Orogenic peridotite and its significance
-
摘要:
造山橄榄岩和蛇绿岩的橄榄岩主要由地幔岩组成,造山橄榄岩代表陆壳下的地幔,蛇绿岩的橄榄岩代表洋壳下的地幔。洋壳下的地幔与陆壳下的地幔在物质组成上大体接近,但产出的构造背景明显不同。介绍了造山橄榄岩的组成、与造山橄榄岩有关的高压-超高压变质作用、地幔流体作用、成矿作用、造山橄榄岩侵位的机制等,以及中国几个可能的造山橄榄岩的基本情况,讨论了造山橄榄岩的演变过程及其与蛇绿岩的橄榄岩的区别。造山橄榄岩的形成大体经历了初期的陆壳减薄和裂谷阶段、晚期的挤压造山2个构造演化阶段。有些地区只发育裂谷阶段,构造演化在裂谷后即夭折了,也称为造山橄榄岩。蛇绿岩与造山橄榄岩之间的区别不在物质组成和地球化学方面,而是在构造背景上。如有没有深海沉积、混杂堆积,有,是蛇绿岩;没有,则是造山橄榄岩。有没有超高压变质作用、地幔交代作用或地幔交代作用是否强烈,有且很强,可能是造山橄榄岩;没有,则可能是蛇绿岩。岩体是冷侵位还是热侵位,冷侵位是蛇绿岩,热侵位是造山橄榄岩。蛇绿岩出现在造山带,代表已经消失的洋盆;造山橄榄岩一般也出现在造山带,但代表的是减薄和撕裂的陆壳下的地幔。
Abstract:Orogenic peridotite and peridotite of ophiolite are mainly composed of mantlerock.Orogenic peridotite represents the mantle beneath the continental crust, and peridotite of ophiolite represents the mantle beneath the oceanic crust.The mantle beneath the oceanic crust is generally close to the mantle beneath the continental crust in terms of material composition, but the tectonic setting is different.This paper briefly introduces the composition of orogenic peridotites, high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism related to orogenic peridotites, mantle fluids, mineralization, and mechanisms of orogenic peridotite emplacement, and also briefly introduces several possible orogenic peridotites in China such as the Songshugou peridotite in the Qinling Mountain, the Raobazhai rock mass in Anhui, several rock masses in the Yidun-type area in western Sichuan, Santai rock mass in western Yunnan, and Dadaoerji rock mass in Gansu.The evolution process of orogenic peridotite and its difference from ophiolite peridotite are discussed.It is pointed out that the difference between ophiolite and orogenic peridotite is not mainly in material composition and geochemistry, but in tectonic setting.Is there no abyssal sediment? Is it mixed up? Yes, it is peridotite of ophiolite; no, it is orogenic peridotite.Is there any UHP metamorphic effect? Is there mantle metasomatism or strong mantle metasomatism? Some are very strong and may be orogenic peridotites; no, they may be peridotites of ophiolite.Cold emplacement is peridotite of ophiolite, and thermal emplacement is orogenic peridotite.It is pointed out in this paper that the formation of orogenic peridotite has generally experienced two stages of tectonic evolution:the initial thinning of the continental crust, the rifting stage, and the late extruding orogenic belt.In some areas, only the rift stage is developed, and the tectonic evolution finished after the rift, also known as orogenic peridotites, such as Zabargad in the Red Sea, Ronda in Spain, Beni Bousera in Morocco, and Yidun peridotite in China.The peridotite of ophiolite appears in the orogenic belt, representing the ocean basin that has disappeared; the orogenic peridotite generally appears in the orogenic belt, but it represents the thinned and torn continental crust.It is necessary to study and demonstrate whether the peridotite that appears in the orogenic belt is ophiolite because their tectonic meanings are different.
-
Key words:
- orogenic peridotite /
- ophiolite /
- Alps /
- rift /
- ultrahigh pressure metamorphism /
- fluid /
- oceanic crust /
- continental crust
-

-
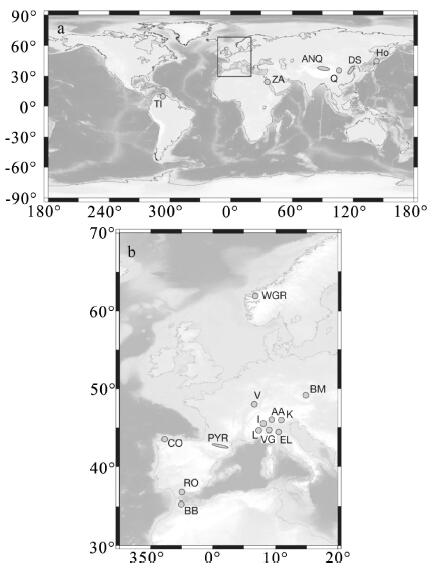
图 1 造山橄榄岩的全球分布[21]
Figure 1.
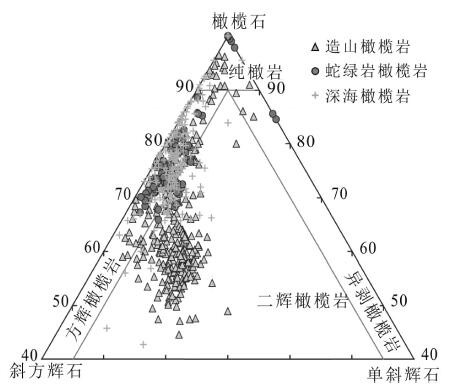
图 2 造山橄榄岩、蛇绿岩和深海橄榄岩组成[21]
Figure 2.
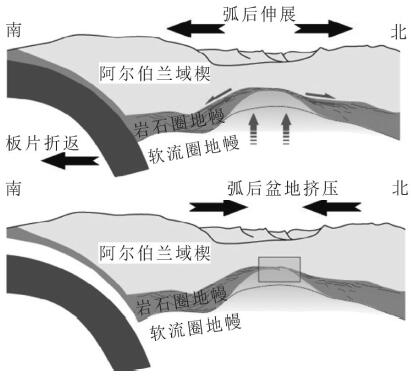
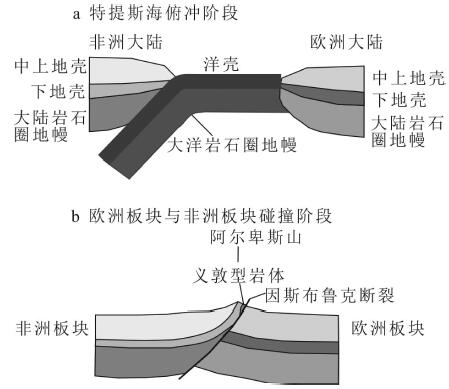
图 3 西地中海新生代构造演化示意图[68]
Figure 3.
图 4 西班牙Ronda岩体底部剖面图(展示了从岩体底部向下变质程度逐渐降低的变化[54]; a、b、c分别表示原作者详细研究部位,本文在此省略; 蓝色星号表示原作者取样位置)
Figure 4.
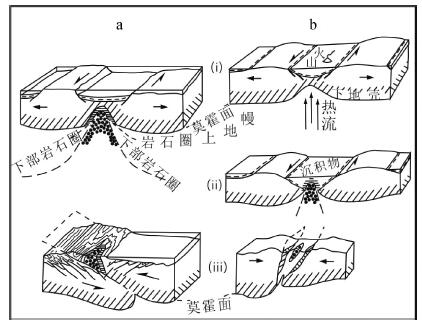
图 5 超镁铁岩-麻粒岩组合侵位模式[96]
Figure 5.
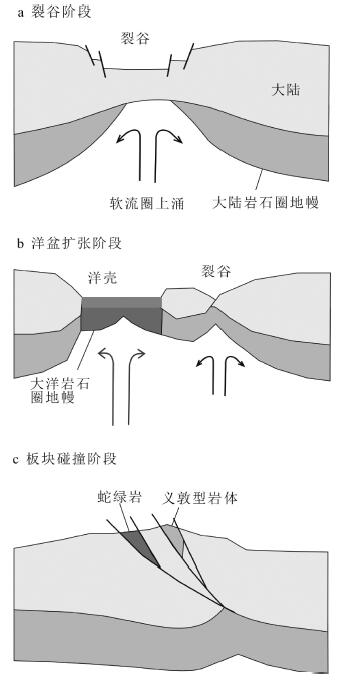
图 6 造山橄榄岩(义敦型岩体)形成模式之一:裂谷模式[5]
Figure 6.
图 7 造山橄榄岩形成模式之二:陆壳基底剥蚀抬升模式[5]
Figure 7.
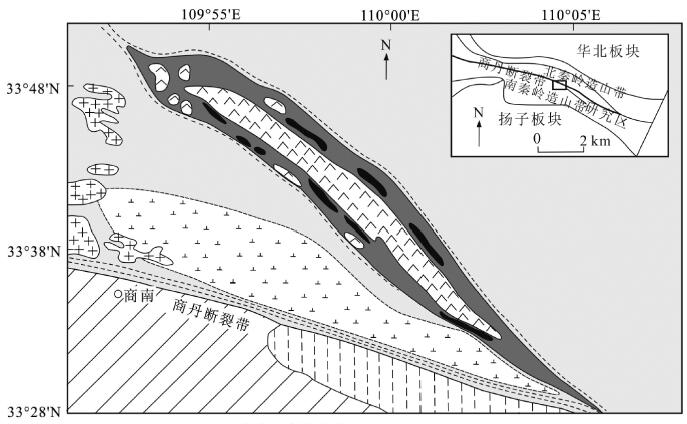
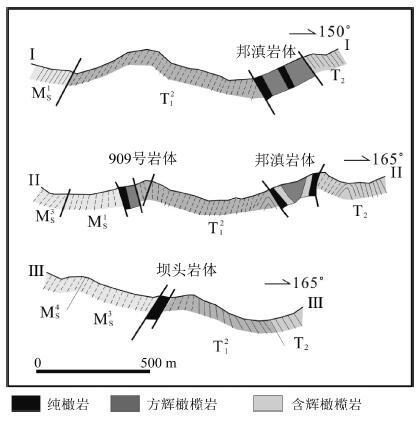
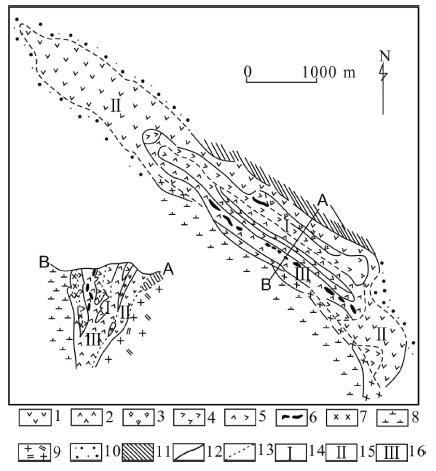
图 8 中国北秦岭松树沟超镁铁质岩体地质略图[27]
Figure 8.
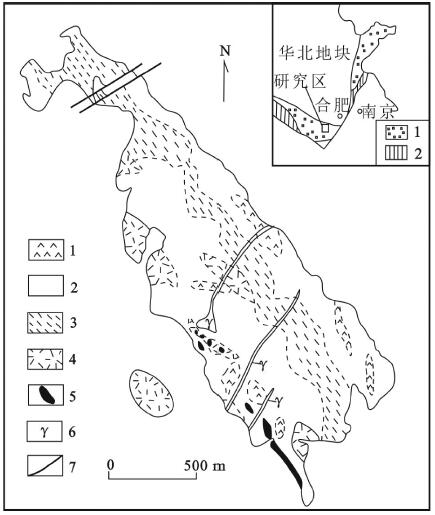
图 9 饶拨寨岩体地质图[113]
Figure 9.
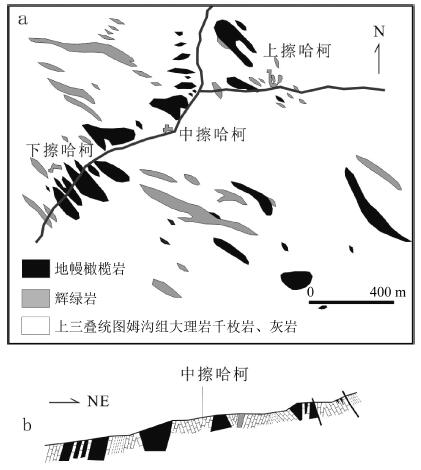
图 10 四川白玉县擦哈柯地质草图[3]
Figure 10.
图 12 大道尔吉岩体地质示意图[122]
Figure 12.
-
[1] 张旗, 张魁武, 李达周.横断山区基性-超基性岩的类型[J].岩石学报, 1987, (3):46-53.
[2] 张旗, 李达周, 张魁武, 等.义敦型镁铁-超镁铁岩的主要特征及其与蛇绿岩的对比[J].岩石学报, 1990, 6(3):33-42.
[3] 张旗, 张魁武, 李达周.横断山区镁铁-超镁铁岩[M].北京:科学出版社, 1992.
[4] 张旗, 周德进, 赵大升, 等.滇西古特提斯造山带的威尔逊旋回:岩浆活动记录和深部过程讨论[J].岩石学报, 1996, 12(1):17-28
[5] 张旗.镁铁-超镁铁岩的分类及其构造意义[J].地质科学, 2014, 49(3):982-1017
[6] 张旗, 周国庆.中国蛇绿岩[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:1-182.
[7] Nicolas A, Jackson E D.Repartition en deux province des peridotites des chaines alpines longeant la Mediterranee:implications geotectoniques[J].Schweiz.Petrogr.Mitt., 1972, 52:479-495.
[8] Menzies M A.Chemical and isotopic heterogeneities in orogenic and ophiolitic peridotites[C]//Ophiolites and Oceanic Lithosphere.Blackwell Sci., Pnbl., Oxford, London, 1984: 231-240.
[9] Lorand J P, Schmidt G, Palme H, et al.Highly siderophile element geochemistry of the Earth's mantle:new data for the Lanzo(Italy) and Ronda(Spain) orogenic peridotite bodies[J].Lithos, 2000, 53:149-164. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00017-7
[10] Doblas M, Oyarzun M."Mantle core complexes" and Neogene extensional detachment tectonics in the western Betic Cordilleras, Spain:an alternative model for the emplacement of the Ronda peridotite[J].EPSL, 1989, 93:76-84. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(89)90185-4
[11] Den Tex E.Origin of ultramafic rocks, their tectonic settings and history:A contribution to the discussion of the paper "The origin of ultramafic and ultrabasic rocks" by P J Wyllie[J].Tectonophy, 1969, 7:457-488. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(69)90016-X
[12] Ernst W G.Petrochemical Study of Lherzolitic Rocks from the Western Alps[J].Journal of Petology, 1978, 19:341-392. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.341
[13] Nicolas A.Lherzolites of the western Alps: a stracturalreview[C]//Kimberlites, II: The Mantle and Crust-mantle relationship, Elsevier, Amstedam, 1984: 333-346.
[14] Trommsdorff V, Hermann J, Muntener O, et al.Geodynamic cycles of subcontinental lithosphere in the Central Alps and the Arami enigma[J].Journal of Geodynamics, 2000, 30:77-92. doi: 10.1016/S0264-3707(99)00028-9
[15] Bonatti E, Michael P J.Mantle peridotites from continental rifts to ocean basins to subduction zones[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1989, 91:297-311. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(89)90005-8
[16] Gueddari K, Piboule M, Amosse J.Differentiation of platinum-group elements(PGE) and of gold during partial melting of peridotites in the lherzolitic massifs of the Betico-Rifean range(Ronda and Beni Bousera)[J].Chemical Geology, 1996, 134:181-197. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00085-X
[17] Snow J E, Schmidt G.Proterozoic melting in the northern peridotite massif, Zabargad island:Os isotopic evidence[J].Terra Nova, 1999, 11:45-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.1999.00223.x
[18] Boudier F, Nicolas A, Ji S, et al.The gneiss of Zabargad Island—deep crust of a rift[J].Tectonophysics, 1988, 150: 209-227. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(88)90302-2
[19] Lorand J P, Bodinier J L, Dupuy C, et al.Abundances and distribution of gold in the orogenic-type spinel peridotites from Arie'ge(Northeastern Pyrenees, France)[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53:3085-3090. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90188-9
[20] Muntener O, Piccardo G B, Polino R, et al.Revisiting the Lanzo peridotite(NW-Italy):'Asthenospherization' of ancient mantle lithosphere[J].Ofioliti, 2005, 30:111-124.
[21] Bodinier J L, Godard M.Orogenic, ophiolitic, and abyssal peridotites[C]//Holland H D, Turekian K K.Treatise on Geochemistry.2nd ed.Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014, 103-167.
[22] Crespo E, Luque F J, Rodas M, et al.Graphite-sulfide deposits in Ronda and Beni Bousera peridotites(Spain and Morocco) and the origin of carbon in mantle-derived rocks[J].Gondwana Research, 2006, 9:279-290. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.10.003
[23] Gonzalez-Jimenez J M, Marchesi C, Griffin W L, et al.Zircon recycling and crystallization during formation of chromite-and Ni-arsenide ores in the subcontinental lithospheric mantle(Serranía de Ronda, Spain)[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90:193-209. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.012
[24] Tubía J.The Ronda peridotites(Los Reales nappe):An example of the relationship between lithospheric thickening by oblique tectonics and late extensional deformation within the Betic Cordillera(Spain)[J].Tectonophysics, 1994, 238:381-398. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(94)90065-5
[25] Ishiwatari A.Alpine ophiolites:product of low-degree mantle melting in a Mesozoic transcurrent rift zone[J].EPSL, 1985, 76:93-108. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(85)90151-7
[26] Bodinier J L, Menzies M A, Thirlwall M.Continental to oceanic mantle transition—REE and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of the Lanzo lherzolite massif.Orogenic lherzolites and mantle processes[J].Journal of Petrology, 1991, 20:191-210. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-015-8979-6_29
[27] 苏犁, 宋述光, 周鼎武.秦岭造山带松树沟纯橄岩体成因:地球化学和岩浆包裹体的制约[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2005, 35(1):38-47.
[28] Dong Y P, Zhou M F, Zhang G W, et al.The Grenvillian Songshugou ophiolite in the Qinling Mountains, Central China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32:325-335. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.010
[29] Nie H, Yang J Z, Zhou G Y, et al.Geochemical and Re-Os isotope constraints on the origin and age of the Songshugou peridotite massif in the Qinling orogen, central China[J].Lithos, 2019, 344/345:207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.06.029
[30] Cao Y, Song S G, Su L, et al.Highly refractory peridotites in Songshugou, Qinling orogen:Insights into partial melting and melt/fluid-rock reactions in forearc mantle[J].Lithos, 2016, 252/253:234-254. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.03.002
[31] Sun S S, Dong Y P, Sun Y L, et al.Re-Os geochronology, O isotopes and mineral geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic Songshugou ultramafic massif in the Qinling Orogenic Belt, China[J].Gondwana Research, 2019, 70:71-87. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.12.016
[32] Tang L, Santosha A, Dong Y P, et al.Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Qinling orogenic belt:Evidence from geochemistry, phase equilibrium modeling and geochronology of metamorphosed mafic rocks from the Songshugou ophiolite[J].Gondwana Research, 2016, 30:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.10.006
[33] 李晔, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等.北秦岭早古生代两期变质作用:来自松树沟基性岩岩石学及锆石U-Pb年代学的记录[J].地球科学, 2012, 37(增刊):111-124.
[34] 刘良, 廖小莹, 张成立, 等.北秦岭高压-超高压岩石的多期变质时代及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(5):1634-1656.
[35] Yu H, Zhang H F, Santosh M.Mylonitized peridotites of Songshugou in the Qinling orogen, central China:A fragment of fossil oceanic lithosphere mantle[J].Gondwana Research, 2017, 52:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.08.007
[36] 张宏福, 于红.造山带橄榄岩岩石学与构造过程:以松树沟橄榄岩为例[J].地球科学, 2019, 44(4):1057-1066.
[37] 钱加慧, 杨秀清, 刘良, 等.北秦岭松树沟榴闪岩锆石U-Pb定年、矿物包裹体和Lu-Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(9):3087-3098.
[38] 陈丹玲, 任云飞, 宫相宽, 等.北秦岭松树沟榴辉岩的确定及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(7):1841-1854.
[39] 郑永飞, 赵子福, 陈伊翔.大陆俯冲隧道过程:大陆碰撞过程中的板块界面相互作用[J].科学通报, 2013, 58:2233-2239.
[40] 郑永飞, 陈伊翔, 戴立群, 等.发展板块构造理论:从洋壳俯冲带到碰撞造山带[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45:711-735.
[41] 郑建平, 熊庆, 赵伊, 等.俯冲带橄榄岩及其记录的壳幔相互作用[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49:1037-1058.
[42] 陈意, 苏斌, 郭顺.大别-苏鲁造山带橄榄岩:进展和问题[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(9):1245-1269.
[43] 陈意, 苏斌, 郭顺.造山带橄榄岩起源和大陆俯冲带壳幔相互作用[J].地球科学, 2019, 44(12):4086-4094.
[44] 陈仁旭, 尹壮壮, 夏春鹏.大别-苏鲁造山带橄榄岩记录的碰撞造山过程中地幔楔的地壳交代作用[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(3):459-484.
[45] 陈仁旭, 郑永飞.造山带橄榄岩记录的大陆俯冲带多期壳幔相互作用[J].地球科学, 2019, 44(12):4095-4101.
[46] Zheng Y F.Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones[J].Chemical Geology, 2012, 328:5-48. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.02.005
[47] Zheng Y F.Subduction zone geochemistry[J].Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 10:1223-1254. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.02.003
[48] Beccaluva L, Piccardo G B, Serri G.Petrology of northern Apennian ophiolites and comparison with other Tethyan ophiolites[C]//Ophiolites.Proc, Inter, Ophi, Symp, Cyprus, 1980: 314-331.
[49] Lemoine M, Tricart P, Boillot G.Ultramafic and gabbroic ocean floor of the Ligurian Tethys(Alps, Corsica, Apennines):in search of a genetic model[J].Geology, 1987, 15:622-625. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1987)15<622:UAGOFO>2.0.CO;2
[50] Li X H, Faure M, Lin W, et al.New isotopic constraints on age and magma genesis of an embryonic oceanic crust:the Chenaillet Ophiolite in the Western Alps[J].Lithos, 2013, 160/161:283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.12.016
[51] Li X H, Faure M, Rossi P, et al.Age of Alpine Corsica ophiolites revisited:Insights from in situ zircon U-Pb age and O-Hf isotopes[J].Lithos, 2015, 220/223:179-190. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.02.006
[52] O'Hara M J.Mineral parageneses in ultramafic rocks[C]//Wyllie P J.Ultramafic and Related Rocks, New York: Wiley, 1967: 393-403.
[53] Frey F A, Suen C J, Stockman H W.The Ronda high temperature peridotite:Geochemistry and petrogenesis[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49:2469-2491. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90247-9
[54] Bartoli O, Acosta-Vigil A, Tajcmanová L, et al.Using nanogranitoids and phase equilibria modeling to unravel anatexis in the crustal footwall of the Ronda peridotites(Betic Cordillera, S Spain)[J].Lithos, 2016, 256/257:282-299. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.03.016
[55] Acosta-Vigil A, Rubatto D, Bartoli O, et al.Age of anatexis in the crustal footwall of the Ronda peridotites, S Spain[J].Lithos, 2014, 210/211:147-167. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.08.018
[56] Su B, Chen Y, Guo S, et al.Origins of orogenic dunites:petrology, geochemistry and implications[J].Gondwana Research, 2016, 29:41-59. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.08.001
[57] Su B, Chen Y, Mao Q, et al.Minor elements in olivine inspect the petrogenesis of orogenic peridotites[J].Lithos, 2019, 344/345:207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.06.029
[58] Weyer S, Munker C, Mezger K.Nb/Ta, Zr/Hf and REE in the depleted mantle:implications for the differentiation history of the crust-mantle system[J].EPSL, 2003, 205:309-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01059-2
[59] Mazzucchelli M, Zanetti A, Rivalenti G, et al.Age and geochemistry of mantle peridotites and diorite dykes from the Baldissero body:Insights into the Paleozoic-Mesozoic evolution of the Southern Alps[J].Lithos, 2010, 119:485-500. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.002
[60] Gervilla F, Leblanc M.Magmatic ores in high-temperature alpine-type lherzolite massifs(Ronda, Spain, and Beni Bousera, Morocco)[J].Econ.Geol., 1990, 85:112-132. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.85.1.112
[61] Beslier M O, Girardeau J, Boillot G.Kinematics of peridotite emplacement during North Atlantic continental rifting, Galicia, northwestern Spain[J]Tectonophysics, 1990, 184:321-343. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90446-F
[62] Imai A, Ozawa K.Tectonic implications of the hydrated garnet peridotites near Mt Kinabalu, Sabah, East Malaysia[J].Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1991, 6:431-445. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(91)90086-D
[63] Morishita T, Arai S, Ishida Y.Occurrence and chemical composition of amphiboles and related minerals in corundum-bearing mafic rock from the Horoman Peridotite Complex, Japan[J].Lithos, 2007, 95:425-440. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.006
[64] Leblanc M, Temagoult A.Chromite pods in a lherzolite massif(Collo, Algeria):Evidence of oceanic-type mantle rocks along the West Mediterranean Alpine Belt[J].Lithos, 1989, 23:153-162. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90002-9
[65] Tubia J M, Cuevas J, Ibarguchi J I G.Sequential development of the metamorphic aureole beneath the Ronda peridotites and its beating on the tectonic evolution of the Betic Cordillera[J].Tectonophysics, 1997, 279:227-252. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00124-8
[66] Zhang R Y, Liou J G, Yang J S, et al.Petrochemical constraints for dual origin of garnet peridotites from the Dabie-Sulu UHP terrane, eastern-central China[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18:149-166. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00248.x
[67] Marchesi C, Garrido C, Bosch D, et al.Mantle refertilization by melts of crustal-derived garnet pyroxenite:Evidence from the Ronda peridotite massif, southern Spain[J].EPSL, 2013, 362:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.11.047
[68] Hidas K, Booth-Rea G, Garrido CJ, et al.Backarc basin inversion and subcontinental mantle emplacement in the crust:kilometre-scale folding and shearing at the base of the proto-Alborán lithospheric mantle(Betic Cordillera, southern Spain)[J].J.Geol.Soc., 2013, 170:47-55. doi: 10.1144/jgs2011-151
[69] Tubía J M, Cuevas J, Esteban J J.Localization of deformation and kinematic shift during the hot emplacement of the Ronda peridotites(Betic Cordilleras, southern Spain)[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2013, 50:148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.06.010
[70] Morishita T, Arai S, Gervilla F.High-pressure aluminous mafic rocks from the Ronda peridotite massif, southern Spain:significance of sapphirine-and corundum-bearing mineral assemblages[J].Lithos, 2001, 57:143-161. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00036-6
[71] Bailey E, Holloway J R.Experimental determination of elastic properties of talc to 800℃, 0.5 GPa; calculations of the effect on hydrated peridotite, and implications for cold subduction zones[J].EPSL, 2000, 183:487-498. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00288-0
[72] Liu C Z, Wu F Y, Wilde S A, et al.Anorthitic plagioclase and pargasitic amphibole in mantle peridotites from the Yungbwa ophiolite(southwestern Xizang Plateau) formed by hydrous melt metasomatism[J].Lithos, 2010, 114:413-422. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.10.008
[73] Wang J X, Zhou H Y, Salters V, et al.Mantle melting variation and refertilization beneath the Dragon Bone amagmatic segment(53°E SWIR):Major and trace element compositions of peridotites at ridge flanks[J].Lithos, 2019, 324/325:325-339. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.11.014
[74] Nozaka T.Metasomatic hydration of the Oeyama forearc peridotites:Tectonic implications[J].Lithos, 2014, 184/187:346-360. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.11.012
[75] Woodland A B, Komprobst J, McPherson E, et al.Metasomatic interactions in the lithospheric mantle:petrologic evidence from the Lherz massif, French Pyrenees[J].Chemical Geology, 1996, 134:83-112 doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00082-4
[76] Agrinier P, Mével C, Bosch D, et al.Metasomatic hydrous fluids in amphibole peridotites from Zabargad Island(Red Sea)[J].EPSL, 1993, 120:187-205. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(93)90239-6
[77] McPherson E, Thirlwall I M F, Parkinson I J.Geochemistry of metasomatism adjacent to amphibole-bearing veins in the Lherz peridotite massif[J].Chemical Geology, 1996, 134:135-157. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00084-8
[78] Grieco G, Ferrario A, Mathez E A.The effect of metasomatism on the Cr-PGE mineralization in the Finero Complex, Ivrea Zone, Southern Alps[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2004, 24:299-314. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2003.05.004
[79] Beccaluva L, Bianchini G, Bonadiman C, et al.Coexisting anorogenic and subduction-related metasomatism in mantle xenoliths from the Betic Cordillera(southern Spain)[J].Lithos, 2004, 75:67-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2003.12.015
[80] Lucassen F, Franz T G, Viramonte J, et al.The late Cretaceous lithospheric mantle beneath the Central Andes:Evidence from phase equilibria and composition of mantle xenoliths[J].Lithos, 2005, 82:379-406. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.08.002
[81] Marocchi M, Hermann J, Morten L.Evidence for multi-stage metasomatism of chlorite-amphibole peridotites(Ulten Zone, Italy):Constraints from trace element compositions of hydrous phases[J].Lithos, 2007, 99:85-104. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.05.010
[82] Frezzotti M L, Ferrando S, Peccerillo A.Chlorine-rich metasomatic H2O-CO2 fluids in amphibole-bearing peridotites from Injibara(Lake Tana region, Ethiopian plateau):Nature and evolution of volatiles in the mantle of a region of continental flood basalts[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74:3023-3039. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.02.007
[83] Tommasia A, Langone A, Padrón-Navarta J A, et al.Hydrous melts weaken the mantle, crystallization of pargasite and phlogopite does not:Insights from a petrostructural study of the Finero peridotites, southern Alps[J].EPSL, 2017, 477:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.08.015
[84] Kang H, Jung H.Lattice-preferred orientation of amphibole, chlorite, and olivine found in hydrated mantle peridotites from Bjrkedalen, southwestern Norway, and implications for seismic anisotropy[J].Tectonophysics, 2019, 750:137-152. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.11.011
[85] 张旗, 马宝林, 刘若新, 等.一个消减带之上的大陆岩石圈地慢残片:安徽饶拨寨超镁铁岩的地球化学特征[J].中国科学(B), 1995, 35(8):867-873.
[86] 支霞臣, 靳永斌, 孟庆, 等.大别山北部饶拔寨超镁铁岩体微量元素地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20:463-472.
[87] Pedrera A, Galindo-Zaldívar J, Acosta-Vigil A, et al.Serpentinization-driven extension in the Ronda mantle slab(Betic Cordillera, S.Spain)[J].Gondwana Research, 2016, 37:205-215. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.05.008
[88] 仇东东.陕西省松树沟铬铁矿床成因与成矿预测研究[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
[89] 芮会超.北秦岭松树沟超镁铁质岩石及条带状铬铁矿成因研究[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
[90] 鲍佩声, 王希斌.对大道尔吉铬铁矿成因的新认识[J].矿床地质, 1998, 8(1):3-18.
[91] 王希斌, 郝治国, 鲍佩声, 等.中国造山带蛇绿岩中铬铁矿床的成因类型及其成矿的若干特征[J].矿床地质, 1992, 11(1):21-34.
[92] 苟国朝, 田培昭, 张新虎, 等.大道尔吉蛇绿岩型超镁铁岩铬铁矿中铂族元素分布特征[J].西北地质, 1994, 15(1):11-18.
[93] Estebana J J, Sanchez-Rodriguez L, Seward D, et al.The late thermal history of the Ronda area, southern Spain[J].Tectonophysics, 2004, 389:81-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2004.07.050
[94] Reuber I, Michard A, Chalouan A, et al.Structure and emplacement of the Alpine-type peridotites from Beni Bousera, Rif, Morocco:A polyphase tectonic interpretation[J].Tectonophysics, 1982, 82:231-251. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(82)90047-6
[95] Obata M, Karato S I.Ultramafic pseudotachylite from the Balmuccia peridotite, Ivrea-Verbano zone, northern Italy[J].Tectonophysics, 1995, 242:313-328. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(94)00228-2
[96] Kornprobst J, Vielzeuf D.Transcurrent crustal thinning: a mechanism for the uplift of deep continental crust/upper mantle associations[C]//Limberlites.II, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984: 347-359.
[97] 张宗清, 张旗.北秦岭晚元古代宽坪蛇绿岩中变质基性火山岩的地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊):165-177.
[98] 仇东东, 焦建刚, 姜建超, 等.北秦岭松树沟铬铁矿床三维地质建模及其找矿意义[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1):210-217.
[99] 李海勇.大陆俯冲带交代作用: 苏鲁造山带橄榄岩地球化学制约[D].中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2017.
[100] 李犇, 朱赖民, 弓虎军, 等.北秦岭松树沟橄榄岩与铬铁矿矿床的成因关系[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(5):1487-1502.
[101] 徐树桐, 江来利, 刘贻灿, 等.大别山(安徽部分)的构造格局和演化过程[J].地质学报, 1992, 59(4):279-285.
[102] 李曙光, 聂永红, Jagoutz E, 等.大别山俯冲陆壳的再循环——地球化学证据[J].中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(5):412-418.
[103] 吴元保, 陈道公, 程昊, 等.北大别饶拔寨退变质榴辉岩的地球化学特征[J].地震地质, 2000, 22(增刊):99-103.
[104] 靳永斌, 支霞臣, 孟庆, 等.大别山北部饶拔寨超镁铁岩体的形成时代:Re-Os同位素定年[J].科学通报, 2003, 48:2560-2565.
[105] Zhi X C.Re-Os isotopic system and formation age of subcontinental lithosphere mantle[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45:193-200. doi: 10.1007/BF02884671
[106] Zhi X C, Jin Y B, Meng Q, et al.The Re-Os isotope geochemistry of the Raobazhai ultramafic complex of Dabieshan, central China[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2003, 67(18S):A83. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02900973
[107] 王希斌, 杨经绥, 陈松永, 等.也谈铙钹寨超镁铁岩体的成因和构造类型的归属问题[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21:1593-1608.
[108] 王希斌.对"也谈铙钹寨超镁铁岩体的成因和构造类型的归属问题"一文评论的答疑[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):3084-3089.
[109] 张旗.铙钹寨岩体是蛇绿岩吗?——评王希斌等:"也谈铙钹寨超镁铁岩体的成因和构造类型的归属问题"[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):3079-3084.
[110] Zheng L, Zhi X C, Reisberg L.Re-Os systematics of the Raobazhai peridotite massifs from the Dabie orogenic zone, eastern China[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 268:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.06.021
[111] 匡少平, 凌文黎, 张本仁.大别造山带中镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石和榴辉岩有关问题的讨论[J].地质论评, 1999, 45(6):584-595.
[112] 游振东, 桑隆康, 钟增球, 等.大别山北麓尖晶石橄榄岩中石榴辉石岩包体的成因矿物学信息[J].现代地质, 2001, 15(2):161-167.
[113] 杨锡庸.安徽大别地区一个超镁铁质冷侵入体:对霍山县饶拨寨岩体的再认识[J].中国地质科学院南京地质矿产研究所所刊, 1983, (4):81-99.
[114] 钟大赉, 等.滇川西部古特提斯造山带[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002:1-231.
[115] 王奕萱, 王根厚, 袁国礼, 等.滇西三台山地幔橄榄岩的成因及其构造意义:来自地质学、矿物学和岩石地球化学的证据[J].地学前缘, 2018, 25(1):138-156.
[116] 储著银, 王伟, 陈福坤, 等.云南潞西三台山超镁铁岩体Os-Nd-Pb-Sr同位素特征及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(12):3221-3228.
[117] 刘慧明.云南三台山超基性岩与盈江超基性岩形成构造环境对比与含矿性研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2018.
[118] 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 张建新, 等.北祁连走廊南山加里东俯冲杂岩增生地体及其动力学[J].地质学报, 1994, 68:1-15.
[119] 张旗, 郭原生, 王岳明, 等.祁连山地区镁铁-超镁铁岩的多样性[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12(5):324-330.
[120] 王二七, 张旗, Burchfiel C B.青海拉鸡山:一个多阶段抬升的构造窗[J].地质科学, 2000, 35:493-500.
[121] 冯益民, 何世平.祁连山大地构造与造山作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996.
[122] 师占义.西北几个主要含矿超基性岩体的岩石矿物特征及意义[J].地质论评, 1980, 26(4):307-318.
[123] Boulller A M, Firdaous K, Boudier F.Fluid circulation related to deformation in the Zabargad gneisses(Red Sea rift)[J].Tectonophysics, 1997, 279:281-302. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00116-9
[124] Takla M A, Eldougdoug A A, Hussein A A A, et al.Petrogenesis of Zabargad ultramafic rocks and origin of peridot, Zabargad Island, Red Sea, Egypt[J].Annals of the Geological Survey of Egypt, 1997, 20:451-478.
[125] Marshak S, Bonatti E, Brueckner H, et al.Fracture-zone tectonics at Island, Red Sea(Egypt)[J].Tectonophysics, 1992, 216:379-385. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(92)90407-W
[126] Pelletier L, Müntener O.High-pressure metamorphism of the Lanzo peridotite and its oceanic cover, and some consequences for the Sesia-Lanzo zone(northwestern Italian Alps)[J].Lithos, 2006, 90:111-130. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.01.006
[127] Piccardo G B, Zanetti A, Muntener O.Melt/peridotite interaction in the southern Lanzo peridotite:Field, textural and geochemical evidence[J].Lithos, 2007, 94:181-209. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.07.002
[128] Rubatto D, Gebauer D, Compagnoni R.Dating of eclogitefacies zircons:the age of Alpine metamorphism in the Sesia-Lanzo Zone(Western Alps)[J].EPSL, 1999, 167:141-158. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00031-X
[129] 刘欣雨, 张旗, 张成立.基于大数据方法建立大洋安山岩构造环境判别图[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(12):1963-1970. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20191204&flag=1
[130] 张旗, 李明超, 陈万峰, 等.岩石大地构造学说的兴起、没落与新生[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(2):289-296.
[131] Sanfilippo A, Tribuzio R, Ottolini L, et al.Water, lithium and trace element compositions of olivine from Lanzo South replacive mantle dunites(Western Alps):New constraints into melt migration processes at cold thermal regimes[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 214:51-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.07.034
[132] Pognante U, Rsli U, Toscani L.Petrology of ultramafic and mafic rocks from the Lanzo peridotite body(Western Alps)[J].Lithos, 1985, 18:201-214. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(85)90025-8
[133] Hartmann G, Wedepohl K H.The composition of peridotite tectonites from the Ivrea Complex, northern Italy:Residues from melt extraction[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57:1761-1782. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90112-A
[134] Bodinier J L, Menzies M A, Thirlwall M.Continental to oceanic mantle transition—REE and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of the Lanzo lherzolite massif.Orogenic lherzolites and mantle processes[J].Journal of Petrology, 1991, 20:191-210. https://academic.oup.com/petrology/article/42/1/233/1461786
-



 下载:
下载: