Se coupling relation and biological effectiveness study of the soil-wheat system in Yanqi Basin, southern Xinjiang
-
摘要:
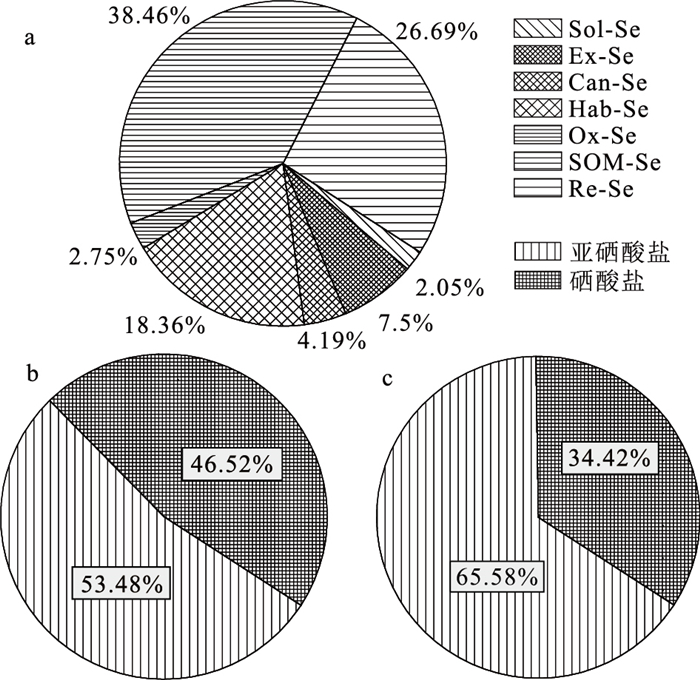
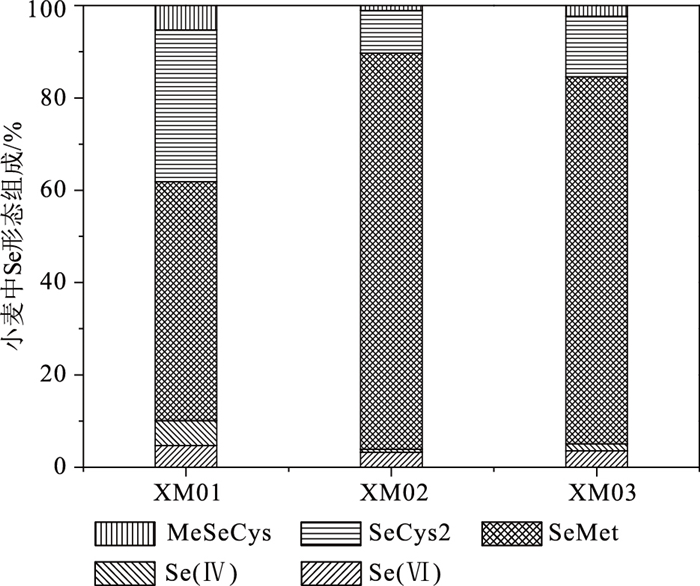
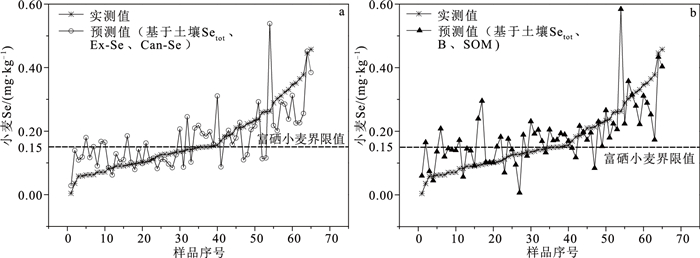
为研究土壤-小麦系统硒的关联性,采集南疆焉耆盆地小麦主要种植区小麦及对应根系土样品,通过相关分析、多元逐步线性回归方法,探讨土壤、小麦中Se含量及形态,查明影响小麦中硒的主要控制因素。结果表明,强有机质结合态硒(SOM-Se)和残渣态硒(Re-Se)是土壤硒的主要赋存形态,占土壤总Se含量的65.15%;土壤中硒受土壤风化程度、土壤质地和有机质含量影响明显;小麦籽粒中硒主要以有机硒形式存在,无机硒仅占全Se含量的6.39%,小麦硒的可给性高;土壤总Se含量可以很好地指示小麦Se含量水平,水溶态硒(Sol-Se)、离子交换态硒(Ex-Se)为有效硒的重要指标。基于土壤总Se、B、SOM构建的小麦硒吸收模型,可解释小麦吸收硒67%的方差。结合实际生产,给出了研究区高效富硒(含硒)小麦判别标准。据此编制富硒土壤高效利用区划图,有效地支撑了焉耆盆地富硒小麦标准化管理和面粉加工,提高了富硒土壤划定的科学性和实用性。
Abstract:Wheat is an important grain crop in southern Xinjiang.Samples of wheat and corresponding root soil were collected from the main planting areas of wheat in Yanqi Basin of southern Xinjiang in order to study the correlation of Se in the soil-wheat system.Correlation analysis and multiple stepwise linear regression were used to find out the main controlling factors of Se in wheat by study of the content and Se speciation in soil and wheat, and the results show that strong organic matter bound Se (SOM-Se) and residual Se (Re-Se) are the main existing forms of Se, accounting for 65.15% of total Se in soil.The content of Se in soil is highly impacted by the degree of soil weathering, soil texture and organic matter.Organic Se is the mainly form in wheat, and inorganic Se accounts for 6.39%, which shows that Se in wheat is of high availability for human beings.The total Se in soil can indicate the content of Se in wheat, and water-soluble Se (Sol-Se) and ion-exchange Se (Ex-Se) are important indexes of Se available.The regression models based on total Se, B, SOM can explain the variance of 67% of Se in wheat.The standard of high effective Se-rich (Se-containing) wheat in the study area are given in combination with the factor of actual production, and the zoning map of high-efficiency utilization of Se-enriched soil is made, which supports the standardized management of Se-enriched wheat and flour processing, and improves the scientificity and practicability of Se -enriched soil delineation.
-
Key words:
- Yanqi Basin /
- soil-wheat /
- Se available /
- organic Se /
- high-efficiency utilization
-

-
表 1 土壤中Se与理化指标相关系数
Table 1. Correlation between Se and physical and chemical properties in soil
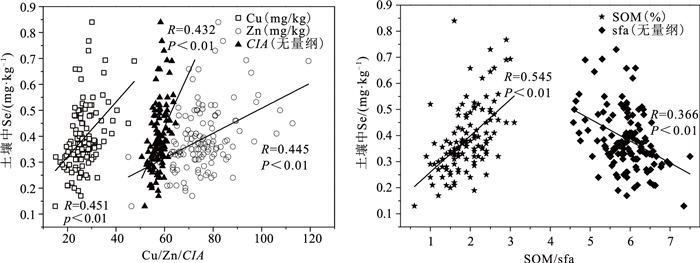
指标 Se Sol-Se Ex-Se Can-Se Hab-Se Ox-Se SOM-Se Re-Se pH -0.161 -0.040 -0.340** -0.363** -0.155 -0.278* -0.095 -0.329** N 0.297** 0.210 0.002 -0.037 0.270* 0.061 0.172 0.090 P 0.119 0.137 0.091 0.042 0.134 0.164 0.057 0.089 K 0.059 0.043 0.121 0.070 0.073 -0.009 0.042 0.344** Cu 0.451** 0.185 0.094 0.102 0.288* 0.108 0.310* 0.386** Zn 0.445** 0.149 0.043 0.069 0.250* 0.070 0.268* 0.358** B 0.254** 0.035 0.108 0.233 0.154 0.368** 0.258* 0.356** Fe 0.351** 0.125 0.045 0.005 0.232 -0.017 0.207 0.418** Mn 0.273** -0.012 0.053 0.089 0.195 0.078 0.240 0.501** S 0.093 -0.092 0.052 0.196 -0.120 0.170 -0.037 0.266* Pb 0.223* 0.257* 0.141 0.027 0.279* -0.051 0.192 0.393** As 0.335** 0.188 0.131 0.061 0.265* -0.022 0.203 0.506** Hg 0.339** 0.385** 0.162 0.075 0.403** -0.016 0.452** 0.351** Cd 0.374** 0.271* 0.067 0.006 0.388** -0.016 0.256* 0.373** Cr 0.419** 0.202 0.068 -0.015 0.244* -0.001 0.203 0.370** Cl 0-.033 -0.169 0.072 0.242 -0.068 0.167 -0.067 0.173 SOM 0.545** 0.127 -0.086 0.018 0.418** -0.001 0.452** 0.099 SiO2 -0.300** -0.031 0.180 0.046 -0.113 -0.056 -0.183 0.052 Al2O3 0.081 0.121 0.133 0.006 0.113 -0.084 0.026 0.354** Fe2O3 0.341** 0.146 0.070 0.038 0.221 0.020 0.200 0.438** FeO 0.405** -0.022 -0.096 0.005 0.217 0.023 0.295* 0.227 MnO 0.176* 0.011 0.085 0.140 0.187 0.128 0.250* 0.524** CaO 0.080 0.051 -0.188 -0.163 -0.008 -0.098 -0.021 -0.303* K2O 0.004 0.054 0.135 0.074 0.065 -0.006 0.009 0.342** Na2O -0.412** -0.142 0.099 0.045 -0.295* -0.036 -0.331** -0.091 MgO 0.181* -0.183 -0.045 0.213 -0.001 0.373** 0.203 0.019 P2O5 0.318** 0.015 0.187 0.355** 0.268* 0.375** 0.397** 0.358** sfa -0.366** -0.151 0.012 0.023 -0.212 0.011 -0.200 -0.341** CIA 0.432** 0.193 -0.017 -0.062 0.318** -0.042 0.298* 0.282* 注:Se与理化指标相关分析样本数为128件,Se各形态与理化指标相关性分析样本数为66件;*为在0.05水平上显著相关,**为在0.01水平上显著相关 表 2 小麦Se与土壤Se、Se形态及理化指标相关系数
Table 2. Correlation between Sewheat and Setot, Se speciation, physical and chemical properties in soil
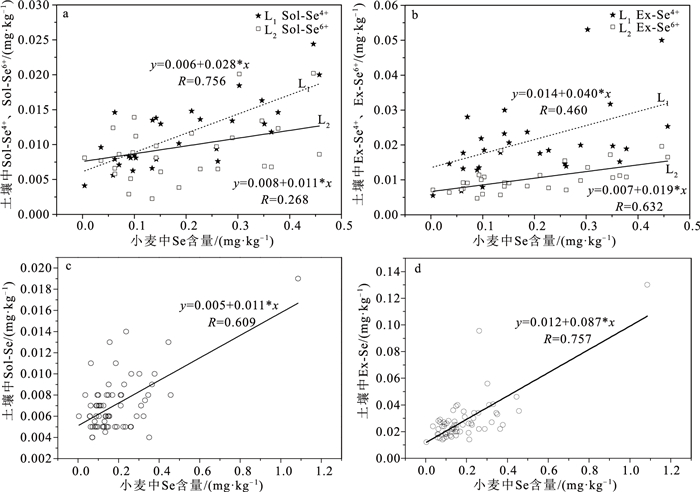
指标 相关系数R1 偏相关系数R2 pH -0.097 0.126 N 0.091 -0.034 P 0.163 0.127 K -0.042 -0.216 S -0.078 -0.171 As 0.079 -0.194 Se 0.745** / B -0.100 -0.463 Pb 0.070 -0.184 Cu -0.025 -0.389 Zn -0.074 -0.413 SOM -0.043 -0.382 SiO2 0.191 0.348 Al2O3 0.063 -0.063 Fe2O3 -0.019 -0.313 FeO -0.134 -0.422 CaO -0.075 0.021 K2O -0.033 -0.190 Na2O 0.112 0.396 MgO -0.204 -0.407 P2O5 0.095 -0.284 MnO 0.026 -0.277 Sol-Se 0.609** 0.313 Ex-Se 0.757** 0.349 Can-Se 0.503** -0.217 Hab-Se 0.634** -0.077 Ox-Se 0.381** -0.252 SOM-Se 0.618** -0.293 Re-Se 0.643** 0.004 #Se4+ 0.590** 0.047 #Se6+ 0.459* -0.017 #Sol-Se4+ 0.756** 0.517 #Sol-Se6+ 0.268 -0.125 #Ex-Se4+ 0.460* -0.182 #Ex-Se6+ 0.632** 0.212 注:#表示样本数为29件,其他为66件;*为在0.05水平上显著相关,**为在0.01水平上显著相关 表 3 富硒小麦等级划分标准
Table 3. Standard for classification of Se-enriched wheat grades
等级说明 面粉Se含量/(mg·kg-1) 等级说明 研究区小麦Se含量要求/(mg·kg-1) 研究区小麦占比/% 南疆小麦Se含量平均值/(mg·kg-1) 南疆小麦占比/% Se保有率/% 富Se面粉 ≥0.15 高效富Se小麦 ≥0.25 60 0.09 40 80 含Se面粉 0.075~0.15 高效含Se小麦 0.065~0.25 60 0.09 40 80 普通面粉 <0.075 普通小麦 <0.065 60 0.09 40 80 -
[1] Shardendu U, Salhani N, Boulyga S F, et al.Phytore-mediation of selenium by two helophyte species in subsurface flow constructed wetland[J].Chemosphere, 2003, 50:967-973. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00607-0
[2] Yu T, Hou W L, Hou Q Y, et al.Safe utilization and zoning on natural selenium-rich land resources: a case study of the typical area in Enshi County, China[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00519-0. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00519-0
[3] Fordyce F.Selenium geochemistry and health[J].Ambio, 2007, 36(1):94-97. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[94:SGAH]2.0.CO;2
[4] 樊海峰, 温汉捷, 凌宏文, 等.表生环境中硒形态研究现状[J].地球与环境, 2006, (2):19-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200602002.htm
[5] 王桂兰, 薛澄泽, 康靖全, 等.(土娄)土中硒含量和玉米、小麦、谷子生长的关系[J].农业环境科学学报, 1990, (5):15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH199005004.htm
[6] 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 李正文, 等.土壤-植物系统中硒的迁移转化及低硒地区食物链中硒的调节[J].土壤与环境, 2002, (4):388-391. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2002.04.016
[7] Li Z, Liang D L, Peng Q, et al.Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability:A review[J].Geoderma, 2017, 295:69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.019
[8] 梁东丽, 彭琴, 崔泽玮, 等.土壤中硒的形态转化及其对有效性的影响研究进展[J].生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705010.htm
[9] 郭宇, 鲍征宇, 马真真, 等.湖北恩施地区土壤-植物系统中Se元素的地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(1):151-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.01.019 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120119&flag=1
[10] Silva J E C, Wadt L H O, Silva K E, et al.Natural variation of selenium in Brazil nuts and soils from the Amazon region[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 188:650-658. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.158
[11] Michele L W T, Juli W F, John G E, et al.Contaminants from cretaceous black shale:Ⅱ.Effect of geology, weathering, climate, and land use on salinity and selenium cycling, Mancos Shale landscapes, southwestern United States[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 46:72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.12.011
[12] Xu Y F, Hao Z, Li Y H, et al.Distribution of selenium and zinc in soil-crop system and their relationship with environmental factors[J].Chemosphere, 2020, 242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653519325299
[13] 商靖敏, 罗维, 吴光红, 等.洋河流域不同土地利用类型土壤硒(Se)分布及影响因素[J].环境科学, 2015, 36(1):301-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201501046.htm
[14] 安永龙, 黄勇, 张艳玲, 等.北京房山南部地区富硒土壤生物有效性特征及来源[J].地质通报, 2020, 39(2/3):387-399. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2020020319&flag=1
[15] 陆晓奇, 王健, 朱元元, 等.典型富硒植物中硒形态和生物可给性研究[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1229-1234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806028.htm
[16] 赵晗, 蔡超.恩施地区玉米硒的生物可给性及其健康风险评估[J].江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(4):228-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY201804058.htm
[17] 姜超强, 沈嘉, 祖朝龙.水稻对天然富硒土壤硒的吸收及转运[J].应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3):809-816. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201503023.htm
[18] Chang C Y, Yin R S, Wang X, et al.Selenium translocation in the soil-rice system in the Enshi seleniferous area, Central China[J].The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 669:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.451
[19] Yu T, Yang Z F, Lv Y Y, et al.The origin and geochemical cycle of soil selenium in a Se-rich area of China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139:97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.09.006
[20] 陈建军.新疆焉耆盆地中生代原盆面貌及其演化与改造[D].西北大学博士学位论文, 2007.
[21] 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 阿吉古丽·马木提, 买托合提·阿那依提, 等.焉耆盆地小麦地土壤重金属污染及生态风险[J].农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(5):921-929. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201705015.htm
[22] 唐玉霞, 王慧敏, 刘巧玲, 等.河北省麦田土壤硒的含量、形态及其有效性研究[J].华北农学报, 2010, 25(S1):194-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNB2010S1045.htm
[23] Shardendu, Salhani N, Boulyga S F, et al.Phytoremediation of selenium by two helophyte species in subsurface flow constructed wetland[J].Chemosphere, 2003, 50(8):967-973. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00607-0
[24] Harada T, Takahashi Y.Origin of the difference in the distribution behavior of tellurium and selenium in a soil-water system[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(5):1281-1294. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.12.008
[25] Susanta Paikaray.Origin, Mobilization and Distribution of Selenium in a Soil/Water/Air System:A Global Perspective With Special Reference to the Indian Scenario[J].Clean-Soil, Air, Water, 2016, 44(5):474-487. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/clen.201300454
[26] Cary L, Naveau A, Migeot V, et al.From Water-rock Interactions to the DNA:A Review of Selenium Issues[J].Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2017, 17:698-701. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2016.12.157
[27] 姬丙艳, 张亚峰, 马瑛, 等.青海东部富Se土壤及Se赋存形态特征[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(1):302-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.01.039
[28] 韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201806017.htm
[29] 王琪.水稻和小麦对有机硒的吸收、转运及形态转化机制[D].中国农业大学博士学位论文, 2017.
[30] Whanger P D.Selenium and its relationship to cancer:an update[J].The British Journal of Nutrition, 2004, 91(1):11-28. http://ps.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1079/BJN20031015&link_type=DOI
[31] Schrauzer G N.Selenomethionine and selenium yeast:appropriate forms of selenium for use in infant fomuilas and nutritional supplements[J].Journal of Medicial Food, 1998, 1(3):201-206. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201302911894
[32] Dai Z H, Muhammad I, Muhammad R, et al.Dynamics of Selenium uptake, speciation, and antioxidant response in rice at different panicle initiation stages[J].The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 691:827-834. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.186
[33] 龚如雨, 钟松臻, 张宝军, 等.富硒、非富硒大米有机硒的组成及硒的可利用度分析[J].食品研究与开发, 2017, 38(20):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.20.002
[34] 徐树建, 倪志超, 丁新潮.山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(2):353-359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.017
[35] 张秀芝, 赵相雷, 李波.基于区域土壤元素地球化学的河北平原土壤质地类型划分[J].第四纪研究, 2017, (1):25-35.
[36] 孙朝, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等.典型土壤环境中硒的迁移转化影响因素研究——以四川省成都经济区为例[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(6):1760-1768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.023
[37] 周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔, 等.土壤中硒含量、形态及有效性分析[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6):527-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ201406008.htm
[38] 曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐.土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究——以湖北恩施沙地为例[J].现代地质, 2018, 32(1):105-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201801011.htm
[39] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等.海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201205000.htm
[40] Cartes P, Gianfreda L, Mora M L.Uptake of selenium and its antioxidant activity in ryegrass when applied as selenate and selenite forms[J].Plant and Soil, 2005, 276(1/2):359-367. doi: 10.1007/s11104-005-5691-9
① 中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心.新疆焉耆盆地1: 5万土地质量地球化学调查2019年度成果报告.2019.
② 巴州明有食品有限公司.面粉质量手册.2018.
-




 下载:
下载: