The critical geological events in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain during the Late Cenozoic
-
摘要:
晚新生代以来,青藏高原的隆升导致中国地貌格局、古气候系统及晚新生代沉积体系发生巨变。青藏高原以东至边缘海的广大区域形成统一水系,将巨量沉积物搬运至中国东部连续堆积形成黄淮海平原。太行山的隆升、边缘海陆架的沉降,黄河的贯通及晚第四纪大规模海侵等,深刻改造了黄淮海平原的自然环境,至今仍然影响其社会经济的发展,成为重要的科学问题。针对这些事件的研究,对于理解晚新生代黄淮海平原的形成和演化具有重要意义,也可为缓解该地区目前紧张的人地关系提供理论基础。对晚新生代黄淮海平原形成发育的构造地貌过程、黄河贯通和晚第四纪海侵等重大事件研究现状进行了综合分析,认为:①青藏高原隆升是黄淮海平原当今地貌及海陆格局形成的根本原因;②黄河贯通对黄淮海平原地表过程、水系演化及源-汇体系带来深远影响;③沿海地区晚更新世以来3次重要的海侵事件及相关的海陆相互作用,不但造成了沉积环境的变化,还形成了下切河谷特殊地貌景观;④晚新生代黄淮海地区重大地质事件的时间节点是中新世和晚第四纪。系统总结了黄淮海平原在构造-气候相互作用、地貌动态演化和年代学研究中存在的问题,认为未来亟需对黄淮海平原开展多学科系统性的工作。
Abstract:The uplift of the Xizang Plateau since the Late Cenozoic has led to the important adjustment in the geomorphology patterns, paleoclimate systems and sedimentary systems in China.The unified drainage system was formed in the vast area from the eastern Xizang plateau to marginal sea and the persistent sedimentation controlled by this drainage system resulted in the emergency of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in the Eastern China.The critical geological events such as the uplift of the Taihang Mountain, subsidence of the continental shelf in the marginal sea, the connection of the Huang River and the large scale of transgression in the Late Quaternary profoundly changed the natural environment of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, which until now still affect the social and economic development and become an important concerned scientific issue.The study of these events is of great significance to the understanding of the formation and evolution of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in the Late Cenozoic, and can also provide a theoretical basis for easing the current tense human-earth relationship in this area.The comprehensive analysis of the tectonic and geomorphic processes of the formation and development of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in the late Cenozoic, the opening of the Yellow River and the transgression of the late Quaternary results in the following conclusions.The uplift of the Xizang Plateau was the root causes for the formation of the present geomorphology and land-sea pattern of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain; the connection of the Huang River led to significant change of the earth surface processes, drainage evolution and source-sink processes in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain; three large scale transgression events in the coastal area and related land-sea interaction not only brought about the change of the sedimentary environment but also formed the special landscapes of deeply incised valley; the key time of the above critical geological events in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is Miocene and Late Quaternary.This paper also summarized the problems in the study of the tectono-climatic interaction, the dynamic evolution of the geomorphology and chronology in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.Urgent works should be carried out on the multidisciplinary and systematic research in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.
-
Key words:
- Huang-Huai-Hai Plain /
- critical geological events /
- Late Cenozoic /
- earth surface process
-

-
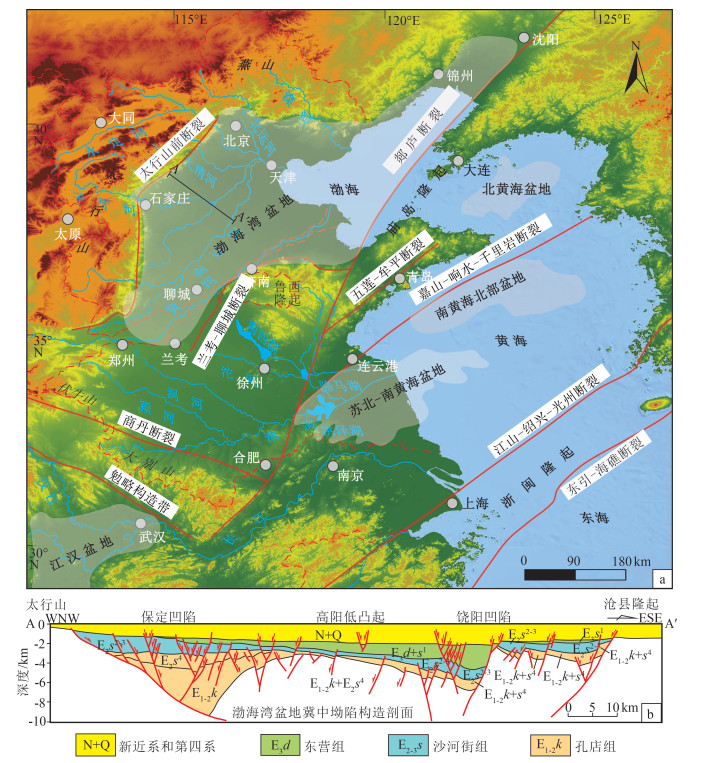
图 1 中国东部黄淮海平原地貌、主要水系、流域边界、断裂及盆地(a)和渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷构造剖面图(b,据参考文献[9]修改)
Figure 1.
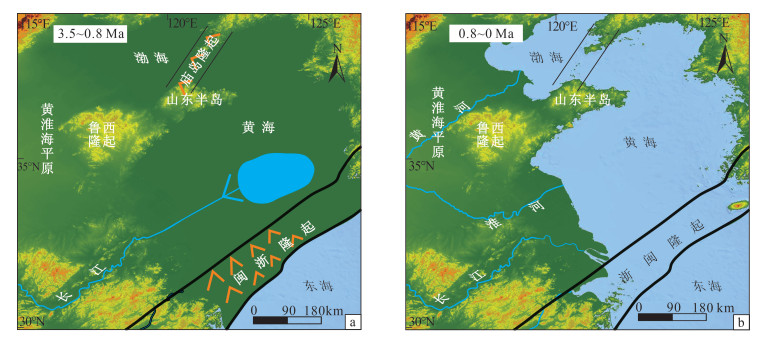
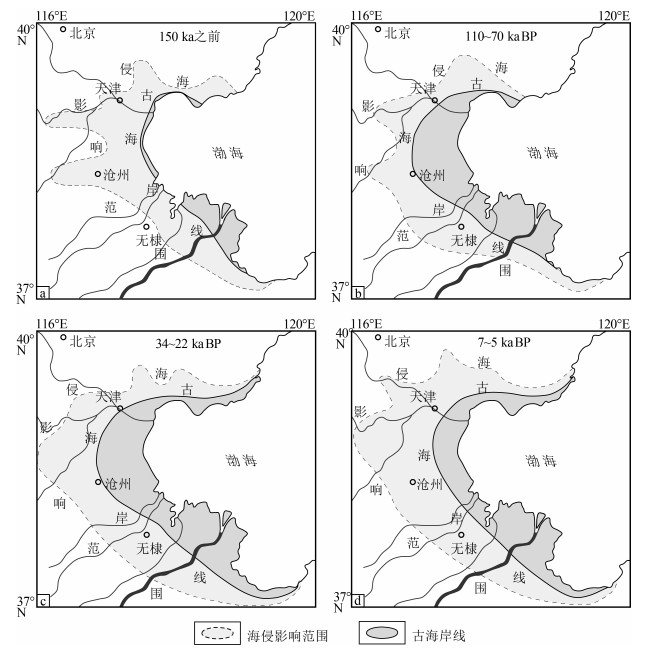
图 5 闽浙隆起的沉降导致黄海和渤海地区沉积环境发生变化(据参考文献[74]修改)
Figure 5.
图 6 黄淮海平原第四纪演化(据参考文献[5]修改)
Figure 6.
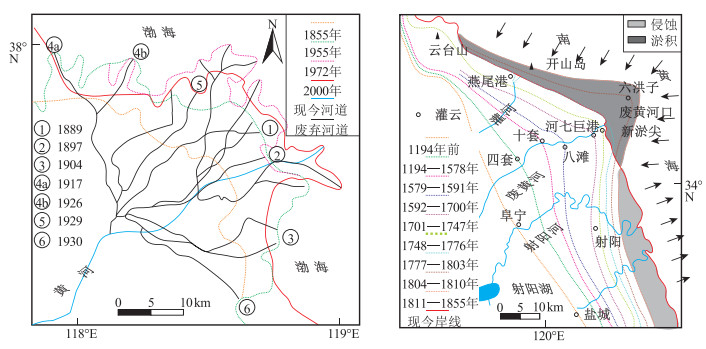
图 9 渤海西岸晚第四纪海侵影响范围及古海岸线图(据参考文献[183]修改)
Figure 9.
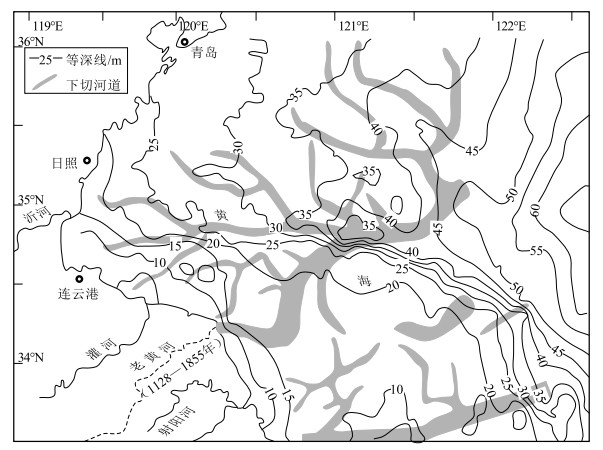
图 11 MIS3期至末次冰期南黄海西部陆架上发育的下切河道[172]
Figure 11.
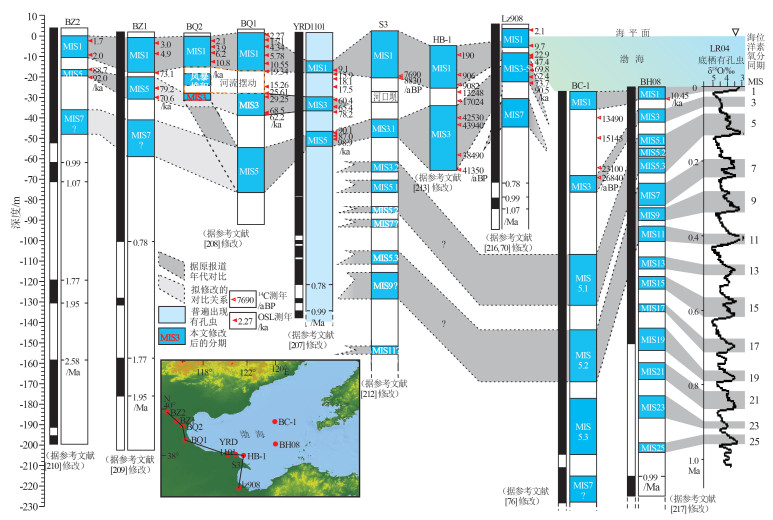
表 1 钻孔揭露的闽浙隆起带和庙岛隆起的沉降过程
Table 1. The subsidence process of Min-Zhe and Miaodao uplifts revealed by boreholes
研究地点/对象 主要观点 主要证据 参考文献 闽浙隆起 舟山群岛ESC-DZ1孔 约2.0 Ma出现沉降;1.7~0.2 Ma间发生抬升;0.2 Ma之后彻底沉降 研究区位于闽浙隆起带之上。约2.0 Ma出现海相层;1.7~0.2 Ma出现沉积间断;0.2 Ma之后为海陆交互沉积 [61] 南黄海第四系地震层序学研究 闽浙隆起带对南黄海沉积环境和沉积地层发育的控制作用直到晚更新世距今128 ka才终止 128 ka之前南黄海地区仅发育小规模海相层,对海平面波动的响应不明显;128 ka之后,南黄海地区出现大规模海相层,其形成很好地响应了低频高振幅的海平面波动 [69] 南黄海西部CSDP-1孔 1.66 Ma出现小幅沉降;0.83 Ma进一步沉降 3.5~1.66 Ma以河流环境为主,1.66~0.83 Ma为潮坪-潮下带与河流环境的交替,0.83 Ma以来现代海洋环境逐步建立 [66] 长江口PD钻孔 中更新世前后彻底沉降 早更新世物源发生扩张,中更新世发生物源再次发生变化 [67] 冲绳海槽U1428站位 约416 ka出现大规模沉降 钻孔中约416 ka出现岩性变化 [62] 庙岛隆起 莱州湾Lz908 约260 ka发生沉降,约130 ka完全沉降 钻孔中约260 ka湖相沉积结束,海相沉积开始;约130 ka渤海发育为现今内陆架 [70] 渤海BH08等多个钻孔 约0.3 Ma出现沉降, 0.1 Ma完全沉降 研究区约3.7 Ma之前以河流相为主;3.7~0.3 Ma盆地稳定沉降,形成“渤海古湖”,其中1.0 Ma高海平面时期发育微弱海侵;0.3 Ma典型海相沉积出现,0.1 Ma之后大规模海侵出现 [71] 黄河三角洲YRD-1101孔 0.83 Ma小幅沉降,MIS5期大规模沉降 0.83 Ma出现微弱海侵;MIS5早期出现强烈海侵 [72] 表 2 黄河贯通三门峡的时代
Table 2. Ages of the cut through of the Sanmen Gorge by Yellow River
研究对象 贯通时代 主要证据 参考文献 构造地貌 黄河扣马段河流阶地 >1.165 Ma 最高级阶地上1.165 Ma开始堆积黄土 [81] 黄河三门峡段河流阶地 3.63~1.24 Ma 黄河三门峡段上新世夷平面之下发育5级河流阶地;夷平面以及最高级阶地的形成时代分别为3.63 Ma和1.24 Ma [82] 三门峡段河流阶地及渭河盆地河湖相沉积 1.3~1.4 Ma 三门峡最高级河流阶地之上和渭河盆地中具有黄河上游碎屑锆石年龄分布特征的沉积物分别出现于1.3 Ma和1.4 Ma [83] 沉积响应 三门峡盆地黄底沟剖面 0.15 Ma 三门古湖0.15 Ma结束湖相沉积 [84-85] 邙山黄土 0.15 Ma L2以上粒度偏粗,沉积速率增大 [86] 200~250 ka 利用磁化率和粒度重新标定了邙山黄土的时代,发现S2之后沉积速率及粒度发生明显变化 [87] 约900 ka L9黄土(约900 ka)中已经出现了黄河物源 [88] 河南东部平原沉积物 0.78 Ma 黄河冲积平原B/M界线(0.78 Ma)上下沉积物特征、孢粉特征以及重矿物组合明显不同 [89] 汾渭盆地与河南平原更新统介形类化石 0.78~1.0 Ma 更新统介形类化石组合特征中更新世前后发生了明显变化 [90] 黄河三角洲石化2孔 早更新世 钻孔埋深223 m处上下沉积物元素组成存在明显差异,其上与黄河接近,其下与黄河明显不同 [91] 渤海湾西岸G4孔 渤海BH08孔及南黄海NHH01孔 1.6 Ma 地球化学组成指示1.6 Ma物源发生变化 [92] 南黄海西部CSDP-1孔 880 ka 稀土元素和粘土矿物组成指示物源在880 ka由近源小型山地河流为主,转变为以远源多组分的黄河沉积物为主 [93] 渤海湾西岸G2、G3及CK3 0.8 Ma 粘土矿物和Sr-Nd同位素指示物源在0.8 Ma由长江转为了黄河为主 [79] 1.6~1.5 Ma G2、G3及CK3中的碎屑锆石年龄谱在1.6~1.5 Ma发生了明显变化 [94] 表 3 黄淮海平原沿海地区海侵期次划分
Table 3. Division of transgression periods in the coast area of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
地点 海侵期次及名称 参考文献 黄骅、沧州、保定等地 渤海海进(早更新世)、海兴海进(中更新世)、黄骅海进(晚更新世早期)、白洋淀海进(晚更新世早期)、沧州海进(晚更新世早期)、天津海进(全新世) [184] 渤海湾西岸 沧州海侵(102~70 ka)、献县海侵(39~23 ka)和黄骅海侵(8~2 ka) [185] 河北平原东部 海兴海进、黄骅海进、青县海进、沧西海进(40~20 ka)、献县海进(8.5~5.5 ka)、沧东海进(5~3.5 ka) [186] 中国东部平原 星轮虫海侵(110~70 ka)、假轮虫海侵(40~25 ka)、卷转虫海侵(15~2 ka) [187] 台湾海峡以北沿海平原 盘旋虫海侵(中更新世早期)、星轮虫海侵(晚更新世早期)、假轮虫海侵(晚更新世中期)、卷转虫海侵(全新世) [188] 渤海西、南岸平原 早更新世(2.26 Ma)、中更新世(约0.30 Ma),晚更新世(约100 ka),晚更新世(39~24 ka)、全新世(<10 ka) [189-190] 长江三角洲 如皋海侵(早更新世中期)、上海海侵(中更新世早期)、太湖海侵(晚更新世早期)、滆湖海侵(晚更新世晚期)、镇江海侵(全新世) [191] -
[1] Wang P. Cenozoic deformation and the history of sea-land interactions in Asia[J]. Geophysical Monograph Series, 2004, 149: 1-22. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/149GM01/pdf
[2] 汪品先. "海源陆生"化石与中国新生代海侵问题[J]. 同济大学学报, 1995, 23(增刊): 129-135.
[3] 王强, 刘立军, 王卫东, 等. 环渤海地区及华北平原第四纪古环境变迁机制[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2004, 27(3): 129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2004.03.001
[4] 邵时雄, 郭盛乔, 韩书华. 黄淮海平原地貌结构特征及其演化[J]. 地理学报, 1989, 56(3): 314-322. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.03.008
[5] 蒋复初, 薛滨. 中原邙山黄土及构造与气候耦合作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ901.006.htm
[6] 王强, 田国强. 中国东部晚第四纪海侵的新构造背景[J]. 地质力学学报, 1999, 5(4): 41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.04.005
[7] 刘国纬. 黄河下游治理的地学基础[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(10): 1511-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201110014.htm
[8] National Research Council. Landscapes on the edge: New horizons for research on Earth's surface[M]. National Academies Press, 2010.
[9] Qi J, Yang Q. Cenozoic structural deformation and dynamic processes of the Bohai Bay basin province, China[J]. Marine&Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(4): 757-771. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817209001421
[10] 张旗, 金惟俊, 王元龙, 等. 晚中生代中国东部高原北界探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(4): 689-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200704002.htm
[11] 张旗, 钱青, 王二七, 等. 燕山中晚期的中国东部高原: 埃达克岩的启示[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(2): 248-255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.02.014
[12] 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 等. 晚中生代的中国东部高原: 证据、问题和启示[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1404-1430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.004 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080904&flag=1
[13] 邓晋福, 赵国春. 中国东部燕山期火成岩构造组合与造山——深部过程[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(1): 41-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.01.006
[14] Davis G A, Yadong Z, Cong W, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces, northern China[J]. Memoirs-Geological Society of America, 2001: 171-198. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10011069689
[15] 徐宝亮, 李祥辉, 陈云华, 等. 中国"东部高原" 东北部黏土矿物特征研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2007, 27(3): 166-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2007.03.004
[16] 李祥辉, 徐宝亮, 陈云华, 等. 华北-东北南部地区中生代中晚期粘土矿物与古气候[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(5): 683-691. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200805014.htm
[17] Hu J, Zhao Y, Liu X, et al. Early Mesozoic deformations of the eastern Yanshan thrust belt, northern China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010, 99(4): 785-800. doi: 10.1007/s00531-009-0417-5
[18] 夏国清, 伊海生, 赵西西, 等. 晚中生代中国东部高原古高程定量研究[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(23): 2220-2230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201223012.htm
[19] 汪品先. 新生代亚洲形变与海陆相互作用[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(1): 1-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200501000.htm
[20] 曹现志. 华北地块中部中新生代构造地貌演变过程与机制[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
[21] Sun J, Windley B F, Zhang Z, et al. Diachronous seawater retreat from the southwestern margin of the Tarim Basin in the late Eocene[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 116: 222-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.020
[22] 张家声, 徐杰. 太行山山前中-新生代伸展拆离构造和年代学[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(4): 207-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.04.005 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020461&flag=1
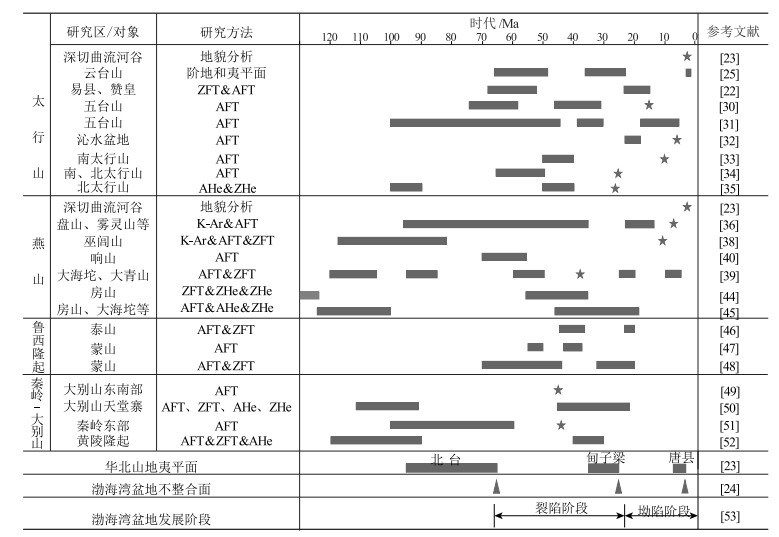
[23] 吴忱, 张秀清, 马永红. 太行山、燕山主要隆起于第四纪[J]. 华北地震科学, 1999, 17(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD199903000.htm
[24] 徐杰, 高战武, 孙建宝, 等. 区域伸展体制下盆-山构造耦合关系的探讨——以渤海湾盆地和太行山为例[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(2): 165-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.02.004
[25] 马寅生, 赵逊, 赵希涛, 等. 太行山南缘新生代的隆升与断陷过程[J]. 地球学报, 2007, 28(3): 219-233. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2007.03.001
[26] 龚明权. 新生代太行山南段隆升过程研究[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2010.
[27] 张蒙, 李鹏霄. 太行山南段主要隆升时期探讨[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2014, 4: 55-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZY201404020.htm
[28] 张蕾, 张绪教, 武法东, 等. 太行山南缘晚更新世以来河流阶地的发育及其新构造运动意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 791-798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.04.005
[29] 张哲, 张军龙. 第四纪太行山南段隆升问题的探讨[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(10): 87-92 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202010013.htm
[30] 庆建春, 季建清, 王金铎, 等. 五台山新生代隆升剥露的磷灰石裂变径迹研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008, 51(2): 384-392 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.02.011
[31] Chang J, Qiu N, Liu S, et al. Post-Triassic multiple exhumation of the Taihang Mountains revealed via low-T thermochronology: Implications for the paleo-geomorphologic reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 68: 34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.11.007
[32] 孟元库, 汪新文, 陈杰. 太行山新生代构造隆升的地质学证据——来自沁水盆地沁参1井的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015, 35(1): 15-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2015.01.003
[33] 李庶波, 王岳军, 张玉芝, 等. 南太行山中新生代隆升过程: 磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(3): 460-469. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201503010.htm
[34] 曹现志, 李三忠, 刘鑫, 等. 太行山东麓断裂带板内构造地貌反转与机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 88-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304010.htm
[35] Wu L, Wang F, Yang J, et al. Meso-Cenozoic uplift of the Taihang Mountains, North China: evidence from zircon and apatite thermochronology[J]. Geological Magazine, 2019, 157(7): 1097-1111. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/337993775_Meso-Cenozoic_uplift_of_the_Taihang_Mountains_North_China_evidence_from_zircon_and_apatite_thermochronology
[36] 吴珍汉, 崔盛芹. 燕山山脉隆升过程的热年代学分析[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(1): 49-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.01.007
[37] 吴珍汉, 崔盛芹, 朱大岗, 等. 燕山南缘盘山岩体的热历史与构造-地貌演化过程[J]. 地质力学学报, 1999, 5(3): 28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.005
[38] 马寅生, 崔盛芹, 吴淦国, 等. 辽西医巫闾山的隆升历史[J]. 地球学报, 2000, 21(3): 245-253. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.03.003
[39] 吴中海, 吴珍汉. 燕山及邻区晚白垩世以来山脉隆升历史的低温热年代学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(3): 399-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.011
[40] 李越, 季建清, 涂继耀, 等. 燕山东部柳江地区构造属性新解与郯庐断裂系活动[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(3): 675-681. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200903021.htm
[41] 陈祥高, 张忠奎. 北京房山花岗闪长岩裂变径迹年龄测定和热史的探讨[J]. 科学通报, 1983, 28(6): 357-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198306010.htm
[42] 陈详高, 张忠奎, 臧文秀. 北京房山花岗闪长岩中锆石的裂变径迹年龄测定和热历史研究[J]. 岩石学报, 1986, 2(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1986.01.005
[43] 翟鹏济, 张峰, 赵云龙. 从裂变径迹分析探讨房山岩体地质热历史[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(2): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200302012.htm
[44] 冯乾乾, 邱楠生, 常健, 等. 房山岩体构造-热演化: 来自(U-Th)/He年龄的约束[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(6): 1972-1982. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201806015.htm
[45] 陈子健. 燕山西段延庆-丰宁地区白垩纪岩体剥露过程的低温热年代学研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2019.
[46] 李理, 钟大赉. 泰山新生代抬升的裂变径迹证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(2): 457-464. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200602018.htm
[47] 王振兰, 王金铎, 季建清, 等. 鲁西隆起与济阳坳陷箕状断陷形成时代研究[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(2): 206-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.02.009
[48] 唐智博, 李理, 时秀朋, 等. 鲁西隆起蒙山晚白垩世-新生代抬升的裂变径迹证据[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 50(2): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ201102027.htm
[49] Grimmer J C, Jonckheere R, Enkelmann E, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic history of the southern Tan-Lu fault zone: apatite fission-track and structural constraints from the Dabie Shan(eastern China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2002, 359(3/4): 225-253. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195102005139
[50] 周祖翼, 许长海, 杨凤丽. 大别山天堂寨地区晚白垩世以来剥露历史的(U-Th)/He和裂变径迹分析证据[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(6): 598-602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.06.015
[51] Hu S, Raza A, Min K, et al. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic thermotectonic evolution along a transect from the north China craton through the Qinling orogen into the Yangtze craton, central China[J]. Tectonics, 2006, 25(6): TC6009.
[52] Ge X, Shen C, Yang Z, et al. Low-temperature thermochronology constraints on the mesozoic-cenozoic exhumation of the Huangling massif in the Middle Yangtze Block, Central China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(4): 541-552. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0348-8
[53] 漆家福, 张一伟, 陆克政, 等. 渤海湾盆地新生代构造演化[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 19(S1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX5S1.000.htm
[54] 孙振营, 王强, 李亚平, 等. 第四纪以来天津北部燕山隆升与山前盆地的形成[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(5): 893-908. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201805013.htm
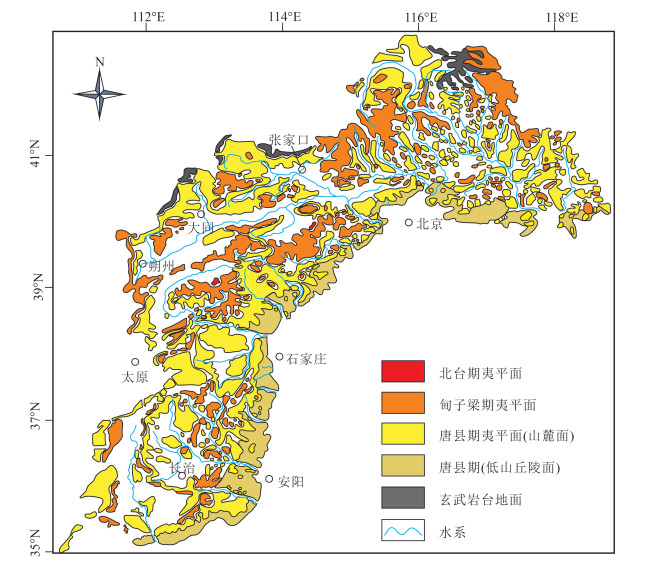
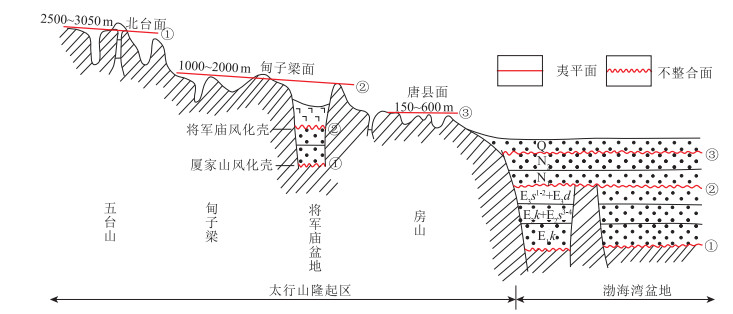
[55] 吴忱. 华北地貌环境及其形成演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.
[56] Xiong J, Li Y, Zheng W, et al. Climatically driven formation of the Tangxian planation surface in North China: An example from northwestern Zhongtiao Shan of the Shanxi Graben System[J]. Lithosphere, 2018, 10(4): 530-544. doi: 10.1130/L720.1
[57] Cao X, Li S, Xu L, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution and mechanism of tectonic geomorphology in the central North China Block: Constraint from apatite fission track thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 114: 41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.041
[58] 侯贵廷, 钱祥麟, 蔡东升. 渤海湾盆地中、新生代构造演化研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 37(6): 845-851. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2001.06.016
[59] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 黃海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989.
[60] 孙镇诚, 杨藩, 李东明, 等. 咸化湖泊中海相世系生物的来源[C]//孙镇诚, 杨藩, 张枝焕, 等. 等. 中国新生代咸化湖泊沉积环境与油气生成. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 108-114.
[61] Yi L, Ye X, Chen J, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and luminescence dating on a sedimentary sequence from northern East China Sea: constraints on evolutionary history of eastern marginal seas of China since the Early Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349: 316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.07.038
[62] Zhao D, Wan S, Jiang S, et al. Quaternary sedimentary record in the northern Okinawa Trough indicates the tectonic control on depositional environment change[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 516: 126-138. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.12.001
[63] Wageman J M, Hilde T W C, Emery K O. Structural framework of East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1970, 54(9): 1611-1643.
[64] 金翔龙, 喻普之. 黄海、东海地质构造[C]//中国科学院海洋研究所. 黄东海地质. 北京: 科学出版社, 1982: 1-22.
[65] 王强. 晚新生代以来华北断块板内环境变迁动力学[C]//天津地质矿产所. 前寒武纪第四纪地质文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 171-182.
[66] Liu J, Zhang X, Mei X, et al. The sedimentary succession of the last~3.50 Myr in the western South Yellow Sea: Paleoenvironmental and tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 399: 47-65. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.11.005
[67] Chen J, Wang Z H, Wei T Y, et al. Clay minerals in the Pliocene-Quaternary sediments of the southern Yangtze coast, China: Sediment sources and palaeoclimate implications[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 3(3): 297-308. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=GUDL201403004
[68] Yue W, Jin B, Zhao B. Transparent heavy minerals and magnetite geochemical composition of the Yangtze River sediments: Implication for provenance evolution of the Yangtze Delta[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 364: 42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.12.006
[69] 杨继超. 南黄海盆地中部第四纪地震层序与地层学[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2014.
[70] Yi L, Deng C, Xu X, et al. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary: Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 319: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.01.005
[71] Yi L, Deng C, Tian L, et al. Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin(East Asia): demise of Bohai Paleolake and transition to marine environment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29403. doi: 10.1038/srep29403
[72] Liu J, Wang H, Wang F, et al. Sedimentary evolution during the last~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016b, 451: 84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.03.012
[73] 杨子赓. Olduvai亚时以来南黄海沉积层序及古地理变迁[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(4): 357-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199304006.htm
[74] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.
[75] Shi X, Yao Z, Liu Q, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1 Ma and implications for sea-level changes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.07.002
[76] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986.
[77] Yao Z, Guo Z, Xiao G, et al. Sedimentary history of the western Bohai coastal plain since the late Pliocene: Implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54-55: 192-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.013
[78] 周墨清, 葛宗诗. 南黄海及相邻陆区松散沉积层磁性地层的研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1990, 10(4): 2. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199004002.htm
[79] Zhang J, Wan S, Clift P D, et al. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5 Ma: Tectonic or climate forcing?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 216: 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.002
[80] 王书兵, 蒋复初, 傅建利, 等. 关于黄河形成时代的一些认识[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4): 705-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.08
[81] 潘保田, 王均平, 高红山, 等. 河南扣马黄河最高级阶地古地磁年代及其对黄河贯通时代的指示[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(3): 255-261. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.03.010
[82] Hu Z, Pan B, Bridgland D, et al. The linking of the upper-middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River as a result of fluvial entrenchment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 324-338. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.02.026
[83] Kong P, Jia J, Zheng Y. Time constraints for the Yellow River traversing the Sanmen Gorge[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(2): 395-407. doi: 10.1002/2013GC004912
[84] 吴锡浩, 王苏民. 关于黄河贯通三门峡东流入海问题[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 2: 186. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.02.014
[85] 王苏民, 吴锡浩, 张振克, 等. 三门古湖沉积记录的环境变迁与黄河贯通东流研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, (9): 760-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200109007.htm
[86] Jiang F, Fu J, Wang S, et al. Formation of the Yellow River, inferred from loess-palaeosol sequence in Mangshan and lacustrine sediments in Sanmen Gorge, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2007, 175(1): 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.03.022
[87] Zheng H, Huang X, Ji J, et al. Ultra-high rates of loess sedimentation at Zhengzhou since Stage 7: Implication for the Yellow River erosion of the Sanmen Gorge[J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3/4): 131-142. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169555X06003096
[88] Shang Y, Prins M A, Beets C J, et al. Aeolian dust supply from the Yellow River floodplain to the Pleistocene loess deposits of the Mangshan Plateau, central China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age spectra[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 131-143. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.01.001
[89] 刘书丹, 李广坤, 李玉信, 等. 从河南东部平原第四纪沉积物特征探讨黄河的形成与演变[J]. 河南地质, 1988, 6(2): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD198802003.htm
[90] 薛铎. 黄河东段形成时代管见[J]. 河南地质, 1996, 14(2): 110-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD602.005.htm
[91] 杨守业, 蔡进功, 李从先, 等. 黄河贯通时间的新探索[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200102003.htm
[92] 杨吉龙, 胥勤勉, 胡云壮, 等. 渤海湾西岸钻孔记录的沉积演化过程和沉积物风化强度、物源重建[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(S1): 287-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX2018S1025.htm
[93] Yao Z, Shi X, Qiao S, et al. Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least~880 ka ago[J]. Scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x
[94] Xiao G, Sun Y, Yang J, et al. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River I: Detrital-zircon evidence from the North China Plain[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 546: 109691. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109691
[95] 张信宝, 刘彧, 王世杰, 等. 黄河、长江的形成演化及贯通时间[J]. 山地学报, 2018, 36(5): 661-668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201805001.htm
[96] Liang H, Zhang K, Fu J, et al. Bedrock river incision response to basin connection along the Jinshan Gorge, Yellow River, North China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 114: 203-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.07.010
[97] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[98] Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: the importance of small mountainous rivers[J]. The journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5): 525-544. doi: 10.1086/629606
[99] Wang S, Fu B, Piao S, et al. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2016, 9(1): 38-41. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2602
[100] 石长青, 董玉良. 论黄河冲积平原中、上部的地质-地理背景和区域性土壤改良水文地质条件[C]//中国地质科学院水文地质工程地质研究所所刊(第2号). 北京: 中国地质学会, 1986: 154-179.
[101] 叶青超. 华北平原地貌体系与环境演化趋势[J]. 地理研究, 1989, 8(3): 10-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ198903001.htm
[102] 张磊, 刘嘉麒, 秦小光. 第四纪黄河入淮成因机制与环境效应的研究现状及存在问题[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(2): 441-453.
[103] 李容全, 郑良美, 耿侃. 黄河决徙与黄河冲积扇发育关系初探[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1987, 4: 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ198704015.htm
[104] 徐近之. 淮北平原与淮河中游的地文[J]. 地理学报, 1951, 20(2): 203-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB195302006.htm
[105] 冯大奎, 张光业. 全新世黄河下游平原地貌和自然环境的演变[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 1: 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZR198801006.htm
[106] 曹银真. 黄河冲积扇和三角洲变迁过程中的临界意义[J]. 地理科学, 1988, 8(1): 54-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX198801006.htm
[107] 马玉凤, 李双权, 潘星慧. 黄河冲积扇发育研究述评[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(1): 49-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201501005.htm
[108] 叶青超, 杨毅芬, 张义丰. 黄河冲积扇形成模式和下游河道演变[J]. 人民黄河, 1982, 4: 32-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH198204008.htm
[109] 陈瑾. 1128年以来黄河变迁与丰沛地区地理环境响应研究[D]. 江苏师范大学硕士学位论文, 2016.
[110] Xue C. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(3/4): 321-330. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002532279390025Q
[111] Saito Y, Yang Z, Hori K. The Huanghe(Yellow River) and Changjiang(Yangtze River) deltas: a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2-3): 219-231. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00118-0
[112] 薛春汀, 成国栋. 渤海西岸贝壳堤及全新世黄河三角洲体系[C]. //杨子赓, 林和茂. 中国近海及沿海地区第四纪进程与事件. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989, 117-125.
[113] He L, Xue C, Ye S, et al. New evidence on the spatial-temporal distribution of superlobes in the Yellow River Delta Complex[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 214: 117-138. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.05.003
[114] 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1): 48-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.01.006
[115] 庞家珍, 司书亨. 黄河河口演变——Ⅰ. 近代历史变迁[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1979, (2): 136-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197902005.htm
[116] 叶青超. 试论苏北废黄河三角洲的发育[J]. 地理学报, 1986, 53(2): 112-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1986.02.002
[117] 王长耀, 赵英时, 张圣凯. 利用遥感技术研究黄淮海平原水域的演变[J]. 环境遥感, 1988, 3(1): 1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB198801001.htm
[118] 吴忱, 王子惠, 许清海. 河北平原的浅埋古河道[J]. 地理学报, 1986, 53(4): 332-340. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1986.04.005
[119] 吴忱, 朱宣清, 何乃华, 等. 华北平原古河道的形成研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1991, 2: 188-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199102010.htm
[120] 吴忱, 许清海, 阳小兰. 论华北平原的黄河古水系[J]. 地质力学学报, 2000, 6(4): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2000.04.001
[121] 吴忱. 华北山地的水系变迁与新构造运动[J]. 华北地震科学, 2001, 19(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2001.04.001
[122] 张祖陆. 鲁北平原黄河古河道初步研究[J]. 地理学报, 1990, 57(4): 457-466. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1990.04.008
[123] Wu C, Xu Q, Zhang X, et al. Palaeochannels on the North China Plain: types and distributions[J]. Geomorphology, 1996, 18(1): 5-14. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(95)00147-W
[124] Wu C, Zhu X, He N, et al. Compiling the map of shallow-buried palaeochannels on the North China Plain[J]. Geomorphology, 1996, 18(1): 47-52. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(95)00151-T
[125] Xu Q, Wu C, Yang X, et al. Palaeochannels on the North China Plain: relationships between their development and tectonics[J]. Geomorphology, 1996, 18(1): 27-35. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(95)00149-Y
[126] Xu Q, Wu C, Zhu X, et al. Palaeochannels on the North China Plain: stage division and palaeoenvironments[J]. Geomorphology, 1996, 18(1): 15-25. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(95)00148-X
[127] 谭其骧. 西汉以前的黄河下游河道[J]. 历史地理, 1981, 1: 48-64.
[128] 潘明涛. 海河平原水环境与水利研究(1360-1945)[D]. 南开大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
[129] 谭徐明. 海河流域水环境的历史演变及其主要影响因素研究[J]. 水利发展研究, 2002, 2(12): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1408.2002.12.005
[130] 靳怀堾. 海河的生命历程: 从分散到统一从依附到独立[J]. 中国三峡, 2015, 12: 22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6349.2015.02.005
[131] 方旭辉. 大清河水系变迁及其对雄安新区建设的影响[D]. 河北农业大学硕士学位论文, 2019.
[132] 金权, 等. 安徽淮北平原第四系[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990.
[133] 吴梅. 淮河水系的形成与演变研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2013.
[134] 荀德麟. 黄河夺淮述略[J]. 江苏水利, 1999, 6: 47-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSSL199906026.htm
[135] 彭安玉. 黄河夺淮后江苏淮北地区自然环境的变迁[J]. 南京林业大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2013, 13(4): 56-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1165.2013.04.009
[136] 蒋慕东, 章新芬. 黄河"夺泗入淮"对苏北的影响[J]. 淮阴师范学院学报(哲学社会科学版), 2006, 2: 226-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8444.2006.02.018
[137] 赵筱侠. 黄河夺淮对苏北水环境的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2013, 13(3): 92-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1165.2013.03.011
[138] 祁正卫, 张嘉涛, 刘志中. 河夺淮的历史演变[J]. 江苏水利, 1998, 7: 47-48.
[139] 张瑞虎. 洪泽湖的成因及其水灾治理[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2012, 2(3): 72-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NZYJ201203028.htm
[140] 张淑萍, 张修桂. 《禹贡》九河分流地域范围新证——兼论古白洋淀的消亡过程[J]. 地理学报, 1989, 56(1): 86-93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.01.009
[141] 邹逸麟. 黄河下游河道变迁及其影响概述[J]. 复旦学报: 社会科学版, 1980, (S1): 12-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FDDX1980S1002.htm
[142] 张义丰. 黄河下游大陆泽和大野泽的变迁初探[J]. 河南师大学报(自然科学版), 1984, 3(1): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZR198401011.htm
[143] 石超艺. 15~20世纪大陆泽与宁晋泊演变的影响因素分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(5): 522-529. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.005
[144] 张超. 河北平原中南部晚更新世以来古湖泊演化初探[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2020.
[145] 郭永盛. 历史上山东湖泊的变迁[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1990, 3: 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFB199003002.htm
[146] 张振克, 王苏民. 黄河下游南四湖地区黄河河道变迁的湖泊沉积响应[J]. 湖泊科学, 1999, 11(3): 231-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX199903006.htm
[147] 喻宗仁, 窦素珍, 赵培才, 等. 山东东平湖的变迁与黄河改道的关系[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(4): 469-479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.04.009
[148] 王乃昂. 梁山泊的形成和演变[J]. 兰州大学学报: 社会科学版, 1988, 4: 74-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDSK198804012.htm
[149] Zhang Z, Wang S, Yang X, et al. Evidence of a geological event and environmental change in the catchment area of the Yellow River at 0.15 Ma[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117(1): 35-40. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00114-9
[150] 薛春汀, 刘健, 孔祥淮. 全新世淮河三角洲初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(5): 892-901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.05.06
[151] 任美锷, 史运良. 黄河输沙及其对渤海, 黄海沉积作用的影响[J]. 地理科学, 1986, 6(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX198601000.htm
[152] Ren M, Shi Y. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River(China) and its effect on the sedimentation of the Bohai and the Yellow Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1986, 6(6): 785-810. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(86)90037-3
[153] Prins M A, Zheng H, Beets K, et al. Dust supply from river floodplains: the case of the lower Huang He(Yellow River) recorded in a loess-palaeosol sequence from the Mangshan Plateau[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science: Published for the Quaternary Research Association, 2009, 24(1): 75-84. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103013303.html
[154] Milliman J D, Yun-Shan Q, Mei-e R, et al. Man's influence on the erosion and transport of sediment by Asian rivers: the Yellow River(Huanghe) example[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1987, 95(6): 751-762. doi: 10.1086/629175
[155] Alexander C R, DeMaster D J, Nittrouer C A. Sediment accumulation in a modern epicontinental-shelf setting: the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1991, 98(1): 51-72. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90035-3
[156] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 236(3/4): 165-187. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229440950_Sedimentary_evolution_of_the_Holocene_subaqueous_clinoform_off_the_Shandong_Peninsula_in_the_Yellow_Sea
[157] Yang Z S, Liu J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 240(1/4): 169-176. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025322707000540
[158] 秦亚超, 李日辉, 姜学钧. 黄海中北部和渤海东部表层沉积物轻矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(3): 611-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.03.15
[159] Zhou L, Liu J, Saito Y, et al. Coastal erosion as a major sediment supplier to continental shelves: example from the abandoned Old Huanghe(Yellow River) delta[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 82: 43-59. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.015
[160] Zhang L, Chen S, Yi L. The sediment source and transport trends around the abandoned Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Marine Georesources&Geotechnology, 2015, 34(5): 440-449. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1064119X.2015.1025928
[161] 王青. 试论史前黄河下游的改道与古文化的发展[J]. 中原文物, 1993, 4: 65-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYWW199304009.htm
[162] 王海峰, 杨剑萍, 庞效林, 等. 鲁北平原晚第四纪地层结构及沉积演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(1): 90-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201601008.htm
[163] 耿秀山. 黄渤海地貌特征及形成因素探讨[J]. 地理学报, 1981, 48(4): 423-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1981.04.008
[164] 李凡, 于建军. 南黄海埋藏古河系研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1991, 22(6): 501-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ199106000.htm
[165] Kong X, Liu J, Du Y, et al. Seismic geomorphology of buried channel systems in the western South Huanghai Sea: retrodiction for paleoenvironments[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 30(1): 47-58. doi: 10.1007/s13131-011-0090-y
[166] Liu S, Feng A, Du J, et al. Evolution of the buried channel systems under the modern Yellow River Delta since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349: 327-338. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.061
[167] 杨守业, 张家强. 苏北滨海平面全新世沉积物物源: 元素地球化学与重矿物方法比较[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(3): 458-463. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.1999.03.020
[168] Zhang L, Qin X, Liu J, et al. Geochemistry of sediments from the Huaibei Plain(east China): Implications for provenance, weathering, and invasion of the Yellow River into the Huaihe River[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 121: 72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.02.008
[169] 蔡德陵, 石学法, 周卫健, 等. 南黄海悬浮体和沉积物的物质来源和运移: 来自碳稳定同位素组成的证据[J]. 科学通报, 2001, S1: 16-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2001S1002.htm
[170] 蓝先洪, 张训华, 张志珣. 南黄海沉积物的物质来源及运移研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2005, 4: 53-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2005.04.008
[171] 魏建伟, 石学法, 辛春英, 等. 南黄海黏上矿物分布特征及其指示意义[J]. 科学通报, 2001, S1: 30-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2001S1004.htm
[172] 薛春汀, 刘健, 孔祥淮. 1128-1855年黄河下游河道变迁及其对中国东部海域的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 25-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201105007.htm
[173] 胡邦琦. 中国东部陆架海泥质沉积区的物源识别及其环境记录[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2010.
[174] Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X, et al. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary, East China Sea, during the last 13, 000 years, with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(17/18): 2424-2438. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379110002106
[175] 张志忠, 李双林, 董岩翔, 等. 浙江近岸海域沉积物沉积速率及地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(3): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200503003.htm
[176] Yang W, Chen M, Li G, et al. Relocation of the Yellow River as revealed by sedimentary isotopic and elemental signals in the East China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(6): 923-927. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.03.019
[177] 秦蕴珊, 廖先贵. 渤海湾海底沉积作用的初步探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1962, 4(3/4): 199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ1962Z2007.htm
[178] 韩宗珠, 张军强, 邹昊, 等. 渤海湾北部底质沉积物中黏土矿物组成与物源研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 41(11): 95-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY201111015.htm
[179] 廖永杰, 范德江, 刘明, 等. 1855年黄河改道事件在渤海的沉积记录[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(2): 88-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY201502012.htm
[180] Wu X, Bi N, Kanai Y, et al. Sedimentary records of the modern Huanghe(Yellow River) delta and their response to deltaic river channel shifts over the last 200 years[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 108: 68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.028
[181] 范勇勇, 毕乃双, 李云海, 等. 百年来黄河三角洲东北部毗邻海域沉积记录演化及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4): 29-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201604005.htm
[182] Hu L, Guo Z, Shi X, et al. Temporal trends of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from the sedimentary record[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(10): 1181-1193. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.08.009
[183] 吴标云, 李从先. 长江三角洲第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版杜, 1987.
[184] 林景星. 华北平原第四纪海进海退现象的初步认识[J]. 地质学报, 1977, 51(2): 109-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE197702001.htm
[185] 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9(1): 15-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197801001.htm
[186] 杨子赓, 李幼军, 丁秋玲, 等. 试论河北平原东部第四纪地质几个基本问题[J]. 石家庄经济学院学报, 1978, 3: 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE197904000.htm
[187] 王靖泰, 汪品先. 中国东部晚更新世以来海面升降与气候变化的关系[J]. 地理学报, 1980, 47(4): 299-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1980.04.003
[188] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华, 等. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 1981, 55(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198101000.htm
[189] 王强. 渤海湾西岸海相与海陆过渡相介形类动物群与古地理[J]. 海洋地质研究, 1982, 2(3): 36-46.
[190] 王强, 李凤林, 李玉德, 等. 对渤海西、南岸平原第四纪海侵命名的讨论[J]. 海洋学报, 1986, 8(1): 72-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC198601010.htm
[191] 王强, 李凤林. 渤海湾西岸第四纪海陆变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(4): 83-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198304012.htm
[192] 高秀林, 王强, 李玉德, 等. 从天津P8孔看中更新世末期以来海侵期, 气候期对比问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(1): 53-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198601007.htm
[193] 王强, 张玉发, 袁桂邦, 等. MIS3阶段以来河北黄骅北部地区海侵与气候期对比[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(1): 79-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.01.009
[194] 安芷生, 魏兰英, 卢演俦, 等. 顺5孔的磁性地层学和早松山世的北京海侵[J]. 地球化学, 1979, 12(4): 343-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1979.04.008
[195] 王乃文, 何希贤. 北京平原钙质超微化石的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 1982, 27(13): 805-808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198213010.htm
[196] 庞其清, 黄兴根. 北京延庆盆地第四纪早期有孔虫化石的发现及海侵的探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(2): 93-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198402006.htm
[197] 关绍曾, 萧宗正, 张清波, 等. 北京延庆盆地第四纪早期介形类动物群, 古生态及对该区古环境的认识[J]. 化工矿产地质, 1995, 17(4): 217-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC504.000.htm
[198] 关绍曾, 萧宗正, 张清波, 等. 北京地区第四纪早期海相介形类[J]. 微体古生物学报, 1997, 14(2): 191-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT702.005.htm
[199] 王乃文, 何希贤, 张丽仙. 北京平原第四纪海相微体化石的研究[J]. 北京自然博物馆, 1983, 22: 1-12.
[200] Cann J H, de Deckker P. Fossil Quaternary and living foraminifera from athallassic(non-marine) salina lakes, southern Australia[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 1981, 55: 660-670.
[201] 王世杰, 董丽敏, 林文祝, 等. 泥河湾组有孔虫化石群的锶同位素研究[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(22): 2072-2074. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.22.017
[202] 王世杰, 刘秀明, 贾玉鹤, 等. 泥河湾盆地第四系有孔虫化石群锶同位素及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(3): 302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.03.017
[203] 王世杰, 刘秀明, 贾玉鹤, 等. 陆相有孔虫形成环境的地球化学证据——以小渡口剖面为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(8): 677-682. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200108008.htm
[204] 肖应凯, 肖军, 赵志琦, 等. 延庆杨户庄第四纪有孔虫的非海相生存环境: 硼和锶同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(7): 801-806. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.07.010
[205] 王强. 运城盐湖及桑干-汾渭断陷带海相世系微体生物的发现及其生存环境[C]//孙镇诚, 杨藩, 张枝焕, 等. 中国新生代咸化湖泊沉积环境与油气生成. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 101-108.
[206] 王强, 李彩光, 田国强, 等. 7.1 Ma以来运城盆地地表系统巨变及盐湖形成的构造背景[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30(4): 420-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200004011.htm
[207] Liu J, Liu Q, Zhang X, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a long Quaternary sediment core in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 144: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.025
[208] 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾西岸晚更新世沉积的差异性特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3): 321-326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.002
[209] 肖国桥, 郭正堂, 陈宇坤, 等. 渤海湾西岸BZ-1钻孔的磁性地层学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(5): 909-916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.014
[210] 姚政权, 郭正堂, 陈宇坤, 等. 渤海湾海陆交互相沉积的磁性地层学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(1): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200601003.htm
[211] 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 等. 渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(8): 1352-1367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201108010.htm
[212] 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 等. 渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2): 27-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ902.003.htm
[213] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(4/5): 318-331. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912009001394
[214] 张欣, 刘健, 王飞飞, 等. 黄河三角洲地区YRD-1402孔沉积物光释光年代学与沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(3): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201603003.htm
[215] Zhang Z, Liu E, Zhang Y, et al. Environmental evolution in the salt-water intrusion area south of Laizhou Bay since late Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2008, 18(1): 37-45. doi: 10.1007/s11442-008-0037-1
[216] 姚菁, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 等. 莱州湾地区含卤层系沉积特征与卤水的形成[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(4): 473-477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.04.007
[217] Yao Z, Shi X, Liu Q, et al. Paleomagnetic and astronomical dating of sediment core BH08 from the Bohai Sea, China: Implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoe-cology, 2014.393: 90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.11.012
[218] 郑守仪, 郑执中, 王喜堂, 等. 山东打渔张灌区第四纪有孔虫及其沉积环境的初步探讨[C]//海洋科学集刊(第13集). 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 16-78.
[219] 袁路朋, 王永, 姚培毅, 等. 河北雄县全新世中期海侵地层的发现[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(6): 911-915. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190602&flag=1
[220] 陈宇坤, 李振海, 邵永新, 等. 天津地区第四纪年代地层剖面研究[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(2): 383-399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.02.005
[221] 陈永胜, 王宏, 裴艳东, 等. 渤海湾西岸晚第四纪海相地层划分及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(3): 747-759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201203019.htm
[222] Yi L, Lai Z, Yu H, et al. Chronologies of sedimentary changes in the south Bohai Sea, China: constraints from luminescence and radiocarbon dating[J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(2): 267-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2012.00271.x
[223] Yao J, Yu H, Xu X, et al. Paleoenvironmental changes during the late Quaternary as inferred from foraminifera assemblages in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(10): 10-18. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0536-0
[224] Li Y, Shang Z, Tsukamoto S, et al. Quartz and K-feldspar luminescence dating of sedimentation in the North Bohai coastal area(NE China) since the late pleistocene[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 152: 103-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.036
[225] 赵华, 卢演俦, 张金起, 等. 天津大直沽晚第四纪沉积物红外释光测年及环境变迁年代学[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(2): 174-183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.02.005
[226] Li Y, Tsukamoto S, Shang Z, et al. Constraining the transgression history in the Bohai Coast China since the Middle Pleistocene by luminescence dating[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 416: 105980. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105980
[227] 王强, 李凤林, 李玉德, 等. 十五万年来渤海西、南岸平原海岸线变迁[C]//国际地质对比计划第200号项目中国组. 中国海平面变化. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1986: 43-53.
[228] 苍树溪, 黄庆福, 张宏才, 等. 渤海晚更新世以来的海侵与海平面波动[C]//国际地质对比计划第200号项目中国组. 中国海平面变化. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1986: 35-43.
[229] Klein G D. A sedimentary model for determining paleotidal range[J]. Bulletin of Geological Society of America, 1971, 82: 2582-2592. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1971GSAB...82.2585D
[230] Chappell J, Shackleton N J. Oxygen isotopes and sea level[J]. Nature, 1986, 324(6093): 137-140. doi: 10.1038/324137a0
[231] Siddall M, Rohling E J, Almogi-Labin A, et al. Sea-level fluctuations during the last glacial cycle[J]. Nature, 2003, 423(6942): 853-858. doi: 10.1038/nature01690
[232] 魏灵, 贾玉连, 易朝路, 等. 近4万年渤海西岸海侵时古海面的现代标高对比研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3): 361-369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.007
[233] 姚政权, 石学法. 渤海湾沿岸第四纪海侵研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(2): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201502002.htm
[234] 李从先, 王强, 范代读. 第十五章: 海洋三角洲沉积[C]//冯增昭. 中国沉积学(第二版). 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013: 812-905.
[235] 王强, 李从先. 中国东部沿海平原第四系层序类型[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 26(4): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200904010.htm
[236] Craddock W H, Kirby E, Harkins N W, et al. Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during headward basin integration[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(3): 209-213. doi: 10.1038/ngeo777
[237] 鲁庆伟, 王强, 詹健, 等. 渤海湾西岸沧县隆起中更新世的地层间断[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(4): 665-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201804011.htm
[238] 郭正堂. 黄土高原见证季风和荒漠的由来[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(4): 421-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201704006.htm
[239] 赵勇, 王强, 李瑞杰, 等. 北京平原区南部PGZ01孔第四纪地层划分及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(2): 337-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201802014.htm
[240] 胡健民, 陈虹. 覆盖区区域地质填图指导思想与方法体系的创新与探索[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 1001-1002. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201905027.htm
[241] 胡健民, 陈虹, 邱士东, 等. 覆盖区区域地质调查(1: 50000)思路、原则与方法[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(12): 4291-4312.
[242] 中国科学院地学部地球科学发展战略研究组. 21世纪中国地球科学发展战略报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
[243] 王尧, 陈睿山, 郭迟辉, 等. 近40年黄河流域资源环境格局变化分析与地质工作建议[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(1): 1-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2021.01.001
[244] 王颖, 邹欣庆, 殷勇, 等. 河海交互作用与黄东海域古扬子大三角洲体系研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, (6): 1055-1064. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.01
① 王强. 河北省唐山榛子镇KK01孔微体生物鉴定报告. 2018.
-



 下载:
下载: