Ratio Optimization of Slag Cementitious Material and the Properties of Filling Body
-
摘要:
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。针对某铅锌矿全尾砂充填以水泥为胶凝材料成本过高和充填体后期强度低的问题,采用丰富的炉渣固废资源,开发低成本炉渣胶凝材料满足矿山充填体的质量需求。在对尾砂、炉渣和水泥熟料进行物化分析后,通过充填料浆坍落度实验和炉渣胶凝材料配比探索实验,确定满足流动性的料浆浓度为70%左右,炉渣与水泥熟料比值为2~4为较优配比区间;通过全面实验法探究了不同配比炉渣胶凝材料充填体强度,充填料浆的泌水率和凝结特性。结果表明:炉渣胶凝材料配比为炉渣添加量75%~80%,水泥熟料添加量20%~25%,充填体能够满足强度0.5~3.5 MPa,充填料浆泌水率小于5%的充填质量要求。
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of ceramics and composites. To solve the problems of high-cost for cement cementitious material and low strength of cement filling body at the later stage in a lead-zinc mine, abundant slag solid waste resources were adopted and low-cost slag cementitious materials were developed in this paper to meet the quality requirement of mine fillings. After physical and chemical analysis of tailings, slag and cement clinker, the physical and chemical analysis of tailings, slag and cement clinker was carried out. Then, through the filler slurry slump test and the exploration test of the ratio of slag cementitious material, it is determined that the slurry concentration satisfying the fluidity is about 70%, and the ratio of slag to cement clinker is 2~4. The strength, bleeding rate and coagulation characteristics of filling body with different proportions of slag cementitious materials were investigated by comprehensive test. The results show that the ratio of slag cementitious material is 75%~80% slag and 20%~25% cement clinker, the filling body can meet the filling quality requirements of 0.5 ~3.5 MPa compressive strength and the filling slurry bleeding rate is less than 5%.
-
Key words:
- Ceramics and composites /
- Backfilling mining method /
- Slag /
- Cementitious material /
- Whole tailings
-

-
表 1 全尾砂颗粒级配常数
Table 1. Distribution constant of the whole tailings particle size
d10/μm d30/μm d50/μm d60/μm d90/μm Cu Cc 6.02 29.92 76.1 121.4 410 20.17 1.22 注:Cu= d60/d10; 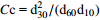 [11]
[11]表 2 炉渣粒径分布
Table 2. Distribution of slag particle size
粒级/μm -5 +5-10 +10-20 +20-30 +30-40 +40 产率/% 12.2 37.69 28.19 15.86 5.77 0.29 累计/% 12.2 49.89 78.08 93.94 99.71 100.00 表 3 炉渣化学成分/%
Table 3. Chemical composition of slag
CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO SO3 Fe2O3 TiO2 MnO 39.50 33.27 10.70 7.78 2.20 1.70 1.18 1.13 表 4 不同胶砂比不同料浆浓度下尾砂料浆坍落度
Table 4. Slump of tailings slurry under different cement-sand ratio and slurry concentration
胶砂比 坍落度/cm 76% 74% 72% 70% 68% 1∶4 23.4 27.4 28.0 28.5 29.1 1∶8 23.3 26.9 27.8 28.3 28.8 1∶12 23.1 26.5 27.3 28.0 28.5 1∶16 23.0 26.4 27.2 27.8 28.4 表 5 炉渣胶凝材料配比实验结果
Table 5. Ratio test results of slag cementitious materials
组号 炉渣∶水泥
熟料炉渣/% 水泥
熟料/%单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 14 d 1 1∶4 20 80 0.673 1.131 1.732 2 1∶2 33 67 0.490 1.142 1.750 3 1∶1 50 50 0.320 1.165 2.269 4 2∶1 67 33 0.297 1.238 2.809 5 4∶1 80 20 0.283 1.052 2.640 6 水泥 0.539 1.022 1.580 表 6 炉渣胶凝材料1充填体强度配比实验
Table 6. Strength ratio test of slag cementitious material 1 filling body
组号 胶砂比 浓度/% 炉渣/% 水泥熟料/% 单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 1 1∶6 72 80 20 0.67 1.64 4.15 2 1∶6 70 80 20 0.52 1.52 3.85 3 1∶6 68 80 20 0.43 1.13 3.31 4 1∶8 72 80 20 0.38 1.21 3.05 5 1∶8 70 80 20 0.32 1.03 2.43 6 1∶8 68 80 20 0.27 0.79 2.01 7 1∶10 72 80 20 0.32 0.76 2.40 8 1∶10 70 80 20 0.24 0.67 1.81 9 1∶10 68 80 20 0.21 0.58 1.58 10 1∶12 72 80 20 0.31 0.71 2.08 11 1∶12 70 80 20 0.23 0.65 1.73 12 1∶12 68 80 20 0.20 0.56 1.34 表 7 炉渣胶凝材料2充填体强度配比实验
Table 7. Strength ratio test of slag cementitious material 2 filling body
组号 胶砂比 浓度/% 炉渣/% 水泥熟料/% 单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 13 1∶6 72 75 25 0.70 1.73 4.39 14 1∶6 70 75 25 0.51 1.58 3.51 15 1∶6 68 75 25 0.42 1.22 3.14 16 1∶8 72 75 25 0.37 1.22 3.14 17 1∶8 70 75 25 0.32 1.07 2.41 18 1∶8 68 75 25 0.27 0.82 1.98 19 1∶10 72 75 25 0.31 0.84 2.92 20 1∶10 70 75 25 0.27 0.67 2.12 21 1∶10 68 75 25 0.22 0.57 1.79 22 1∶12 72 75 25 0.28 0.77 2.10 23 1∶12 70 75 25 0.26 0.61 2.01 24 1∶12 68 75 25 0.21 0.53 1.57 表 8 炉渣胶凝材料3充填体强度配比实验
Table 8. Strength ratio test of slag cementitious material 3 filling body
组号 胶砂比 浓度/% 炉渣/% 水泥熟料/% 单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 25 1∶6 72 70 30 0.60 1.59 3.77 26 1∶6 70 70 30 0.48 1.40 3.61 27 1∶6 68 70 30 0.38 1.12 3.33 28 1∶8 72 70 30 0.36 1.12 3.09 29 1∶8 70 70 30 0.29 0.94 2.20 30 1∶8 68 70 30 0.24 0.73 1.78 31 1∶10 72 70 30 0.33 0.80 2.69 32 1∶10 70 70 30 0.26 0.66 1.94 33 1∶10 68 70 30 0.22 0.56 1.66 34 1∶12 72 70 30 0.25 0.66 2.02 35 1∶12 70 70 30 0.23 0.59 1.57 36 1∶12 68 70 30 0.19 0.51 1.33 表 9 炉渣胶凝材料4充填体强度配比实验
Table 9. Strength ratio test of slag cementitious material 4 filling body
组号 胶砂比 浓度/% 炉渣/% 水泥熟料/% 单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 37 1∶6 72 65 35 0.66 1.62 4.05 38 1∶6 70 65 35 0.56 1.43 3.61 39 1∶6 68 6 35 0.47 1.08 3.01 40 1∶8 72 65 35 0.36 1.08 3.05 41 1∶8 70 65 35 0.31 0.92 2.41 42 1∶8 68 65 35 0.26 0.68 1.99 43 1∶10 72 65 35 0.31 0.82 2.75 44 1∶10 70 65 35 0.30 0.63 2.37 45 1∶10 68 65 35 0.23 0.54 1.89 46 1∶12 72 65 35 0.25 0.69 1.90 47 1∶12 70 65 35 0.23 0.53 1.62 48 1∶12 68 65 35 0.21 0.48 1.43 表 10 水泥胶凝材料充填体强度配比实验
Table 10. Strength ratio test of cement cementitious material filling body
组号 胶砂比 浓度/% 单轴抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 49 1∶6 72 1.02 1.65 2.65 50 1∶6 70 0.89 1.47 2.32 51 1∶6 68 0.67 1.12 2.01 52 1∶8 72 0.71 1.28 1.68 53 1∶8 70 0.54 1.06 1.46 54 1∶8 68 0.48 0.83 1.06 55 1∶10 72 0.68 0.87 1.31 56 1∶10 70 0.49 0.75 1.15 57 1∶10 68 0.41 0.67 0.86 58 1∶12 72 0.54 0.66 0.94 59 1∶12 70 0.44 0.57 0.76 60 1∶12 68 0.37 0.49 0.65 表 11 充填料浆凝结时间
Table 11. Setting time of filing slurry
编号 胶砂比 浓度/% 初凝
时间点/h终凝
时间点/h初终凝
时间差/h1 1∶6 72 11.25 31.50 20.25 2 70 12.00 32.25 20.25 3 68 12.50 33.00 20.25 4 1∶8 72 13.75 34.25 20.25 5 70 14.25 35.75 21.50 6 68 15.00 37.25 22.25 7 1∶10 72 16.00 39.25 23.25 8 70 16.50 40.50 24.00 9 68 17.50 42.00 24.50 10 1:12 72 18.75 43.25 24.50 11 70 19.50 44.25 24.75 12 68 20.50 45.50 25.00 -
[1] 张国胜, 高谦, 郭斌, 等. 全尾砂胶凝材料开发及泡沫砂浆充填试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(12):74-80. ZHANG G S, GAO Q, GUO B, et al. Development of whole tailings cementitious material and experimental study on foam mortar filling[J]. Metal Mine, 2020(12):74-80. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202012012
ZHANG G S, GAO Q, GUO B, et al. Development of whole tailings cementitious material and experimental study on foam mortar filling[J]. Metal Mine, 2020(12): 74-80. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202012012
[2] 杨晓炳, 王永定, 高谦, 等. 利用脱硫灰渣和粉煤灰开发充填胶凝材料[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):130-134. YANG X B, WANG Y D, GAO Q, et al. Research on a new cementitious materials with desulphurization ash and fly ash[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):130-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.028
YANG X B, WANG Y D, GAO Q, et al. Research on a new cementitious materials with desulphurization ash and fly ash[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4): 130-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.028
[3] 胡敏, 彭丽, 郭娜, 等. 磷石膏- 炭化污泥胶凝材料力学性能试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):196-201. HU M, PENG L, GUO N, et al. Study on mechanical properties of phosphogypsum-carbonized sludge composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
HU M, PENG L, GUO N, et al. Study on mechanical properties of phosphogypsum-carbonized sludge composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4): 196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
[4] 梁晓杰, 常钧, 吴昊泽. 钢渣粉粒度对复合胶凝材料水化性能的影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(3):180-186. LIANG X J, CHANG J, WU H Z. Effect of particle size of steel slag powder on hydration performance of composite cementitious material[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3):180-186.
LIANG X J, CHANG J, WU H Z. Effect of particle size of steel slag powder on hydration performance of composite cementitious material[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3): 180-186.
[5] 何良玉, 谯理格, 赵日煦, 等. 钢渣作胶凝材料和细集料制备高性能砂浆的研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(6):94-100. HE L Y, JIAO L G, ZHAO R X, et al. Study on preparation of high performance mortar using steel slag as cementitious material and fine aggregate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6):94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.021
HE L Y, JIAO L G, ZHAO R X, et al. Study on preparation of high performance mortar using steel slag as cementitious material and fine aggregate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.021
[6] 李夕兵, 刘冰. 硬岩矿山充填开采现状评述与探索[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(4): 492-502.
LI X B, LIU B. Review and exploration of current situation of backfill mining in hard rock mines[J]. Gold Science and Technology. 2018, 26(4): 492-502.
[7] 邢行, 杨仕教. 某铅锌矿超细全尾砂炼铅炉渣-水泥复合充填胶凝材料研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(7): 2232-2240.
XING X, YANG S J. Study on the composite filling cementitious material for the lead smelting slag-cement with superfine full tailings in a lead zinc mine[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society. 2020, 39(7): 2232-2240.
[8] 李兵, 杨仕教, 王洪武, 等. 某冶炼厂炼铅炉渣制备胶凝材料的试验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2014, 33(3):583-588. LI B, YANG S J, WANG H W, et al. Experimental research on producing cementing material using smelter's lead refinery slag[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 33(3):583-588. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2014.03.020
LI B, YANG S J, WANG H W, et al. Experimental research on producing cementing material using smelter's lead refinery slag[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 33(3): 583-588. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2014.03.020
[9] 杨超, 郭利杰, 李文臣. 铜镍冶炼渣新型充填胶凝材料制备及其力学性能研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2020, 40(8): 50-54.
YANG C, GUO L J, LI W C. Preparation of new cementitious backfill materials with copper and nickel smelting slag and its mechanical properties[J]. Mining Research and Development. 2020, 40(8): 50-54.
[10] 朱庚杰, 齐兆军, 寇云鹏, 等. 分级细尾砂胶结充填强度和料浆流变性能试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2020, 40(4): 18-22.
ZHU G J, QI Z J, KOU Y P, et al. Experimental study on cemented backfill strength and slurry rheological properties of graded fine tailings[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering. 2020, 40(4): 18-22.
[11] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.
LI G X. Advanced Soil Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Publishing House Co. , Ltd. 2004.
[12] 陈杰, 梁杨芝, 王俊, 等. 高沙充填材料的输送性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(1): 194-198.
CHEN J, LIANG Y Z, WANG J, et al. Research on transport characteristic of high sand content filling material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society. 2020, 39(1): 194-198.
-




 下载:
下载:




