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry, 6th revised and updated edition[J]. Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2008:136-150.
[43] Clark I and Fritz P. Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology[M]. New York: Lewis Publishers, 1997: 328.
[44] Faure G. Principles of isotope Geology [M]. New York: 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, 1986: 589.
[45] 刘家军, 何明勤, 李志明, 等. 云南白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区碳氧同位素组成及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(1):1-10. LIU J J, HE M Q, LI Z M, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of silver-copper polymetallic ore concentration area in Baiyangping, Yunnan and its significance[J]. Geology of Deposits, 2004, 23(1):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.01.001
[46] 刘建明, 刘家军. 滇黔桂金三角区微细浸染型金矿床的盆地流体成因模式[J]. 矿物学报, 1997, 17(4):448-456. LIU J M, LIU J J. Basin fluid genetic model of micro disseminated gold deposits in the golden triangle area of Yunnan, Guizhou and Guangxi[J]. Journal of Minerals, 1997, 17(4):448-456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1997.04.012
[47] 毛景文, 赫平, 丁悌平. 胶东金矿形成期间地幔流体参与成矿过程的碳氧氢同位素证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(2):121-127. MAO J W, HE P, DING T P. Carbon, oxygen and hydrogen isotopic evidence of mantle fluid participating in the metallogenic process during the formation of Jiaodong gold deposit[J]. Deposit Geology, 2002, 21(2):121-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.02.004
-




 下载:
下载: