Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age, Lu-Hf isotopes and tectonic setting of the Early Paleozoic gneissic granites from the Nyainrong microcontinent, Tibet Plateau
-
摘要:
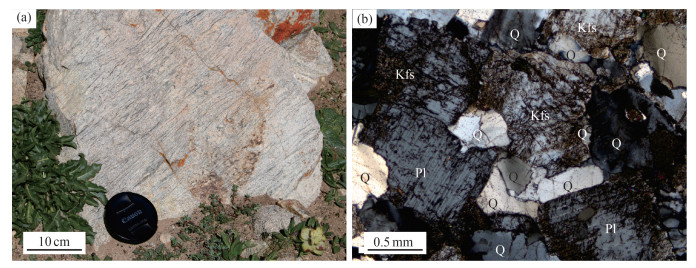
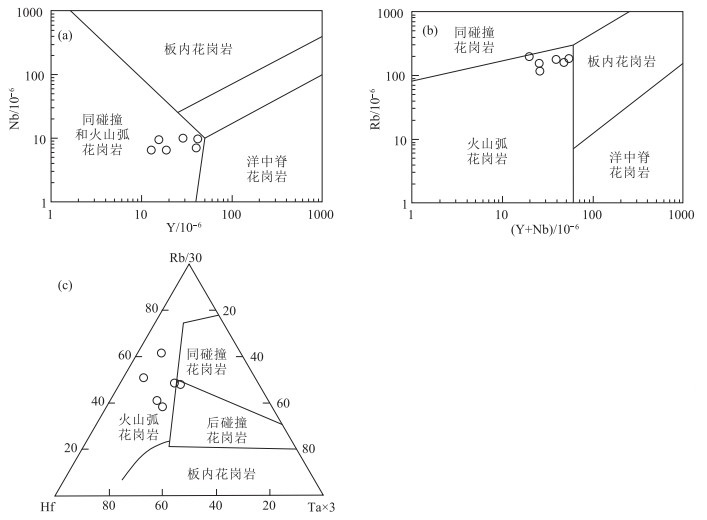
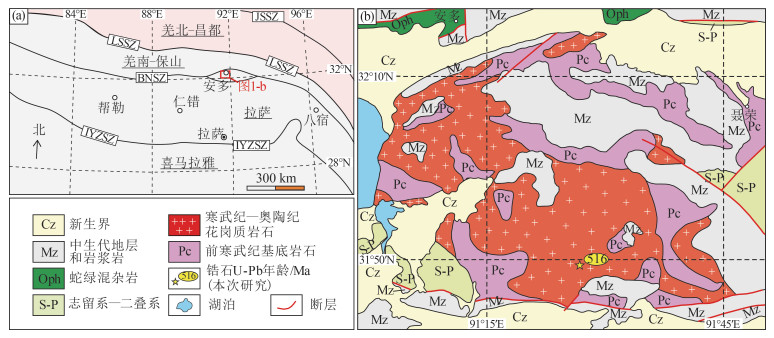
报道了西藏中部聂荣微陆块片麻状花岗岩的全岩地球化学、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素研究资料。获得花岗岩中锆石206Pb/238U年龄为516±3 Ma(n=20,MSWD=1.60)。花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性岩石系列,具有类似I型花岗岩的地球化学特征,其稀土元素配分模式为轻稀土元素富集的右倾曲线,伴随负Eu异常,而微量元素蛛网图表现出Ba、Nb、Ta、Sr、P、Ti亏损和Rb、Th、Pb相对富集的分布特征。花岗岩具有富集的锆石Hf同位素组成(εHf(t)= -3.0~-0.1)、古老的锆石Hf模式年龄(tDMC= 1472~1659 Ma)和较高的Mg#值(32~47),可能形成于地幔岩浆对元古宙沉积物质的改造。综合上述测试结果及区域地质背景,推测聂荣微陆块寒武纪片麻状花岗岩应当是冈瓦纳大陆北缘安第斯型岩浆弧的一部分。
Abstract:The geochemistry of the Cambrian gneissic granite from the Nyainrong microcontinent, central Tibet, and its zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages and Hf isotope data are reported.The granite was formed at 516±3 Ma(n=20, MSWD=1.60), and belongs to high-K calc-alkaline I-type.It is characterized by negative Eu anomaly and right-dip chondrite-normalized rare-earth element patterns, enrichment of Rb, Th, and Pb, and depletion of Ba, Nb, Ta, Sr, P, and Ti.It exhibits negative zircon εHf(t) values of -3.0~-0.1 and relatively high Mg# values of 32~47, and yields old zircon Hf model age of 1472~1659 Ma, suggesting a magma source of Proterozoic sedimentary materials modified by mantle-derived magma.Based on the above study results and regional geological setting, it is suggested that the Cambrian gneissic granite from the Nyainrong microcontinent could be attributed to one part of the Andean-type magmatic arc along the northern margin of the Gondwana supercontinent.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan plateau /
- Nyainrong microcontinent /
- granite /
- geochemistry /
- zircon U-Pb dating
-

-
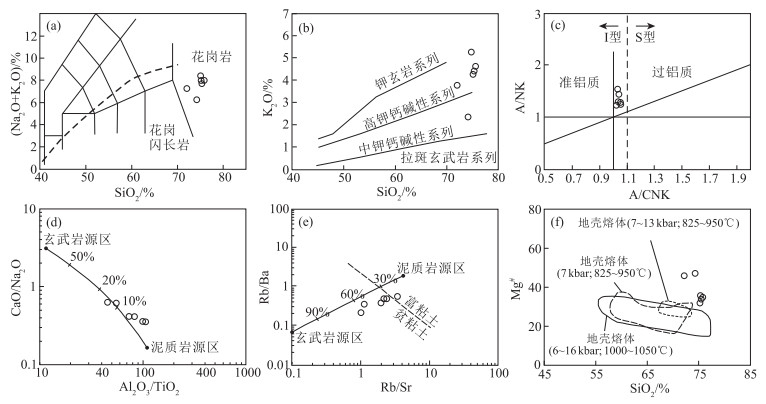
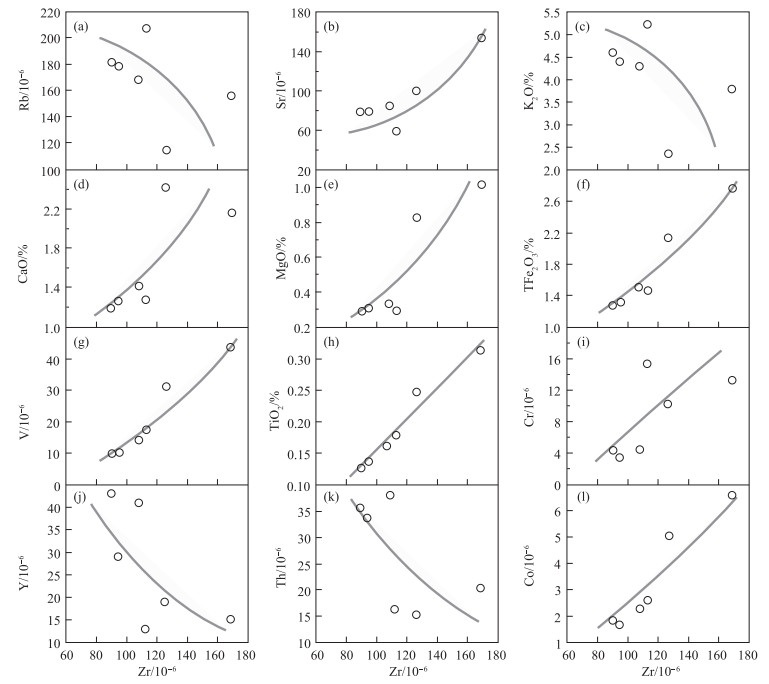
图 3 聂荣微陆块早古生代片麻状花岗岩SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)(a)、SiO2-K2O(b)、A/CNK-A/NK(c)、Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O(d)、Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba(e)和SiO2-Mg#(f)图解(底图据参考文献[26])
Figure 3.
图 5 聂荣微陆块早古生代片麻状花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b) (标准化值据参考文献[30])
Figure 5.
表 1 聂荣微陆块早古生代片麻状花岗岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 1. Concentrations of major, trace elements and REE of the Early Paleozoic gneissic granite from the Nyainrong microcontinent
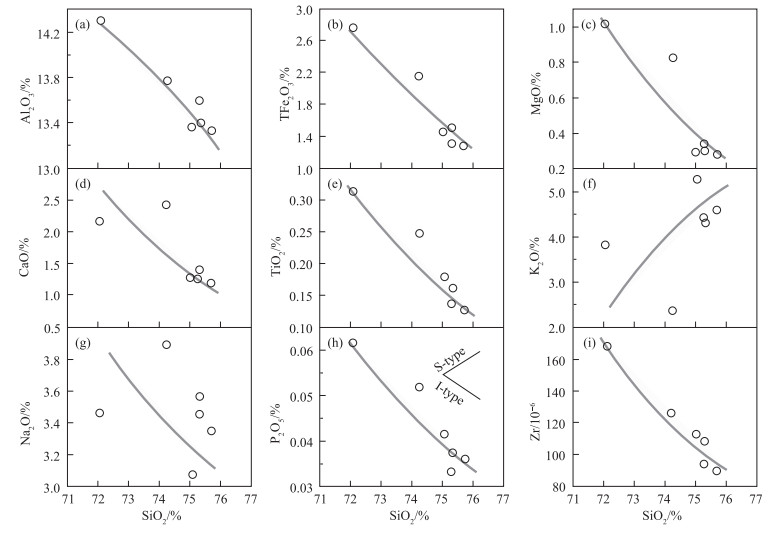
编号 16T160 17T082 17T083 17T084 17T085 16T097 SiO2 75.27 75.77 75.50 75.33 74.27 71.83 TiO2 0.18 0.13 0.16 0.13 0.25 0.31 Al2O3 13.41 13.34 13.43 13.60 13.78 14.26 TFe2O3 1.46 1.29 1.51 1.30 2.14 2.76 MnO 0.03 0.09 0.06 0.10 0.05 0.06 MgO 0.30 0.29 0.34 0.31 0.83 1.01 CaO 1.28 1.19 1.42 1.27 2.42 2.15 Na2O 3.08 3.35 3.45 3.57 3.89 3.45 K2O 5.26 4.60 4.32 4.40 2.37 3.79 P2O5 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.06 烧失量 0.59 0.77 0.49 0.69 0.78 0.88 总计 100.89 100.85 100.71 100.73 100.83 100.56 Li 13.8 26.1 21.3 27.5 15.8 17.8 Be 1.70 1.91 1.37 2.06 2.17 1.86 Sc 2.52 7.93 7.54 7.77 7.82 7.04 V 17.5 10.3 14.0 10.5 31.3 43.7 Cr 15.5 4.35 4.53 3.53 10.2 13.3 Co 2.63 1.82 2.29 1.71 5.03 6.60 Ni 11.4 3.87 2.93 2.90 7.10 8.38 Ga 11.6 14.4 13.7 13.9 13.1 14.7 Rb 207 181 168 178 115 157 Sr 59.4 79.4 85.3 79.6 100 154 Zr 113 90.0 108 94.4 126 169 Nb 6.68 10.1 7.03 10.01 6.77 9.53 Cs 3.38 4.61 2.44 4.19 3.18 3.68 Ba 343 361 415 358 322 700 Ta 0.31 0.97 0.28 0.82 0.68 0.75 Pb 28.7 39.8 30.6 40.9 15.4 35.3 Th 16.3 35.8 38.3 33.8 15.5 20.5 U 1.44 2.32 1.91 2.05 0.91 1.10 Y 12.8 42.9 40.9 29.1 18.7 15.1 La 16.9 31.2 24.8 30.2 27.3 36.5 Ce 48.1 69.3 57.9 65.5 54.3 69.8 Pr 4.45 7.81 6.17 7.30 5.47 7.07 Nd 15.1 29.4 23.9 29.9 20.1 25.8 Sm 2.70 7.29 5.99 6.53 3.66 4.30 Eu 0.57 0.74 0.76 0.74 0.77 0.82 Gd 2.44 6.86 6.02 5.74 3.30 3.39 Tb 0.32 1.08 0.98 0.89 0.52 0.47 Dy 1.71 6.82 6.31 5.29 3.31 2.80 Ho 0.32 1.31 1.31 1.02 0.64 0.53 Er 0.86 4.02 3.82 3.36 1.99 1.47 Tm 0.13 0.72 0.62 0.63 0.32 0.23 Yb 0.80 4.89 3.92 4.67 1.99 1.50 Lu 0.13 0.83 0.60 0.83 0.32 0.25 Hf 3.38 3.66 4.59 3.94 4.02 5.39 Mg# 35 34 35 47 46 32 A/CNK 1.06 1.04 1.05 1.03 1.04 1.02 ΣREE 172 143 163 124 155 94.6 Eu/Eu* 0.32 0.39 0.37 0.68 0.66 0.68 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 聂荣微陆块早古生代片麻状花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 2. U-Th-Pb isotope composition of the zircons in the Early Paleozoic gneissic granite from the Nyainrong microcontinent as measured by LA-ICP-MS
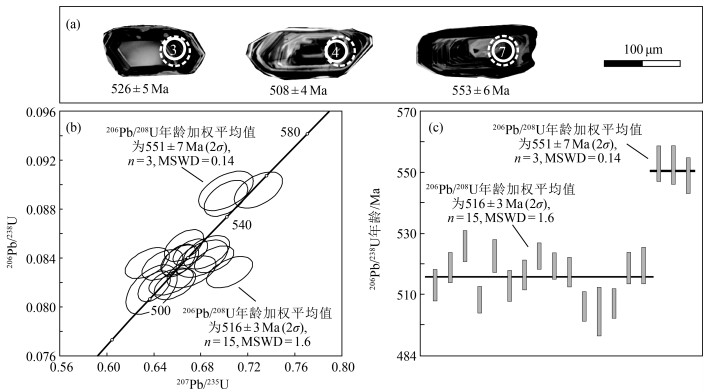
点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1.1 70 524 740 0.71 0.0586 0.0012 0.672 0.014 0.0829 0.0009 550 43 522 8 513 5 2.1 84 544 917 0.59 0.0572 0.0010 0.662 0.011 0.0838 0.0008 498 69 516 6 519 5 3.1 108 735 1163 0.63 0.0567 0.0009 0.666 0.011 0.0850 0.0009 480 31 518 7 526 5 4.1 54 360 597 0.60 0.0579 0.0011 0.655 0.012 0.0821 0.0007 524 44 511 8 508 4 5.1 61 386 656 0.59 0.0588 0.0010 0.685 0.013 0.0845 0.0009 567 37 530 8 523 5 6.1 48 315 510 0.62 0.0619 0.0012 0.704 0.013 0.0828 0.0008 672 47 541 8 513 5 7.1 91 607 988 0.61 0.0591 0.0010 0.729 0.014 0.0896 0.0010 569 37 556 8 553 6 8.1 43 255 464 0.55 0.0563 0.0010 0.647 0.011 0.0834 0.0008 465 34 507 7 517 5 9.1 104 806 1081 0.75 0.0576 0.0008 0.671 0.010 0.0845 0.0007 517 31 521 6 523 4 10.1 105 481 1179 0.41 0.0597 0.0009 0.691 0.011 0.0839 0.0007 594 36 534 7 519 4 11.1 66 653 641 1.02 0.0551 0.0011 0.634 0.012 0.0836 0.0008 417 46 499 8 517 5 12.1 112 965 1138 0.85 0.0569 0.0009 0.640 0.009 0.0817 0.0008 487 35 503 6 506 5 13.1 111 542 1242 0.44 0.0568 0.0011 0.701 0.015 0.0895 0.0011 483 43 540 9 553 6 14.1 58 327 635 0.52 0.0568 0.0010 0.638 0.014 0.0814 0.0013 483 39 501 9 505 8 15.1 52 536 497 1.08 0.0582 0.0010 0.658 0.012 0.0819 0.0008 539 37 513 7 507 5 16.1 99 752 1040 0.72 0.0572 0.0008 0.661 0.010 0.0838 0.0009 498 25 515 6 519 5 17.1 45 284 481 0.59 0.0589 0.0014 0.681 0.015 0.0839 0.0010 565 45 527 9 520 6 18.1 106 703 1146 0.61 0.0571 0.0009 0.701 0.012 0.0889 0.0010 498 35 540 7 549 6 表 3 聂荣微陆块早古生代片麻状花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据
Table 3. Hf isotopic composition of the zircons from the Early Paleozoic gneissic granite of the Nyainrong microcontinent
点号 206Pb/238U年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) 2σ tDM /Ma tDMC/Ma fLu/Hf 1.1 513 0.0303 0.0004 0.001022 0.000012 0.282405 0.000025 0.282395 -13.0 -2.1 0.9 1199 1606 -0.97 2.1 519 0.0749 0.0025 0.002274 0.000067 0.282410 0.000015 0.282388 -12.8 -2.2 0.5 1233 1618 -0.93 3.1 526 0.0394 0.0027 0.001322 0.000087 0.282425 0.000015 0.282412 -12.3 -1.2 0.5 1180 1559 -0.96 4.1 508 0.0268 0.0002 0.000908 0.000008 0.282434 0.000015 0.282426 -11.9 -1.1 0.5 1154 1540 -0.97 5.1 523 0.0313 0.0003 0.001081 0.000011 0.282385 0.000017 0.282375 -13.7 -2.6 0.6 1228 1645 -0.97 6.1 513 0.0607 0.0011 0.002046 0.000032 0.282424 0.000016 0.282404 -12.3 -1.7 0.6 1205 1585 -0.94 7.1 553 0.0391 0.0012 0.001343 0.000038 0.282471 0.000018 0.282457 -10.6 1.0 0.6 1115 1441 -0.96 8.1 517 0.1291 0.0033 0.004199 0.000109 0.282456 0.000019 0.282415 -11.2 -1.2 0.7 1231 1557 -0.87 9.1 523 0.0278 0.0005 0.001008 0.000015 0.282414 0.000016 0.282404 -12.7 -1.5 0.6 1185 1579 -0.97 10.1 519 0.0304 0.0008 0.001043 0.000024 0.282426 0.000016 0.282415 -12.3 -1.2 0.6 1170 1556 -0.97 -
[1] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 梁凤华, 等. 喜马拉雅地体的泛非-早古生代造山事件年龄纪录[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501001.htm
[2] Cawood P A, Johnson M R W, Nemchin A A. Early Palaeozoic orogenesis along the Indian margin of Gondwana: Tectonic response to Gondwana assembly[J]. Earth and Planetary Letters, 2007, 255: 70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.006
[3] 张泽明, 王金丽, 沈昆, 等. 环冈瓦纳大陆周缘的古生代造山作用: 东喜马拉雅构造结南迦巴瓦岩群的岩石学和年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24: 1627-1637. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200807020.htm
[4] 王晓先, 张进江, 杨雄英, 等. 藏南吉隆地区早古生代大喜马拉雅片麻岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18: 127-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201102014.htm
[5] Garzanti E, Casnesi R, Jadoul F. Sedimentary evidence of a Cambro-Ordovician orogenic event in the northwestern Himalaya[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 48: 237-265. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(86)90032-1
[6] Stöcklin J. Geology of Nepal and its regional frame[J]. Geological Society Journal, 1980, 137: 1-34. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.137.1.0001
[7] Kumar R, Shah A N, Bingham D K. Positive evidence of a Precambrian tectonic phase in central Napal, Himalaya[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 1978, 19: 519-522. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285772638_Positive_evidence_of_a_Precambrian_tectonic_phase_in_central_Nepal_Himalaya
[8] Valdiya K S, Gupta V J. A contribution to the geology of Northeastern Kumaun, with special reference to the Hercunian gap in Tethys Himalaya[J]. Himalaya Geology, 1972, 2: 1-33. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285029390_A_contribution_to_the_geology_of_northeastern_Kumaon_with_special_reference_to_the_Hercynian_gap_in_Tethys_Himalaya
[9] Gupta V J. Indian Precambrian stratigraphy[M]. Hindustan Publishing Corporation Printing Press, Delhi(India), 1977: 1-333.
[10] 刘文灿, 梁定益, 王克友. 藏南康马地区奥陶系的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(4): 247-248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.04.026
[11] Gehrels G, Kapp P, DeCelles P, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogeny[J]. Tectonics, 2011, 30: 1-27.
[12] Pullen A, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, et al. Metamorphic rocks in central Tibet: lateral variations and implications for crustal structure[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123: 585-600. doi: 10.1130/B30154.1
[13] 胡培远, 李才, 苏犁, 等. 青藏高原羌塘中部蜈蚣山花岗片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年——泛非与印支事件的年代学记录[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37: 1050-1061. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.019
[14] Guynn J, Kapp P, Gehrels G, et al. U-Pb geochronology of basement rocks in central Tibet and paleogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 43(1): 23-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.09.003
[15] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane, southern Tibet: Record of an early Paleozoic An-dean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328(18): 290-308.
[16] 计文化, 陈守建, 赵振明, 等. 西藏冈底斯构造带申扎一带寒武系火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(10): 1350-1354. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090926&flag=1
[17] 解超明, 李才, 苏犁, 等. 藏北安多地区花岗片麻岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(12): 1737-1744. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101202&flag=1
[18] Zhang Z M, Dong X, Liu F, et al. Tectonic Evolution of the Amdo Terrane, Central Tibet: Petrochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Geochronology[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2012, 120: 431-451. doi: 10.1086/665799
[19] 解超明, 李才, 苏犁, 等. 藏北聂荣微陆块泛非-早古生代构造热事件: 年代学与地球化学制约[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(3): 414-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201403003.htm
[20] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
[21] 李才. 青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(1): 105-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.012
[22] 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010
[23] Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1/2): 47-69. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/el/00092541/2004/00000211/00000001/art00004
[24] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
[25] Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(1/2): 105-126. http://www10215.edu6.org/biaozhun/wu%202006.pdf
[26] Hu P Y, Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, et al. Early Ordovician granites from the South Qiangtang terrane, northern Tibet: Implications for the early Paleozoic tectonic evolution along the Gondwanan proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Lithos, 2015, 220/223: 318-338. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.12.020
[27] LeBas M J, Lemaitre R W, Streckeisen A, et al. A chemical classification of volcanic-rocks based on the total alkali silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27: 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
[28] Chappell B W, White A J R. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974, 8: 173-174.
[29] Chappell B W, White A J R. I-and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 1992, 83: 1-26. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007720
[30] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. J. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ., 1989, 42: 313-345.
[31] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 8: 1589-1604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm
[32] Polat A, Hofmann A W. Alteration and geochemical patterns in the 3.7-3.8 Ga Isua greenstone belt, West Greenland[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 126(3/4): 197-218. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Albrecht_Hofmann/publication/223844130_Alteration_and_geochemical_patterns_in_the_3.73.8_Ga_Isua_greenstone_belt_West_Greenland/links/53d698030cf220632f3db810
[33] Hu P Y, Li C, Wu Y W, et al. Opening of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancangjiang ocean: constraints from plagiogranites[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(25): 3188-3199. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0434-z
[34] Wolf M B, London D. Apatite dissolution into peraluminous haplogranite melts: an experimental study of solubilities and mechanisms[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58: 4127-4145. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90269-0
[35] Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J, Foster G L, et al. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5814): 980-983. doi: 10.1126/science.1136154
[36] Sylvester P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45: 29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
[37] Liu Y M, Xie C M, Li C, et al. Breakup of the northern margin of Gondwana through lithospheric delamination: Evidence from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2019, 131(3/4): 675-697.
[38] Wang H T, Zhai Q G, Hu P Y, et al. Early Paleozoic granitic rocks of the South Qiangtang Terrane, northern Tibetan Plateau: implications for subduction in the Proto-(Paleo-) Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 204: 104579. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104579
[39] Hu P Y, Li C, Wang M, et al. Cambrian volcanism in the Lhasa terrane, southern Tibet: Record of an early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc along the Gondwana proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 77: 91-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.015
[40] Miller C, Thöni M, Frank W, et al. The early Palaeozoic magmatic event in the Northwest Himalaya, India: source, tectonic setting and age of emplacement[J]. Geological Magazine, 2001, 138: 237-251. doi: 10.1017/S0016756801005283
[41] Lee J, Whitehouse M J. Onset of mid-crustal extensional flow in southern Tibet: evidence from U/Pb zircon ages[J]. Geology, 1998, 148: 115-136.
[42] Quigley M C, Yu L J, Gregory C, et al. U-Pb SHRIMP zircon geochronology and T-t-p history of the Kampa Dome, southern Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 446: 97-113. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.004
[43] 时超, 李荣社, 何世平, 等. 藏南亚东地区片麻状含石榴子石黑云花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(12): 1745-1753. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101203&flag=1
[44] 林仕良, 丛峰, 高永娟, 等. 腾冲地块东南缘高黎贡山群片麻岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 258-263. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020307&flag=1
[45] 杨学俊, 贾小川, 熊昌利, 等. 滇西高黎贡山南段公养河群变质基性火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 264-276. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020308&flag=1
[46] 刘倚胜, 叶培胜, 吴中海. 滇西高黎贡山南段奥陶纪花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 250-257. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020306&flag=1
[47] 熊昌利, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 等. 滇西龙陵地区勐冒奥陶纪二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 277-286. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020309&flag=1
[48] 马泽良, 蔡志慧, 戚学祥, 等. 保山地体新元古代-早古生代沉积岩碎屑锆石年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(4): 546-561. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190407&flag=1
[49] 孙载波, 胡绍斌, 周坤, 等. 滇西南勐海布朗山奥陶纪花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(11): 2044-2054. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20181110&flag=1
[50] Gehrels G E, Decelles P G, Martin A. Initiation of the Himalayan orogen as an early Paleozoic thin-skinned thrust belt[J]. GSA Today, 2003, 13: 4-9. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/250949245_Initiation_of_the_Himalayan_Orogen_as_an_Early_Paleozoic_Thin-skinned_Thrust_Belt
[51] Ramezani J, Tucker R D. The Saghand Region, Central Iron: U-Pb geochronology, petrogenesis and implications for Gondwana tectonics[J]. American Journal of Science, 2003, 303: 622-665. doi: 10.2475/ajs.303.7.622
[52] Hassanzadeh J, Stockli D F, Horton B K. U-Pb zircon geochronology of upper Neoproterozoic-Early Cambrian granitoids in Iran: Implica-tions for paleogeography, metallogeny, and exhumation history of Iranian basement[J]. Tectonophysics, 2008, 451: 71-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.062
[53] Ustaömer P A, Ustaömer T, Collins A S, et al. Cadomian(Ediacaran-Cambrian) arc magmatism in the Bitlis Massif, SE Turkey: magmatism along the developing northern margin of Gondwana[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 473: 99-112. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.06.010
[54] Kusky T M, Abdelsalam M, Stern R J, et al. Evolution of the East African and related orogens, and the assembly of Gondwana[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 123: 81-85. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00062-7
[55] Liu S, Hu R Z, Gao S, et al. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope constraints on the age and origin of Early Palaeozoic I-type granite from the Tengchong-Baoshan Block, Western Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36: 168-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.05.004
[56] Harris N B W, Pearce J A, Tindle A G, et al. Geochemical characteristics of collision zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society Special Publication, London, 1986, 19: 67-81. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04
[57] Pearce J A, Peate D W. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic ARC magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1995, 23(1): 251-285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343
-



 下载:
下载: