Cobalt-rich crust obtains high contents of key elements from seawater: element absorption and distribution
-
摘要:
富钴结壳是大洋低温海水中的溶解元素在海山边坡沉淀形成的壳状铁锰矿产,广泛分布于全球海山、海底高原斜坡之上,储量巨大。铁锰结壳高度富集Co、Ni、Pt、REE、Te等元素,达到海水丰度的105~1010倍,是未来新能源、高新技术元素的重要来源,具有极大的潜在经济价值。前人通过淋滤实验、吸附实验、现代海洋观测方法、海水化学分析、高分辨率精细矿物学研究等方法对富钴结壳中元素的赋存状态和富集机理进行了广泛而深入的研究。研究结果表明,富钴结壳主要由含铁水羟锰矿和铁氢氧化物组成,在海山附近的海洋化学过程中,含铁水羟锰矿和铁氢氧化物胶体分别优先吸附Co、Ni、Pt、REE和Cu、Pb、Te、REE等元素,表面氧化/置换作用造成了含铁水羟锰矿中Co、Pt、Ni、Ce及铁氢氧化物中Te、Ce的持续积累。富钴结壳极其缓慢的生长速率(1~10 mm/Ma)、超高孔隙度(60%)、极大的体表面积(300 m2/g)都促进了结壳中关键元素的超常富集。对富钴结壳关键元素富集机理的理解是富钴结壳古海洋反演研究的基础,海域富钴结壳地球化学差异的控制因素需要进一步研究,这些关键科学问题的理解有助于富钴结壳资源的勘探工作。
Abstract:Cobalt-rich crust is formed from precipitation of dissolved elements in low temperature seawater on the slope of seamounts.It is widely distributed on the slope of seamounts and undersea plateau in the oceans, with huge reserves.Ferromanganese crusts have high contents of Co, Ni, Pt, REE, Te, which reach 105-1010 times of the seawater.They are important sources of new energy and high-tech elements in the future and have great potential economic value.The former researchers have focused on the association and enrichment mechanism of the elements in the cobalt-rich crust, with the help of step leaching, absorption experiment, modern ocean observation, water chemistry, high resolution of fine mineralogy.It reveals that cobalt-rich crusts are mainly composed of ferruginous vernadite and amorphous Iron hydroxide.In the process of marine chemistry near seamounts, ferrugvnous vernadite colloid and iron hydroxide colloid preferentially adsorb Co, Ni, Pt, REE and Cu, Pb, Te, REE, respectively.Surface oxidation/lattice replacement result in the continuous accumulation of Co, Pt, Ni, Ce in ferrugvnous Vernadite and Te, Ce in iron hydroxide.The extremely slow growth rate (1~10 mm/Ma), ultra-high porosity (60%) and large surface area (300 m2/g) of cobalt-rich crusts all promote the high enrichment of key elements in the crusts.The trace elements enrichment mechanism of the cobalt-rich crust is key to paleo-oceanography inversion.On the other way, the factors controlling the geochemical differences of cobalt-rich crust in the ocean need further study, understanding which will contribute to the exploration of cobalt-rich crust resources.
-
Key words:
- Cobalt-rich crust /
- key elements /
- ultra-enriched
-

-
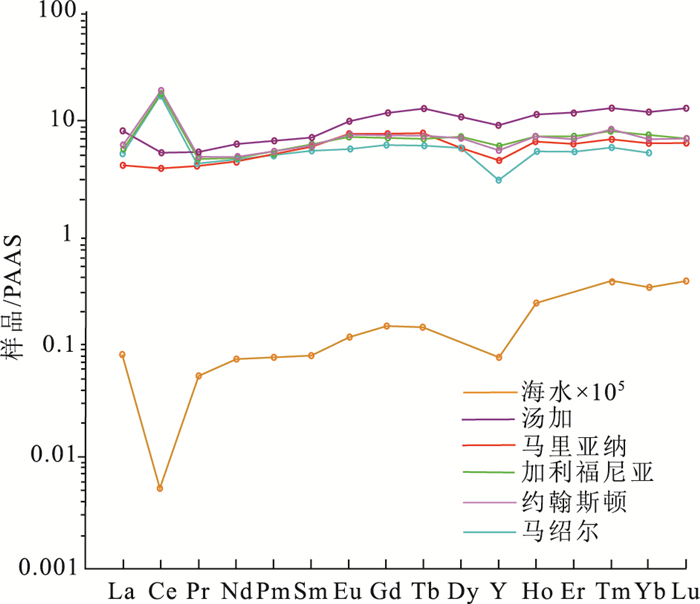
图 2 太平洋富钴结壳稀土元素配分模式图[2]
Figure 2.
-
[1] 韦振权, 何高文, 邓希光, 等. 大洋富钴结壳资源调查与研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44, (3): 460-472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201703006.htm
[2] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[J]. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits, 2000, 18: 239-273. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10026538570
[3] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[4] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079-4094. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00231-7
[5] Halbach P, Puteanus D, Manheim F T, et al. Platinum concentrations in ferromanganese seamount crusts from the Central Pacific[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 1984, 71(11): 577-579. doi: 10.1007/BF01189182
[6] Moore J, Normark W R, Holcomb R T. Giant Hawaiian underwater landslides[J]. Science, 1994, 264(5155): 46. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5155.46
[7] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳中稀土元素的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 90(2): 37-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201702004.htm
[8] Koschinsky A, Hein J R, Kraemer D, et al. Platinum enrichment and phase associations in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules based on a multi-method approach[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 539: 119426. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119426
[9] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2014, (13): 273-289. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080959757011116
[10] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Halliday A N. Global occurrence of tellurium-rich ferromanganese crusts and a model for the enrichment of tellurium[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(6): 1117-1127. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01279-6
[11] Takahashi Y, Manceau A, Geoffroy N, et al. Chemical and structural control of the partitioning of Co, Ce, and Pb in marine ferromanganese oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(4): 984-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.11.016
[12] Peacock C L, Sherman D M. Crystal-chemistry of Ni in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules[J]. American Mineralogist, 2007, 92(7): 1087-1092. doi: 10.2138/am.2007.2378
[13] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: Evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[14] Ren Y, Sun X, Guan Y, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements plus yttrium among major mineral phases of marine Fe-Mn crusts from the South China Sea and Western Pacific Ocean: A Comparative Study[J]. Minerals, 2018, 9(1): 1-19. doi: 10.3390/min9010001
[15] Hein J R. Manganese Nodules[M]. Encyclopedia of earth science series, 2016: 408-412.
[16] Jiang X D, Sun X M, Chou Y M, et al. Geochemistry and origins of carbonate fluorapatite in seamount Fe Mn crusts from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 423: 106135. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025322720300232
[17] Turner D R, Whitfield M, Dickson A A G. The equilibrium speciation of dissolved components in freshwater and sea water at 25℃ and 1 atmpressure[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(6): 855-881. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90115-0
[18] Byrne R H, Kump L R, Cantrell K J. The influence of temperature and ph on trace metal speciation in seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1988, 25(2): 163-181. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(88)90062-X
[19] Byrne RH. Inorganic speciation of dissolved elements in seawater: the influence of pH on concentration ratios[J]. Geochemical Transactions, 2002, 3(1): 11-16. doi: 10.1186/1467-4866-3-11
[20] Usui A, Hino H, Suzushima D, et al. Modern precipitation of hydrogenetic ferromanganese minerals during on-site 15-year exposure tests[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4
[21] Tebo B M, Clement B G, Dick G J. Biotransformations of manganese[C]//Hurst C J, Crawford R L, Garland J L, et al. Manual of Environmental Microbiology. Washington, DC: ASM Press, 2007: 1223-1238.
[22] Villalobos M, Bargar J, Sposito G. Trace metal retention on biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticles[J]. Elements, 2005, 1(4): 223-226. doi: 10.2113/gselements.1.4.223
[23] Templeton A S, Knowles E J, Eldridge D L, et al. A seafloor microbial biome hosted within incipient ferromanganese crusts[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(12): 872-876. doi: 10.1038/ngeo696
[24] Halbach P, Segl M, Puteanus D, et al. Co-fluxes and growth rates in ferromanganese deposits from central Pacific seamount areas[J]. Nature, 1983, 304(5928): 716-719. doi: 10.1038/304716a0
[25] Maeno M Y, Ohashi H, Yonezu K, et al. Sorption behavior of the Pt(Ⅱ) complex anion on manganese dioxide(δ-MnO2): a model reaction to elucidate the mechanism by which Pt is concentrated into a marine ferromanganese crust[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2016, 51(2): 211-218. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0599-7
[26] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 张辉, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳中铂族元素赋存状态与富集机理[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 115-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201908012.htm
[27] De Carlo E H, McMurtry G M. Rare-earth element geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from the Hawaiian Archipelago, central Pacific[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 95(3/4): 235-250. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419290014V
[28] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and sea water[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(2): 1709-1725. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0016703796000634
[29] Byrne R H, Kim K H. Rare earth element scavenging in sea water[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10): 2645-2656. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90002-3
[30] Takahashi Y, Shimizu H, Usui A, et al. Direct observation of tetravalent cerium in ferromanganese nodules and crusts by X-ray absorption near-edge structure(XANES)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(17): 2929-2935. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00403-8
[31] Moffet J W. A radiotracer study of cerium and manganese uptake onto suspended particles in Chesapeake Bay. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(2): 695-703. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90499-5
[32] Elderfield H, Greaves M J. Determination of the Rare Earth Elements in Sea Water[M]. Springer, 1983: 427-445.
[33] 崔迎春, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素相关性的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2008, 27(3): 61-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2008.03.009
[34] Halbach P. Co-rich and platinum bearing manganese crust deposits on seamounts: nature, formation and metal potential[J]. Marine Mineral, 1989, 8(1): 23-39. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80004833577
[35] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, Carlo De E. 大洋磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素富集的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(5): 403-407. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.05.003
[36] 任向文, 石学法, 朱爱美, 等. 麦哲伦海山群MK海山富钴结壳稀土元素的赋存相态[J]. 吉林大学学报, 2011, 41(3): 707-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201103012.htm
-




 下载:
下载: