Rb-Sr ISOCHRON AGE OF FLUID INCLUSIONS IN THE QUARTZ OF XUJIACUN GOLD DEPOSIT, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE
-
摘要:
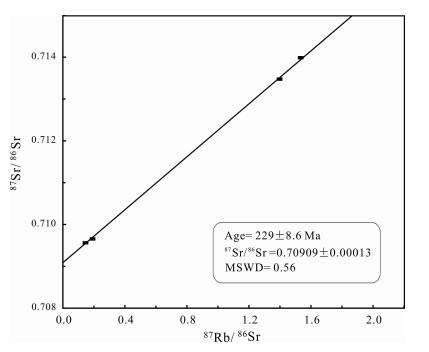
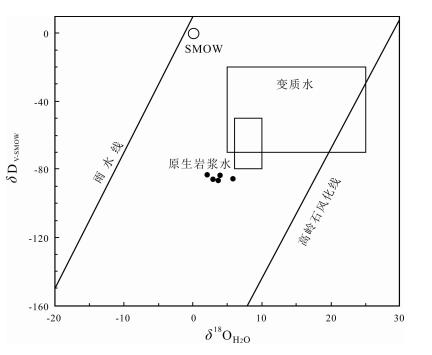
徐家村金矿床位于佳木斯地块西南部,矿体赋存于晚二叠世二长花岗岩中.通过对含金石英脉石英中的流体包裹体进行Rb-Sr同位素年龄及H、O同位素测定,获取成矿年龄,探讨成矿流体来源及其与赋矿花岗岩的成因联系.结果显示:石英流体包裹体Rb-Sr等时线年龄为229±8.6 Ma,比含矿岩体形成时代(254.2±0.95 Ma、230.44±0.54 Ma)稍晚或接近.石英中H、O同位素特征显示成矿流体应为晚二叠世花岗岩浆分异出的热液,后期有少量的大气降水的加入,暗示了含矿石英脉与赋矿花岗岩体具有密切的成因联系.综合认为,成岩成矿可能发生在同一地质事件中,即与古亚洲洋板块向佳蒙地块俯冲作用有关.
Abstract:The Xujiacun gold deposit is located in the southwest of Jiamusi block, with the orebody occurred in the Late Permian monzogranite. The metallogenic age is obtained and the ore-forming fluid source and its genetic relation with the host granite are discussed through the determination of Rb-Sr isotope age and H and O isotopes of fluid inclusions in the quartz of gold veins. The results show that the Rb-Sr isochron age is 229±8.6 Ma, slightly later or close to the formation time of ore-bearing rock mass (254.2±0.95 Ma, 230.44±0.54 Ma). The H and O isotopic characteristics of quartz indicate that the ore-forming fluid was the hydrothermal solution differentiated from the Late Permian granitic magma, with a small amount of atmospheric precipitation added later, suggesting that there is a close genetic relation between the ore-bearing quartz vein and the host granite. From the above, it is believed that the diagenesis and mineralization may occur in the same geological event, both related to the subduction of Paleo-Asian Ocean Plate into the Jiamusi-Mongolia block.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusion /
- Rb-Sr isochron /
- H and O isotopes /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
图 1 研究区地质图(据文献[15])
Figure 1.
图 4 徐家村金矿成矿流体δD-δ18OH2O图解(底图据文献[18])
Figure 4.
表 1 徐家村金矿床石英Rb-Sr同位素分析结果
Table 1. Rb-Sr isotope analysis results of the quartz in Xujiacun gold deposit
样品号 样品名称 Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 (87Rb/86Sr)N (87Rb/86Sr)N 2ó NL1-2 石英 5.05 75.3 0.1939 0.709658 0.000013 NL1-3 石英 1.33 26.1 0.1478 0.7109469 0.000012 NL1-4 石英 9.45 17.9 1.5297 0.714076 0.000012 NL1-5 石英 5.42 11.1 1.4069 0.713663 0.00001 表 2 徐家村金矿石英中氢、氧同位素组成
Table 2. compositions of H and O isotopes in the quartz o XUNJiacun gold deposit
样品原号 矿物 δ18OV-PDB δ18OV-SMOW δ18OH2O δDV-SMOW 均一温度℃ NLl-1 石英 -17.8 12.6 1.89 -82.8 216.3 NLl-2 石英 -16.7 13.7 4.11 -87.1 237 NLl-3 石英 -16.2 14.2 5.63 -85.6 258.3 NLl-4 石英 -16.4 14 4 -83.1 229 NLl-5 石英 -16.3 14.1 2.96 -85.9 209 表中均一温度为对应石英样品中流体包裹体均一温度的平均值(数据未发表).包裹体测试由核工业北京地质研究所完成,测试仪器为LINKAM THMS600型冷热台,温度控制精度为±0.1 ℃.含量单位:%. -
[1] 莫测辉, 王秀璋, 程景平, 等.冀西北东坪金矿床含金石英脉石英流体包裹体Rb-Sr等时线及其地质意义[J].地球化学, 1997, 26(3):20-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1997.03.003
[2] 孙敬博, 张立明, 陈文, 等.东天山红石金矿床石英Rb-Sr同位素定年[J].地质论评, 2013, 59(2):382-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.02.019
[3] 陈好寿, 李华芹.云开隆起金矿带流体包裹体Rb-Sr等时线年龄[J].矿床地质, 1991, 10(4):333-341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCDZ199104006.htm
[4] Shepherd T J, Darbyshire D P F. Fluid inclusion Rb-Sr isochrons for dating mineral deposits[J]. Nature, 1981, 290(5807):578-579. doi: 10.1038/290578a0
[5] Changkakoti A, Gray J, Krstic D, et al. Determination of radiogenic isotopes (RbSr, SmNd and PbPb) in fluid inclusion waters:An example from the Bluebell Pb-Zn deposit, British Columbia, Canada[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(5):961-967. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90251-7
[6] 杨屹.阿尔金大平沟金矿床成矿时代Rb-Sr定年[J].新疆地质, 2003, 21(3):303-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2003.03.009
[7] 毛光周, 华仁民, 龙光明, 等.江西金山金矿成矿时代探讨——来自石英流体包裹体Rb-Sr年龄的证据[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(4):532-539. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.04.011
[8] 李华芹, 王登红, 陈富文, 等.湖南雪峰山地区铲子坪和大坪金矿成矿作用年代学研究[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):900-905. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.006
[9] 陈卓, 李向文, 张胜江, 等.黑龙江十五里桥金矿龙江组火山岩地球化学特征及构造背景分析[J].地质与资源, 2019, 2(5):413-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.002 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8415.shtml
[10] 郑全波, 马江水, 杨晓平.黑龙江黑河五道沟地区区域地球化学特征及其与成矿的关系[J].地质与资源, 2018, 27(2):141-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.02.006 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8448.shtml
[11] 刘桂香, 张春鹏, 吕骏超, 等.大兴安岭甲乌拉铅锌银矿床石英二长斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学及地质意义[J].地质与资源, 2018, 27(5):424-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.05.003 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8488.shtml
[12] Norman D I, Landis G P. Source of mineralizing components in hydrothermal ore fluids as evidenced by 87Sr/86Sr and stable isotope data from the Pasto Bueno deposit, Peru[J]. Economic Geology, 1983, 78(3):451-465. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.78.3.451
[13] Rossman G R, Weis D, Wasserburg G J. Rb, Sr, Nd and Sm concentrations in quartz[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9):2325-2329. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=856f434e3c0f4150f8c0162a78c93997&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] 薛明轩.黑龙江省内生金矿成矿作用研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2012.
[15] 王升鹏, 田丙强, 李葆华, 等.黑龙江省徐家村金矿床赋矿二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石, 2018, 38(4):98-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201804012
[16] 刘汉彬, 金贵善, 李军杰, 等.铀矿地质样品的稳定同位素组成测试方法[J].世界核地质科学, 2013, 30(3):174-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2013.03.009
[17] Clayton R N, Rex R W, Syers J K, et al. Oxygen isotope abundance in quartz from Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(21):3907-3915. doi: 10.1029/JC077i021p03907
[18] Taylor H P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69(6):843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843
[19] 宋叔和, 康永孚, 涂光炽, 等.中国矿床(中)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994.
[20] 马小双, 陈新跃, 曹有金, 等.铲子坪金矿矿床地球化学特征及Rb-Sr年龄[J].矿业工程研究, 2016, 31(2):57-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kygcyj201602011
[21] 崔革, 于静秋, 高艳秋.黑龙江省东部晚石炭-晚白垩世地层的古地磁特征及其地质意义[J].黑龙江地质, 1991, 2(2):41-49. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/97312X/199102/516382.html
[22] 孙革.中国吉林天桥岭晚三叠世植物群[M].长春:吉林科学技术出版社, 1993:25-130.
[23] 吴福元, WildeS, 孙德有.佳木斯地块片麻状花岗岩的锆石离子探针U-Pb年龄[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(3):443-452. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200103013
[24] 孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 等.西拉木伦河-长春-延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(2):174-181. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200402003
[25] DavisG A, Xu B, Zhang Y D, et al. Indosinian extension in the Solonkersuture zone:the SonidZuoqi metamorphiccore complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3):135-144. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY200403019.htm
[26] 孟恩, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等.佳木斯地块东缘及东南缘二叠纪火山作用:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(8):956-965. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.08.016
[27] 黄映聪, 任东辉, 张兴洲, 等.黑龙江省东部桦南隆起美作花岗岩的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(4):631-638. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200804014
[28] Miao L C, Fan W M, Liu D Y, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshanophiolitic complex:Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(5/6):348-370. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257552965_Geochronology_and_geochemistry_of_the_Hegenshan_ophiolitic_complex_Implications_for_late-stage_tectonic_evolution_of_the_Inner_Mongolia-Daxinganling_Orogenic_Belt_China
[29] 赵寒冬.东北地区小兴安岭南段-张广才岭北段古生代火成岩组合与构造演化[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009.
[30] 李怡欣.黑龙江省老柞山金矿床的成因与成矿地质模式[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2012.
[31] 包真艳, 王建, 杨言辰, 等.黑龙江平顶山金矿赋矿花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其构造意义[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(3):407-420. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201403009.htm
[32] 张琳, 杨言辰, 韩世炯, 等.黑龙江新立金矿床片麻状花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(5):638-648. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.05.007
[33] 李晓敏, 周喜文, 魏存弟.老柞山金矿床成矿时代研究[J].地质找矿论丛, 2001, 16(2):131-134, 139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2001.02.011
[34] 单强, 廖思平, 卢焕章, 等.岩浆到热液演化的包裹体记录——以骑田岭花岗岩体为例[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(5):1511-1520. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201105023
[35] Canbaz O, Gokce A. Microthermometric and stable isotopic(O and H) characteristics of fluid inclusions in the porphyry related Çöpler (İliç-Erzincan) gold deposit, central eastern Turkey[J]. Central European Journal of Geosciences, 2014, 6(2):139-147. https://link.springer.com/article/10.2478/s13533-012-0173-0
[36] Hedenquist J W, Lowenstern J B. The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature, 1994, 370(6490):519-527. doi: 10.1038/370519a0
[37] Ohmoto H. Stable isotope geochemistry of ore deposits[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1986, 16(1):491-559. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201801010
[38] Rye R O. The evolution of magmatic fluids in the epithermal environment:the stable isotope perspective[J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(3):733-752. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.3.733
[39] 张理刚.稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用——金属活化热液成矿作用及找矿[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1985.
-




 下载:
下载: