Excretion Rate and Accumulating Rate of p, p'-DDE in Beijing Resident during Consecutive Lactation
-
摘要:
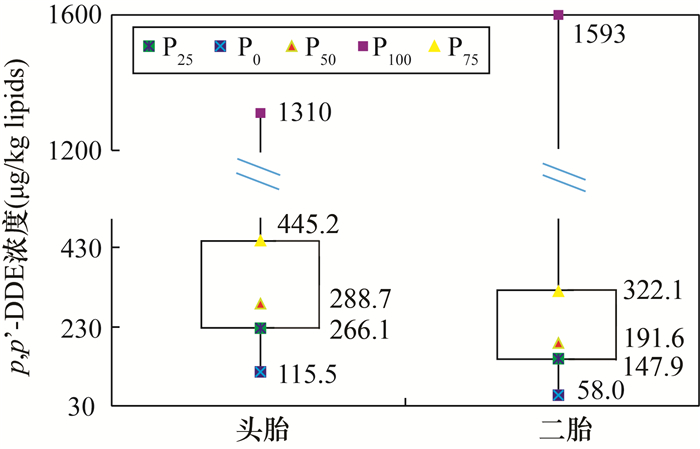
母乳中p,p’-DDE浓度是监测母体短期内p,p’-DDE的“静态”蓄积水平,估算婴幼儿每日摄入量的重要技术手段。本文旨在通过监测北京女性两个相邻哺乳期内母乳中p,p’-DDE浓度及变化,估算两次分娩间隔期母体内p,p’-DDE的“动态”富集速度,并根据每日摄入量掌握人体p,p’-DDE的长期变化趋势。在2009年至2019年期间,收集了43名女性首次分娩后六个月内和18名女性第二次分娩后六个月内的母乳样本,并采用气相色谱法检测了母乳中p,p’-DDE的浓度。实验结果表明,母乳中p,p’-DDE浓度在哺乳期持续下降。年龄和分娩次数是母乳中p,p’-DDE浓度的影响因素,p,p’-DDE浓度随母亲年龄增大而升高,随分娩次数增多而降低。18名母亲两个哺乳期内母乳中p,p’-DDE平均排泄速度计算结果表明,排泄速度从18.9μg/kg lipid/month降低到16.8μg/kg lipids/month。而母体两次分娩隔期内p,p’-DDE年富集速度估算值为正,分布在10.9~14.9μg/kg lipids/year之间,每日摄入量分布在29.8~40.8ng/day/kg.b.w.之间。因此北京女性哺乳期母体内p,p’-DDE月排泄速度与母体年富集速度数值相当,母体p,p’-DDE每日摄入量远低于世界卫生组织(WHO)建议值,北京女性是低风险暴露人群。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Monitoring of p, p'-DDE in breast milk was a significant way to evaluate the p, p'-DDE accumulation level in human beings within a short-term and calculate daily intake for infants. Although the investigation of classic organic chlorine pesticides in Beijing breast milk showed that p, p'-DDE was detected with the highest residue level. The study on the accumulating rate of p, p'-DDE, indicated a dynamic and long-term change, in Beijing females this was neglected and scarce.
OBJECTIVES To detect p, p'-DDE in breast milks from two consecutive lactations, estimate the excreted speed during each lactation along with the impact of delivery times on residue level of p, p'-DDE in mothers, and estimate its annual accumulating rate in Beijing residents.
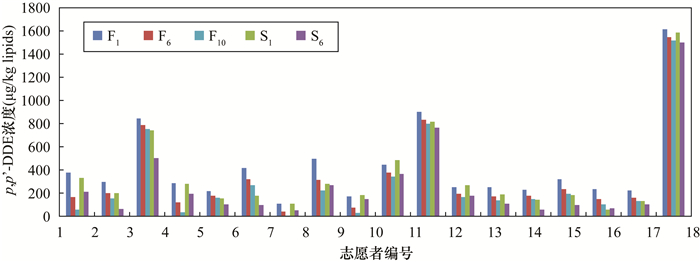
METHODS During 2009-2019, breast milk samples were collected from 43 mothers during their first lactation and 18 of them during their two consecutive lactations. The concentration of p, p'-DDE in breast milk was determined by gas chromatography.
RESULTS The analytical results showed that the p, p'-DDE in breast milk decreased continuously during each lactation. Age and the number of childbirths were the influencing factors of the concentration of p, p'-DDE in breast milk. The concentration of p, p'-DDE increased with the age of mothers and decreased with the number of childbirths. In addition, the average excretion speed of p, p'-DDE in breast milk from 18 twice-birth mothers decreased from 18.9μg/kg lipids per month within the first lactation to 16.8μg/kg lipids per month within the second lactation. The estimated value of the annual enrichment rate of p, p'-DDE in the interval between two births of the mother was positive, from 10.9μg/kg lipids per year to 14.9μg/kg lipid per year during the consecutive deliveries. Daily intake of p, p'-DDE was from 29.8ng/day/kg.b.w. to 40.8ng/day/kg.b.w..
CONCLUSIONS The depurated dose of p, p'-DDE in mothers within a month of lactation was equal to the accumulating dose in a year. The estimated daily intake of p, p'-DDE was far lower than the suggested value of WHO. The Beijing female was in a low exposure risk environment.
-
Key words:
- p, p'-DDE /
- breast milk /
- gas chromatography /
- excretion rate /
- accumulating rate /
- Beijing female
-

-
表 1 志愿者及样品信息
Table 1. Information of donors and samples
志愿者数(人) 分娩次数 样品编号 样品数量 年龄范围(岁) 43 1 F1,F6 86 26~31 18 2 F1, F6, S1,S6 72 32~36 表 2 p, p’-DDE的排泄速度和富集速度
Table 2. Excretion speed and accumulating speed of p, p'-DDE
参数a 单位 取所有值计算 去极值计算 取P25~P75b区间值计算 F1 μg/kg lipids 429.0 374.3 297.1 F6 μg/kg lipids 337.2 279.7 227.8 Vec μg/kg lipids/month 18.3 18.9 13.9 F10 μg/kg lipids 263.9 204.1 172.3 S1 μg/kg lipids 352.7 293.5 238.0 S6 μg/kg lipids 293.5 209.4 152.3 Ved μg/kg lipids/month 16.0 16.8 17.1 Va μg/kg lipids/year 14.8 14.9 10.9 EDI ng/kg/day b.w. 40.5 40.8 29.8 注:a表示模拟计算值;b表示取值范围在最小四分位数和较大四分位数之间;c和d分别表示第一和第二个哺乳期内p, p’-DDE的平均排泄速度的估算值。 -
[1] Taiwo A M. A review of environmental and health effects of organochlorine pesticide residues in Africa[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 1126-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.001
[2] Ma J, Pan L B, Yang X Y, et al. DDT, DDD, and DDE in soil of Xiangfen County, China: Residues, sources, spatial distribution, and health risks[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 163: 578-583. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.050
[3] Han X, Zhang F, Meng L L, et al. Exposure to organochlorine pesticides and the risk of type 2 diabetes in the population of East China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 190: 110125. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110125
[4] Zheng Q, Li J, Wang Y, Lin T, et al. Levels and enantiomeric signatures of organochlorine pesticides in Chinese forest soils: Implications for sources and environmental behavior[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 262: 114-139. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0269749119359500
[5] Yang R Q, Zhang S J, Li A, et al. Altitudinal and spatial signature of persistent organic pollutants in soil, lichen, conifer needles, and bark of the Southeast Tibetan Plateau: Implications for sources and environmental cycling[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47: 12736-12743. doi: 10.1021/es403562x
[6] Qu C, Albanese S, Lima A, et al. The occurrence of OCPs, PCBs, and PAHs in the soil, air, and bulk deposition of the Naples metropolitan area, southern Italy: Implications for sources and environmental processes[J]. Environmental International, 2019, 124: 89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.031
[7] Helou K, Harmouche-Karaki M, Karake S, et al. A review of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in Lebanon: Environmental and human contaminants[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 231: 357-368. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.109
[8] Gakuba E, Moodley B, Ndungu P, et al. Partition dis-tribution of selected organochlorine pesticides in water, sediment pore water and surface sediment from uMngeni River, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa[J]. Water SA, 2018, 44: 232-249. http://www.scielo.org.za/pdf/wsa/v44n2/09.pdf
[9] Huang H, Ding Y, Chen W, et al. Two-way long-range atmospheric transport of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) between the Yellow River source and the Sichuan Basin, western China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 3230-3240. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.133
[10] Jin X, Liu Y, Qiao X, et al. Risk assessment of organo-chlorine pesticides in drinking water source of the Yangtze River[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 182: 109390. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109390
[11] Zhou S S, Tang Q Z, Jin M Q, et al. Residues and chiral signatures of organochlorine pesticides in mollusks from the coastal regions of the Yangtze River Delta: Source and health risk implication[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 114: 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.108
[12] Mahmoud A F A, Ikenaka Y, Yohannes Y B, et al. Distribution and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) residue in edible cattle tissues from northeastern part of Egypt: High accumulation level of OCPs in tongue[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 1365-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.016
[13] Ngweme G N, Salah D M M A, Laffite A, et al. Occurrence of organic micropollutants and human health risk assessment based on consumption of Amaranthus viridis, Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 754(1): 142-175. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720357041
[14] Olisah C, Okoh O O, Okoh A I. Occurrence of organochlorine pesticide residues in biological and environmental matrices in Africa: A two-decade review[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6: e03518. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03518
[15] Song S L, Ma X D, Pan M, et al. Excretion kinetics of three dominant organochlorine compounds in human milk within the first 6 months postpartum[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190: 457. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6850-9
[16] Samira S, Andrea Tove F, Corey D B J, et al. The metabolic fingerprint of p, p'-DDE and HCB exposure in humans[J]. Environment International, 2016, 88: 60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.12.015
[17] Berghuis S A, Bos A F, Sauer P J J, et al. Developmental neurotoxicity of persistent organic pollutants: An update on childhood outcome[J]. Archives of Toxicology, 2015, 89: 687-709. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1463-3
[18] Abolhassani M, Asadikaram G, Paydar P, et al. Organochlorine and organophosphorous pesticides may induce colorectal cancer: A case-control study[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 178: 168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.030
[19] Dardiotis E, Aloizou A M, Sakalakis E, et al. Organochlorine pesticide levels in Greek patients with Parkinson's disease[J]. Toxicology Report, 2020, 7: 596-601. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.03.011
[20] Yin S J, Wei J, Wei Y H, et al. Organochlorine pesticides exposure may disturb homocysteine metabolism in pregnant women[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708: 135146. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135146
[21] Carvalho F P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2017, 6(2): 48-60.
[22] Girones L, Oliva A L, Marcovecchio J E, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of residual organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in South American marine environments[J]. Current Environmental Health Reports, 2020, 7: 147-160. doi: 10.1007/s40572-020-00272-7
[23] Santiago E C, Cayetano M G. Organochlorine pesticides in ambient air in selected urban and rural residential areas in the philippines derived from passive samplers with polyurethane disks[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2011, 86: 50-55. doi: 10.1007/s00128-010-0160-4
[24] Yu Y X, Tao S, Liu W X, et al. Dietary intake and human milk residues of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in two Chinese cities[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2009, 43: 4830-4835. doi: 10.1021/es900082v
[25] Sun H W, An T C, Li G Y, et al. Distribution, possible sources, and health risk assessment of SVOC pollution in small streams in Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(17): 10083-10095. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3031-4
[26] Tang J, An T, Xiong J. The evolution of pollution profile and health risk assessment for three groups SVOCs pollutants along with Beijiang River, China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39: 1487-1499. doi: 10.1007/s10653-017-9936-3
[27] 宋淑玲, 田芹, 佟玲, 等. 生物样品母乳中有机氯农药类化合物近二十年研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5): 339-347. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.002
Song S L, Tian Q, Tong L, et al. Research application and development of organochlorine pesticides in breast milk in the recent twenty years[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5): 339-347. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.002
[28] Waliszewski S M G, Melo-Santiesteban R. Breast milk excretion kinetic of β-HCH, p, p'-DDE and p, p'-DDT[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 83: 869-873. doi: 10.1007/s00128-009-9796-3
[29] Tue N M, Sudaryanto A, Minh T B, et al. Kinetic differences of legacy organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in Vietnamese human breast milk[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 81: 1006-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.013
[30] LaKind J S, Berlin C M, Sjödin A, et al. Do human milk concentrations of persistent organic chemicals really decline during lactation? Chemical concentrations during lactation and milk/serum partitioning[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2009, 117(10): 1625-1631. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900876
[31] Man Y B, Chan J K Y, Wang H S, et al. DDTs in mothers' milk, placenta and hair, and health risk assessment for infants at two coastal and inland cities in China[J]. Environment International, 2014, 65: 73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.01.001
[32] 郭晓辰, 饶竹, 高冉. 气相色谱法测定地下水中拟除虫菊酯有机氯百菌清等24种农药残留[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(3): 406-412. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/77935fc3-6812-484c-8002-d3aaaf02d772
Guo X C, Rao Z, Gao R. Determination of 24 pesticides including pyrethroids, organochlorines and chlorothalonil in underground water by gas chromatography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(3): 406-412. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/77935fc3-6812-484c-8002-d3aaaf02d772
[33] 徐殿斗, 马玲玲, 李淑珍, 等. 北京石景山区夏季大气中有机氯农药的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(5): 599-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201005006.htm
Xu D D, Ma L L, Li S Z, et al. Organochloride pesiticides in the atmosphere in the Shijingshan District of Beijing[J]. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(5): 599-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201005006.htm
[34] 张春辉, 吴永贵, 杨少博, 等. 广东沿海3种食用鱼中有机氯农药的残留特征及风险评价[J]. 贵州农业科技, 2015, 43(11): 174-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GATE201511044.htm
Zhang C H, Wu Y G, Yang S B, et al. Residual feature and health risk assessment of organo-chlorine pesticides in three edible fish from Guangdong Coast[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(11): 174-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GATE201511044.htm
[35] 王晓华, 母清林, 张庆红, 等. 舟山近岸海域贝类中有机氯农药残留水平及人体健康风险评估[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(10): 59-62, 67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201410013.htm
Wang X H, Mu Q L, Zhang Q H, et al. Residue level of organochlorine pesticides in shellfish of Zhoushan coastal areas and assessment of its risk to human health[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2014, 36(10): 59-62, 67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201410013.htm
[36] Sudaryanto A, Kunisue T, Kajiwara N, et al. Specific accumulation of organochlorines in human breast milk from Indonesia: Levels, distribution, accumulation kinetics and infant health risk[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 139: 107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.04.028
-



 下载:
下载: