Hydrocarbon geological conditions and exploration prospects of Lower Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin
-
摘要:
钻探、包裹体分析及地球化学探测表明,南黄海盆地深部海相中—古生界存在油气充注过程,具备较好的油气资源潜力。基于南黄海盆地最新的地震资料解释成果和邻区下扬子陆域最新的钻井资料的充分认识,通过对南黄海中—古生代海相盆地的构造区划、下古生界成藏要素及油气成藏组合的系统分析,阐述了下古生界油气地质条件与勘探前景。研究结果表明:①南黄海盆地是受多期构造运动叠加改造形成的残留盆地,下古生界构造形变作用较弱,地层保存较完整,盆地中部崂山断隆带的高石稳定带构成了下古生界构造相对稳定带;②下古生界油气地质条件较优越,下寒武统烃源岩厚度较大且有机质含量较高,以Ⅰ型干酪根为主,中寒武统—奥陶系多发育交代白云岩和颗粒灰岩,可作为较好的储集层,上奥陶统—下志留统厚层泥质岩广泛发育,具备较好的封盖能力,可作为一套区域性盖层;③下古生界生储盖组合配置良好,相对稳定的高石稳定带发育多个大型构造圈闭且存在油气充注,构造圈闭与油气形成时空匹配较好,后期构造破坏较弱,油气保存条件较好,可作为南黄海盆地深部海相油气勘探的有利区带。
Abstract:Drilling, inclusion analysis and geochemical prospecting indicate that oil and gas charging process exists in the deep marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin, which is endowed with a good potential of oil and gas resources.Based on the latest seismic data interpretation of the South Yellow Sea Basin and fully understanding of the latest drilling data in its adjacent Yangtze Platform, the geological conditions and exploration prospects of oil and gas in the Lower Paleozoic are described through systematic analysis on tectonic division of the Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine basins, hydrocarbon accumulation elements and assemblages of Lower Palaeozoic.The results show that: a.The South Yellow Sea Basin is a residual basin formed by the superposition and reconstruction resulting from multi-stage tectonic movements.As the Lower Paleozoic tectonic deformation is weak, the strata are relatively well preserved.The Gaoshi stabilized zone of the Laoshan fault uplift in the middle of the basin constitutes the Lower Paleozoic tectonic stable zone.b.Palaeozoic strata possess relatively superior geological conditions for oil and gas resources, of which the Cambrian source rock is characterized by great thickness and high contents of organic substance dominated by typeⅠkerogen.Metasomatic dolomite and granular limestone are mainly developed in Middle Cambrian to Ordovician, which can be used as better reservoirs.The thick argillaceous rocks of Upper Ordovician to Lower Silurian are widely developed and have good sealing ability, which can be used as a set of regional caprocks.The source-reservoir-caprock combination is well developed in Lower Paleozoic, and several large structural traps and hydrocarbon charging exist in the Gaoshi stable zone.As the structural traps match well with the formation of oil and gas in time and space, and the late structural destruction is relatively weak, the oil and gas preservation conditions are good.Therefore, it can be a favorable area for marine oil and gas exploration in South Yellow Sea Basin.
-

-
图 5 崂山断隆带高石稳定带油气运聚成藏模式(据参考文献[41]修改)
Figure 5.
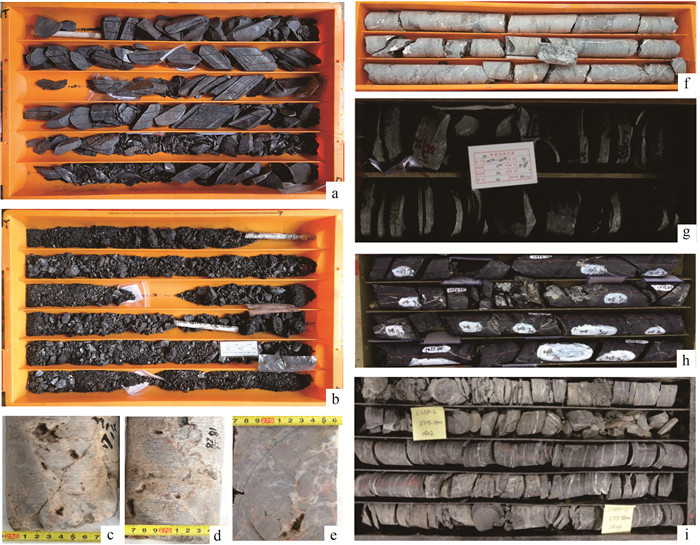
表 1 下扬子陆域代表性钻井下寒武统烃源岩主要特征
Table 1. Characteristics of Cambrian source rocks of representative wells in the Lower Yangtze Platform
表 2 下扬子陆域代表性钻井下古生界储层特征
Table 2. Lower Paleozoic Reservoir rocks of the representative wells in the Lower Yangtze Platform
代表性
钻井层位 (潜在)储
层厚度/m孔隙度
/%渗透率
/mD储集空
间类型苏121井 炮台山组 68 0.2~8.51 / 溶孔、溶洞 许24井 炮台山组 83.2 0.6~5.7 / 溶孔、缝洞、溶洞 兴参1井 观音台组 4 9.2~34.4 29.7~1164.1 蜂窝状溶孔、裂缝 苏103井 观音台组 5.6 0.63~2.73 / 溶孔、溶洞、晶间孔 许9井 观音台组 81.2 0.5~3 / 溶孔、缝洞、溶洞 N2井 红花园组 >54 / / 溶孔、缝洞、溶洞 昆3井 仑山组 / 最高5.54 0.42~21 晶间孔 注:部分数据据参考文献[21-22]整理;“/”为无相关数据 -
[1] 戴春山, 李刚, 蔡峰, 等. 黄海前第三系及油气勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(4): 225-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200304000.htm
[2] 陈建文, 雷宝华, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地油气资源调查新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803001.htm
[3] 陈建文, 梁杰, 张银国, 等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6): 1-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201906001.htm
[4] Li W, Liu Y, Xu J. Onshore-offshore structure and hydrocarbon potential of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 90: 127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.04.024
[5] 陈建文, 龚建明, 李刚, 等. 南黄海盆地海相中-古生界油气资源潜力巨大[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201601001.htm
[6] Zhang M, Xu D, Chen J. Geological structure of the Yellow Sea area from regional gravity and magnetic interpretation[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2007, 4(2): 75-83. doi: 10.1007/s11770-007-0011-1
[7] 夏在连, 花彩霞, 刘计勇, 等. 下扬子区下古生界油气有利勘探区带探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 66-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803006.htm
[8] 郭兴伟, 朱晓青, 宋世杰. 大陆架科钻CSDP-2井在南黄海海相地层中首次钻遇油气显示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 5: 124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201505019.htm
[9] 许振强, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起中、古生界油气保存条件分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 125-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803012.htm
[10] Cai L, Xiao G, Guo X, et al. Assessment of Mesozoic and Upper Paleozoic source rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin based on the continuous borehole CSDP-2[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.028
[11] 李双林, 董贺平, 王建强, 等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起中南部海域油气目标地球化学探测: 海底油气渗漏与双环状地球化学异常[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2): 847-858. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202002014.htm
[12] 陈建文, 施剑, 张异彪, 等. 地震调查技术突破南黄海海相中-古生界成像技术瓶颈[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6): 847-858. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201706001.htm
[13] Pang Y, Guo X, Shi B, et al. Hydrocarbon generation evaluation, burial history, and thermal maturity of the Lower Triassic Silurian organic-rich sedimentary rocks in the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin, East Asia[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34: 4565-4578. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c00552
[14] 梁杰, 张鹏辉, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海盆地海相中-古生界油气保存条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(5): 10-19.
[15] 刘计勇, 张飞燕, 印燕铃. 下扬子下寒武统岩相古地理及烃源岩条件研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 85-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803008.htm
[16] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 陈建平, 等. 中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(一): 南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2008.02.001
[17] 黄正清, 周道容, 李建青, 等. 下扬子地区寒武系页岩气成藏条件分析与资源潜力评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 94-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201901013.htm
[18] 樊佳莉. 下扬子地区下寒武统富有机质页岩的岩相与沉积环境[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5): 156-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705021.htm
[19] 唐显春, 曾辉, 张培先, 等. 宣城地区荷塘组页岩含气性浅析[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2011, 1(1/2): 78-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ2011Z1018.htm
[20] Xiao S, Hu J, Yuan X, et al. Articulated sponges from the Lower Cambrian Hetang Formation in southern Anhui, South China: Their age and implications for the early evolution of sponges[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 220(1): 89-117. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031018204005796
[21] 王英华. 中、下扬子区海相碳酸盐岩成岩作用研究[M]. 北京: 科学技术文献出版社, 1991.
[22] 梁兵, 段宏亮, 李华东. 下扬子地区海相层系成藏条件及勘探评价[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013.
[23] 张敏强, 高顺莉, 谭思哲. 南黄海盆地中、古生界地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 24-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803002.htm
[24] 梁杰, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 南黄海盆地中、古生界盖层条件[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2): 353-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.010
[25] 张淮, 周荔青, 李建青. 下扬子地区海相下组合油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2006, 28(1): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2006.01.003
[26] 张训华, 肖国林, 吴志强, 等. 南黄海油气勘探若干地质问题认识和探讨[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.
[27] 贾东, 胡文瑄, 姚素平, 等. 江苏省下志留统黑色页岩浅井钻探及其页岩气潜力分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2016, 22(1): 127-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201601013.htm
[28] 熊强青, 王中鹏, 张娣, 等. 下扬子巢湖地区皖含地1井五峰组-高家边组下段生物地层[J]. 地层学杂志, 2020, 44(1): 46-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ202001005.htm
[29] Chen Q, Fan J, Zhang L, et al. Paleogeographic evolution of the Lower Yangtze region and the break of the "platform-slope-basin" pattern during the Late Ordovician[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 625-636. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9170-y
[30] Yang S, Hu W, Wang X, et al. Duration, evolution, and implications of volcanic activity across the Ordovician-Silurian transition in the Lower Yangtze region, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 518: 13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2019.04.020
[31] 潘继平, 乔德武, 李世臻, 等. 下扬子地区古生界页岩气地质条件与勘探前景[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(2/3): 338-341. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2011020318&flag=1
[32] 方朝刚, 黄正清, 滕龙, 等. 下扬子地区晚奥陶世凯迪期-早志留世鲁丹期岩相古地理及其油气地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 144-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202001013.htm
[33] 张海啟, 陈建文, 李刚, 等. 地震调查在南黄海崂山隆起的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(3): 107-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200903019.htm
[34] 金春爽, 乔德武, 沈怀磊, 等. 海域油气资源战略调查与选区[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013.
[35] Yao Y, Chen C, Feng Z, et al. Tectonic Evolution and Hydrocarbon Potential in Northern Area of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2010, 21(1): 71-82. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0006-3
[36] 郭彤楼. 下扬子地区中古生界叠加构造特征与多源多期成藏[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(4): 319-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.04.002
[37] 徐旭辉, 周小进, 彭金宁. 从扬子地区海相盆地演化改造与成藏浅析南黄海勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(5): 523-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201405002.htm
[38] 马永生, 楼章华, 郭彤楼, 等. 中国南方海相地层油气保存条件综合评价技术体系探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(3): 406-417. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.03.013
[39] 张鹏辉, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等. 中国叠合盆地深部海相地层油气保存条件剖析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201901001.htm
[40] Brun J, Sokoutis D, Driessche J V D. Analogue modeling of detachment fault systems and core complexes[J]. Geology, 1994, 22(4): 319-322. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=9412281119&site=ehost-live
[41] Yan D P, Zhang B, Zhou M F, et al. Constraints on the depth, geometry and kinematics of blind detachment faults provided by fault-propagation folds: An example from the Mesozoic fold belt of South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2009, 31(2): 150-162. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191814108001909
[42] 陈春峰, 施剑, 徐东浩, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起形成演化及对油气成藏的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 55-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803005.htm
-



 下载:
下载: