Study on Characteristics of Bentonite in Huludao, Liaoning
-
摘要:
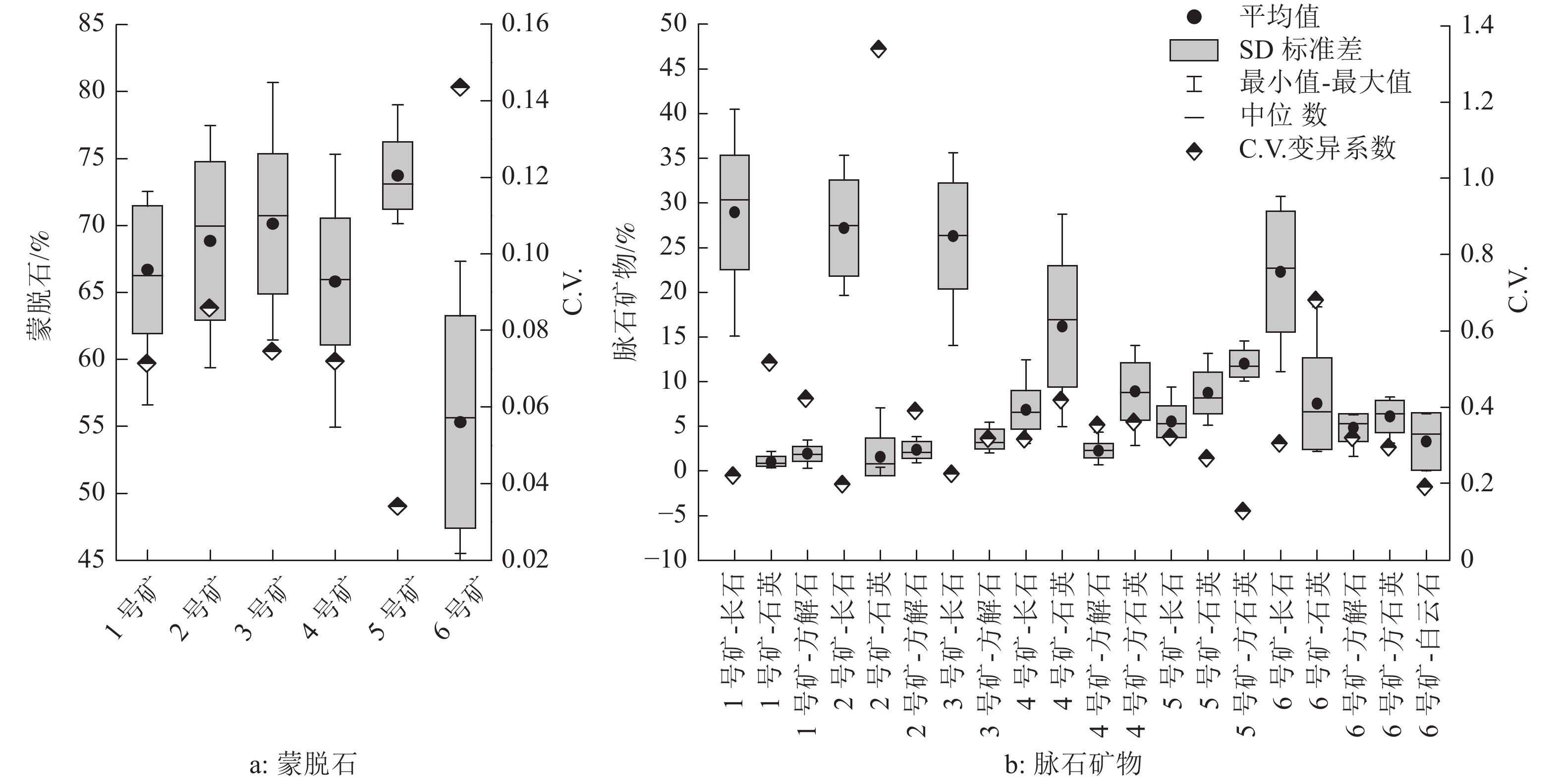
葫芦岛市位于锦西-哈尔套膨润土成矿带的最南端,为探究葫芦岛膨润土的特性,对葫芦岛的6个膨润土矿进行了研究,通过测定试样的膨胀容、亚甲基蓝吸收量、阳离子交换容量和X射线衍射分析,对葫芦岛膨润土的表观特性、矿物组成、膨胀性能和阳离子交换性等性能进行了评价和表征。研究表明:葫芦岛膨润土矿均为钙基膨润土矿,总体质量较好,大部分膨润土的粒度均匀、自然白度较高,蒙脱石平均含量接近或高于70%。葫芦岛膨润土矿的石英、长石、方解石是主要脉石矿物,矿物组成比较简单,阳离子交换性能较好,在辽西地区膨润土矿中处于中上等地位,具有较强的代表性。然而,辽西膨润土普遍含有方石英,限制了产品的应用范围。
Abstract:Huludao is the starting point of the Jinxi-Hartao metallogenic belt. In order to explore the characteristics of Huludao bentonite, six bentonite mines in Huludao were studied. Crystalline phases, montmorillonite content, swelling property, cation exchange performance of the samples were characterized and evaluated by X-ray diffraction, swelling volume, cation exchange capacity and methylene blue index, respectively. By comparing Huludao bentonite with other bentonites in western Liaoning, the characteristics of bentonite in western Liaoning were summarized. Huludao bentonite belongs to calcium-base bentonite and has the following advantages: high whiteness, high montmorillonite content, simple mineral composition, good cation exchange performance and stable ore quality, which has a strong representativeness in western Liaoning. However, bentonite in the western Liaoning generally contains cristobalite, which limits the application range of the product.
-
Key words:
- Bentonite /
- Cristobalite /
- Mineral composition
-

-
表 1 葫芦岛膨润土的形貌特征
Table 1. Apparent characteristics of Huludao bentonite
编号 颜色 表观白度 粒度均匀 质感 块矿占比 其他 1 灰白 高 × 砂质 多 2 灰白、浅褐色 中 √ 砂质 无 3 灰白、褐色 低 √ 砂质 少 4 灰白 高 √ 砂质 少 5 土黄色、灰绿色 中 × 蜡质 多 柔软、有塑形 6 深褐色 低 × 岩石质 少 坚硬、难破碎 表 2 吸蓝量、CEC、膨胀容和pH值测试结果
Table 2. Test results of MBI, CEC, SV and pH value
No. 1号 2号 3号 4号 5号 6号 吸蓝量换算的蒙脱石含量/ % min 60.8 61.3 64.3 58.8 72.3 45.7 max 76.3 78.5 83.3 78.0 81.0 69.7 mean 70.2 70.9 72.3 67.9 75.4 57.3 CEC/mmol·(100 g)-1 min 64.47 71.33 70.75 65.33 80.54 52.63 max 86.53 95.53 96.87 88.87 92.05 76.52 mean 78 81.16 82.02 76.71 85.39 64.51 膨胀容/ (mL·g-1) min 6 9 10 8 8 8 max 13 14 13 15 14 12 mean 9 11 12 11 12 10 pH值 min 7.5 7.6 7.6 7.3 7.6 7.9 max 8.1 8.4 8.5 8.7 8.2 8.9 mean 7.8 8.1 8.0 8.1 7.9 8.5 表 3 辽西地区膨润土主产地膨润土矿的特征
Table 3. Characteristics of bentonite in western Liaoning
序号 产地 类型 蒙脱石/% 性质与特征 1 建平 镁基 62.32 胶质价46;膨胀容8;脉石矿物:石英[21] 2 钙基 85.06 胶质价96.3;膨胀容10.4[22];pH值 8.6;CEC 36.5;脉石矿物:石英、云母、长石[21] 3 阜蒙 钠基 57.67 胶质价62.30;膨胀容8.1;pH 8.60 ;CEC 59.90[23] 4 钙基 56.04 胶质价100;膨胀容10.75;pH 9.15;CEC 56.04 5 钙基 40-70 CEC 49-69;[23]脉石矿物:石英8~20%、长石12~27%、水云母2.3~5.6%、方英石1%以下[24] 6 凌源 钙基/钠基 60~80 pH 值7.5~8.2(钙基);9.01~9.89(钠基);胶质价87~100;膨胀容8-9; 脉石:方英石、斜长石、方解石、少量伊利石、沸石和石英[8] 7 黑山 钙基 50~60 胶质价80~100;膨胀倍数 12-33;脉石:沸石、方英石、伊利石、石英、长石、云母[8] 8 阜新 钠基 65 脉石:方石英、石英、长石、方解石[5] 9 北票 钙基 68.5 胶质价68.55;膨胀容8.87;pH 8.75脉石:方英石、长石,少量石英和方解石[25] 10 钙基 73.8 胶质价99.45;膨胀容18.9;pH值8.06;脉石:方英石、长石,少量石英和方解石[25] 11 钙基 88.1 胶质价56.55;膨胀容6.10;pH8.22;脉石:方英石、长石,少量石英和方解石[25] 12 彰武 钙基 55.83~78.33 CEC:51.39~82.09;脉石:高岭土、伊利石和少量长石、石英、方解石、黑云母[26] 注:胶质价(mL/15 g) 膨胀容(mL/g) CEC(mmol/100 g) -
[1] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 中国矿产资源报告2019[M]. 中国地质出版社, 2019.
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. China mineral resources report 2019 [M]. China Geological Publishing House, 2019.
[2] Zhang Yaozu. Review on Research Progress of Bentonite[J]. Advances in Environmental Protection, 2019, 3(9):496-501.
[3] 王新江, 雷建斌. 我国膨润土资源概况及开发利用现状[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2010(3):13-15. WANG X J, LEI J B. General situation of bentonite resources in my country and status quo of development and utilization[J]. China Non-Metallic Mineral Industry Guide, 2010(3):13-15.
[4] 施春辉, 吕品, 王立林. 辽宁省膨润土工业现状及发展建议[J]. 辽宁化工, 2018, 47(9):954-956. SHI C H, LV P, WANG L L. Status quo and development suggestions of bentonite industry in Liaoning Province[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(9):954-956.
[5] 代连铎. 辽宁西部膨润土矿控矿条件与地质特征浅析[J]. 中国科技纵横, 2015(21):157-158, 160. DAI L D. An analysis of ore-controlling conditions and geological characteristics of bentonite deposits in western Liaoning[J]. China Science and Technology, 2015(21):157-158, 160.
[6] 于政海. 辽西地区膨润土矿控矿条件与地质特征探析[J]. 中国金属通报, 2019(5):177, 179. YU Z H. Exploration and analysis of ore-controlling conditions and geological characteristics of bentonite deposits in western Liaoning[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2019(5):177, 179.
[7] 高恩忆. 辽西中生代火山岩中珍珠岩、沸石、膨润土成矿因素探讨[J]. 辽宁地质, 1986(1):35-46. GAO E Y. Discussion on mineralization factors of perlite, zeolite and bentonite in Mesozoic volcanic rocks in western Liaoning[J]. Liaoning Geology, 1986(1):35-46.
[8] 王楚杰. 辽西义县组主要非金属矿床地质特征及成矿条件研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2014.
WANG C J. Study on the geological characteristics and metallogenic conditions of the main non-metallic deposits of Yixian Formation in western Liaoning [D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2014.
[9] 李小彬. 辽西地区火山岩型沸石、膨润土、珍珠岩成矿机制与找矿方向探讨[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2013(16):101. LI X B. Discussion on the mineralization mechanism and prospecting direction of volcanic zeolite, bentonite and perlite in western Liaoning[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2013(16):101.
[10] 李广有. 陆相火山沉积岩系非金属矿床的地质特征及控矿条件[J]. 现代地质, 2005(3):361-368. LI G Y. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling conditions of non-metallic deposits in continental volcanic sedimentary rocks[J]. Modern Geology, 2005(3):361-368.
[11] 李广有. 火山沉积型非金属矿床成矿机理与成矿模式探讨[J]. 安徽地质, 2006(2):88-93. LI G Y. Discussion on metallogenic mechanism and model of volcanic sedimentary non-metallic deposits[J]. Geology of Anhui, 2006(2):88-93.
[12] 葫芦岛市人民政府. 葫芦岛市矿产资源总体规划(2016-2020)[R]. 2017.
People's Government of Huludao City. Overall planning of mineral resources in Huludao City (2016-2020) [R]. 2017.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 膨润土[S]. . 2007.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administrators Association. Bentonite [S]. 2007.
[14] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 出口颗粒膨润土中白度、酸度及膨胀容的检验方法[S]. 2001.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Inspection method for whiteness, acidity and swelling volume of export granular bentonite [S]. 2001.
[15] 陈智杰, 管俊芳, 高惠民, 等. 膨润土中蒙脱石定量分析研究进展[Z]. 中国安徽合肥: 2016.
CHEN Z J, GUAN J F, GAO H M, et al. Research progress in quantitative analysis of montmorillonite in bentonite [Z]. Hefei, Anhui, China: 2016
[16] Checkoway H, Heyer N J, Seixas N S, et al. Dose-response associations of silica with nonmalignant respiratory disease and lung cancer mortality in the Diatomaceous Earth Industry[J]. American Journal of Epidemiology, 1997, 145(8):680-688. doi: 10.1093/aje/145.8.680
[17] Ruehlmann J, Körschens M. Soil particle density as affected by soil texture and soil organic matter: 2. Predicting the effect of the mineral composition of particle-size fractions[J]. Geoderma. 2020, 375: 114543.
[18] Xu G, Li Z, Li P. Fractal features of soil particle-size distribution and total soil nitrogen distribution in a typical watershed in the source area of the middle Dan River, China[J]. CATENA. 2013, 101: 17-23.
[19] 1988 osha pel project-cristobalite niosh cdc, (2011-09-28), https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/pel88/14464-46.html.
[20] Carcinogen list - occupational cancer niosh cdc, (2012-05-30), https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/cancer/npotocca.html#c.
[21] 林涛, 任建晓, 殷学风. 建平膨润土锂化研究[J]. 铸造, 2013, 62(3):245-248. LIN T, REN J X, YIN X F. Research on lithation of Jianping bentonite[J]. Foundry, 2013, 62(3):245-248.
[22] 李彩霞, 白阳, 赵靖雨, 等. 建平膨润土提纯及制备球团黏结剂实验研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2017, 40(3):54-56. LI C X, BAI Y, ZHAO J Y, et al. Experimental study on purification of Jianping bentonite and preparation of pellet binder[J]. Non-metallic Minerals, 2017, 40(3):54-56.
[23] 刘殿鹤, 张雪花. 辽宁省二道河膨润土矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2015, 37(2):85-92. LIU D H, ZHANG X H. Geological characteristics and genesis of Erdaohe bentonite deposit in Liaoning Province[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2015, 37(2):85-92.
[24] 李坛, 胡墨田, 王吉平. 辽宁省阜蒙县北窝铺膨润土矿床地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 化工矿产地质. 2014, 36(3): 161-166.
LI T, HU M T, WANG J P. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the bentonite deposit in Beiwopu, Fumeng County, Liaoning Province [J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals. 2014, 36(3): 161-166.
[25] 许凤林, 徐传云, 何雪寒, 等. 辽宁北票膨润土制备活性白土试验研究[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊. 2009(6): 31-33.
XU F L, XU C Y, HE X H, et al. Experimental study on preparation of activated white clay from Beipiao Bentonite in Liaoning [J]. China Non-Metallic Mineral Industry Guide. 2009(6): 31-33.
[26] 董军. 辽宁省彰武县三道沟地区膨润土矿床特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质. 2015, 29(2): 221-224.
DONG J. Characteristics and genesis of bentonite deposits in Sandaogou area, Zhangwu County, Liaoning Province [J]. Mineral Resources and Geology. 2015, 29(02): 221-224.
[27] Idiart A, Laviña M, Cochepin B, et al. Hydro-chemo-mechanical modelling of long-term evolution of bentonite swelling[J]. Applied Clay Science. 2020, 195: 105717.
[28] Lim J, de Kretser R G, Scales P J. Investigating the influence of total electrolyte concentration and sodium–calcium ion competition on controlled dispersion of swelling clays[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing. 2009, 93(2): 95-102.
[29] Li X, Li C, Xu Y. Representation of volume change for bentonite in saline solution based on modified effective stress[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering. 2019, 23(5): 2065-2073.
[30] 印航, 高惠民, 管俊芳, 等. 新疆某地钠基膨润土提纯试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2009(5):17-20. YIN H, GAO H M, GUAN J F, et al. Experimental study on the purification of sodium bentonite in a certain area of Xinjiang[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2009(5):17-20.
-




 下载:
下载: